Combustion And Flame Points To Remember
Combustion: The process of burning a substance in the presence of air (oxygen) and undergoing a chemical reaction to produce heat and light.
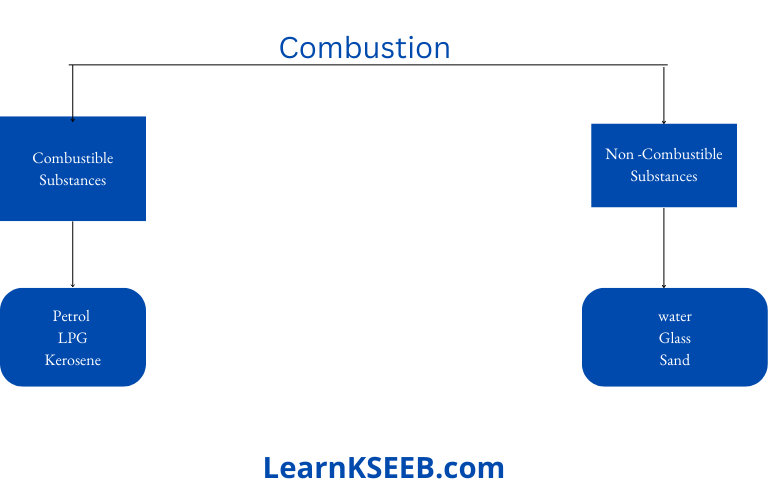
The substances which burn in the air are called combustible.
Oxygen (in the air) is essential for combustion.
During the process of combustion, heat and light are given out.
Ignition temperature: This is the lowest temperature at which a combustible substance catches fire.
Types of combustion: The type of combustion differs depending on the type of fuel. Based on nature and intensity combustions are classified into three types. They are:
1. Rapid combustion
2. Spontaneous combustion
3. Explosion
Flame: It is a zone of burning vapour. The substances which vaporise during burning give flames. Example: Kerosene oil and molten wax.
Inflammable substances have very low ignition temperatures.
Fire can be controlled by removing one or more requirements essential for producing fire.
Water is commonly used to control fires.
Water cannot be used to control fires involving electrical equipment or oils.
There are three different zones of flame — dark zone, luminous zone, and non-luminous zone.
Fuel is any material that is burned to obtain energy that can be used to heat or move another object.
A good fuel must
1. Be readily available.
2. Be cheap.
3. Burn easily at a moderate rate.
4. Produce a large amount of heat.
5. Do Not leave behind any undesirable substances.
Fuels differ in efficiency and cost.
Fuel efficiency is expressed in terms of its calorific value which is expressed in units of kilojoules per kg.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame PDF
Types of Fuels:
1. Solid Fuels: Combustible substances which are solid at room temperature.
Examples: coal, coke, wood, charcoal, etc.
2. Liquid fuels: Volatile liquids. which produces combustible vapour.
Examples: Petrol, kerosene, alcohol, diesel, etc.
3. Gaseous fuels: Combustible gases or a mixture of combustible gases.
Examples: Natural gas, LPG, biogas, coal gas, etc.
Effects of Burning of Fuels:
1. Carbon fuels like wood, and coal petroleum release unburnt carbon particles. These are dangerous pollutants causing respiratory diseases, such as asthma.
2. Incomplete combustion of carbon fuels gives carbon monoxide which is a poisonous gas.
3. Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is believed to cause global warming.
4. Oxides of Sulphur and nitrogen dissolve in rainwater and form acids. Such rain is called acid rain. It is very harmful to crops, buildings and soil.
Unburnt carbon particles in the air are dangerous pollutants causing respiratory problems.
The incomplete combustion of fuel gives poisonous carbon monoxide gas.
An increased percentage of carbon dioxide in the air has been linked to global warming.
Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen produced by the burning of coal, diesel and petrol cause
Acid rain is harmful to crops, buildings and soil.

Karnataka Board Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Solutions
Combustion And Flame NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1. List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer: Conditions under which combustion can take place are as follows:
1. Air
2. The ignition temperature
3. Inflammable substance.
Question 2. Fill in the blanks.
1. Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
2. A liquid fuel, used in the home is LPG.
3. Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
4. Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
Question 3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer: The use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities because CNG does not produce any poisonous gas on burning. That is why pollution in our cities is reduced.
Question 4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer: LPG burns easily and produces more heat in comparison to wood. Besides, it is a clean fuel, it does not produce fume and ashes as wood do. LPG can be stored and transported easily and conveniently.
Question 5. Give reasons.
1. Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
2. LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
3. Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer:
1. Water is not used to control fire produced by electrical equipment because water is the conductor of electricity and may result in electric shock.
2. LPG is a substance which is readily available. It is cheaper and burns easily in the air at a moderate rate, It produces a large amount of heat and does not leave behind any undesirable substance.
3. Paper catches fire easily: but when it is wrapped around an aluminium pipe, the ignition temperature does not meet as heat is transferred to aluminium to lower the temperature of paper.
Combustion and Flame Class 8 KSEEB Solutions with Answers
Question 6. Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer:
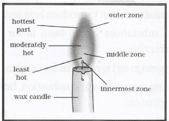
Question 7. Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed
Answer: The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in kilojoules per kg (kj/kg).
Question 8. Explain how CO, is able to control fires.
Answer: Carbon dioxide being heavier than oxygen covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between fuel and oxygen is cut off the fire is controlled. The added advantage of carbon dioxide is that in most cases it does not harm electrical appliances.
Question 9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer:
Green leaves contain a lot of water. So, when we try to burn green leaves, water contained in the leaves cools the combustible materials, so that their temperature is brought below its ignition temperature.
This prevents the burning of green leaves.
In the case of dry leaves, water is absent in them so the burning process starts as the temperature is raised above the ignition temperature and the leaves catch fire easily.
Question 10. Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer: The goldsmith uses the outermost zone of a flame with a metallic blowpipe for melting gold and silver. The flame in the outermost zone has the highest temperature sufficient to melt the gold and silver.
Question 11. In an experiment, 45kg of fuel has completely burnt The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 Kj. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel
Answer: Calorific value of a fuel =Total heat produced/ total mass burnt.
Here, the mass of fuel = 4.5 kg.
The heat produced = 180,000 Kj.
Therefore, the calorific value of fuel = 180,000 / 4.5kg =40,000 kj/kg.
KSEEB Class 8 Science Combustion and Flame Exercise Solutions
Question 12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer: Yes, the process of rusting can be called combustion, in fact, slow combustion, because rusting also takes place in the air in presence of humidity in the atmosphere.
Question 13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water, will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer: The water in Ramesh’s beaker will get heated in a shorter time because the outermost part of the flame is the hottest.
Combustion And Flame Additional Questions
Question 1. Name the most common fuel used in homes.
Answer: Liquefied Petroleum Gas. (LPG)
Question 2. What are the states in which fuel may exist?
Answer: A fuel may exist in a solid, liquid or gaseous state.
Question 3. What acts as fuel for our body?
Answer: Food
Question 4. Give two examples of non-combustible substances.
Answer: Water, sand
Question 5. Where were matchsticks first used?
Answer: Egypt
Question 6. What is the composition of the head of a matchstick?
Answer: Antimony trisulphide and potassium chlorate.
Question 7. Comparing the calorific values of coal and petrol, a state which fuel is better.
Answer: The calorific value of coal is about 25000—33,000 kJ/kg, whereas that of petrol is 45,000 kJ/kg. Hence, petrol is a better fuel.
Question 8. What does coal produce during its combustion?
Answer: Coal produces carbon dioxide, heat and light during its combustion.
Karnataka Board 8th Science Chapter 10 Important Questions and Answers
Question 9. How does a matchstick catch fire?
Answer: By rubbing a matchstick against a rough surface (friction), it attains its ignition temperature and thus catches fire.
Question 10. What is rapid combustion?
Answer: When a substance burns instantly and produces a huge amount of heat and light, the combustion is called rapid combustion
Example: The instant burning of LPG in a gas stove.
Question 11. Mention any three characteristics of good fuel.
Answer: Any three characteristics of a good fuel are the following:
It has a high calorific value.
It is very easy to transport.
It is cheap, affordable and economic.
