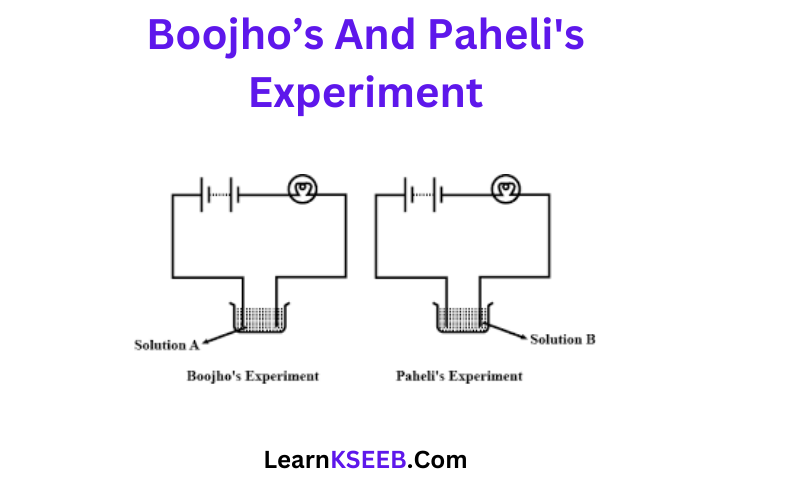
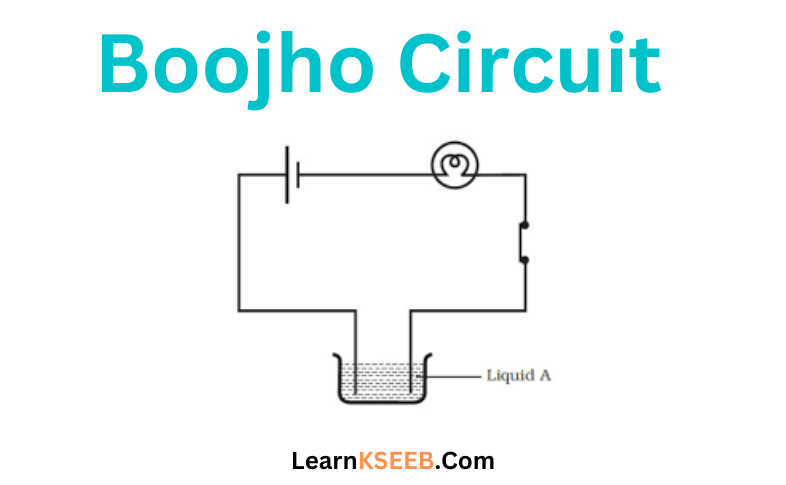
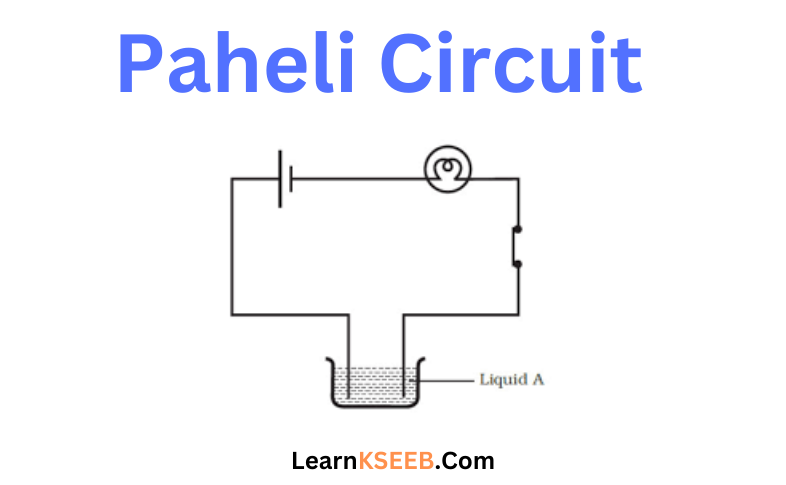
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend And Foe Points To Remember
Microorganisms: Living organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Types: Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa, Algae, viruses.
Friendly microorganisms:
1. Making curd and bread
2. production of alcohol and wine
3. production of vaccines and antibiotics
4. increases soil fertility
5. cleaning of the environment.
