KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Civics Chapter 3 Why Do We Need a Parliament? Textbook Questions
Question 1 Why do you think the nationalist movement supported the idea that all adults have a right to vote?
Answer. Indian National Congress was established in 1885 and Nationalist leaders demanded that there should be elected members n the legislature with a right to
discuss the budget and ask questions. The Government, of India Act 1909 introduced the indirect, election to the I legislative Assembly. Nat on leaders were not satisfied with this Act because the right to vote was very restricted and limited.
Under the act of 1919 and 1935 voter numbers increased but adult franchise was not introduced. Indian leaders demanded adult franchises and hence when they got a chance to frame the Constitution for India, adult franchise was introduced.
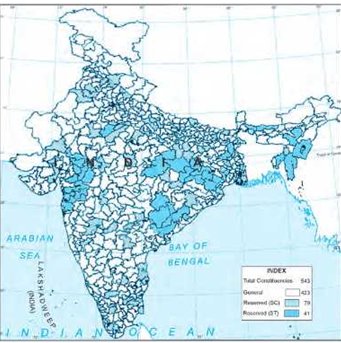
Question 2 In this 2004 map of Parliamentary constituencies alongside, roughly identify the constituencies in your State. What is the name of the MP from your constituency? How many MPs does your state have? Why are certain constituencies colored green while others are colored blue?
Answer. LokSabha Constituency Kamal-Sh. Arvind Sharma (Congress MP) State Haryana: Lok Sabha Seats-10. Constituent es colored green are reserved for S.T. and Constituencies colored blue are reserved for S.C.
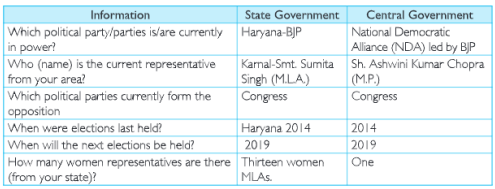
Question 3 You have read in Chapter I that the ‘Parliamentary form of government that exists in India has three tiers. This includes the Parliament (central government} and the various State Legislatures (state governments). Fill in the following table Answer with information on the various representatives from your area:
Answer.
Why Do We Need a Parliament? Text Questions
Question 1 What do you think the artist is trying to convey through the image of Parliament on the previous page?
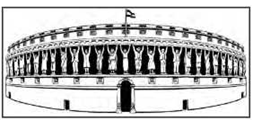
Answer Through the above photograph, the artist is trying to depict that Indians play a huge part in running the government. People are the pillars of our parliament, meaning they play a vital role in the functioning of the government Being a democracy, citizens participate in the selection and smooth functioning of the government.
Question 2 Give one reason why you think there should be Universal Adult Franchise. Do you think there would be any difference if the class monitor was selected by the teacher or elected by the students? Discuss.
Answer Universal Adult Franchise should prevail as it contains equality among the people. Men and women should have an equal contribution towards the decision-making process. Yes, there would be a difference if the class monitor was selected by the teacher rather than being elected by the students. The monitor selected by the teacher will not represent the whole class. Whereas the monitor elected by the students would have been democratically elected and he/she would be the true representation of the class strength.
Question 3 Use the terms ‘constituency’ and ‘represent’ to explain who an MLA is and how the person gets elected.
Answer The Palam constituency is represented by Dharam Dev Solanki as an MLA of the Delhi Vidhan Sabha. The procedure to select an MLA is as follows
- Tickets are allotted to the party candidates for contesting elections.
- The members fill their nominations and file them with the returning officer.
- They campaign with their policies and programs.
- The citizens vote on the day of the elections and the person getting the highest number of votes is selected as an M LA of that particular constituency.
Question 4 Discuss with your teacher the difference between a State Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) and a Parliament (Lok Sabha).
Answer

Question 5 From the list below, identify the work of a State government and that of a Central government.
(a) The decision of the Indian government to maintain peaceful relations with China.
(b) The decision of the Madhya Pradesh government to discontinue Board exams in Class VIII for all schools under this Board.
(c) A new train connection between Ajmer and Mysore will be introduced.
(d) Introduction of a new 1,000 rupee note.
Answer.
