Light Points To Remember
Light: The natural agent that stimulates sight and makes things visible. Light is reflected from all surfaces. It is a form of energy.
Objects that give out light on their own are called luminous objects.
Objects that do not give out light on their own are called non-luminous objects.
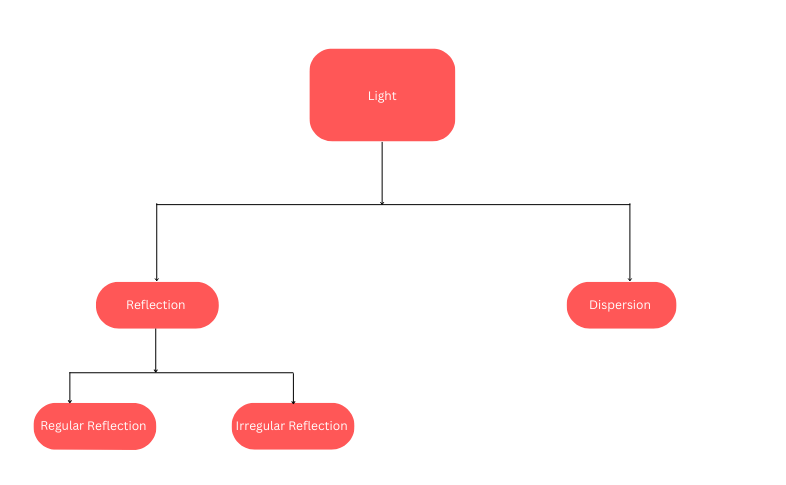
Reflection of Light: Bouncing back of light after striking a shiny or polished surface, in the same medium, is called reflection.
Types of Reflection:
1. Regular Reflection: When a beam of parallel light rays is incident on a smooth and plane surface, the reflected rays will also be parallel. This type of reflection is called Regular Reflection. The reflection from a plane mirror is an example of regular reflection.
2. Diffused or Irregular Reflection: When light is incident upon a rough or uneven surface, it is reflected in many directions due to the presence of irregularities on that surface.
If a reflected light ray is reflected again on being incident on another surface, it is termed multiple reflection. Multiple reflections are used in periscopes. Periscopes are used in submarines, war tanks, and by soldiers in bunkers to see objects that are not visible directly. In a kaleidoscope, beautiful patterns are formed due to multiple reflections.
Laws of reflection:
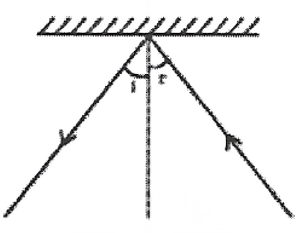
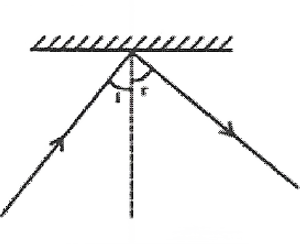
1. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
2. Incident ray reflected ray, and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface, lie in the same plane.
3. Lateral inversion is the effect produced by a plane mirror in reversing images from left to right. For e.g. our left hand will appear as right and vice versa.
The image formed by a plane mirror is:
1. Of the same size as that of the object
2. Left-right inverted
3. Erect and virtual
4. Formed behind the mirror at the same distance as the distance the object in front of the mirror
Two mirrors inclined to each other give multiple images. Sunlight is called white light; consists of seven colors. The splitting of light into its constituent colors is known as dispersion. Visually challenged persons can read and write using the Braille system.
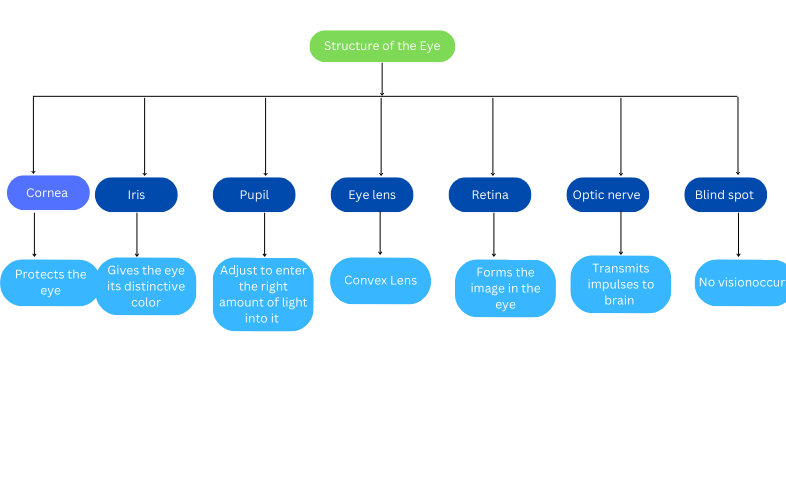
Parts of the Human Eye:
1. Cornea: Transparent bulge on the front surface of the eyeball which protects the eye and helps in the refraction of light.
2. Lris: Coloured diaphragm behind the cornea which controls the amount of Light entering the eye.
3. Pupil: Dark hole in the middle of the iris through which light enters the eye.
4. Eye lens: Transparent, crystalline structure behind pupil and iris.
5. Ciliary muscles: Hole in the eye lens in position and control the focal length of the eye lens.
6. Retina: The surface of the rear part of the eyeball where the light entering the eye is focused.
7. Rods and Cones: Rod cells respond to the brightness of light while cone cells respond to colours.
8. Blindspot It is the least sensitive point where no rods and cones are present.
9. The space between the cornea and the eye lens is filled with aqueous humor.
10. The space between the eye lens and the retina is filled with vitreous humor.
Light NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the ream? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Answer: We cannot see objects in dark rooms. But we can see objects outside the room, in case there is a light outside the room. To see an object needs light which must reflect from the object to the eyes.
