KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Points To Remember
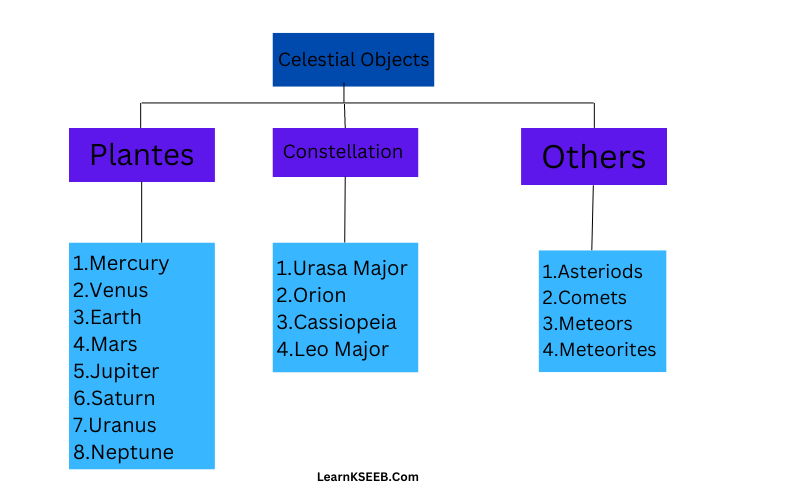
Celestial Bodies: All natural bodies visible in the sky, outside the Earth’s atmosphere, constitute the celestial bodies, e.g. stars, planets, their moons, comets, asteroids, meteors, etc.
The Moon is the celestial body closest to us. Stars are celestial bodies that emit light of their own. Our sun is also a star.
It is convenient to express the distances of stars in light years. A light year is a distance covered by light in one year. Stars appear to move from east to west. The pole star appears to be stationary from the Earth because it is situated close to the direction of the axis of rotation of the Earth.
Solar system: The Sun and the celestial bodies that revolve around it form the solar system. It comprises a large number of bodies like planets (8 known to date), their moons, comets, asteroids, meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites. These objects are held together in the solar system due to Sun’s gravitational pull.
Sun: It is the source of almost all energy on Earth. It continuously emits huge amounts of heat and light.
Planets: Planets reflect sunlight that is incident on them. They have no light of their own, so they don’t wrinkle like the stars. Planets have definite paths called orbits in which they revolve around the sun.
The time taken by a planet to complete one full revolution around the sun is called it’s period of revolution. The time taken by a planet to rotate a full 360 degrees on its axis is called it’s period of rotation. The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution increases as the distance from the sun increases.
There are eight planets in our solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Venus is the brightest planet in the night sky. Jupiter is the largest planet of the solar system
Other members of our solar system are:
1. Asteroids: These are rocky planetary bits or- biting around the sun, asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter.
2. Comets: These are celestial bodies that revolve around the sun. It appears generally as a bright head with a long tail. The tail of a comet is always directed away from the Sun. A comet is made up of rock, dust water, ice, and frozen gases.
3. Meteors and Meteorites: Meteoroids are chunks of rock or particles of debris in our solar system. They are smaller than comets. When meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere they are called meteors. Most meteors burn up in the at atmosphere, but if they survive the frictional heating and strike the surface of the Earth they are called meteorites. As a meteor glows brightly when it falls to the ground it is called a shooting star.
4. Satellites A body revolving around another body is called a satellite. Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. Some planets also have natural satellites.
Artificial Satellites: Man-made objects sent into space to orbit the earth, Example: IRS, EDUSAT, INSAR. The artificial satellites revolve around the Earth. They are much closer than the moon Artificial satellites are used for weather forecasting, long-distance communication, and remote sensing.
Stars are luminous bodies that appear as points of light in the night sky. Our Sun is also a star. Many of the stars that we see in the sky are much bigger than the sun. But as they are quite far away from us, they appear very small.
Constellations: A group of stars forming some kind of recognizable figures or patterns is known as a constellation. Constellations appear to move from east to west as Earth rotates from west to east, Orion- the Hunter, Ursa Major- the Great Bear or Saptarishi, and Cassiopeia are some constellations.