(a) Central Government
(b) State Government
(c) Central Government
(d) Central Government
Class 8 Civics Why Do We Need A Parliament KSEEB Notes
Question 6 Fill in the blanks with the following words: Universal adult franchise; MLAs; Representative; Directly
Answer. Democratic governments in our times are usually referred to as representative democracies. In representative democracies, people do not participate directly but, instead, choose their representative through an election process. These MMs meet and make decisions for the entire population. These days, a government cannot call itself democratic unless it allows what is known as the universal adult franchise. This means that all adult citizens in the country- are allowed to vote.
Question 7 You have read that most elected member, whether in the Panchayat, the Vidhan Sabha, or the Parliament, is elected for a fixed period of five years. Why do we have a system where the representatives are elected for a fixed period and not for life?
Answer. The choices of the people keep on changing. If elected for life, a minister, MLA, etc., may neglect .his/her duty thinking that he/she has held over
the people. The people should get an opportunity
to voice their concerns and change the government if it is not happy with the work the elected representatives are doing.
Question 8 You have read that people participate in other ways and not just through elections to express approval or disapproval of the actions of the government. Can you describe three such ways through a small skit?
Answer. Three ways are Public rallies, Mass Media and Campaigning.
Question 9 Use the table given on page 35 to answer the questions below:
• Who will form the government? Why?
• Who will be presented for discussions in the Lok Sabha?
• Is this process similar to what you have read about in Class VII?
Answer.
• Indian National Congress will win because it secured a two-thirds majority in the Lok Sabha.
• MPs will be presented.
• Yes, it is a similar process.
Question 10 The photograph shows results from the 3rd Lok Sabha elections held in 1962.
Use the photograph to answer the following questions:
(a)Which state has the highest number of MPs in the Lok Sabha? Why do you think this is so?
(b)Which state has the least number of MPS in the Lok Sabha?
(c)Which political party has won the most seats in all states?
(d)Which party do you think will form the government? Give reasons why.
Answer.
(a) Uttar Pradesh. This is because it is the state with the largest number of constituencies.
(b) Manipur and Tripura have the lowest number of MPs in the Lok Sabha.
(c) Congress.
(d) Congress.
Question 11 In the above question, what information is being sought from the Minister of Women and Child Development? If you were a Member of Parliament (MP), list two questions that you would like to ask.
Answer. The school nutritional policy of the government is being asked from the Minister of Women and Child Development. If I was a Member of Parliament (MP), the two quests ones that I would like to ask are:
- What new schemes are being launched for the upliftment of the status of rural women?
- Although mid-day meals are being provided, why is the student t most shocking low in the rural areas?
Question 12 Looking at the table given on page 39, would you say that people’s participation during the past 50 years has decreased/increased/been stable after initial increase?
Answer. The voter turnout during the past 50 years has been unstable. During the 4th Lok sabha election, the voter turnout was 61 %, which declined to 55% during
the 5th election. The 8th elections saw 63% of the population, which dropped to 56% in the I Oth and 58% in the 14th elections.
Question 13 Why do you think there are so few women in Parliament? Discuss.
Answer. There are few women in the parliament as there is discrimination against women in every field. It has been recently suggested that there should be more reservations of women in parliament.
Why Do We Need a Parliament Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1 How many members are nominated in the Rajya Sabha by the President?
Answer. Twelve members are nominated in the Rajya Sabha from amongst the scholars, art sts, and social workers.
Question 2 What does Parliament consist of?
Answer. The Parliament of India consists of the President of India, the Council of the States (Rajya Sabha}, and the House of the People (Lok Sabha). Rajya Sabha is the Upper House and Lok Sabha is the Lower House.
Question 3 How are members of Lok Sabha elected?
Answer. The members of Lok Sabha are elected directly by the people. Every citizen of 18 years has a right to vote.
Question 4 How many seats are reserved for scheduled castes in the Lok Sabha?
Answer. In Lok Sabha, 34 seats are reserved for scheduled castes.
Question 5 How many seats are reserved for scheduled tribes in Lok Sabha?
Answer. In Lok Sabha, 47 seats are reserved for scheduled tribes.
Question 6 In the 15th Lok Sabha elections held in 2009 the Congress got a large number of seats but still not enough to form the majority party in the Lok Sabha. Thus, it formed a United Progressive Alliance (UPA) with the other political parties, who were their allies.
Answer. The alliance of the Congress Party was: DMK; NCP; T.M.C. and N.C.
Question 7 Under which Act, the British government allowed some elected representation?
Answer. The British Government allowed for some elected representation under the Government of India Act 1909.