Question 2. Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer:
Regular reflection
1. The reflected rays are parallel to incident rays.
2. It occurs when an incident ray falls on a smooth or polished surface.
Diffused reflection
1. The reflected rays are not parallel to incident rays.
2. It occurs when an incident falls on a rough surface. No, diffused reflection is not the failure of the laws of reflection.
Question 3. Mention against each following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
1. Polished wooden table
2. Chalk powder
3. Cardboard surface
4. Marble floor with water
5. Mirror
6. Piece of paper.
Answer:
1. Regular reflection will occur because of the polished surface.
2. Diffused reflection will take place because it is a rough surface.
3. Diffused reflection will take place because it is not a polished surface.
4. Diffused reflection will take place because marble and water will form a prism.
5. Regular reflection takes place because a plane mirror is a polished surface.
6. Diffused reflection due to rough surface.
Question 4. State the law of reflection.
Answer: The laws of reflection are
1. The angle of the incident is equal to the angle of reflection.
2. The ray of incidence, ray of reflection, and normal to-the-point incidence lie in the same plane.
Question 5. Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer:
Material required: a white sheet of paper, a drawing board, drawing pins, and a comb.
Procedure:
1. A white sheet of paper on a drawing board is fixed.
2. A strip of plane mirror is taken and placed in the path of the light ray.
3. The ray of light will be reflected.
4. Angle of incidence and angle of reflection on the sheet of paper is drawn,
5. The incident and reflected rays along the paper is observed. Now the sheet of paper is bent a little at the position of the reflected lay.
6. Keeping the incident ray and the normal in the plane of the drawing board, the reflected ray is tried to be seen now
Observation: The incidence ray, reflected ay, and normal lie in the same plane.
Question 6. Fill in the blanks in the following.
1. Person 1 min front of a plane mirror seems to be 2m away from this image.
2. If you touch your left ear with a right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with your left hand.
3. The size of the pupil becomes large when you see in dim light.
4. Night birds have less cones than rods in their eyes.
Question 7. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of | Ans: Laser torch can harm or even damage the eye. So,reflection.
1. Always
2. Sometimes
3. Under special conditions
4. Never
Answer: 1. Always.
Question 8. The image formed by a plane mirror is
1. Virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
2. Virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
3. Real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
4. Real, behind the mirror, and of the same size as the object
Answer: 2. Virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Question 9. Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Answer: A kaleidoscope is an optical instrument used to see a number of beautiful patterns. It is made up of a circular cardboard tube or tube of thick chart paper in which rectangular mirror strips are joined together to form a prism. At one end of the tube, touching these mirrors, a circular glass plate is fixed, Several small pieces of colored glass are placed upon it. This end is closed by a ground glass plate and beautiful patterns are seen through the other end of the kaleidoscope.
Question 10. Draw a labeled sketch of the human eye.
Answer:
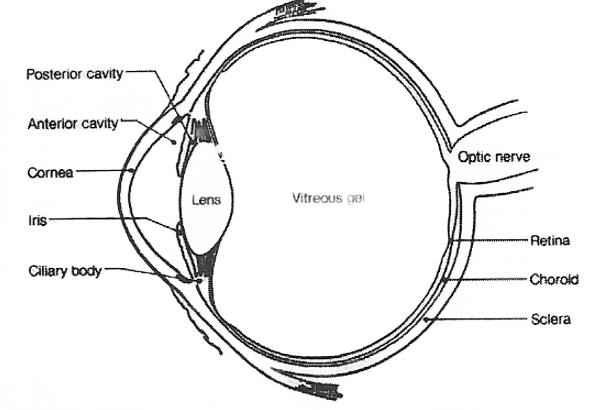
Question 11. Gurmit wanted to perform using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher’s advice?
Answer: Laser torch can harm or even damage the eye. So her teacher advised her not to do so.
Question 12. Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Answer: The following care should be taken to keep our eyes healthy:
1. We should not look at the sun or a powerful light source directly.
2. Too light too much light is bad for the eyes.
3. If advised, suitable spectacles should be used.
4. We should always read from a normal distance for distinct vision.
5. We should never rub our eyes if any small particle or dust goes into the eyes.
6. Food containing Vitamin A should be used.
Question 13. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected rays are at an angle of 90 degrees to the incident?
Answer: The angle of incidence is 45°
Question 14. How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Answer: Infinite number of images of the candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors.
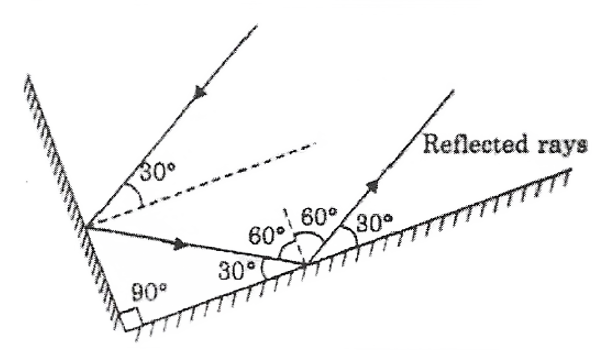
Question 15. Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.

