KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Points To Remember
Synthetic Fibres: Fibres artificially made by man.
Synthetic Fibres: They are made of very large units called polymers, (chemicals). Polymers are made up of many smaller units called monomers by the process of polymerisation.
Characteristics of synthetic fibres: dry up quickly, durable, less expensive, easy to maintain.
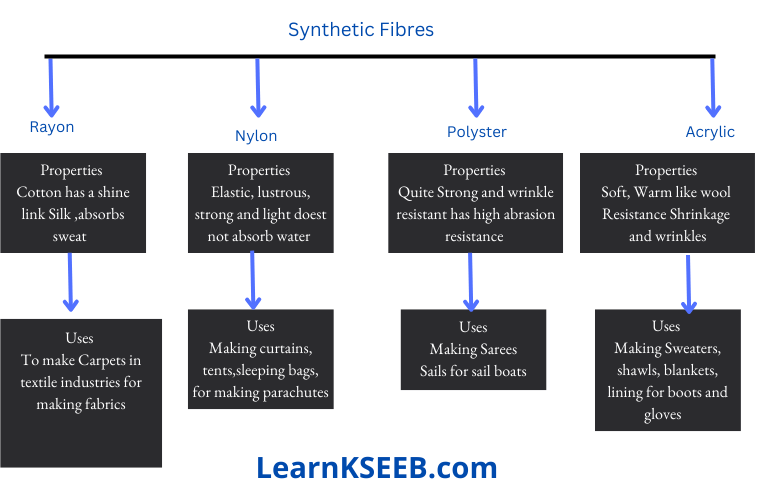
Types of synthetic fibres: Rayon, Nylon, Polyester, Acrylic.
Rayon was the first artificially manufactured fibre from wood pulp.
Coal and petroleum are raw materials to manufacture nylon.
Polyester has many ester units linked together
Acrylic is used as a substitute for wool
Plastics: Synthetic organic polymers that can be shaped when soft and later hardened to set to shape.
Characteristics of plastics: Non-reactive, light, strong durable, poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Types of plastics: Thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics
Thermoplastics: get deformed easily on heating. Examples: PVC, polyethene
Thermosetting plastics: cannot be bent easily. Example: Bakelite, melamine
Effect of plastics on the Environment: Non-bio-degradable, pollute the environment, and release poisonous fumes on burning.
Non-biodegradable – substances that cannot decay by the natural process of decomposers.

Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Pdf
Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Textbook Exercises
Question 1. Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer: Some fibres are called synthetic because they are made by man using chemicals. These are made of small units that join together to form long chains.
Question 2. Mark ( ✓ ) the correct answer :
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
(1)it has a silk-like appearance.
(2)it is obtained from wood pulp
(3)its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres
(4)none of the above.
Answer: (2)
Question 3. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1)Synthetic fibres are also called______or______fibres.
2)Synthetic fibres are synthesised from a raw material called _____
3)Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a________
Answer:
1)artificial, man-made
2)petrochemicals
3)polymer
Question 4. Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer:
They are used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
They are used in making seat – belts, fishing nets, tyre cords, a string for sports rackets and musical instruments.
Question 5. Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer: Plastic containers are favoured for storing food because
Plastics do not react with food stored in them.
Plastics are lightweight and strong
They are easy to handle and safe.
Question 6.Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics
Answer: Thermoplastics
These plastics soften on heating and can be bent easily.
They do not lose their plasticity.
Examples: PVC, polyethene.
Thermosetting plastics
These plastics once moulded can’t be softened again.
They lose their plasticity
Example: Bakelite and melamine
Karnataka Board Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Question 7. Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
1)Saucepan handles
2)Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
Answer:
(1) Since thermosetting plastics are bad conductors of heat and do not get heated up while cooking, they are used for making saucepan handles.
(2)Since thermosetting plastics are bad conductors of electricity and the electric current does not pass through such plastics, they are used for making electric plugs/switches/plugboards
Question 8. Categorise the materials of the following products into can be recycled and ‘cannot be recycled.
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, and electrical switches.
Answer:
Can be recycled: Plastic toys, carry bags, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs.
Cannot be recycled: Telephone instruments, cooker handles, ballpoint pens, electrical switches.
