KSEEB Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metals and Non-Metals Points To Remember
Physical properties: Metals are
- Malleable
- Ductile
- Good conductors of heat and electricity
- Lustrous
- Solids at room temperature except for mercury.
- High melting and boiling points.
- Hard except for sodium and potassium
- Sonorous
Non-metals are:
- Nonmalleable
- Non – ductile
- Bad conductors of heat and electricity
- Non-lustrous
- Generally solids and gases at room temperature
- Have low melting and boiling points
- Are soft except for diamond
- Non – sonorous
Chemical properties :
- Metal oxides are basic in nature, which turn red litmus blue
- Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature, which turn blue litmus red
- Metals react with water to produce metal hydroxide and evolve hydrogen gas.
- Metals react with dilute acids forming a salt and evolving hydrogen gas.
- The process where metal gets eaten away due to a chemical reaction with atmospheric gases and moisture is known as corrosion.
- The arrangement of metals in the order of their decreasing reactivity is the reactivity series.
- Graphite is used for making electrodes, cru- cables and pencil lead.
- Phosphorus is used in the match stick industry and in fireworks
- Sulphur is used in the vulcanisation of rubber
- Copper and aluminium are used to make electrical wires.
- Alloys are the mixtures of two or more metals or metals and non-metals.

Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials Metals And Non-Metals
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Ncert Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
1. Zinc
2. Phosphorus
3. Sulphur
4. Oxygen
Answer: 1. Zinc
Question 2. Which of the following statements is correct?
1) All metals are ductile
2) All non-metals are ductile
3) Generally, metals are ductile
4) Some, non-metals are ductile
Answer: 3) Generally, metals are ductile
Question 3. Fill in the blanks :
(1) Phosphorusisavery_____non-metals.
(2) Metals are ______ conductors of heat and _______
(3) Iron is _______ reactive than copper.
(4) Metals react with acids to produce ______ gas.
Answer:
(1)Reactive
(2) Good, Electricity
(3) More
(4) Hydrogen
Question 4. Mark ‘T” if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(1) Generally, non-metals react with acids.
(2) Sodium is a very reactive metal.
(3) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate
(4) Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
(1) False
(2) True
(3) False
(4) False
Karnataka Board Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Solutions
Question 5. Some properties are listed Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties.
Answer:
Properties
1. Appearance
2. Hardness
3. Malleability
4. Ductility
5. Heat Conduction
6. Conduction of electricity
Metals
1. Lustrous
2. Hard
3. Malleable
4. Ductile
5. Good Conductors
6. Good
Non-metals
1. Dull
2. Soft
3. Non-malleable
4. Non-ductile
5. Bad conductors
6. Bad conductors
Question 6. Give reasons for the following
1)Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
Answer: Because aluminium metal is malleable and therefore, it can be beaten into thin foils.
2) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
Answer: Because metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
3) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt. solution.
Answer: Because copper is less reactive than zinc.
4) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer: Because they are highly reactive elements and can catch fire easily when in contact with air.
Question 7. Can you store the lemon pickles in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer: Lemon pickle cannot be stored in aluminium utensils because lemon pickle contains acids, which can react with aluminium (metal) liberating hydrogen gas, and can lead to the spoiling of the pickle.
Question 8. Match the substances in column A with their applications given in column B
Column A Column B
(substance) (Application)
Gold (1) Thermometer
Iron (2) Electric wires
Aluminium (3) Wrapping food
Carbon (4) Jewellery
Copper (5) Machinery
Mercury (6) Fuel
Answer: Gold-(4) Jewellery
Iron-(5) Machinery
Aluminium-(3) Wrapping food
Carbon -(6) Fuel
Copper -(2) Electric wires,
Mercury-(1) Thermometer
Question 9. What happens when
1) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate?
2) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution?
Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Answer:
1) No reaction will take place because copper is very less reactive.
2) Iron being more reactive displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution. In this reaction, the blue colour of copper sulphate fades and there is a deposition of copper on the iron nail.
Iron + Copper sulphate — Iron sulphate + copper
Materials Metals And Non-Metals Class 8 Kseeb Solutions With Answers
Question 10. Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
1) How will she find the nature of the gas?