Answer:
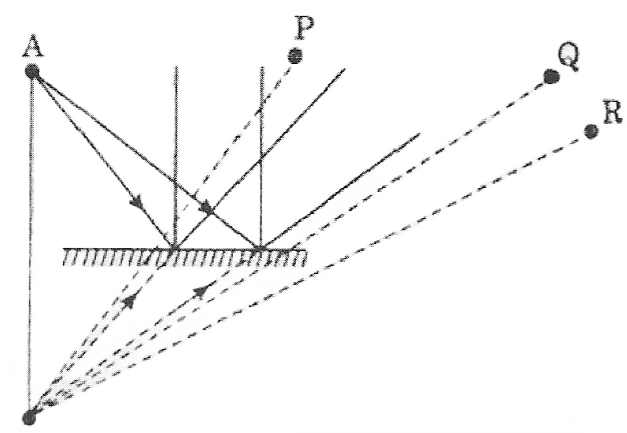
Question 16. Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror Can he see himself in the mirror? Also, can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q, and R?

Answer: No, Boojho can’t see himself in the mirror. He can see the image of the object at P and 0 but not of R.
Question 17.
1. Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror
2. Can Paheli at B see this image?
3. Can Boojho at C see this image?
4. When Paheli moves from B to C. where does the image of A move?
Answer: It is shown in the following picture.
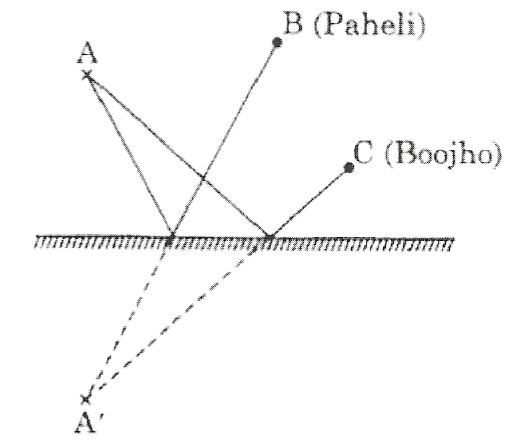
1. Yes, Paheli can see the image of A.
2. Yes, Boojho can see the image of A.
3. Image of the object at A will not move as an object is not moving.
Light Activities
Question 1. Fix a white sheet of paper on a drawing board or a table. Take a comb and close all its openings except one in the middle. You can use a strip of black paper for this purpose. Hold the comb perpendicular to the sheet of paper. Throw light from a torch through the opening of the comb from one side With a slight adjustment of the torch and the comb you will see a ray of light along the paper on the other side of the comb. Keep the comb and the torch steady. Place a strip of the plane mirror in the path of the light ray What do you observe?

Answer: It is observed that after striking the mirror, the ray of light is reflected in another direction.
Question 2. Perform again. This time use a sheet of stiff paper or chart paper. Let the sheet project a little beyond the edge of the Table Cut the projecting portion of the sheet in the middle. Look at the reflected ray. Make sure that the reflected ray extends to the projected portion of the paper. Bend that part of the projected portion on which the reflected ray falls. Can you still see the reflected ray? Bring the paper back to its original position. Can you see the reflected ray again? What do you infer?
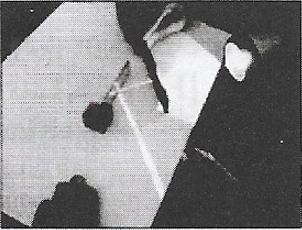
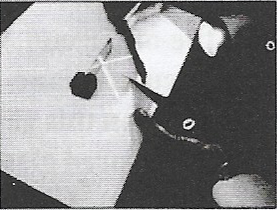
Answer: Yes, the reflected ray of light is seen on the sheet. It is concluded that the entire sheet fixed on the drawing board represents a plane. The incident reflected rays and the normal lie in the plane of the paper.
Question 3. A source of light 0 is placed in front of a plane mirror PQ. Two rays OA and OC are incident on it Can you find out the direction of the reflected rays? Draw normals to the surface of the mirror PQ, at points A and C. Then draw the reflected rays at points A and C. How would you draw these rays? Call the reflected rays AB and CD, respectively. Extend them further. Do they meet? Extend them backward. Do they meet now? If they meet, mark this point as I. For a viewer’s eye at E do the reflected rays appear to come from point ? Since the reflected rays do not actually meet at I, but only appear to do so, we say that a virtual image of the point O is formed at I. As you have learned already in Class VII, such an image cannot be obtained on a screen.
picture
Answer: An image formed by a plane mirror cannot be obtained on a screen. Thus, the plane mirror forms a virtual image.
Question 4. Imagine that parallel rays are incident on an irregular surface Remember that the laws of reflection are valid at each point of the surface. Use these laws to construct reflected rays at various points. Are they parallel to one another? You will find that these rays are reflected in different directions.
