KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Points To Remember
Some objects can be charged by rubbing with other objects. There are two kinds of charges positive charge and negative charge. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other. The electrical charges produced by rubbing are called static charges. When charges move, they constitute an electric current An electroscope may be used to detect whether a body is charged or not.
The process of transfer of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing. The process of an electric discharge between clouds and the earth or between different clouds causes lightning. A lightning strike could destroy life and property. Protective measures are of utmost importance during lightning strikes, Taking shelter in interiors(houses or other closed places) and vehicles(closed e.g. cars) are the most preferred measures.
Lightning conductors can protect buildings from the effects of lightning. A natural phenomenon that cannot be predicted is an earthquake, which is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth which lasts for a very short time. The earth consists of three major layers, called the crust, the mantle, and the core. The core is further divided into the inner core and the outer core. The mantle consists of semi-solid material above which the crust floats.
The crust consists of oceans and continents. The crust is divided into several parts, called tectonic plates. The regions where one tectonic plate slides against another are referred to as fault zones, and these are the regions where an earthquake is likely to occur. Hence, these zones are referred to as seismic zones. The place in the interior of the earth where an earthquake occurs is the focus, and the region on the surface of the earth that is the closest to focus is likely to experience the largest damage. This region is called the epicenter of the earthquake.
The instrument that measures the severity of an earthquake is a seismograph. The energy released at the focus of an earthquake propagates outwardly in form of waves known as seismic waves. The destructive energy of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale. It is a logarithmic scale, ranging from | to 10 for indicating the intensity of an earthquake.
An earthquake measuring 7 or more on the Richter scale can cause severe damage to life and property.
Protective measures for earthquakes:
1. If you are at home: Take shelter under a table and stay there till the shaking stops. Stay away from tall and heavy objects that may fall on you.
If you are in bed, do not get up. Protect your head with a pillow.
2. If you are outdoors: Find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees, and overhead power lines. Drop to the ground. If you are in a car or bus, do not come out. Ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot Do not come out till the tremors stop.

Class 8 Science KSEEB Some Natural Phenomena Notes
Some Natural Phenomena NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
1. A plastic scale
2. A copper rod
3. An inflated balloon
4. A woolen cloth
Answer: 2. A copper rod.
Question 2. When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
1. And the clothes both acquire a positive charge.
2. Becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
3. And the cloth both acquire a negative charge.
4. Becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Answer: 2. Becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
Question 3. Write T against true and F against false in the following statements.
1. Like charges attract each other. (T/F)
2. A charged glass rod attracts a charged plastic straw. (T/F)
3. Lightning conductors cannot protect a building from lightning. (T/F)
4. Earthquakes can be predicted in advance. (T/F)
Answer: 1. F, 2.T, 3. F, 4. F
Question 4. Sometimes, a crackling sound is heard while taking off a sweater during winter. Explain?
Answer: The cracking sound is heard because when the sweater is mobbed while taking it off, it acquires a small charge
Question 5. Explain why a charged body loses its charge.
Answer: Our body is a conductor of electricity. When we touch a charged body with our hand, the charged body loses charge to the earth through our body.
Question 6. Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answer: The destructive energy of an earthquake is measured on a scale called the Richter scale. An earthquake measured 3 on this scale will be recorded by a seismograph. Whoever, it s not likely to cause much damage
Question 7. Suggest three measures to protect ourselves
Answer:
1. Hearing thunder, we should rush to a safer place like a house or building. cloth has a negative charge.
2. If no proper shelter is available and in open, never hide under a tree of an electric pole.
3. The telephone cord’s electric wires and metal
4. Becomes negatively charged while the pipes should be avoided from touching. cloth has a positive charge.
Question 8. Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon.
Answer: A charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon because both have the same charge and we know that like charges repel each other. But charged balloons attract an uncharged balloon and lose its own charge to the other balloon.
Question 9. Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument that can be used to detect a charged body.
Answer:
A device that is used to test whether an object is carrying charge or not is known as an electroscope It consists of a metal rod on which two leaves of aluminum foil are fixed to one end and a metal disc at the other end. The leaves are kept inside a conical flask and it is corked to isolate them from the atmospheric air. When a charged body comes in contact with the metal disc, the aluminum leaves move away from each other because some charges get transferred to aluminum leaves through the metal rod. This process is called charging by conduction. The charges on the leaves and the charged body are of the same in nature and thus the leaves of aluminum repel each other. If the body is not charged then they would attract each other.