2) Write down the word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer: 1) Saloni can find the nature of the gas by using a wet litmus paper. After bringing the litmus paper in contact with the gas, if it turns the blue litmus paper into red, it is acidic, and if it turns red litmus into blue, it is basic.
2) Carbon + Oxygen — Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide + lime water — Milky
or
Carbon dioxide + water — carbonic acid (Blue litmus red)
KSEEB Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Important Questions
Question 11. One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. The next day, when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Answer: The gold jewellery is dipped into an acidic solution called aquaria (a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid) for polishing. On dipping the gold jewellery in the acid solution, the outer layer of gold dissolves and the inner shiny layer appears. This causes a slight loss in weight.
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Activities
Take a small iron nail, a coal piece, a piece of thick aluminium wire and a pencil lead. Beat the iron nail with a hammer
 (But take care that you don’t hurt yourself in the process). Try to hit hard. Hit hard the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal piece and pencil lead. Record your observations Malleability of Materials
(But take care that you don’t hurt yourself in the process). Try to hit hard. Hit hard the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal piece and pencil lead. Record your observations Malleability of Materials
Object/Material Change in Shape
Iron wall Flattens (Flattens/Breaks into Pieces)
Coal piece Breaks into pieces
Aluminium wire Flattens
Pencil lead Breaks into pieces
Answer: This activity shows that iron and aluminium are malleable while coal pieces and pencil lead are brittle. Thus, metals are malleable and non-metals are non-malleable.
Question 2. Recall how to make an electric circuit to test whether electricity can pass through an object or not.
 You might have performed the activity with various objects in Class VI. Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors.
You might have performed the activity with various objects in Class VI. Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors.
Materials Good Conductor/Poor Conductor
Iron rod/nail Good conductor
Sulphur Poor conductor
Coal piece Poor conductor
Copper wire Good conductor
Answer: It shows that metals are good conductors of electricity and non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
Question 3. Let us check the nature of rust formed as a result of the reaction between iron, oxygen and water. Collect a spoonful of rust and dissolve it in a very little amount of water. You will find that the rust remains suspended in water. Shake the suspension well. Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers, What do you observe? Is the solution acidic or basic?
 Answer: We observed that the red litmus paper turns blue which shows that the injury of rust is basic. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Answer: We observed that the red litmus paper turns blue which shows that the injury of rust is basic. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Kseeb Class 8 Science Materials Metals And Non-Metals Exercise Solutions
Question 4. (To be demonstrated by the teacher in the (class)
Take a small amount of powdered sulphur in a deflagrating spoon and heat it. If the deflagrating spoon is not available, you may take a metallic cap of any bottle and wrap a metallic wire around it and give it the shape.
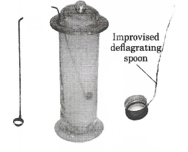 As soon as sulphur start burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass tumbler. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
As soon as sulphur start burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass tumbler. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
 Answer: We observed that the solution of oxide turns the blue litmus red which shows that the solution is acidic in nature. This also shows that the oxide of non-metals is acidic in nature.
Answer: We observed that the solution of oxide turns the blue litmus red which shows that the solution is acidic in nature. This also shows that the oxide of non-metals is acidic in nature.
Question 5. Take a 250 ml. beaker/glass tumbler. Fill half of it with water. Now carefully cut a small piece of sodium metal. Dry it using filter paper and wrap it in a small piece of cotton. Put the sodium piece wrapped in cotton into the beaker. Observe carefully.
When the reaction stops, touch the beaker. What do you feel? Has the beaker become hot? Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers. Is the solution acidic or basic?
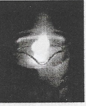 Answer: On touching the beaker, it felt hot. The solution turns the red litmus paper to blue which shows it is basic in nature. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Answer: On touching the beaker, it felt hot. The solution turns the red litmus paper to blue which shows it is basic in nature. Blue litmus paper does not show any colour change with the solution.
Question 6. Take samples of metals and non-metals given in separate test tubes and label them as A, B, C, D, E and F. With the help of a dropper add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid to each test tube one by one. Observe the reactions carefully. If no reaction occurs in the cold solution, warm the test tube gently. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of each test tube. Repeat the same activity using dilute sulphuric acid instead of dilute hydrochloric acid.