The Moon is the celestial body closest to us. It is the only natural satellite of the Earth. It is a non-luminous body and it reflects the sunlight incident on it. Due to its revolution around the Earth, when it is at different positions in its path, the apparent disc of the Moon changes, which gives rise to its phases.

Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars And The Solar System Pdf
Stars And The Solar System NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
1. An asteroid
2. A constellation
3. A satellite
4. A comet
Answer: 2. A constellation
Question 2. Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
1. Sirius
2. Mercury
3. Saturn
4. Earth
Answer: 1. Sirius
Question 3. Phases of the moon occur because
1. We can see only that part of the moon that reflects light toward us.
2. Our distance from the moon keeps changing.
3. The shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon’s surface.
4. The thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer: 1. We can see only that part of the moon that reflects light toward us.
Question 4. Fill in the blanks.
1. The planet which is farthest from the Sun is Neptune.
2. The planet which appears reddish in color is Mars.
3. A group of stars, which appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a constellation.
4. A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a satellite.
5. Shooting stars are actually not stars.
6. Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Karnataka Board Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Solutions
Question 5. Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F).
1. Pole star is a member of the solar system. ( )
2. Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system. ( )
3. Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. ( )
4. INSAT is the artificial satellite. ( )
5. There are nine planets in the solar system. ( )
6. Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( )
Answer: True/False
1. False
2.True
3. False
4.True
5. False
6. False
Question 6. Match items in column A with one or more items in column B.
Column A Column B
Inner planets 1. Saturn
Outer planets 2. Great Bear
Constellation 3. Moon
Satellite of the Earth 4. Mars
Answer:
Column A Column B
Inner planets 4. Mars
Outer planets 1. Saturn
Constellation 2. Great Bear
Satellite of the Earth 3. Moon
Question 7. In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer: Venus appears in the western sky just after sunset.
Question 8. Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer: Jupiter is the largest planet of the solar system.
Question 9. What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer: The stars forming a group that has a recognizable shape is called a constellation.
Stars And The Solar System Class 8 Kseeb Solutions With Answers
Question 10. Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in
1. Ursa Major and
2. Orion.
Answer:


Question 11. Name two objects other than planets that are members of the solar system.
Answer: Satellites and asteroids are objects that are members of the solar system.
Question 12. Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer: To locate the Pole Star we should look toward the northern part of the sky and identify UrsaMajor. We may look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. A straight line passing through these stars is imagined and is extended towards the north direction. This line leads to a star that is not too bright. This is the Pole Star.
Question 13. Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer: No, no star moves in the sky. They appear to move from east to west because the Earth rotates from west to east about its axis.
Question 14. Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years?
Answer: The distance of stars is so large that it cannot be expressed in terms of kilometers. That is why very large distances are expressed in another unit known as a light year. One light year is the distance traveled by light in one year. If the distance of a star is eight light years, it means that this distance is the distance traveled by light in one year.
Question 15. The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the earth. How many earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer: The radius of the Earth is r.Then, the radius of Jupiter is 11r. So, the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and Earth
formula
So, the ratio of the voLumes of Jupiter and Earth is 1331:1
So, 133:1 Earth can accommodate Jupiter.
Kseeb Class 8 Science Stars And The Solar System Exercise Solutions
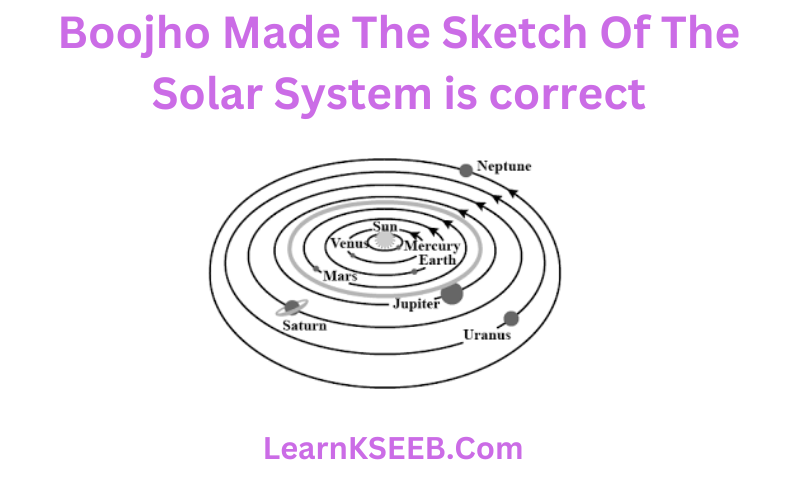
Question 16. Boojho made the following sketch of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not correct it.