Harmful microorganisms:
1. Diseases like cholera, TB, Typhoid, Measles, and Malaria are caused by micro-organisms in Humans.
2. Diseases like anthrax and foot and mouth disease are caused by bacteria and viruses in cattle.
3. Diseases like citrus canker, rust of wheat, and yellow vein mosaic of okra in plants.
3. Foods are spoilt by microorganisms.
Food preservation:
1. Chemical method
2. By sugar
3. Heat and cold treatments
4. By common salt
5. By oil and vinegar
6. Storage and packing

Class 8 Science KSEEB Microorganisms Friend and Foe Notes
Microorganisms Friend And Foe Ncert Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Fill in the blanks.
(1)Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a
(2) Blue-green algae fix directly from the air to enhance the fertility of the soil.
(3)Alcohol is produced with the help of
(4)Cholera is caused by
Answer:
(1) microscope
(2) nitrogen
(3) yeast
(4) bacteria
Question 2.Tick the correct answer:
1)Yeast is used in the production of
(1)sugar
(2) Alcohol
(3)hydrochloric acid
(4) oxygen
2)Which of the following is an antibiotic?
(1)Sodium bicarbonate
(2) Streptomycin
(3) Alcohol
(4) yeast
3)Carrier of malaria-causing protozoa is
(1)female Anopheles mosquito
(2)cockroach
(3)housefly
(4)butterfly
4)The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(1)ant
(2) housefly
(3) dragonfly
(4) spider
5)The bread or idli dough rises because of
(1) heat
(2) housefly
(3) growth of yeast cells
(4) kneading
(6)The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(1) nitrogen fixation
(2) molding
(3) fermentation
(4) infection
Answer: 1) – (2); 2) – (2); 3) – (1); 4) – (2), (5) – (3); 6) – (3)
Question 3. Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer: Microorganisms cannot be seen by the naked eye because they are very small. They can be seen by using a microscope.
Question 4. What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer: Major groups of microorganisms is as follows:
1. Bacteria
2. Fungi
3. Protozoans
4. Algae
5. Viruses.
Question 5. Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer: Rhizobium.
Question 6. Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer: Uses of microorganisms are as follows :
- They are helpful in cleaning up the environment.
- Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd.
- Bacteria are involved in the making of cheese
- Bacteria and yeast are helpful for the fermentation of rice idlis and dosa batter.
- Use of yeast in the baking industry for making bread, pastries, and cakes.
- Large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and vinegar.
- Microorganisms are helpful in producing vaccines against the disease.
- Antibiotics are produced from bacteria and fungi
- Some bacteria are able to fix nitrogen and increase soil fertility.
- Microorganisms decompose dead and decaying organic matter of plants and animals.
Question 7. Write a short paragraph on the harmful effects of microorganisms.
Answer: Microorganisms cause diseases in plants and animals,
Example: Cholera in humans is caused by bacteria called Vibrio cholera. In animals, the virus causes foot and mouth diseases. Microorganisms spoil the food by decomposing the food material. Some microorganisms spoil leather and clothes. Microorganisms are responsible for food poisoning.
KSEEB Class 8 Science Solutions For Microorganisms Friend And Foe
Question 8. What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
Chemical agents that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotic
Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. Also, one must complete the course prescribed by the doctor.
Microorganisms Friend And Foe Activities
Question 1. Collect some moist soil from the field in a beaker and add water to it. After the soil particles have settled down, observe a drop of water from the beaker under a microscope. What do you see?
Answer: It is observed that some tiny organisms are moving around.
Question 2. Take a few drops of water from a pond. Spread on a glass slide and observe through a microscope.
Answer: It is observed that some tiny organisms are moving around.
 Question 3. Take 1/2 kg flour (atta or maida), add some sugar, and mix with warm water. Add a small amount of yeast powder and knead to make a soft dough. What do you observe after two hours? Did you find the dough rising?
Question 3. Take 1/2 kg flour (atta or maida), add some sugar, and mix with warm water. Add a small amount of yeast powder and knead to make a soft dough. What do you observe after two hours? Did you find the dough rising?
Answer: It is observed that the dough begins to rise up in volume. Yeast reproduces rapidly and releases Co2 during respiration. The stubble of this gas fills the dough and increases its volume.
Question 4. Take 500 ml. beaker filled up to 3/4 with water. Dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of sugar in it. Add half a spoon of yeast powder to the sugar solution. Keep it covered in a warm place for 4-5 hours. Now smell the solution. Can you get a smell?
Answer: It is observed that the solution smell like alcohol. This process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is known as fermentation.