Question 10. List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Answer: The states that fall in seismic zones are Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Gujarat.
KSEEB Class 8 Science Solutions For Some Natural Phenomena
Question 11. Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precautions would you take to protect yourself?
Answer: The following precautions could be taken to protect ourselves ina earthquakes outside the home:
1. First find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees, and overhead wires.
2. If I am in a car or on a bus, I will not come out Instead I will tell the driver slowly to clear the spot and will not come out till the traitors stop.
Question 12. The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Answer: No, I would not carry an umbrella, because the pointed rod of the umbrella can become a target of lightning.
Some Natural Phenomena Activities
Question 1. Take a used ballpen refill and rub it vigorously with a piece of polythene. Bring it close to small pieces of paper. Take care not to touch the rubbed end of the refill with your hand or with a metallic object. Repeat the activity with small pieces of dry leaf, husk and mustard seeds.
Answer: When we rub ballpen refill with polythene, it acquires a small electric charge. On bringing the charged ballpen refill close to small pieces of paper, the bits of paper are attracted to it. A charged plastic refill can attract bits of paper.
Question 2. Collect the objects and the materials listed Try to charge each by rubbing with the materials mentioned in the Table. Record your findings. You can add more items to the Table.
Answer: 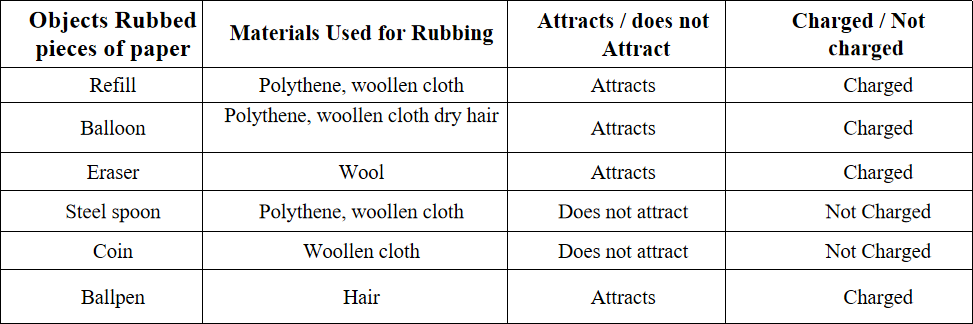
Through this activity, it can be concluded that certain objects acquire charge on being rubbed with certain materials. An object possessing a charge will attract bits of paper.
Question 3.
1. Inflate two balloons. Hang them in such a way that they do not touch each other Rub both balloons with a woolen cloth and release them. What do you observe? Now let us repeat this activity with the used pen refills. Rub one refill with polythene. Place it carefully in a glass tumbler using the tumbler as a stand
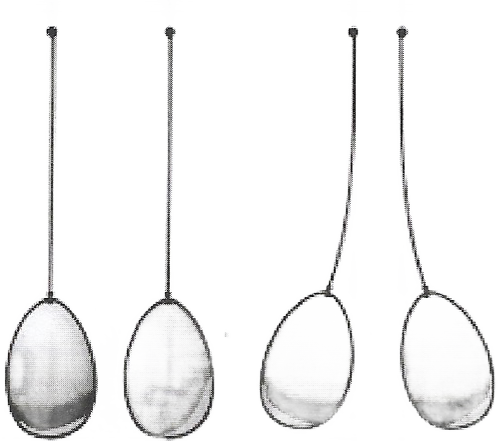
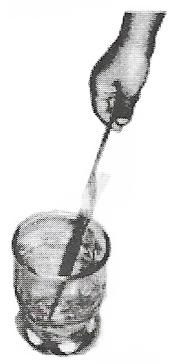
Rub the other refill also with polythene. Bring it close to the charged refill. Be careful not to touch the charged end with your hand. Is there any effect on the refill in the tumbler? Do the two attract each other, or repel each other? In this activity, we have brought close together the charged objects that were made of the same material. What happens if two charged objects made of different materials are brought close to each other? Let’s find out.
2. Rub a refill and place it gently in a glass tumbler as before Bring an inflated charged balloon near the refill and observe.
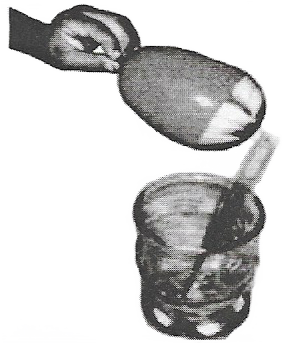
Answer:
1. We observed that balloons repelled each other in the first case. Thus, like charges repel each other. In the second case, a charged refill repelled another charged refill due to the presence of like charges on them.