Question 9. Rana wants to buy shirts for summer should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer: He should buy cotton shirts. This is because cotton has more capacity, to hold moisture than synthetic clothes. In summer, we have extensive sweat which is easily soaked by cotton shirts and hence, cotton clothes are much better than clothes made from synthetic material.
Question 10. Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer:
Plastic containers do not react with items stored in them.
They do not get rusted when exposed to moisture and air.
They do not decompose when left in open for a long period.
Question 11. Should the handle and bristles of a toothbrush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Answer: No, the handle and bristles of a toothbrush should not be made of the same material. This is because our gums are soft and the bristles should be made of soft material so that it does not harm the gums. On the other hand, the handles should be made up of hard material so that they can give a firm grip.
Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Class 8 Kseeb Solutions With Answers
Question 12.‘Avoid plastics as far as possible comment on this advice.
Answer: Plastics must be avoided as far as possible. Materials made of plastics are non-biodegradable. The use of plastics had a bad effect on the environment. When the plastics are burnt, it releases a lot of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. These plastic materials when eaten up by the animals (like cows) choke the- respiratory system. This can cause the death of these animals. The waste particle articles thrown here and there carelessly get into dirty water drains and sewers and block them. In a nutshell, plastics can be considered a threat to our environment.
Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Activities
Question 1. Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm in length. Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it.

Answer: At the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed in it. Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the thread. This weight indicates the strength of the fibre. Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, polyester, silk and nylon. Tabulate the data Arrange the threads in order of their increasing strength.

(Precaution: Note that all threads should be of the same length and most of the same thickness.)
Question 2. Take two cloth pieces of the same size, roughly half a metre square each. One of these should be from natural fibre. The other could be synthetic fibre. You can take the help of your parents in selecting these pieces. Soak the pieces in different mugs each containing the same amount of water. Take the pieces out of the containers after five minutes and spread them in the sun for a few minutes. Compare the volume of the water remaining in each container.
Answer: It is observed that the volume of water in the container in which natural fibre is soaked contains less water as compared to the container in which synthetic fibre is soaked. Thus, natural fibre absorbs more water as compared to synthetic fibre. When both the fibres were spread in the sun, it was observed that synthetic fibre took less time to dry than natural fibre.
Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Additional Questions
Question 1. Distinguish between natural and synthetic fibres.
Answer: Natural fibres
These fibres are naturally obtained from plants and animals. Ex: cotton, silk, etc Synthetic fibres
These fibres are made by men in factories.
Examples: Rayon, polyester, etc.
Question2.Cotton is a natural polymer. What is its chemical name?
Answer: Cellulose
Question 3. Terrycot is made by mixing two types of fibres. Write the names of the fibres.
Answer: Terylene and cotton
Question 4. What is PET?
Answer: Poly-Ethylene
Kseeb 8th Standard Science Chapter 3 Notes And Solutions
Question 5. What is meant by the 4R’s principle?
Answer: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover
Question 6. Why should one never wear polyester clothes while working in the kitchen?
Answer: Polyester clothes are synthetic fibre and melt on heating. If the clothes catch fire, it can be disastrous, the fabric melts and sticks to the body. So, one should never wear synthetic clothes while working in the kitchen.
Question 7. Name some objects made of plastic.
Answer: Containers, buckets, bottles, chairs, baskets, etc.
Question 8. What is polythene?
Answer: Polythene is a polymer of ethene.
Question 9. What is the full form of PVC?
Answer: Polyvinyl Chloride
Question 10.Whether cotton cloth biodegradable or non-biodegradable?
Answer: Biodegradable
Question 11. Name the form of polyester which is replacing materials like glass and is used for making bottles and jars.
Answer: PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
Question 12. Name a synthetic fibre which is polyamide.
Answer: Nylon
Question 13. List any two properties of rayon.
Answer: The two properties of rayon are:
Rayon is a versatile fibre.
It can be dyed in different colours.
Question 14. Write some advantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer: Advantages of synthetic fibres are:
Synthetic fibres are strong and durable.
They do not shrink.
They are moth and insect-resistant.
Kseeb Class 8 Science Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Exercise Solutions
Question 15. List any three properties of plastics.
Answer: The three properties of plastics are:
They are non-corrosive in nature.