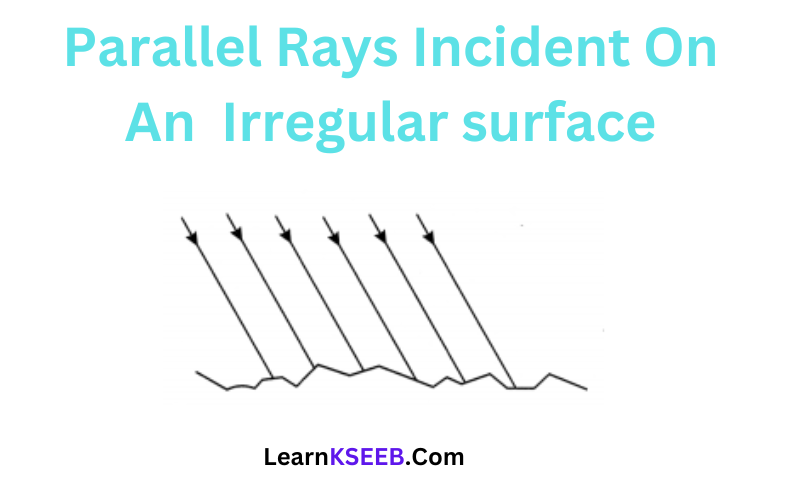

Answer: It is observed that the reflected rays are not parallel to each other due to irregularities in the reflecting surface. This type of reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection.
Question 5. Take two plane mirrors. Set them at right angles to each other with their edges touching To hinge them you can use adhesive tape. Place a coin in between the mirrors. How many images of the coin do you see?
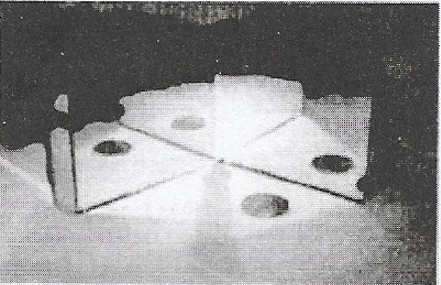

Now hinge the mirrors using the adhesive tape at different angles, say 45°, 60°, 120°, 180°, etc. Place some object (say a candle) in between them. Note down the number of images of the object in each case. Finally, set the two mirrors parallel to each other. Find out how many images of candles placed between them are formed
Answer:
1. When two plane mirrors are joined at right angles, then three images are formed.
2. When two plane mirrors are joined at 45°, 7 images are formed.
3. When two plane mirrors are joined at 60°, 5 images are formed.
4. When two plane mirrors are joined at 120°,2 images are formed.
5. When two plane mirrors are joined at 180°,1 image is formed.
6. When the plane mirrors are parallel to each other, infinite images are formed.
Question 6. To make a kaleidoscope, get three rectangular mirror strips each about 15 cm long and 4 cm wide. Join them together to form a prism Fix them in a circular cardboard tube or tube of thick chart paper. Make sure that the tube is slightly longer than the mirror strips. Close one end of the tube with a cardboard disc having a hole in the center, To make the disc durable, paste a piece of the transparent plastic sheet under the cardboard disc. At the other end, touching the mirrors, fix a circular plane glass plate Place on this glass plate several small pieces of colored glass (broken pieces of colored bangles). Close this end of the tube with a ground glass plate. Allow enough space for the color pieces to move around.

Answer: A variety of patterns are observed in the tube. Kaleidoscope operates on the principle of multiple reflections.
Question 7. Get a plane mirror of a suitable size. Place it in a bowl (Katori) Fill the bowl with water. Put this arrangement near a window in such a way that direct sunlight falls on the mirror. Adjust the position of the bowl so that the reflected light from the mirror falls on a wall. If the wall is not white, fix a sheet of white paper on it. The reflected light will be seen to have many close their right eye. Look at the round mark now and repeat the activity. Does the cross-colors. How can you explain this?
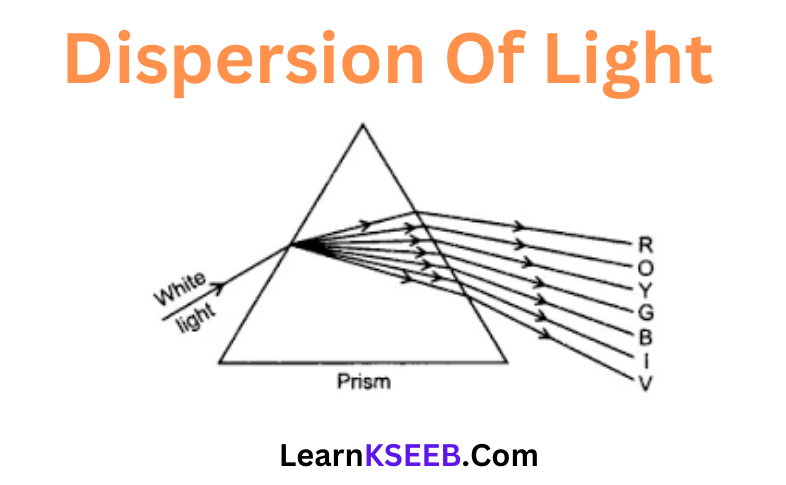
Answer: The mirror and water form a prism and breaks up the light into its colors. The splitting of light into its colors is known as the dispersion of light. A Rainbow is a natural phenomenon showing dispersion.
Question 8. Look into your friend’s eye. Observe the size of the pupil. Throw light on her eye with a torch. Observe the pupil now. Switch off the torch, and observe her pupil once again. Do you notice any change in the size of the pupil? In which case was the pupil larger? Why do you think it was so? In which case do you need to allow more light in the eye, when the light is dim or bright?
Answer: When the light from the torch falls on the pupil, its size becomes smaller to allow less amount of light to enter the retina. When light is switched off, the pupil enlarges to allow more light to enter the retina. Thus, the pupil controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Question 9. Make a round mark and a cross on a sheet of paper with the spot to the light of the cross. The distance between two marks may be 6- 8 cm. Hold the sheet of paper at an arm’s length from the eye. Close your left eye. Look continuously at the cross. Move the sheet slowly towards you, keeping your eye on the cross. What do you find? Does the round mark disappear at some point? Now close your right eye. Look at the round mark now and repeat the activity. Does the cross disappear?