2. A charged balloon attracted a charged refill because the balloon had charges opposite to that on a refill. Thus, opposite charges attract each other.
Question 4. Take an empty jam bottle. Take a piece of cardboard slightly bigger in size than the mouth of the bottle. Pierce a hole in it so that a metal paper clip can be inserted. Open out the paper clip Cut two strips of aluminum foil about 4 cm x 1 cm each. Hang them on the paper clip Insert the paper clip into the cardboard lid so that it is perpendicular to it. Charge a refill and touch it with the end of the paper clip. Observe what happens. Is there any effect on the foil strips? Do they repel each other or attract each other? Now, touch other charged bodies with the end of the paper clip. Do foil strips behave in the same way in all cases? Can this apparatus be used to detect whether a body is charged or not? Can you explain why the foil strips repel each other?
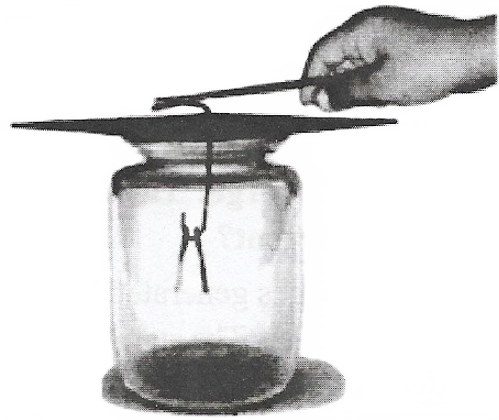

Answer: We observed that aluminum foil strips received the same charge from the charged refill through the metal paper clip as it is a good conductor of electricity. The strips carrying similar charges repelled each other and they became wide open. Such a device that can be used to test the charge on an object is called an electroscope. When we touch the metal paper clip with other charged bodies, the foil strips behave in the same way in all cases. Thus, we find that electrical charges can be transferred from a charged object to another through a metal conductor.
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Question 5. Ask your parents about the huge damage to life and property caused by these earthquakes. Collect a few pictures showing the damage caused by these earthquakes from newspapers and magazines of those days. Prepare a short report on the suffering of the people during and after the earthquakes.

Answer: An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth which lasts for a short time. It is one of the most dreaded and devastating natural calamities. It causes a huge loss and destruction of our life and property. Some of the damaging effects of an earthquake are as follows It brings the destruction of buildings, dams, railway tracks, roads, etc.
1. There is an outbreak of fire due to the breaking of electrical power or gas lines.
2. It ruptures groundwater pipes disrupting the water supply system.
3. Landslides and tsunamis occur respectively in hilly and coastal areas.
4. There is a bursting of sewer pipes releasing sewage water.
5. Communication is completely cut off and the areas get 5 disconnected from the rest of the world.
6. An earthquake also causes floods.
Question 6. Take an outline map of the world. Locate the eastern coast and Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. Mark other countries around the Indian Ocean which could have suffered damage. Collect accounts of the devastation caused by the tsunami in India from your parents, or other elders in the family or in the neighborhood.

Answer:
1. An outline map of the world locating the eastern coast and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands in India. Other countries around the Indian Ocean have been marked in the map given which could have suffered damage.
2. Accounts of the devastation caused by the tsunami in India—A major tsunami occurred in the Indian Ocean on 26th December 2004. At 8.38 a.m. quake of 6.1 magnitudes was felt in Andamans. At 9.00 a.m. as it nears the Chennai coast, the tsunami slowed down but rose higher. This affected India’s South-East coast, predominantly in the state of Tamil Nadu as well as the territories of Andaman and Nicobar Island. Thousands of people died, and the coastal area was devastated completely. Many fishing communities were ruined by the tsunami, most notably the fishing town of Nagapattinam. In fact, it was one of the most devastating natural calamities, people have ever witnessed.
Some Natural Phenomena Additional Questions
Question 1. What are the two natural calamities?
Answer: Lightning and Earthquake.
Question 2. Name the two types of charges.
Answer: Positive and Negative.
Question 3. Mention the interactions of two types of charges.
Answer: Like charges repel each other wMe unlike charges attract each other.
Question 4. Name the device used to protect buildings from lightning.
Answer: Lightning conductor.
Explanation Of Some Natural Phenomena In KSEEB Science
Question 5. In which direction do the shock waves produced by an earthquake travel?
Answer: Both on the surface and inside the earth.