They are light in weight and durable.
They do not conduct heat.
Question 16. Pick the synthetic fibre out of the following?
(1)Cotton
(2)Nylon
(3)Jute
(4)Wool
Answer: (2)Nylon
Explanation: Cotton and Jute are from plant sources, Wool is from animal sources whereas Nylon is a synthetic fibre.
Question 17. Which of the following is a source of rayon?
(1)Wool
(2)PET
(3)Wood pulp
(4)Silk
Answer: (3)Wood pulp
Explanation: Rayon is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp.
Question 18. Polycot is obtained by mixing
(1)nylon and wool
(2)polyester and wool
(3)nylon and cotton
(4)polyester and cotton
Answer: (4) polyester and cotton
Question 19. Which is a thermosetting plastic?
(1)Melamine
(2)Polythene
(3)PVC
(4)Nylon
Answer: (1) Melamine
Explanation: Thermosetting plastics when moulded once can not be softened by heating. Examples are bakelite and melamine.
Question 20. The material similar to silk in appearance is
(1)Nylon
(2) Rayon
(3)Polyester
(4) Terylene
Answer: (2)Rayon
Explanation: Rayon is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp. Rayon is cheaper than silk and can be woven like silk.
Question 21. The most suitable material for the preparation of handles of cooking utensils is
(1) Polythene
(2)PVC
(3) Nylon
(4) Bakelite
Answer: (4) Bakelite
Explanation: Bakelite is a bad conductor of heat and it does not get soft on heating hence Bakelite is used to prepare handles of cooking utensils.
Karnataka Board 8th Science Chapter 3 Important Questions And Answers
Question 22. Which of the following is not a common property of plastics?
(1)Non-reactive
(2)Light in weight
(3)Durable
(4)Good conductor of electricity
Answer: (4) Good conductor of electricity
Explanation: Plastic is a bad conductor of electricity.
Question 23. Which of the following represents the correct match for items in Column A with those in Column B?
ColumnA Column B
Nylon 1) Thermoplastic
PVC 2)Thermosetting plastic
Bakelite 3) Fibre
Answer:
Nylon-2)
PVC-1)
Bakelite-3)
Question 24. Which of the following groups contain all synthetic substances?
(1)Nylon, Terylene, Wool
(2)Cotton, Polycot, Rayon
(3)PVC, Polythene, Bakelite
(4)Acrylic, Silk, Wool
Answer: (3) PVC, Polythene, Bakelite
Explanation:
- In options a) and c) there is wool which is extracted from an animal source.
- In option b) there is cotton which is from a plant source.
- Hence the answer is (c) PVC, Polythene, Bakelite.
Question 25. The material which is commonly used for making kitchen containers is
(1) P V C
(2) Acrylic
(3) Teflon
(4) PET
Answer: (4) PET
Explanation: PET or Polyethylene tetrathionate is lightweight and is used in making kitchen containers.
Question 26. A synthetic fibre which looks like silk is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp. It is, therefore, known as artificial silk. What is its common name?
Answer: Rayon is known as artificial silk.
Question 27. Plastic articles are available in all possible shapes and sizes. Can you tell me why?
Answer: It is very easy to make moulds from plastic hence it is available in all possible shapes and sizes.
Question 28. Plastic is used for making a large variety of articles of daily use and these articles are very attractive. But it is advised to avoid the use of plastic as far as possible. Why?
Answer: Plastic is not bio-degradable and disposing of plastic waste is a major issue. Hence it is advised to avoid the use of plastic as far as possible.
Step-By-Step Solutions For Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Class 8 Karnataka Board
Question 29. Why is it not advisable to burn plastic and synthetic fabrics?
Answer: Burning of plastic releases toxic gases which pollute the air. Hence it is not advisable to burn plastic and synthetic fabrics.
Question 30. Select the articles from the following list which are biodegradable.
(1) Paper
(2) Woollen clothes
(3) Wood
(4) Aluminium can
(5)Plastic bag
(6) Peels of vegetables
Answer: 3
1. Paper
2. Woollen clothes
3. Wood
4. Peels of vegetables
Free KSEEB Notes For Class 8 Science Synthetic Fibres And Plastics
Question 31. A bucket made of plastic does not rust like a bucket made of iron. Why?