Answer: No, the diagram made by Boojho is not correct, because in the solar system the sequence of the planets of their distance from the sun is like; Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Here he had changed the positions of the planets Venus, Mars, Neptune, and Uranus. Besides this, he had shown in the diagram that shows the Asteroids belt in the gap between the orbits of Saturn and Jupiter. This is incorrect The Asteroids belt is located in the middle of the orbits of Jupiter and Mars.
Karnataka Board 8th Science Chapter 17 Important Questions And Answers
Stars And The Solar System Activities
Question 1. Observe the moon continuously for several nights, preferably from one full moon to the next. Make a sketch of the moon every night in your notebook and note the day from the day the part of the sky (east or west) in which the moon is seen.
Answer: We find that there is a change in the shape of the moon every day and the moon appears to be perfectly round on a full moon day. On the fifteenth day of the month, we see that the moon is not visible even if the sky is clear. Thus, the moon goes on increasing every day, till on the fifteenth day and the full face of the moon the bright part of the moon goes on decreases every night and by another fifteen days again the new moon is formed.
Question 2. Draw a circle of about 1 m in diameter on the ground. Ask one of your friends to stand at the center of this circle. You revolve around your friend in such a manner that your face always remains towards him. Can your friend see your back? How many rotations did you complete in one revolution? The moon revolves around the Earth in a similar manner.
Answer: No, my friend cannot see my back. One rotation is completed in one revolution. It is concluded that the moon completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the earth.
Question 3. Stand in the center of a big room and start rotating. In which direction will the objects in the room appear to move? Do you see them moving in the direction opposite to your motion?
Answer: The object appears to move in the opposite direction to our motion.
Kseeb Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Textbook Solutions
Question 4. Take an umbrella and open it. Make about 10-15 stars out of white paper. Paste one star at the position of the central rod of the
umbrella and others at different places on the cloth near the end of each spoke Now rotate the umbrella by holding its central rod in your hand. Observe the stars on the umbrella. Is there any star that does not appear to move? Where is this star located? If there were a star located where the axis of rotation of the Earth meets the sky, could this star also be stationary?
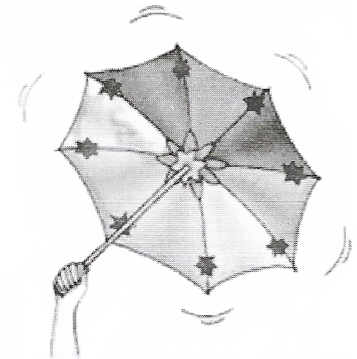
Answer: Yes, the star situated at the central rod of the umbrella does not appear to move. Star located at the axis of the earth meets the sky is also stationary. Thus, the Pole star situated in the direction of the earth’s axis does not appear to move.
Question 5. Observe this constellation (Ursa Major) for a few hours. Do you find any change in its shape? Do you find any change in its position?
Answer: It is observed that the shape of the constellation remains the same but the constellation appears to move in the sky from east to west.
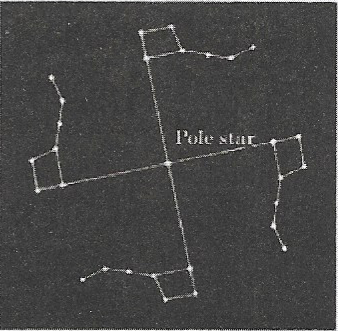
Question 6. This activity should be performed on a clear moonless night during summer at about 9.00 p-m. Look towards the northern part of the sky and identify Ursa Major. You may get help from elders in your family. Look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. Imagine a straight line passing through these stars Extend this imaginary line towards the north direction. (About five times the distance between the two stars.) This line will lead to a star that is not too bright. This is the Pole star. Observe the Pole star for some time. Note that it does not move at all as other stars drift from east to west.