Question 6. Who discovered static electricity or lightning in clouds and when?
Answer: Benjamin Franklin in 1752.
Question 7. What actually causes lightning?
Answer: Lightning is caused by the accumulation of charges in the clouds.
Question 8. What are static &electricity?
Answer: The electrical charge reproduced by rubbing two objects is called static electricity.
Question 9. What are weak zones called?
Answer: Seismic or fault zones.
Question 10. What is the static charge? How does it differ from an electric current?
Answer: The electric charges generated by rubbing are called static charges. The static charges do not move while charges move in electric current.
Question 11. What is earthing? What is the application of earthing?
Answer: The process of transfer of charges from a charged object to the earth is called earthing. It is provided in buildings to protect from electrical shocks due to any leakage of electrical current.
Question 12. How does the electric discharge occur in clouds?
Answer: At the time of thunder negative charges are accumulated near the clouds and positive charges near the ground. When these charges meet, the electric discharge takes place between the ground and clouds. In this process, a large amount of energy is released.
Question 13. What are fault zones? Name the fault zones in India.
Answer: Since earthquakes are caused by the movement of plates, the boundaries of the plates are weak zones where earthquakes are more likely to occur. The weak zones are also known as seismic or fault zones.
Question 14. What are seismic waves? How are these waves recorded?
Answer: The tremors produce waves on the surface of the earth. These are called seismic waves. These waves are recorded by an instrument called the seismograph.
Question 15. What safety measures should be taken during lightning and thunderstorm?
Answer: The following safety measures are advisable to be adopted to protect from lightning and thunderstorm:
1. No open place is safe. A house or a building is a safe place. If traveling by car or by bus, it is safe to stay inside with the windows and doors of the vehicle shut.
2. If we are outside, the following things are important to be kept in mind
3. Open vehicles, like motorbikes, tractors, construction machinery, fields, tall trees, shelters in parks, and elevated places do not protect us from lightning strikes.
4. Carrying an umbrella is not at all a good idea during thunderstorms.
5. If no shelter is available and we are in an open field, we should keep away from all trees. We should stay away from poles or other metal objects. We should not be on the ground. Sitting in a pose is advisable.
6. If we are inside the house, we should take care as advised further:
7. Lightning can strike telephone cords, electrical wires, and metal pipes. During a thunderstorm, contact with r these should be avoided.
8. It is safer to use mobile phones and cordless phones, However, it is not wise to call up a person with a wired phone. Bathing should be avoided. Electrical appliances should be unplugged.
KSEEB Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Important Questions
Some Natural Phenomena Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. An electroscope is a device that is used to find if an object is
1. Charged
2. Magnetic
3. Free of cracks
4. Hot
Answer: 1. Charged
Explanation: An electroscope is a device that is used to find whether the object is charged or not. It consists of two metallic strips which are closely placed.
Question 2. Electric current is to be passed from one body to another. For this purpose, the two bodies must be joined by
1. Cotton thread
2. Plastic string
3. Copper wire
4. Plastic string
Answer: 3. Copper wire
Explanation: Copper is a good conductor of electricity. Plastic, rubber, and cotton are bad conductors of electricity.
Question 3.The movement of the earth’s plates causes
1. Cyclones
2. Lightning
3. Earthquakes
4. Thunderstorms
Answer: 3. Earthquakes
Explanation: When the earth’s plates brush past one another it leads to earthquakes. Earth can cause damage to buildings and dams.
Question 4. Two charged objects are brought close to each other. Choose the most appropriate statement from the following options:
1. They may attract
2. They may repel
3. They may attract or repel depending on the type of charges they carry
4. There will be no effect
Answer: 3. They may attract or repel depending on the type of charges they carry
Explanation: The charges are like charges they repel each other and if the charges are unlike charges they attract each other.
Question 5. Which of the following is not likely to cause Tsunami?
1. A major nuclear explosion undersea
2. Earthquake
3. Volcanic eruption
4. Lightning
Answer: 4. Lightning
Explanation: Tsunami is caused due to disturbances caused deep down the sea. Lightening will not cause any disturbance to the sea whereas earthquakes, major nuclear explosions undersea, and Volcanic eruptions can cause a disturbance in the sea.
Question 6. The earth’s plate responsible for causing earthquakes is
1. The crust of the earth
2. The mantle of the earth
3. The inner core of the earth
4. The outer core of the earth
Answer: 1. The crust of the earth
Explanation: Sudden trembling or shaking of the earth due to disturbance deep down its top layer called the crust.