Answer: Yes, the cross disappears. The disappearance of the cross or the round mark shows that there is a point on the retina which cannot send messages to the brain when light falls on it.
Question 10. Get a square piece of cardboard of size 6-8 cm. Make two holes Thread a string through the two holes. Draw/paste a cage on one side of the cardboard and a bird on the other side. Twist the string and make the card twirl rapidly. Do you see the bird in the cage?

Answer: Yes, we can see the bird in the cage. Thus, the impression of an image persists in the retina for about 1/16th of a second.
Light Additional Questions
Question 1. Define dispersion of light.
Answer: Splitting up white light into seven colors when it passes through a glass prism is known as the dispersion of light.
Question 2. Name the colors in the order they appear in the spectrum of light.
Answer: VIBGYOR — Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red.
Question 3. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Answer: The angle of incidence = 45°
Question 4. What are the two factors responsible for an object being seen?
Answer: To be seen as an object, the sense of vision and light are required.
Question 5. What are illuminated objects?
Answer: Objects which reflect the light falling on them and can be seen are known as illuminated objects
Question 6. What is white light?
Answer: Sunlight is a mixture of seven colors also known as white light.
Question 7. Give one example of natural dispersion.
Answer: Formation of the rainbow.
Question 8. Which kind of spherical mirrors are used in vehicles? Why?
Answer: A convex mirror is used in vehicles because it gives the driver a large field of view.
Question 9. Why is it important to take care of our eyes? Mention any two activities that may cause damage to our eyes.
Answer: Eyes are the most wonderful gift of nature to us and they must serve us for our whole life. Our eyes can be damaged by playing carelessly or by hurting them with sharp projections
Question 10. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Answer: The objects cannot be seen inside the room because there is no light. The objects outside the room can only be seen if there is light outside.
Question 11. Distinguish between real and virtual images.
Answer: Differences:
Real image
1. The rays actually meet at a point.
2. The image can be obtained on a screen.
Virtual image
1. The rays do not meet at a point.
2. The image cannot object obtained on a screen.
Question 12. What is color blindness? Give a reason for this defect.
Answer: Some people cannot distinguish between the different colors. This is known as color blindness. Colour blindness is due to the absence of cones on the nerve endings on the retina.
Question 13. What are cones and rods? What are their functions?
Answer:
1. Cones are nerve endings that are sensitive to color light. They help us to distinguish between colors.
2. Rods are nerve endings that are sensitive to bright light.
Question 14. How do visually impaired people communicate?
Answer: Visually impaired people can communicate by following methods
1. By using the Braille system which employs groups of dots to represent printed letters and numbers.
2. In 1980, Braille computer software was developed. It can input, output, and translate documents to and from Braille.
3. By speech technology that can convert ordinary text into speech.
Question 15. Give some uses of plane mirrors.
Answer: Plane mirrors are used for dressing up, shaving beards, in scientific meters, and far designing periscopes.
Light Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Part of the eye which controls the light entering is called
1. Iris
2. Cornea
3. Lens
4. Retina
Answer: 1. Iris
Explanation: Iris is a dark muscular structure that exists behind the cornea. Its function is to control the entry of light.
Question 2. We can see a non-luminous object when light:
1. Emitted by the object falls on the eye.
2. Is reflected from the object towards our eye.
3. Completely passes through the object.
4. Gets completely absorbed by the object.
Answer: 2. Is reflected from the object towards our eye.
Question 3. Light falling on surfaces S1, S2, and S3 Surfaces on which the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection is/are
1. S1 only
2. S1 and 82 only
3. S2and $3
4. All the three surfaces
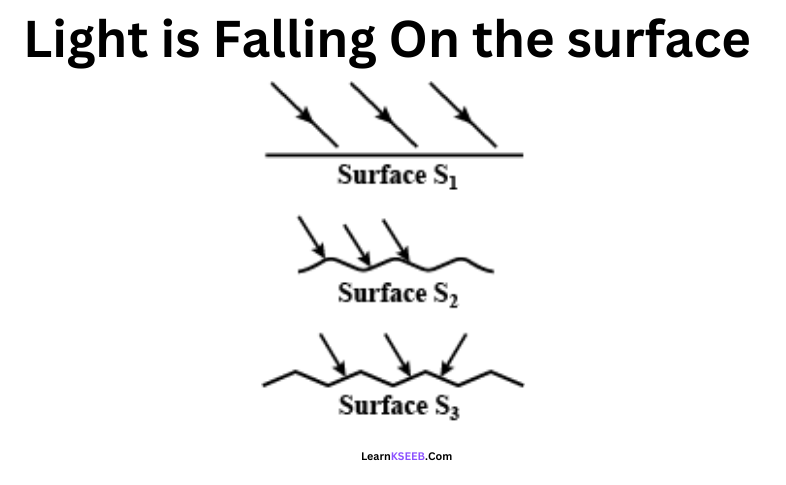
Answer: 4. All the three surfaces
Explanation: Laws of reflection are always followed irrespective of the surface of the object hence the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Answer 4. A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of the eye with respect to the position of the bulb as A, B, C, and D. In which position mirror will be visible?