Answer: Pole star is a prominent star and is aligned with the Earth’s axis of rotation. So Pole star does not move at all with respect to other stars.
Question 7. During a summer night, observe Ursa Major 3-4 times at an interval of 2 to 3 hours. Also, locate the Pole star each time. Does Ursa Major appear to move from east to west? Does it appear to revolve around the Pole star? Compare your observations with those Ursa Major moves around the Pole star
Answer: It is concluded that all the stars of Ursa Major appear to revolve around the Pole star.
Question 8. Go out into the playground with four or five of your friends. Draw four circles of radii 1m, 1.8 m, 2.5 m, and 3.8 m, all having a common center Ask one of your friends to stand in the center and represent the Sun. Your other four friends may represent Mercury, Venus,
Earth and Mars. Ask your friends to move around the Sun in an anti-clockwise direction in their own orbits Do they collide with one another?

Answer: No, they do not collide with one another, because they have fixed orbits of their own. In a similar way, planets move in their own orbits.
Stars And The Solar System Additional Questions
Question 1. Name the planet nearest to the Sun.
Answer: Mercury
Question 2. What is the speed of light?
Answer: 300000 km per second (3 x 10° m/s).
Question 3. Which is the brightest planet in the night sky?
Answer: Venus
Question 4. Which planets do not have satellites of their own?
Answer: Venus and Mercury
Question 5. Why Earth appears blue from space?
Answer: Due to the presence of water Earth appears blue from space
Question 6. Which planet is the least dense among all?
Answer: Saturn
Question 7. Name the unit which is used to measure astronomical distances.
Answer: Lightyear
Kseeb 8th Standard Science Chapter 17 Notes And Solutions
Question 8. What are meteors?
Answer: Meteors are bright streaks of light in the sky produced by the entry of small meteoroids into the Earth’s atmosphere. They are also called shooting stars.
Question 9. Define the phases of the Moon.
Answer: The various shapes of the bright part of the Moon as seen during the month are called phases of the Moon,
Question 10. What makes life possible on planet Earth?
Answer: Some special environmental conditions responsible for the existence and continuation of the life of the Earth are :
1. Right distance from the Sun
2. Right temperature range
3. Presence of water
4. Presence of oxygen and hostile atmosphere
5. Presence of blanket of ozone
Stars And The Solar System Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Question 11. Differentiate between the following :
1. Star and planet
Answer:
Star
1. Star twinkles in the sky.
2. It has its own light.
3. It is fixed at a point.
4. It is very big in size.
Planet
1. Planet does not twinkle in the sky.
2. It has no light.
3. It revolves around the sun.
4. It is very small compared to.the.star.
2. Asteroid and comet
Asteroid
1. Asteroids are made up of metals and rocky materials.
2. It rotates nearer to the sun.
3. It does not has any tail of volatile material.
Comet
1. Comets are made up of ice, dust, and rocky material.
2. It rotates farther from the sun.
3. It has a tail of volatile gases when passing close to the sun.
3. Galaxy and Constellation
Answer:
Galaxy
1. It is a collection of billions of stars.
2. It does not resemble the shape of human beings or animals.
3. There are billions of galaxies in the Universe.
Constellation
1. It is a collection of only a few stars.
2. It is arranged in patterns resembling human beings or some animals.
3. There are only about 88 constellations.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Stars And The Solar System Class 8 Karnataka Board
Question 12. Explain why we see phases of the moon.
Answer: The moon does not have its own light. We see the moon because the sunlight falling on it gets reflected toward us. Thus, we see only that part of the moon that reflects light keeps on changing daily. This happens because the moon revolves around the earth along with this moon also revolves around the sun. Therefore, we see phases of the moon.
Stars And The Solar System Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Morning star is the name given to
1. Pole star
2. Star Sirius.
3. Planet Jupiter
4. Planet Venus
Answer: 4. Planet Venus.
Explanation: Planet Venus is dazzling than any other stars and it is visible in the eastern sky before sunrise.
Question 2. Sun appears to move from east to west around the earth. This means that earth rotates from
1. East to west
2. West to east
3. North to south
4. West to north
Answer:2. West to east
Explanation: Sun appears to move from east to west around the earth which means the earth is rotating in the opposite direction.