Question 8 Give one reason why you think there should be the Universal Adult Franchise.
Answer. Democracy is based on the principle of equality. Hence, all citizens should be given the right to vote on the basis of equality.
Question 9 Who controls and guides the government?
Answer. The Parliament controls and guides the government
Question 10 Which is the supreme law-making institution in India?
Answer. In India, Parliament is the supreme law-making institution.
Question 11 Which state has the highest number of MPs in the Lok Sabha?
Answer. Uttar Pradesh has 30 MPs in the Lok Sabha.
Question 12 Who presides over the Joint session of the Parliament?
Answer. The Speaker of the Lok Sabha presides over the meetings of the Joint Session of the Parliament
KSEEB Class 8 Civics Chapter 3 Questions And Answers
Question 13 Mention any four functions of the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
Answer.
- He allows the members to ask questions.
- No member can address the House without his permission.
- He preserves order in the House.
- He presides over the meetings of the Lok Sabha.
Question 14 What are the various types of bills of the parliament?
Answer. Bills are of three types:
(1) Ordinary Bill
(2) Money Bill and
(3) Constitutional Bill.
Why Do We Need a Parliament? Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1 Discuss the main four features of the Indian Parliament.
Answer.
- Indian Parliament is Bicameral.
- Rajya Sabha (Upper House) of the Parliament is permanent.
- Lok Sabha (Lower House) represents the whole nation.
- Rajya Sabha represents the states.
- The Lok Sabha is more powerful than the Rajya Sabha.
Question 2 Give the names of the two Houses of the Parliament and also their term.
Answer. The two Houses of the Parliament are the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha.
- Term of the Lok Sabha: The members of the Lok Sabha are elected for a period of five years. But the President can dissolve it before the end of the
tenure as well. During an emergency, due to external aggression or internal insurrection on, its term can be extended. - Term of the Rajya Sabha: Rajya Sabha is a permanent house. But after every two years, one-third (I 13) of its members retire and new ones are elected in their place. Thus, every member is elected for a term of six years.
Question 3 Who is the Speaker?
Answer. The Speaker is the presiding officer of the Lok Sabha. He is elected by the members of the Lok Sabha from among themselves. The Speaker ^resides over the meetings of the House; maintains j order in the House and conducts the business of the House in accordance with the Rules of the House. The Constitution also provides for the office of the Deputy Speaker.
Question 4 You have read that most elected members whether in the Panchayat or the Vidhan Sabha or the Parliament are elected for a fixed period of five years. Why do we have a system where the representatives are elected for a fixed period of five years?
Answer. The Panchayats. the Vidhan Sabha and the Parliament members are elected for a fixed tenure of five years and not for life due to the following reasons:
- Fixed tenure for the elected representatives is more democratic than the election for life.
- Representatives elected for fixed tenure generally look after the interest of the masses whereas a person elected for life generally misuses his power for his own interests.
- For a good democratic system, it is essential that the election should be held after a fixed time, so that people get a chance to elect their true representatives.
- Voters or the Public have a check on their representatives and the representatives are responsible for public opinion.
Question 5 Describe the constitutional powers of the Rajya Sabha.
Answer. The Rajya Sabha exercises constitutional functions along with the Lok Sabha. A constitutional bill may originate in either House of the Parliament. The constitutional bill should be passed in each House by a majority of its total membership and by a majority of two-thirds of the members present and voting. The Constitution is silent on how to resolve a deadlock between the two Houses.
Question 6 What do you understand by ‘Zero Hour?
Answer. The time immediately following the ‘Question Hour in both Houses has come to be popularly known as ‘Zero Hour. It is a Zero Hour in more than one sense. It is a non-existent hour. It starts at 12 noon, which is the zero hours of the day. It came to be called an hour also because very often it continued for one full hour until the House rose for lunch at I p.m. In the rules, there is no mention of any Zero Hour at all.
Question 7 Mention the special powers of the Rajya Sabha.
Answer. Under the Constitution, the Rajya Sabha has been vested with two special and exclusive powers. They are:
- Under Article 249, the Rajya Sabha may declare by resolution, passed by a two-thirds majority of its members present and voting, that it is necessary or
expedient in the national interest that Parliament should make laws with respect to any matter enumerated in the State List. - (a) Rajya Sabha is competent to create one or more All India Services if it passes a resolution by a two-thirds majority.