Answer: Plastic is a non-reactive material. To form rust it should react with water and oxygen. Hence plastic does not form rust.
Question 32. Rohit took with him some nylon ropes when he was going rock climbing. Can you tell why he selected nylon ropes instead of ropes made of cotton or jute?
Answer: Nylon ropes are strong, flexible and elastic when compared to jute and cotton ropes. Acrylic blankets are cheap, light in weight, more durable and available in a variety of colours and designs. They can be easily washed at home.
Question 33. A lady went to the market to buy a blanket. The shopkeeper showed her blankets made of acrylic fibres as well as made of wool. She preferred to buy an acrylic blanket. Can you guess why?
Answer: Lady prefers acrylic blankets over wool blankets because acrylic blankets are cheap, light in weight, more durable and available in a variety of colours and designs. They can be easily washed at home.
Kseeb Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Textbook Solutions
Question 34.PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a thermoplastic and is used for making toys, chappals, etc. Bakelite is a thermosetting plastic and is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc. Can you write the major difference between these two types of plastics?
Answer: On heating, Thermoplastics get deformed and they can be easily bent. Whereas Thermosetting plastics cannot be softened by heating.
Question 35. Fill in the blanks.
(1)A polymer is a chain of many small units joined together which are called_______.
(2) synthetic fibres are also known as _____ fibres.
(3)The first fully synthetic fibre was________.
(4)A fibre similar to wool is________.
(5)A plastic used for making crockery is
Answer:
(1) monomers
(2) man-made fibres
(3) Nylon
(4) acrylic
(5)melamine
Question 36.Match items in List A with the items of List B.
List A.
Nylon
PET
Rayon
Thermosetting plastics
Teflon
List B.
(1)non-stick coating
(2)electric switches
(3)parachutes
(4) polyester
(5) artificial silk
Answer:
List A – List B
Nylon – (3) parachutes
PET – (4) polyester
Rayon – (5)artificial silk
Thermosetting plastics – (2) electric switches
Teflon – (1) non-stick coating
Kseeb Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Textbook Solutions
Question 37. Unscramble the jumbled words given below, related to synthetic materials.
(1) Story
(2) Lopmery
(3) Relyteen
(4) Respect
(5) Yespolter
(6) Felton
Answer:
(1) Rayon
(2) Polymer
(3) Terylene
(4) Plastic
(5) polyester
(6) Teflon
Question 38. Indicate whether the following statements are True or False. Also, write false statements in their correct form.
(1)The fabric terry wool is obtained by mixing terylene and wool.
(2)Synthetic fibres do not melt on heating.
(3)It is risky to wear synthetic clothes while working in the kitchen.
(4)Most plastics are biodegradable.
Answer:
1) True
2)False- Synthetic fibres melt on heating.
3)True because synthetic clothes melt on exposure to heat
4)False- Plastics are non-biodegradable
Question 39. Write about the importance of synthetic polymers in our life.
Answer: Following are the points to justify the importance of synthetic polymers in our life.
1. Nylon It is used for making ropes for rock climbing, fishing nets, raincoats, parachutes and tyre cords, etc.
2. Acrylic It is used for sweaters, tracksuits, linings for boots and gloves and In furnishing fabrics and carpets.
3. Terylene It is used in the textile industry to make clothes like sarees, tapestry and dress material. It is also mixed with natural fibre like cotton and wool to make more variety of clothes.
4. Plastics It is used to store food items, water, milk, pickles, dry food, etc. Plastic containers seem the most convenient. This is because of its lightweight, low price, good strength and easy handling as compared to metals. Plastics are used in cars, air crafts and spacecraft.
Question 40. Despite being very useful it is advised to restrict the use of plastic. Why is it so? Can you suggest some methods to limit its consumption?
Answer: Plastic is a non-biodegradable material which poses a serious threat to nature. Disposing of plastic waste is the biggest problem we face to regret the use of plastics. Plastics cause soil pollution and air pollution by burning.
The usage of plastic should be reduced and used plastic should be recycled and reused to reduce its consumption.
Karnataka State Board Syllabus for Class 8 Textbooks Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 4 Materials: metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 7 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 8 Friction
- Chapter 9 Sound
- Chapter 10 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