Question 5. Take two pots and fill each pot half with soil. Mark them A and B. Put plant waste in pot A and things like polythene bags, empty glass bottles, and broken plastic toys in pot B. Put the pots aside. Observe them after 3-4 weeks.
Answer: It is observed that plant waste in pot A has been decomposed, whereas the polythene bags, empty glass bottles, and broken plastic toys in pot B did not undergo such changes.
Microorganisms Friend And Foe Additional Questions
Question 1. Riya’s grandmother always dries vegetables in the sun before pickling them. How does drying help vegetables?
Answer: Drying vegetables help to remove water, which is necessary for microbial growth. So drying helps in preserving them.
Question 2. On a pack of fruit juice, it is printed “IF THE PACKET IS PUFFED DO NOT BUY”. Give reasons.
Answer: Because packed juices may be contaminated by yeast which causes fermentation and makes them unfit for consumption.
Question 3. Name any two antibiotics.
Answer: Streptomycin and tetracycline.
Question 4. Name the scientist who discovered the vaccine for smallpox in 1798.
Answer: Edward Jenner
Question 5. What do you mean by communicable diseases?
Answer: The microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person by some agents like air, water, food, or physical contact are called communicable diseases.
Question 6. Write the name of a bacterium that helps in the formation of curd.
Answer: Lactobacillus
Question 7. Write the use of yeast.
Answer: Yeast is used in the production of alcohol, wine, beer, and other beverages.
Question 8. What are pathogens? Write another name for pathogens.
Answer: Disease-causing microorganisms are known as pathogens. They are also called germs.
Question 9. Define food preservation.
Answer: Food preservation is the method of preserving food from being spoiled by microbes.
Question 10. What is fermentation?
Answer: Fermentation is the process of conversion of food into alcohol.
Microorganisms Friend And Foe Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Question 11. Define communicable diseases. Give some examples.
Answer: Communicable diseases are microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, or another physical contact; e.g., cholera, chicken pox, tuberculosis, common cold, etc.
Question 12. Give two examples of each of the following types of microorganisms:
(1)Algae
(2) Fungi
(3) Protozoa
Answer:
(1) Algae – Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas
(2)Fungi-Aspergillus, yeast
(3)Protozoa – Paramecium, Amoeba
Question 13.Unscramble the jumbled words underlined in the following statements
(1)Curbossulite is an air-borne disease caused by a bacterium.
(2)Xanrhat is a dangerous bacterial disease.
(3)Yeasts are used in the wine industry because of their property of meronettinaf.
(4)Cells of our body produce antidotes to fight pathogens.
(5)Aeeessrrwtip are added to food to prevent the growth of microorganisms.
Answer:
(1) Tuberculosis
(2)Anthrax
(3)Fermentation
(4)antibodies
(5)Preservatives
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 14. Which of the following reproduces only inside a host cell?
(1)Bacteria
(2) Virus
(3) Amoeba
(4) Fungus.
Answer:(2) Virus
Explanation: The virus is considered an intermediate between living and non-living. Outside a host-virus remains inactive. It can perform its life processes and reproduction only when it is inside a host cell.
Question 15. A disease in human beings caused by a virus is
(1)Typhoid
(2) Influenza
(3) Dysentery
(4) Cholera
Answer: (2) Influenza
Explanation:
Typhoid is caused by the bacteria Salmonella typhoid.
Dysentry is caused by an amoeba which is a protozoan.
Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholera bacteria.
Question 16. Pathogenic micro-organisms present in host cells are killed by medicines called
(1) Painkiller
(2) Antibodies
(3) Antibiotics
(4) Vaccines
Answer: (2) Antibiotics
Explanation:
Pain Killers give relief from pain.
Antibodies are produced by our immune system which acts and elicits a specific immune reaction.
Antibiotics that inhibit or kill certain bacteria.
Vaccines provide acquired immunity against a particular disease.
Question 17. The two micro-organisms which live in symbiotic association in lichens are
(1)Fungus and Protozoa
(2)Alga and Bacteria
(3)Bacteria and Protozoa
(4)Alga and Fungus
Answer: (4) Alga and Fungus
Question 18. The gas released during the preparation of bread is
(1)Oxygen
(2) Carbon dioxide
(3) Nitrogen
(4) Sulphur dioxide
Answer: (2) Carbon dioxide
Explanation: Carbon-di-oxide is released due to the fermentation process conducted by yeast. C02 causes the rising of the dough and makes the bread fluffy.