(b) Rajya Sabha alone can in if ate the proposal for removing the Vice-President.
Question 8 How is the Lok Sabha more powerful than the Rajya Sabha?
Answer. Lok Sabha is more powerful than the Rajya Sabha because:
- The members of the Lok Sabha are direct/ elected while those of the Rajya SaDha are indirectly elected.
- A money bill cannot be introduced in the Rajya Sabha. It originates in the Lok Sabha only. It is sent for recommendation to the Rajya Sasha and not
passing. If the Rajya Sabha returns it after 14 days, it is assumed as passed. - The Lok Sabha controls the executive whereas the Rajya Sabha has no effective control over the executive (cabinet).
Question 9 Define the term ‘no-confidence’ and ‘no-confidence motion’.
Answer. No-confidence means that the leader of the House has lost the confidence of the majority of members and is no longer wanted to lead the party and the government. The no-confidence motion is a formal resolution tabled in the House to see whether the leader enjoys the confidence of the members of the House. If the motion is passed, the leader resigns and is replaced by the new incumbent.
Question 10 What is understood by an adjournment motion?
Answer. An adjournment motion is a proposal for postponing the normal business of the House in order to discuss a matter or an urgent public importance, such as a serious riot a case of police firing on a procession or a grave railway accident, and so on.
Why Do We Need A Parliament KSEEB Class 8 Textbook Solutions
Question 11 What are the qualifications for a member of Lok Sabha?
Answer.
- He must be a citizen of India.
- He must have completed 25 years of age.
- He must not hold any office of profit under the Government of India or the Government of any State.
- He must possess such other qualifications as may be prescribed by the Parliament.
- No person can be a member of both the Houses of Parliament.
Question 12 Write down the financial powers of the Lok Sabha.
Answer. Lok Sabha controls the finances of the State. A money bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha and not in the Rajya Sabha If there is a difference of opinion on whether a particular bill is a money bill or any other bill, the decision of the speaker of the Lok Sabha will be final.
Why Do We Need a Parliament? Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1 Describe the powers of the Union Parliament.
Answer. The following are the main powers of the Union Parliament:
- Legislative Powers: The Parliament can frame laws on the subjects mentioned in the Union List and Concurrent List. Under certain special circumstances, the Parliament gets the right to frame laws on the subjects mentioned in the State List
- Financial Powers: The Parliament controls the finances of the country. The budget is passed by the Parliament
- Executive Powers: The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers are responsible to the parliament for their actions and policies. the Parliament has the power to remove the Council of Ministers by passing a vote of no-confidence.
- Judicial Powers: The Parliament can remove the President from the office through impeachment. The Parliament can remove the judges of the High Courts and Supreme Court by passing a resolution to that effect
- Electoral Powers: The elected members of Parliament participate in the election of the President The Vice-President is elected by the members of both the Houses of Parliament
Question 2 Describe the composition of the Indian Parliament.
Answer. The Union Parliament consists of the President and the two Houses to be known respectively as ;
the Council of States (Rajya Sabha) and the house of the People (Lok Sabha).
- Rajya Sabha: Rajya Sabha is the Upper House of the Parliament It can have at the most 250 members in it. The President of India nominates 12 members. These are persons who j have distinguished themselves in the field of art literature, science, and social service. Rest of j the members are elected by the members of State Legislatures. At present, it consists of 245 I (233 + 12) members in all. I/3rd of its members retire after every two years and the other j members are elected to fill up the vacancies. Each member remains in office for a period of j 6 years.
- Lok Sabha: Lok Sabha is the lower House of the Parliament It can have at the most 550 elected members. 530 members can be directly elected by the voters from different States and j 20 members can be elected from the Un on Ter r stories. The members will be elected according ! to the laws framed by the Union Parliament The President can nominate two members of the j Anglo-Indian community if he feels that in the Lok Sabha, this community has not got adequate j representation. In this manner, the maximum strength of the Lok Sabha can be 552. But, at j present Lok Sabha has 543 elected members. The members of the Lok Sabha are elected for a period of 5 years. The President of India can dissolve the Lok Sabha before the expiry of its j term and can order fresh elections. The members of the Lok Sabha elect one Speaker and one Deputy Speaker from among its members.
Important Questions For KSEEB Class 8 Civics Chapter 3
Question 3 Explain the law-making process in the Parliament.