Question 12. What is global warming?
Answer: An increase in the average temperature of the earth’s atmosphere, especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes, is termed as global warming.
Question 13. Why isn’t hydrogen gas used as a domestic or industrial fuel, although it has a very high calorific value? State three reasons for the answer.
Answer: Although hydrogen gas has a very high calorific value, it is not used as a domestic or industrial fuel due to the following reasons:
It is expensive.
It burns with an explosion.
It is extremely inflammable, so it is risky to store and transport hydrogen.
Question 14. It is observed at petrol pumps and airports, that hydrocarbon fire extinguishers are used, instead of soda-acid fire extinguishers. Give reasons why.
Answer: At petrol pumps and airports, there is more probability of a fire breaking out due to oil. In such situations, a soda-acid fire extinguisher does not work as it contains water or uses water to take off the fire by cooling down the place. Water being heavier than oil sinks to the bottom and hence, fire does not get controlled. In such a case, a hydrocarbon fire extinguisher is very useful, as it contains turkey red oil, which causes the foaming of carbon dioxide gas under pressure. The foam covers the surface of the burning substances and dispels the supply of air to control the fire.
Question 15. Explain complete combustion.
Answer: This type of combustion involves the complete burning of the combustible substance. No residue is left behind. Ash or smoke is not given off during or after this type of combustion. Most gases, such as hydrocarbons go through this form of combustion. On combustion, hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide, water and heat.
Question 16. Can the process of cellular respiration be called combustion? Why?
Answer: Yes. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that breaks large molecules into smaller ones with the release of heat. So, this is a slow combustion reaction.
Combustion And Flame Activities
Question 1. Collect some materials like straws, matchsticks, kerosene oil, paper, iron nails,” stone pieces, glass, etc. Under the supervision of your teacher try to burn each of these materials one by one. If combustion takes place mark the material combustible, otherwise mark it non-combustible.
Answer: Combustible and Non-combustible Substances
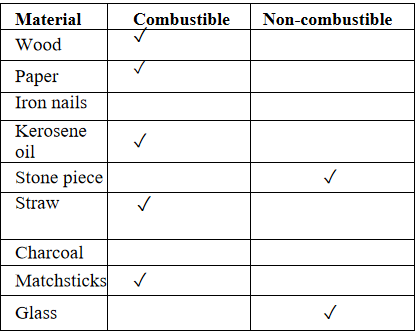
KSEEB Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Textbook Solutions PDF
Question 2. (Caution: Be careful while handling burning candles).
Fix a lighted candle on a table. Put a glass chimney over the candle and rest it on a few wooden blocks in such a way that air can enter the chimney Observe what happens to the flame. Now remove the blocks and let the chimney rest on the table Again observe the flame. Finally, put a glass plate over the chimney Watch the flame again. What happens in the three cases? Does the flame flicker off? Does it flicker and give smoke? Does it burn unaffected? Can you infer anything at all about the role played by air in the process of burning?
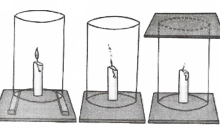
Answer: The candle burns freely
when air can enter the chimney from below.
when air does not enter the chimney from below, the flame flickers and produces smoke.
The flame finally goes off because the air is not available.
Question 3. Place a piece of burning wood or charcoal on an iron plate or Tawa. Cover it with a glass jar or a tumbler, or a transparent plastic jar. Observe what happens. Does charcoal stop burning after some time? Can you think of a reason why it stops burning?
Answer: After burning under the jar for some time, the wood/charcoal stops burning due to the discontinuous supply of air (or oxygen present in the air).
Question 4. (Caution: Be careful while handling burning candles) Make two paper cups by folding a sheet of paper. Pour about 50 ml. of water into one of the cups. Heat both cups separately with a candle What do you observe?
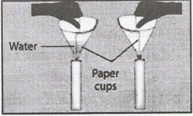
Answer: It is observed that the empty cup catches fire immediately and begins to burn, whereas the cup containing water does not burn; instead, the water present in it becomes hot.
Question 5. Light a candle (Caution: Be careful). Hold a glass tube with a pair of tongs and introduce its one end in the dark zone of a non-flickering candle flame Bring a lighted matchstick near the other end of the glass tube. Do you see a flame? If so, what is it that produces a flame?