Question 19. The disease caused by a protozoan and spread by an insect is.
(1) Dengue
(2) Malaria
(3)Polio
(4) Measles
Answer: (2) Malaria
Explanation: Malaria is caused by a protozoan named Plasmodium vivax which is transmitted by mosquitos. Other options are viral diseases hence they are wrong answers.
Question 20. Paheli dug two pits, A and B, in her garden. In pit A, she put a polythene bag packed with some agricultural waste. In pit B, she dumped the same kind of a waste but without packing it in a polythene bag. She then covered both pits with soil. What did she observe after a month?
(1)Waste in pit A degraded faster than that in pit B.
(2)Waste in pit B degraded faster than that in pit A.
(3) Waste in both pits degraded almost equally.
(4)Waste in both pits did not degrade at all.
Answer: (2) Waste in pit B degraded faster than that in pit A.
Explanation: Waste in pit B degrades faster than waste in pit A because Polythene in pit B is open and receives oxygen for composting whereas polythene in closed in pit A and organisms don’t receive oxygen to compost the waste material in the polythene bag.
Question 21. Suggest a suitable word for each of the following statements.
(1)Chemicals added to food to prevent the growth of microorganisms.
(2)Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms present in the root nodules of legumes.
(3)The agent spreads pathogens from one place to another.
(4)Chemicals that kill or stop the growth of pathogens.
Answer: 1. Preservatives
2. Rhizobium
3. Carrier/ vector
4. Antibiotics
Question 22. Name the process in yeast that converts sugars into alcohol.
Answer: Fermentation is the process in yeast that converts sugars into alcohol.
Question 23.In the soil, which nutrient is enriched by blue-green algae (cyanobacteria)?
Answer: Blue-green-algae enriches Nitrogen in the soil.
Question 24. Why should we avoid standing close to a tuberculosis patient while he/she is coughing?
Answer: Tuberculosis can spread through the air when the infected person coughs. Hence we avoid standing close to a tuberculosis patient while he/she is coughing.
Question 25. Polio drops are not given to children suffering from diarrhea. Why?
Answer: If the children are suffering from diarrhea oral polio drops will get excreted due to frequent motions. Hence children with diarrhea are not given polio drops.
Question 26. Paheli watched her grandmother making mango pickles. After she bottled the pickle, her grandmother poured oil on top of the pickle before closing the lid. Paheli wanted to know why oil was poured. Can you help her understand why?
Answer: Oils prevent the attack of bacteria which will help preserve the pickle for a long period of time.
Explanation Of Microorganisms Friend And Foe In KSEEB Science
Question 27. Classify the following into friendly and harmful microorganisms.
Answer:
Friendly
Yeast
Lactobacillus
Rhizobium
Harmful Microorganisms
Malarial parasite
Bread mold
Bacillus anthracis
Question 28. While returning from school, Boojho ate chaat from a street hawker. When he reached home, he felt ill and complained of stomach ache and fell ill. What could be the reason?
Answer: The probable reason is that the chaat was contaminated by pathogenic microbes due to unhygienic conditions near the shop or the utensil used for serving could have been contaminated.
The reason may be the contamination of food by pathogenic microbes. Contamination may be due to the unhygienic conditions near the shop or the utensil used to serve the chaat.
Question 29. What will happen to ‘pooris’ and ‘unused kneaded flour’ if they are left in the open for a day or two?
Answer: Pooris and unused kneaded flour get spoiled due to microbial activity. Food gets fermented when kept open and it will be spoiled.
Question 30. (1) Name two diseases that are caused by the virus.
(2)Write one important characteristic of the virus.
Answer:
1. Polio, HIV
2. A virus can reproduce only when it is inside the host cell.
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
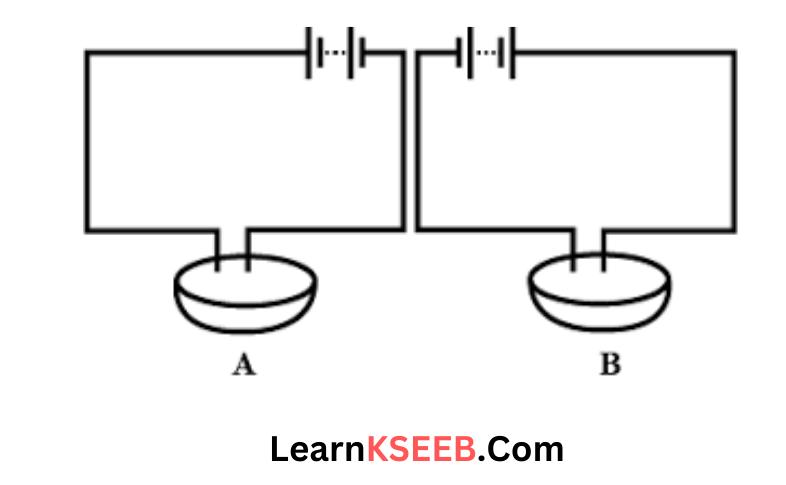
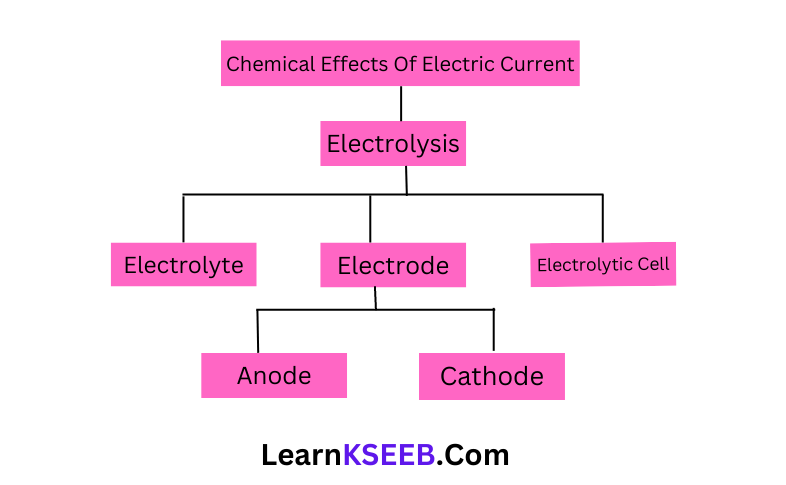
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water















 Answer: From the above actions, we can conclude that force can change the shape of an object.
Answer: From the above actions, we can conclude that force can change the shape of an object. Answer: When unlike poles of the magnet are brought near the other magnet, they attract each other and move in the direction of another magnet. When like poles of a magnet are brought near to the other magnet, they repel each other and move in the direction away from the other magnet. Thus, the force exerted by a magnet on another magnet is a type of non-contact force.
Answer: When unlike poles of the magnet are brought near the other magnet, they attract each other and move in the direction of another magnet. When like poles of a magnet are brought near to the other magnet, they repel each other and move in the direction away from the other magnet. Thus, the force exerted by a magnet on another magnet is a type of non-contact force. Question 8. Take a transparent glass tube or a plastic pipe. The length of the pipe/tube should be about 15 cm and its diameter should be 5-7.5 cm. Also, take a piece of a thin sheet of good quality rubber, say, a rubber balloon. Stretch the rubber sheet tightly over one end of the pipe. Hold the pipe in the middle, keeping it in a vertical position. Ask one of your friends to pour some water into the pipe. Does the rubber sheet bulge out? Note also the height of the water column in the pipe. Pour some more water. Observe again the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe. Repeat this process a few more times. Can you see any relation between the amount of the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe?
Question 8. Take a transparent glass tube or a plastic pipe. The length of the pipe/tube should be about 15 cm and its diameter should be 5-7.5 cm. Also, take a piece of a thin sheet of good quality rubber, say, a rubber balloon. Stretch the rubber sheet tightly over one end of the pipe. Hold the pipe in the middle, keeping it in a vertical position. Ask one of your friends to pour some water into the pipe. Does the rubber sheet bulge out? Note also the height of the water column in the pipe. Pour some more water. Observe again the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe. Repeat this process a few more times. Can you see any relation between the amount of the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe? Answer:
Answer: Answer: Yes, the rubber tube bulge out, and the bulging increases with the amount of water in the bottle. Thus, liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Answer: Yes, the rubber tube bulge out, and the bulging increases with the amount of water in the bottle. Thus, liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container. Answer: We observed different streams of a waterfall at the same distance from the bottle. Thus, it indicates that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.