Question 7. Consider the list of terms given below:
1. Seismic Zone
2. Fault Zone
3. Mantle
4. Inner Core
The boundaries of the earth’s plate are known as
Answer: 1. Seismic Zone,2. Fault Zone
Explanation: An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth which lasts for a very short time. Earthquakes are caused due to the movement of plates. Boundaries of the plates are weak zones where earthquakes are most likely to occur.
Question 8. The outermost layer of the earth is called
1. Mantle
2. Outer core
3. Crust
3. Inner core
Answer: 3. Crust
Explanation: Earth’s top layer is called the crust which is followed by the mantle, outer core, and inner core.
Question 9. Major earthquakes are less likely to occur in
1. North East India
2. Rajasthan
3. Rann of Kutch
4. Orissa
Answer: 4. Orissa
Explanation: Major earthquakes are less likely to occur in Orissa. The most threatened areas in India are Kashmir, the Western and Central Himalayas, the whole of North-East, Rann of Kutch, Rajasthan, and the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
Question 10. Consider the list of terms given below
1. Tsunami
2. Landslide
3. Floods
4. Lightning
Earthquakes can cause
Answer:
1. Tsunami
2. Landslide
3. Floods
Detailed Notes On Some Natural Phenomena KSEEB
Some Natural Phenomena Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. State whether the following are True or False.
1. Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world.
2. The plates of the outermost layer of the earth are always in continuous motion.
3. Tremors on the earth can also be caused by the eruption of a volcano.
4. The process of electric discharge cannot occur between clouds and the earth.
5. Bathing outdoors should be avoided during a thunderstorm.
Answer:
1. True
2. True
3. True
4. False- The process of electric discharge occurs between clouds and the earth.
5. True
Question 2. Is it possible to predict the occurrence of an earthquake?
Answer: No, it is not possible to predict the occurrence of an earthquake.
Question 3. If a charged plastic straw is brought near another uncharged plastic straw, what will happen?
Answer: Plastic straws will attract each other
Question 4. Plastic straws A and B are rubbed with a dry cotton cloth. What will happen if they are brought near each other?
Answer: They will repel each other.
Question 5. During the construction of a building, the lightning conductor was left hanging in the air by mistake. Would the lightning conductor be still effective? Explain.
Answer: It will not be effective because the charge will not pass through to the earth as the lightning conductor was not connected properly to the earth.
Question 6. If air and cloud were good conductors of electricity, do you think lightning could occur? Explain.
Answer: No, lightning will not occur because the separation of charges cannot take place in conductors. Hence charges will not accumulate on clouds and lightning cannot take place.
Question 7. Identify the lightning conductor and the copper plate
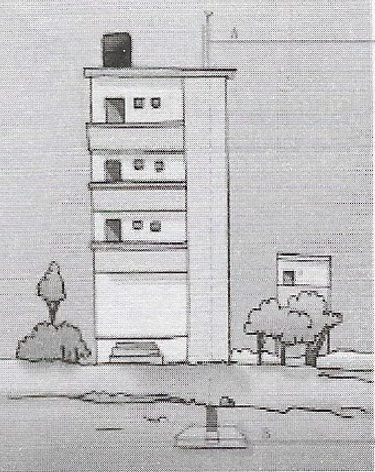
Answer: A is the lightning conductor and B is the copper plate.
Question 8. If the materials used for constructing a building were good conductors, do you think lightning will strike the building? Will the lightning conductor be still required to be installed in the building?
Answer: No installing conductor is not required if the materials used for constructing a building were good conductors.
Question 9. You might have observed on a dry day that when you touch the screen of a television or computer monitor (with a picture tube), you get a slight shock. Why does it happen?
Answer: The electric charge gets accumulated on the screen. On touching the screen the charge discharges through our body. Thus, we get a slight shock.
Question 10. Explain how does lightning conductor protect a building from getting struck by lightning.
Answer: Lightning conductor conducts the charge to the earth hence charge will not accumulate on the build. This protects the building from getting struck by lightning.