1. A, 2. B, 3. C, 4. D
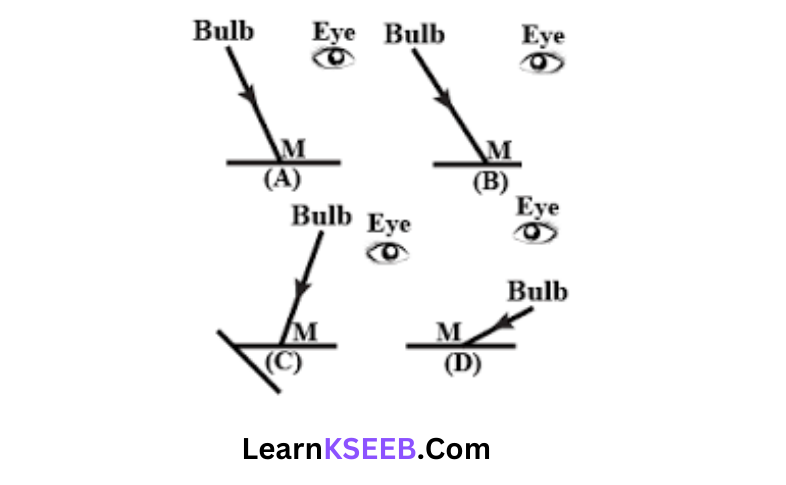
Answer: 1. A
Explanation: In the case of A ray of light from A strikes a mirror and gets reflected back to make an angle of incidence and angle of reflection equal.
Question 5. A small hole P is made in a piece of cardboard. The hole is illuminated bya torch The pencil of light coming out of the hole falls on a mirror. At which point should the eye be placed so that the hole can be seen?
1. A, 2. B 3. C 4. D
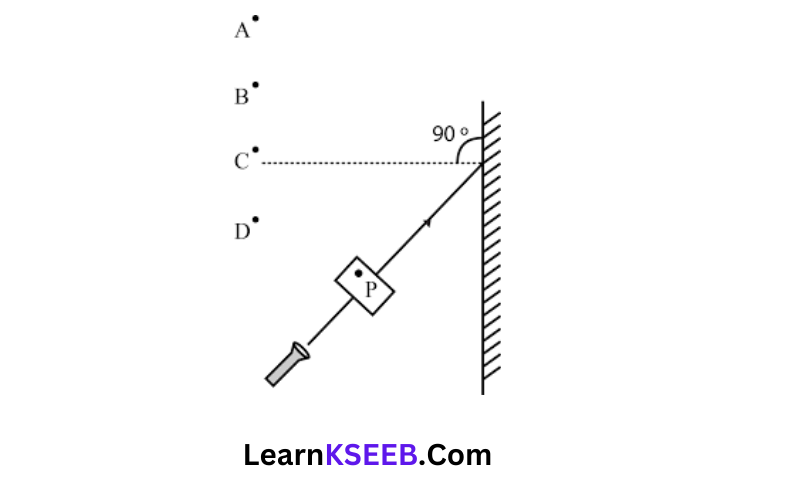
Answer: 1. A
Explanation: The eye should be placed at position A because the hole can be seen only when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 6. Two mirrors A and B are placed at right angles to each other
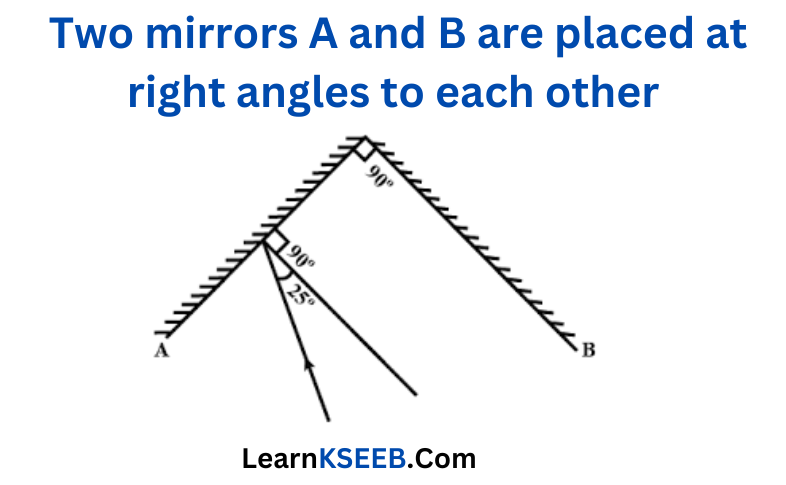
A ray of light incident on mirror A at an angle of 25° falls on mirror B after reflection. The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B would be
1. 25° 2. 50° 3. 65° 4. 115°
Answer: 3. 65°
Explanation: The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B will be 65° because the reflected ray from mirror A forms an incident ray on mirror 6 and is then reflected back by an angle of 65°;
Question 7. Which of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
1. Cones are sensitive to dim light.
2. Cones are sensitive to bright light.
3. Rods are sensitive to bright light.
4. Rods can sense color.
Answer: 2. Cones are sensitive to bright light.
Explanation: Cones are sensitive to bright light hence they sense color whereas rods are sensitive to dim light and they cannot sense color.