Answer: We observed different streams of a waterfall at the same distance from the bottle. Thus, it indicates that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.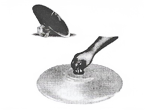 Answer: When we press the sucker, most of the air between its cup and the surface escapes. The sucker sticks to the surface because the pressure of the atmosphere acts on it. To pull the sucker off the surface, the applied force should be large enough to overcome the atmospheric pressure. Thus, this activity gives us an idea about the magnitude of atmospheric
Answer: When we press the sucker, most of the air between its cup and the surface escapes. The sucker sticks to the surface because the pressure of the atmosphere acts on it. To pull the sucker off the surface, the applied force should be large enough to overcome the atmospheric pressure. Thus, this activity gives us an idea about the magnitude of atmospheric Question 2. Make a 50cm x 50cm bed of dry sand about 10cm in thickness. Make sure that its top surface is leveled. Take a wooden or a plastic stool. Cut two strips of graph paper each with a width of 1 cm. Paste them vertically on any leg of the stool—one at the bottom and the other from the top. Now gently put the stool on the sand bed with its legs resting on the sand. Increase the size of the sand bed if required. Now put a load, say a school bag full of books, on the seat of the stool. Mark the level of sand on the graph strip. This would give you the depth, if any, to which the legs of the stool sink in the sand. Next, turn the stool upside down so that now it rests on its seat on the sand bed. Note the depth to which the stool sinks now. Next, put the same load on the stool and note the depth to which it sinks in the sand. Compare the pressure exerted by the stool in the two situations.
Question 2. Make a 50cm x 50cm bed of dry sand about 10cm in thickness. Make sure that its top surface is leveled. Take a wooden or a plastic stool. Cut two strips of graph paper each with a width of 1 cm. Paste them vertically on any leg of the stool—one at the bottom and the other from the top. Now gently put the stool on the sand bed with its legs resting on the sand. Increase the size of the sand bed if required. Now put a load, say a school bag full of books, on the seat of the stool. Mark the level of sand on the graph strip. This would give you the depth, if any, to which the legs of the stool sink in the sand. Next, turn the stool upside down so that now it rests on its seat on the sand bed. Note the depth to which the stool sinks now. Next, put the same load on the stool and note the depth to which it sinks in the sand. Compare the pressure exerted by the stool in the two situations.