The reaction of Metals and Non-metals with Acids
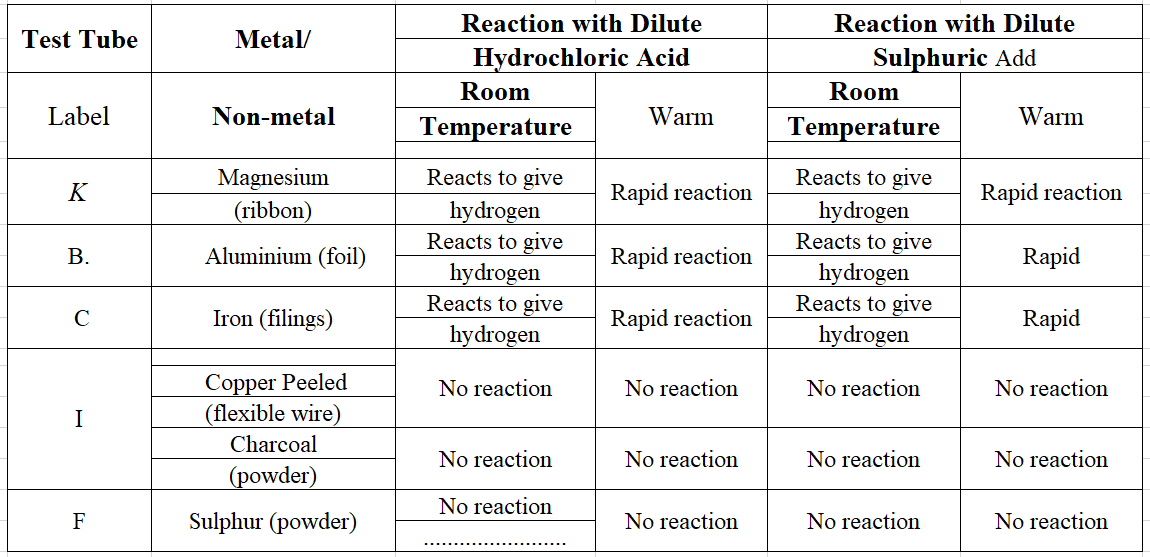
Answer: This activity shows that metals usually displace hydrogen from dilute acids whereas non-metals do not do so and no hydrogen gas is evolved.
Question 7. Prepare a fresh solution of sodium hydroxide in a test tube by dissolving 3-4 pellets of it in 5 mL of water. Drop a piece of aluminium foil into it. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube. Observe carefully.
Answer: We observed that a colourless gas is evolved which burns with a pop sound. This shows that aluminium reacts with bases on heating to produce hydrogen gas.
Question 8. Take five 100 mL beakers and label them A,B, C, D and E. Take about 50 mL of water in each beaker. Dissolve in each beaker a teaspoonful of each substance as indicated
(1) Keep the beakers undisturbed for some time
(2) Record your observations in your notebook.
Karnataka Board 8th Science Chapter 4 Important Questions And Answers
Picture
Beaker A: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Zinc granule (Zn)
Beaker B: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Beaker C: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker D: Iron sulphate (FeSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker E: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Iron nail(Fe)
Answer: In beaker ‘A’ zinc (Zn) replaces copper (Cu) with copper sulphate (CuS04) solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate changes to colourless and a powdery red mass of copper is deposited at the bottom of the beaker. The reaction can be represented as follows:
 In beaker B, iron replaces copper from its solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate changes to the green colour of ferrous sulphate.
In beaker B, iron replaces copper from its solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate changes to the green colour of ferrous sulphate.

In beakers C, D and E no change in colour or heat evolution is observed. This indicates that the metals are unable to displace the other metals from their solution.
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Additional Questions
Question 1. Examples of metals.
Answer: Iron, sodium, aluminium
Question 2. Examples of nonmetals.
Answer: Sulphur, oxygen, hydrogen
Question 3. Name two soft metals
Answer: Sodium, potassium.
Question 4. Which non-metal is essential for our life and all living beings inhale during breathing?