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
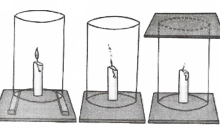
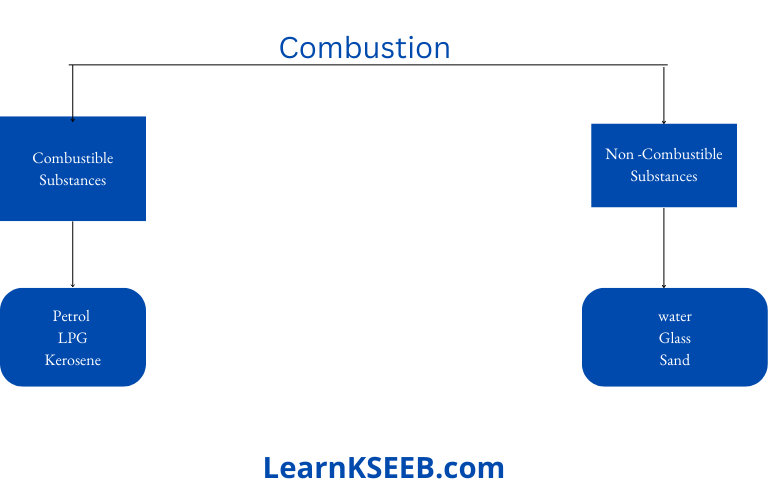
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water


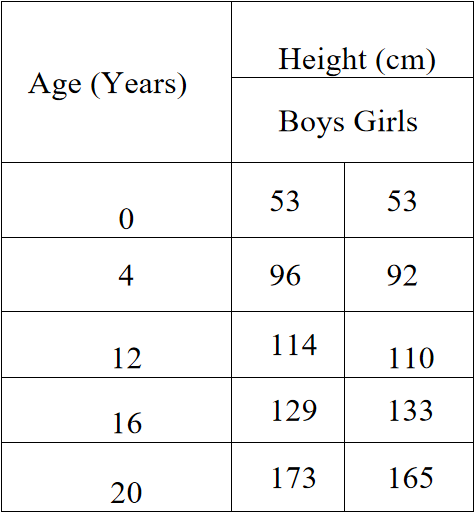
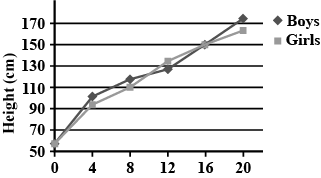






 Animal cell
Animal cell










 Answer: We observed that sound becomes fainter than earlier when we try to suck air. But when we remove the tumbler from our mouths the sound again becomes loud. Thus, sound needs a medium to travel.
Answer: We observed that sound becomes fainter than earlier when we try to suck air. But when we remove the tumbler from our mouths the sound again becomes loud. Thus, sound needs a medium to travel. Answer: We can hear the sound of the bell which indicates that sound can travel through liquids.
Answer: We can hear the sound of the bell which indicates that sound can travel through liquids. Answer: Yes, we find that we can hear the sound of the scratch. But, the people standing around us cannot hear the same sound or we can say that it is limping not audible to them.
Answer: Yes, we find that we can hear the sound of the scratch. But, the people standing around us cannot hear the same sound or we can say that it is limping not audible to them. Answer: The grain jumps up and down because of the vibration caused underneath the stretched rubber. Thus when sound waves fall on the eardrum, it starts vibrating back and forth rapidly.
Answer: The grain jumps up and down because of the vibration caused underneath the stretched rubber. Thus when sound waves fall on the eardrum, it starts vibrating back and forth rapidly. Answer: The sound produced is louder when the tumbler is struck hard. The amplitude of vibration of the tumbler is larger when the glass is struck hard. Thus the loudness of sound depends upon the amplitude of vibration.
Answer: The sound produced is louder when the tumbler is struck hard. The amplitude of vibration of the tumbler is larger when the glass is struck hard. Thus the loudness of sound depends upon the amplitude of vibration.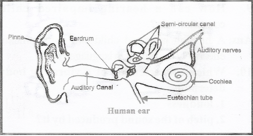
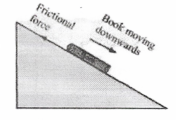 Question 5. You spill a bucket of soapy water on a marble floor accidentally. Would it make it easier or more difficult for you to walk on the floor? Why?
Question 5. You spill a bucket of soapy water on a marble floor accidentally. Would it make it easier or more difficult for you to walk on the floor? Why?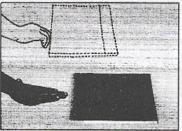

 The pencil cell covers different distances on different surfaces Reapt this activity by spreading a thin layer of sand over the table. Maintain the same slope throughout the activity.
The pencil cell covers different distances on different surfaces Reapt this activity by spreading a thin layer of sand over the table. Maintain the same slope throughout the activity.
 Answer: 2. From left to right (*!)
Answer: 2. From left to right (*!)