 1. The pressure at A> Pressure at B > Pressure at C.
1. The pressure at A> Pressure at B > Pressure at C. Answer: 1. B and C
Answer: 1. B and C Answer: Magnetic force.
Answer: Magnetic force. Answer:
Answer:

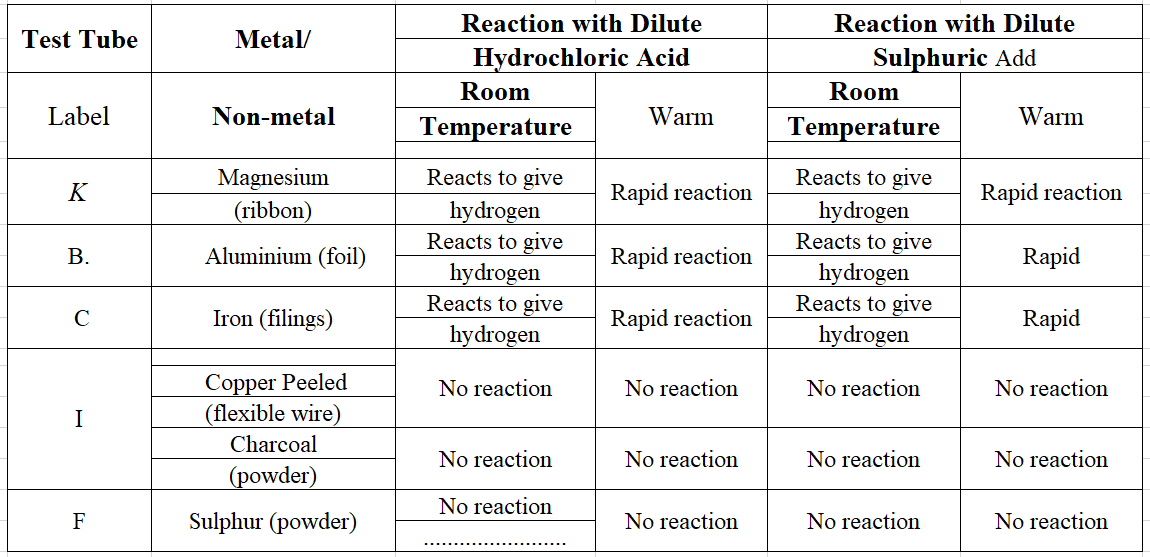
 (But take care that you don’t hurt yourself in the process). Try to hit hard. Hit hard the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal piece and pencil lead. Record your observations Malleability of Materials
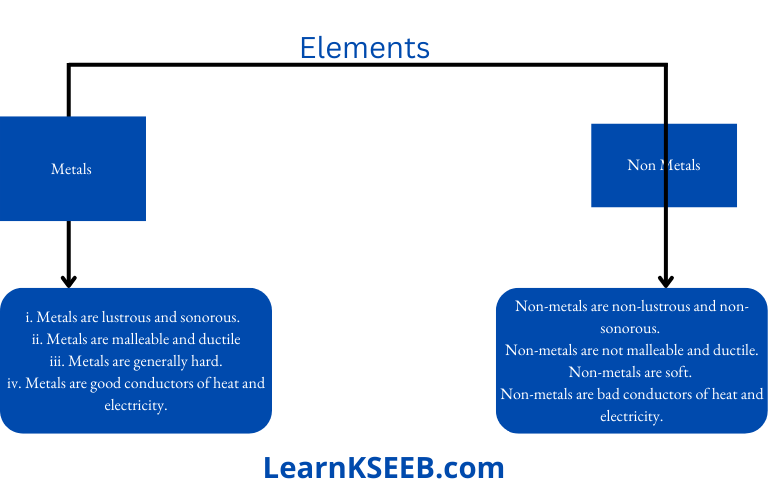
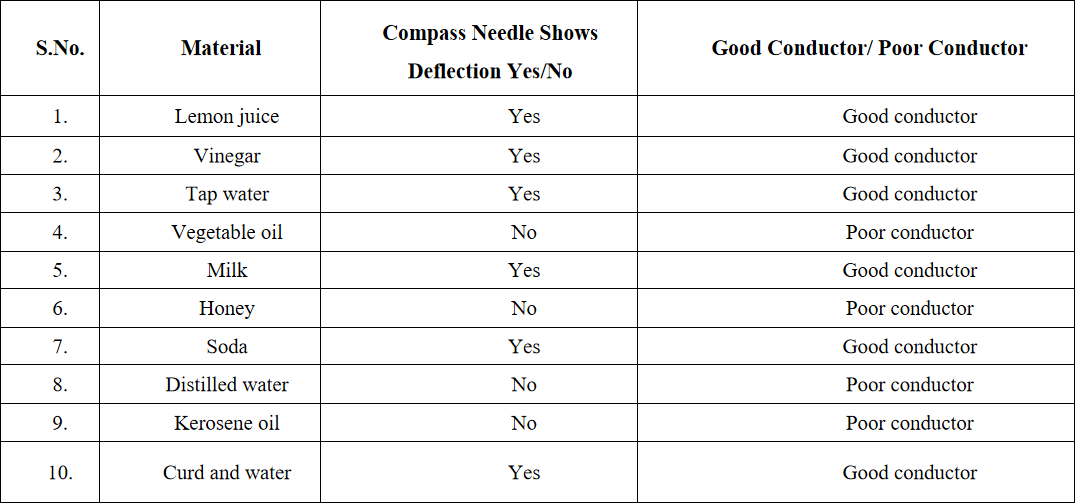
(But take care that you don’t hurt yourself in the process). Try to hit hard. Hit hard the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal piece and pencil lead. Record your observations Malleability of Materials You might have performed the activity with various objects in Class VI. Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors.
You might have performed the activity with various objects in Class VI. Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors. Answer: We observed that the red litmus paper turns blue which shows that the injury of rust is basic. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Answer: We observed that the red litmus paper turns blue which shows that the injury of rust is basic. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.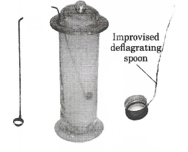 As soon as sulphur start burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass tumbler. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
As soon as sulphur start burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass tumbler. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers. Answer: We observed that the solution of oxide turns the blue litmus red which shows that the solution is acidic in nature. This also shows that the oxide of non-metals is acidic in nature.
Answer: We observed that the solution of oxide turns the blue litmus red which shows that the solution is acidic in nature. This also shows that the oxide of non-metals is acidic in nature. Answer: On touching the beaker, it felt hot. The solution turns the red litmus paper to blue which shows it is basic in nature. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Answer: On touching the beaker, it felt hot. The solution turns the red litmus paper to blue which shows it is basic in nature. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.