Question 8. In the figure of the human eye, the cornea is represented by the letter
1. A 2. B 3. C
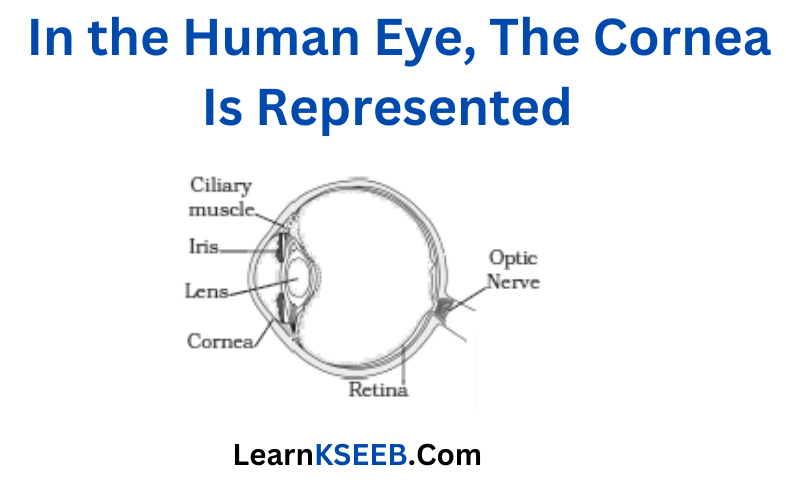
Answer: 3. C
Explanation:
1. Iris
2. Lens
3. Cornea
Question 9. Name the part of the eye which gives color to the eyes
Answer: Iris the part of the eye which gives color to the eyes.
Question 10. Book while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers for it?
Answer: The persistence of vision is the reason for their blurred vision Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred.
Question 11. How many times is a ray of light reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other?
Answer: An infinite number of times a ray of light is reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other.
Question 12. the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 60°. What is the value of the angle of incidence?
Answer: 30°.
Explanation: The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Since the Angle of incident ray + Angle of reflected ray is 60°.
The angle of incidence = 30°
Question 13. The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 24 cm. What is the distance between the mirror and the object?
Answer: The distance will be 12 cm
Explanation: Object + image formed =24 cm
Object + mirror =12 cm
Question 14. What happens to light when it gets dispersed? Give an example.
Answer: When the light gets dispersed it is split into its constituent colors. Ex: rainbow.
Question 15. showing the position of the plane mirror. Also, label the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
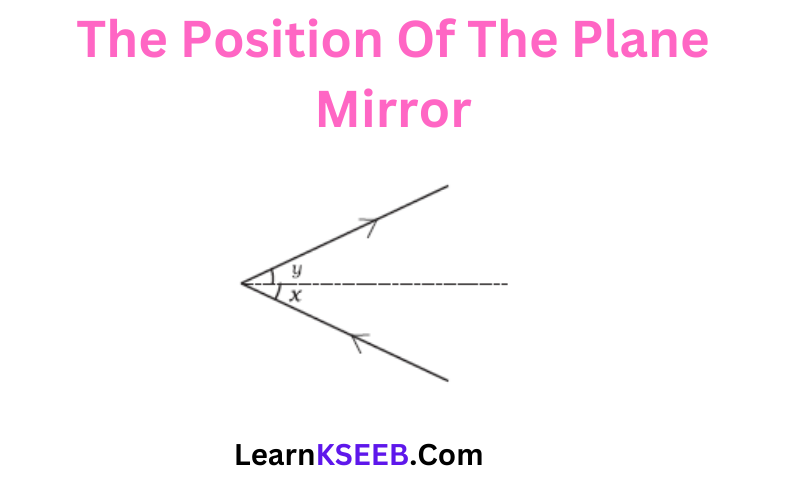
Answer:
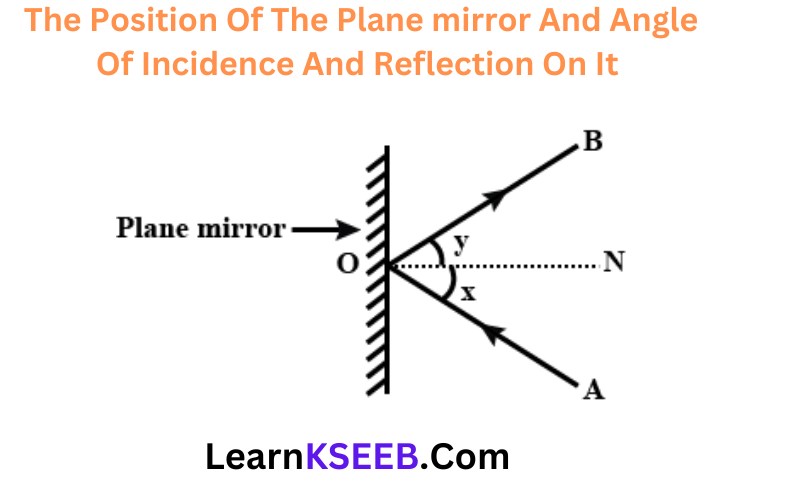
Question 16. Can the image of the child in it be obtained on a screen?

Answer: No, the image of the child cannot be obtained on a screen because the image is a virtual image.
Question 17. Eyes of the nocturnal birds have large cornea and a large pupils. How does this structure help them?
Answer: They can see objects even in faint light. As a large pupil and large cornea allow more light to enter their eyes.
Question 18. What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object?
Answer: Our eyes have a convex type of lens and the image is formed on the retina.
Question 19. Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from cataracts? How is it treated?
Answer: If a person is suffering from cataracts their eye lens will be cloudy. Cataracts can be treated by replacing the opaque lens with an artificial lens.