Answer: When we bring a lighted matchstick near the other end of the glass tube then we observe a flame. The vapourised wax from candles produces this flame.
KSEEB 8th Standard Science Chapter 10 Notes and Solutions
Question 6. Make a model of a fire extinguisher. Place a short candle and a slightly taller candle in a small dish filled with baking soda. Place the dish at the bottom of a large bowl and light both candles. Then pour vinegar into the dish of baking soda. Take care. Do not pour vinegar on the candles. Observe the foaming reaction. What happens to the candles? Why? In what order?
Answer: It is observed that the candles go off. The shorter candle blows off first, and then the longer one. It happens because of the production of carbon dioxide gas, which reaches the shorter candle first, and then the longer candle.
Combustion And Flame Ncert textbook exercises Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. A substance which reacts with oxygen giving heat is called a combustible substance. Which one of the following is a combustible substance?
1. Iron nail
2. Glass
3. Stone piece
4. Wood
Answer: 4. Wood
Explanation: Glass, iron nails and stone pieces will not burn like wood hence they are not combustible. Wood burns in the air and it is called a combustible substance.
Question 2. Which one of the following has the highest calorific value?
1. Kerosene
2. Biogas
3. LPG
4. Petrol
Answer: 3. LPG
Explanation: Calorific represents the amount of heat generated when fuel burns completely.
The calorific value of LPG is 55000-kilo joules/ Kg, which is high when compared to the calorific value of Kerosene, Biogas and petrol.
Question 3. Magnesium ribbon on burning in air produces:
1. Magnesium oxide, water and light.
2. Magnesium oxide and heat.
3. Magnesium oxide, heat and light.
4. Magnesium oxide, water and heat.
Answer: 3. Magnesium oxide, heat and light
Explanation: Magnesium reacts with atmospheric oxygen to get magnesium oxide by liberating heat and light.
The chemical reaction is Mg+O2 MgO2 + Heat+ Light
Question 4. Which of the following is not a combustible substance?
1. Camphor
2. Glass
3. Straw
4. Alcohol
Answer: 2. Glass
Explanation: Camphor, glass, and straw can burn in the air and they are combustible substances. Glass will not burn in the air and it is a non-combustible substance.
Question 5. The substance that does not burn with flame is
1. LPG
2. Camphor
3. Dry grass
4. Charcoal
Answer: 4. Charcoal
Explanation: The charcoal will not vaporize on heating. Hence charcoal will not burn by producing a flame. Charcoal glows on combustion.
Question 6. On placing an inverted tumbler over a burning candle, the flame extinguishes after some time. This is because of the non-availability of
1. Oxygen
2. Water vapours
3. Carbon dioxide
4. Wax
Answer: 1. Oxygen
Explanation: Oxygen is necessary for combustion. When we place an inverted tumbler over a burning candle, the oxygen supply will be stopped, this extinguishes the flame.
Question 7. If a person’s clothes catch fire, the best way to extinguish the fire is to:
1. Throw water on the clothes
2. Use the fire extinguisher.
3. Cover the person with a woollen blanket.
4. Cover the person with a polythene sheet.
Answer: 3. Cover the person with a woollen blanket.
Explanation: By covering a person’s clothes with a woollen blanket we are cutting off the oxygen required for the burning of clothes. Hence fire will be distinguished.
Question 8. The substance expected to have the highest ignition temperature out of the following is
1. Kerosene
2. Petrol
3. Coal
4. Alcohol
Answer: 3. Coal
Explanation: Ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire. Among the given options coal have the highest ignition temperature.
Question 9. Choose the correct statement about inflammable substances from the following. They have:
1. Low ignition temperature and cannot catch fire easily.
2. High ignition temperature and can catch fire easily.
3. Low ignition temperature and can catch fire easily.
4. High ignition temperature and cannot catch fire easily.
Answer: 3. Low ignition temperature and can catch fire easily.
Inflammable substances are substances that easily catch fire. They are substances, which have very low ignition temperatures and when exposed to air, they catch fire easily.