Answer: Oxygen
Question 5. Which property of metals makes them suitable for use in jewellery?
Answer: Ductility
Materials Metals And Non-Metals Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Question 6. Define malleability
Answer: The property of metals by which they can be drawn into thin sheets.
Question 7. Which liquid metal is used for making thermometers?
Answer: Mercury
Kseeb Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Textbook Solutions
Question 8. What do you understand by a displacement reaction? Give example.
Answer: A chemical reaction in which a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Ex: CuSO, +Fe — FeSO, + Cu
Copper sulphate + Iron — Iron sulphate + Copper
Question 9. What is rust?
Answer: Reddish brown coating that is formed on iron objects on exposure to moist air.
Question 10. Name the metal and non-metal which occur in a liquid state.
Answer: Mercury (metal), bromine (non-metal).
Question 11. Due to which property a bell rings?
Answer: Sonority
Simplified Notes For KSEEB Class 8 Science Metals And Non-Metals
Question 12. State the property of non-metals due to which phosphorus is kept in water.
Answer: Non-metals do not react with water.
Question 13. Which metal is used for wrapping food items?
Answer: Aluminium
Question 14. Whose oxides are basic in nature: Metal or non-metal?
Answer: Metal
Question 15. What are the main uses of metals?
Answer: Metals are very useful to us in many ways. For example:
- Due to their thermal and electrical conductivity, metals are used to make utensils, cooking vessels, wires and appliances. For example, copper and aluminium are mainly used for these purposes.
- Metals like iron and steel are used in various tools, machinery, pipes, rods, sheets, doors, windows, and construction works like bridges, roads, buildings, etc.,
- Aluminium is used as packaging and wrapping materials. It is also used in aircraft and automobiles, etc.
- Metals like gold, silver and platinum are used to make jewellery and other decorating items.
- Zinc is used in galvanisation and dry cell and chromium in electroplating.
- Lead is used in making electrodes and batteries.
Question 16. What are the main uses of non-metals?
Answer: Like metals, non-metals also play an important role in our lives. They help us in many ways. For example
- We breathe oxygen which is the basis of life for all living things including human beings. Without it, no living beings can exist alive on this earth.
- CO2, which is a non-metal oxide is essential for plants to carry out photosynthesis.
- Non-metals like nitrogen and phosphorus are used in fertilisers for better yield of plants.
- Phosphorus is used in the manufacturing of matchsticks and fireworks.
- Non-metal-like iodine is used in the purple-coloured solution applied on wounds. Sulphur is also used in preparing skin medicines and making ointments due to its fungicidal properties.
- Non-metal-like chlorine is used in the water purification process. Due to its bleaching properties, it is used to make bleaching powder.
- Carbon, a non-metal, is used in most the fuels
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is not a metal?
(1) Copper
(2) Sulphur
(3)Aluminium
(4) Iron
Answer: (2) Sulphur
Question 2. The substance that will be flattened on beating with a hammer is
(1) Crystalofiodine
(2) Lump of sulphur
(3) Piece of coal
(4) Zine granule
Answer: (4) zinc granule
Explanation: Metals can be beaten into thin sheets whereas non-metals break into pieces on hitting hence answer is (d) zine granule.
Question 3. Boojho has learnt that non-metals on beating with a hammer are generally broken into pieces. Which of the following is a nonmetal?
(1) Iron nail
(2) Aluminium wire
(3) Copperplate
(4) Piece of coal
Answer: (4) Piece of coal
Explanation: Iron, Copper and aluminium are metals whereas coal is a non-metal hence answer is (d) a piece of coal.
Kseeb 8th Standard Science Chapter 4 Notes And Solutions
Question 4. Materials which can be drawn into wires are called ductile. Which of the following is not a ductile material?
(1) Silver
(2) Copper
(3) Sulphur
Answer: (3) sulphur
Explanation: Ductility is the property of metals. Here Sulphur is non-metal which is not have ductile properties.
Question 5. Metals are generally hard. Which of the following metals is an exception and can be cut with a knife?
(1) Iron
(2) Sodium
(3) Gold
(4) Magnesium
Answer: (2) Sodium
Explanation: Sodium is a highly reactive metal which looks soft and can be cut into pieces by using a knife.