Question 3. An astronaut standing on the surface of the moon throws a ball upwards. The ball would
1. Directly fall down from the point it is released.
2. Hang in space.
3. Go up and then come back to the surface of the moon.
4. Keep going up never to come back.
Answer: 3. Go up and then come back to the surface of the moon.
Explanation: On the moon acceleration due to gravity is lesser than earth hence the ball will go up and then come back to the surface of the moon.
Question 4. Suppose a new planet is discovered between Uranus and Neptune. Its time period would be
1. Less than that of Neptune.
2. More than that of Neptune.
3. Equal to that of Neptune or Uranus.
4. Less than that of Uranus.
Answer: 1. Less than that of Neptune.
Explanation: We know that the time period is directly proportional to the distance from the sun. Hence a new planet discovered between Uranus and Neptune will have less time period than the Neptune and greater than the Uranus.
Question 5. The change in seasons on the earth occurs because
1. The distance between the earth and the sun is not constant.
2. The axis of rotation of the earth is parallel to the plane of its orbit.
3. The axis of rotation of the earth is perpendicular to the plane of its orbit.
4. The axis of rotation of the earth is tilted with respect to the plane of its orbit.
Answer: 4. The axis of rotation of the earth is tilted with respect to the plane of its orbit.
Explanation: Axis of rotation of the earth is not perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. The tilt is responsible for the change of seasons on earth.
Explanation Of Stars And The Solar System In KSEEB Science
Question 6. Do stars emit light only during the night?
Answer: Stars emit light always, but cannot see them during the day because of the excessive brightness of the sun.
Question 7. Paheli and Boojho observed a bright object in the night sky that was not twinkling. Paheli says, it itis a star, and Boojho says it is a planet. Who is correct?
Answer: Boojho is right because only planets cannot twinkle whereas stars emit light from a far distance and they twinkle.
Question 8. State whether the following statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’.
1. The planet nearest to us is Jupiter.
2. All the stars are at the same distance from us.
3. The planets do not emit light of their own.
4. The planets keep changing their position with respect to stars.
5. The planet Venus appears in the eastern sky before sunrise.
6. The plane in which the earth revolves around the sun is called the equatorial plane of earth.
Answer:
1. False: Mars and venus are the nearest plans to earth
2. False: Different stars are at distance from us
3. True
4. True
5. True
6. False: Earth revolves around the sun in the orbital plane
Question 9. John saw the full moon on a particular day. After how many days will he be able to see the full moon again?
Answer: Approximately 29 days
Question 10. Astar is ten light-years away from the earth. Suppose it brightens up suddenly today. After how much time shall we see this change?
Answer: We will see the change after 10 years.
Question 11. Meteors are not visible during the daytime. Explain the reason.
Answer: Meteors are not visible during the daytime because the brightness of a meteor is extremely small compared to that of the sun.
Question 12. Why does the moon change its shape daily?
Answer: We see only that part of the moon from which the light of the sun is reflected toward us. Hence the moon changes its shape daily.
Question 13. Paheli saw the moon through a glass window at 8:00 p.m. She marked the position of the moon on the glass pane. She got up at 4 a.m. in the morning. Will the moon be visible in the same position?
Answer: No, Because the position of the moon keeps changing during the night.
Question 14. Suppose the moon emits light of its own. Would it still have phases? Justify your answer
Answer: The moon does not emit its own light and reflects the light of the sun. phases are seen. Because of the revolution of the earth, reflections of different intensities of light fall on the moon. Because of this moon glows continuously forming phases.
Question 15. Explain why we always see the same side of the moon.
Answer: We always see the same side of the moon because the moon’s period of revolution around the earth is equal to the period of rotation of the moon on its axis. Hence we can only the side that faces us.
Question 16. Suppose the distance between earth and sun becomes half of its present distance. What is likely to happen to live?
Answer: Life may no longer exist because some special environmental conditions are needed for the existence and continuation of life on the earth. The right distance of the earth from the Sun is necessary so that it has the right temperature range, the presence of water and a suitable atmosphere, and a blanket of ozone.
Flow Chart:
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