Step-by-step Solutions for Combustion and Flame Class 8 Karnataka Board
Question 10. Choose the incorrect statement from the following. Forest fires are usually due to:
1. Carelessness of humans
2. Heat of the sun
3. Cutting of trees
4. Lightning strike
Answer: 3. Cutting of trees.
Deforestation or Cutting of trees is not the cause of the forest fire. Forest fires are usually caused due to heat of the sun, lightning strikes and the carelessness of humans
Question 11. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called
1. Kilojoule per litre
2. Kilogram per millilitre
3. Kilojoule per gram
4. Kilojoule per kilogram
Answer: 4. Kilojoule per kilogram
Question 12. In villages, people use wood as fuel because:
1. It is considered to be an ideal fuel.
2. Of its easy availability and low cost.
3. It is environment-friendly.
4. It catches fire easily.
Answer: 2. Of its easy availability and low cost.
Question 13. Which among the following is considered the cleanest fuel?
1. Cow dung cake
2. Petrol
3. Kerosene
4. Hydrogen gas
Answer: 4. Hydrogen gas
Explanation: Hydrogen gas is called a clean fuel as it does not produce any dangerous gases. It can only produce heat and water as products.
Question 14. Choose the incorrect statement from the following. A good fuel is one that:
1. Is readily available.
2. Produces a large amount of heat.
3. Leaves behind many undesirable substances.
4. Burns easily in the air at a moderate rate.
Answer: 3. Leaves behind many undesirable substances.
Explanation: Good fuel is readily available and produces a large number of meat. Good fuel burns easily in the air at a moderate rate and will not leave behind any undesirable substances.
Question 15. Shyam was cooking potato curry on a chulha. To his surprise, he observed that the copper vessel was getting blackened from the outside. It may be due to:
1. Proper combustion of fuel.
2. Improper cooking of potato curry.
3. Improper combustion of the fuel.
4. Burning of the copper vessel.
Answer: 3. Improper combustion of the fuel.
The copper vessel was blackened from the outside because of the insufficiency of oxygen.
Question 16. Two glass jars A and B are filled with carbon dioxide and oxygen gases, respectively. In each jar, a lighted candle is placed simultaneously. In which jar will the candle remain lighted for a longer time and why?
Answer: The candle remains in jar B because it is filled with oxygen which is necessary for the combustion and flame. In Jar A candle will not burn due to lack of oxygen.
Question 17. Anu wants to boil water quickly in a test tube. On observing the different zones of the flame, she is not able to decide which zone of the flame will be best for boiling water quickly. Help her in this activity.
Answer: Anu should use the outermost zone of the flame which is the hottest part of the flame.
Question 18. Why is the use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles being replaced by Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in big cities?
Answer: Compared to petrol and diesel CNG is a clean fuel. It produces very less amount of gases which are poisonous hence in big cities CNG is used in place of petrol and diesel.
Question 19. Boojho wants to separate the following materials as combustible and non-combustible. Can you help him?
Charcoal, chalk, stone, iron rod, copper coin, straw, cardboard, glass, paper, and wood.
Answer:
Combustible
Straw
Paper
Wood
Charcoal
Cardboard
Non-Combustible
Chalk
Stone
Iron rod
Copper coin
Glass
Question 20. If you hold a piece of iron wire with a pair of tongs inside a candle flame or a Bunsen burner flame, what will you observe? Will it produce a flame?
Answer: Iron will not produce flame rather it glows red hot.
Question 21. People usually keep Angethi/burning coal in their closed rooms during the winter season. Why is it advised to keep the door open?
Answer: The burning of coal produces carbon monoxide which is poisonous for the people inhaling it. If the door is closed, the oxygen level will be less and the carbon-monoxide level will be high. This is harmful to the person sleeping in the room. Hence the door should be closed.
Question 22. The cracker on the ignition produces sound. Why?
Answer: Upon ignition, the cracker releases gas is released out and the gas is heated by the amount of heat generated by the cracker. This led to an explosion resulting in the production of sound.
Question 23. What do you understand by fuel efficiency?
Answer: Fuel efficiency is determined by its calorific value which is the amount of heat energy produced on the complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in kJ/kg.
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