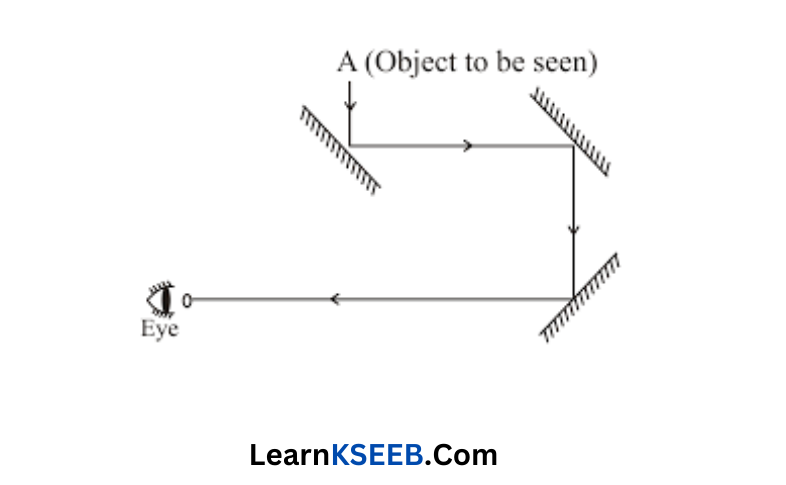
Question 20. Boojho planned an activity to observe object A through pipes so that he could see objects which he could not directly see.
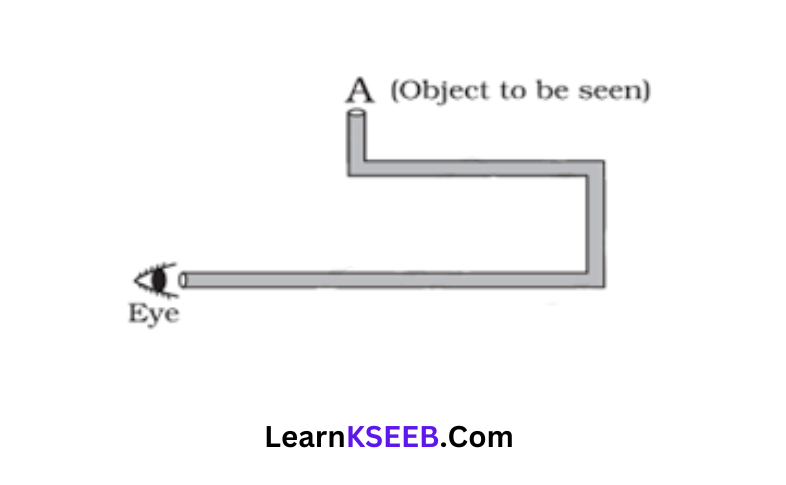
1. How many mirrors should he use to see the objects?
2. Indicate the positions of the mirrors in the figure.
3. What must be the angle with respect to the incident light at which he should place the mirrors?
4. Indicate the direction of the rays
5. If any of the mirrors are removed, will he ee be able to see the objects?
Answer:
1. Three mirrors should he use to see the SHOU AN ee Pio Anat objects.
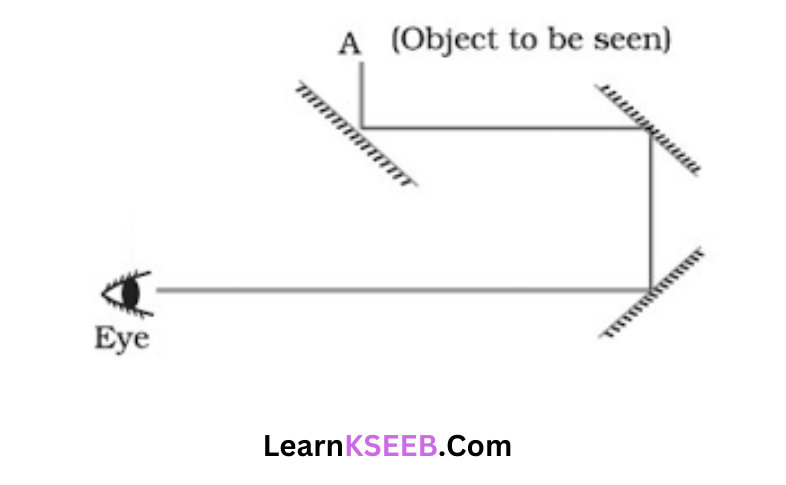
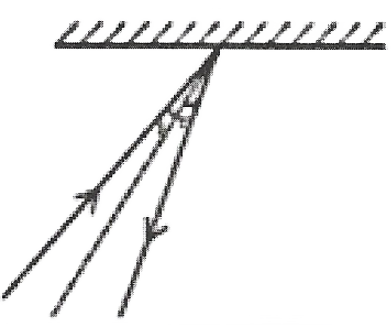
Question 21. There is a mistake in each of the following directly see. ray diagrams given
Answer:
Question 22. Explain the process which enables us to perceive motion in a cartoon film.
Answer: Carton movie is actually a projection of a static picture. 24 pictures per second are shown in a specific order which gives us the perception of movement.
Question 23. How is the phenomenon of reflection used in making a kaleidoscope? What are the applications of a kaleidoscope?
Answer: The kaleidoscope gives a number of images formed by reflection from the mirrors inclined to one another. Designers and artists use kaleidoscopes to get ideas for new patterns to design wallpapers, Jewellery, and fabrics.
Question 24. The word REST wrote in two ways in front of a mirror. Show how the word would appear in the mirror.
Answer:

Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