Question 6. Metals are generally solid. Which of the following metals is in the liquid state at room temperature?
(1) Mercury
(2) Silver
(3)Aluminium
(4) Sodium
Answer: (1) Mercury
Question 7. Metals generally react with dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas. Which one of the following metals does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(1) Magnesium
(2) Aluminium
(3) Iron
(4) Copper
Answer:(4) Copper
Explanation: Less reactive metals like Copper, gold and silver does not react with dilute HCl to produce Hydrogen gas.
Explanation Of Metals And Non-Metals In KSEEB Science
Question 8. Which of the following reacts with cold water vigorously?
(1) Carbon
(2) Sodium
(3) Magnesium
(4) Sulphur
Answer:(2) Sodium
Explanation: Sodium reacts vigorously with water, hence it is stored in kerosene to avoid the reaction of sodium with moisture in the atmosphere and oxygen.
Question 9. The metal which produces hydrogen gas in reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid as well as sodium hydroxide solution is
(1) Copper
(2) Iron
(3) Aluminium
(4) Sodium
Answer:(3) Aluminium
Explanation: Aluminium reacts with dilute HCI as well as NaOH to produce Hydrogen Gas.
Question 10. Which of the following non-metals reacts and catches fire on exposure to air?
(1) Phosphorus
(2) Nitrogen
(3) Sulphur
(4) Hydrogen
Answer: (1) Phosphorus
Question 11. Generally, metallic oxides are basic and nonmetallic oxides are acidic in nature. The solution of which of the following oxides in water will change the colour of blue litmus to red?
(1) Sulphur dioxide
(2) Magnesium oxide
(3) Iron oxide
(4) Copper oxide
Answer: (1) Sulphur dioxide
Explanation: Sulphur forms Sulphur-di-oxide which is acidic in nature and it will convert blue litmus to red.
Question 12. Which of the following property is not responsible for copper being used as electrical conduction wires?
(1) Ductility
(2)Colour
(3) Good conductor of electricity
(4) It is solid
Answer : (2) Colour.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Materials Metals And Non-Metals Class 8 Karnataka Board
Question 13. Name two major non-metals which are present in fertilisers and enhance the growth of plants.
Answer: (1) Nitrogen (2) Phosphorus
Question 14. Which non-metal is used to disinfect water?
Answer: Chlorine.
Question 15. A purple-coloured non-metal forms a brown solution in alcohol which is applied on wounds as an antiseptic. Name the nonmetal.
Answer: Iodine.
Question 16. Zinc sulphate forms a colourless solution in water. Will you observe any colour on adding copper turning in it?
Answer: There will be no change as displacement reaction will not take place.
Question 17. Why are bells made of metals?
Answer: Metals show the sonorous property, hence they are used in making bells.
Question 18. Paheli bought a statue made of copper. To her surprise, it acquired a dull green coating after a couple of months. Explain the reason.
Answer: The green coating on the copper statue is a mixture of Cu(OH), and CuCO, which are formed due to the reaction of moisture and copper.
Question 19. Some of the following statements are incorrect. Find the incorrect statements and correct them.
(1) The property of metals by virtue of which they can be drawn into wires is called ductility.
(2) Metals are good conductors of electricity but poor conductors of heat.
(3) Articles made of metals produce a ringing sound when struck hard.
(4) Oxides of non-metals and metals are acidic in nature.
(5) A less reactive metal replaces a more reactive metal from its salt solution in water.
Answer: Statements 2), 4) and 5) are wrong statements
2) Metals are good conductors of electricity as well as heat.
4) Oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature and oxides of metals are basic in nature.
5) Amore reactive metal replaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution in water.
20. Match the substances in Column A with their applications given in Column B.
Column A (Substance) Column B (Application)
Oxygen for making crackers
Copper for disinfecting water
Sulphur all living beings inhale during breathing
iron for making electric wires
Answer:
Column A(Substance) Column B(Application)
Oxygen all living beings inhale during breathing
Copper for making electric wires
Sulphur for making crackers
Iron for making rails
chlorine for disinfecting water
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