Answer. The Parliament enacts laws for the whole country. The resolution that is introduced in the Parliament for the purpose of making law or changing old law or amending the Constitution is called a bill. An ordinary’ bill has to pass through the following stages to become an act:
- Introduction of the Bill: An ordinary bill can be introduced in any House either by a minister or by a member of the House.
- First Reading: The bill at this stage is not debated and discussed in detail only the objects and the main principles involved are discussed.
- Committee Stage: The members of the selected committee members discuss the bill in detail and debate the merits and demerits o* the bill.
- Second Reading: The report of the committee is discussed in detail. The bill is discussed clause by clause and item by item. The members of the House can suggest amendments in the bill.
- Third Reading: There is not much discussion on the bill at this stage. The entire bill is put to vote at this stage and it is either rejected or passed.
- Bill in the Second House: The bill is to pass through all the stages in this House also.
- Assent of the President: After the bill is passed by both the Houses it is sent to the President for his assent. The bill becomes an act when the President gives his assent to it.
Why Do We Need a Parliament? Hots Corner
Question 1 State the miscellaneous powers of the Parliament.
Answer.
- The elected members of both the Houses of Parliament participate in the election of the President.
- The Vice-President is elected by the members of Doth the House of Parliament.
- The Parliament can recommend to the President the removal of a Judge of the Supreme Court and High Court for their misbehavior or incompetence.
- The Parliament can recommend to the President the removal of the Chief Election Commissioner and the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
Question 2 What are the qualifications of a member of Lok Sabha?
Answer.
- He must be a citizen of India.
- He/She must have completed 25 years of age.
- He/She must not hold any office of profit under the Government of India or the Government of any State.
- He/She must not be of unsound mind and stands so declared by a competent court.
- No person can be a member of both Houses of Parliament.
Question 3 How is Rajya Sabha constituted?
Answer. The maximum strength of the Rajya Sabha can be 250. Out of these, 12 members are nominated by the President The remaining 238 members represent the States and the Union Territories. The representatives of the states are elected by the elected members of their Legislative Assemblies and in the case of the Union, Territories are chosen in such a manner as the Parliament may by law determines. At present, Rajya Sabha consists of 245 members.
Question 4 Write down the financial powers of the Lok Sabha.
Answer. Lok Sabha controls the finances of the State. A money bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha and not in the Rajya Sabha. If there is a difference of
opinion, whether a particular bill is a money bill or any other bill, the decision of the speaker of the Lok Sabha will be final.
Why Do We Need a Parliament? Miscellaneous Questions
A.Multiple Choice Questions Tick the correct option from the choices provided:
Question. I. Who is the head of the state?
(a) Prime Minister
(b) Cabinet
(c) President
(d) Council of Ministers
Ansswer. (c) President
Question.2. What is the present strength of Lok Sabha?
(a) 545 members
(b) 550 members
(c) 515 members
(d) 555 members
Ansswer. (a) 545 members
Question 3 Who acts as a link between the Cabinet and the President of India?
(a) Council of Ministers
(b) Ministers of State
(c) Prime Minister
(d) Vice President
Answer. (c) Prime Minister
Question 4 The Lower House of the Indian Parliament is known as:
(a) Rajya Sabha
(b) Lok Sabha
(c) Legislative Assembly
(d) Council of States
Ansswer. (b) Lok Sabha
Question 5 The tenure of the members of the Rajya Sabha is:
(a) 5 years
(b) 4 years
(c) 6 years
(d) 3 years
Answer. (c) 6 years
Question 6 Who is the presiding officer of the Lok Sabha?
(a) Vice-President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Speaker
(d) Home Minister
Answer. (c) Speaker
KSEEB Civics Chapter 3 Class 8 Multiple Choice Questions
Why Do We Need a Parliament? B.True or False
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- The Parliament consists of the President, Lok Sabha, and Rajya Sabha.
- Prime Minister presides over the meetings of Lok Sabha.
- Vice-President is the presiding officer of the Rajya Sabha.
- Rajya Sabha is more powerful than the Lok Sabha.
- Members of Lok Sabha are directly elected by the people on the basis of a Universal Adult Franchise.
- Rajya Sabha is a permanent House.
- The Lok Sabha can be dissolved by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister.
- The Parliament controls and guides the government.
- Each constituency elects one representative to Lok Sabha.
- Members of the Rajya Sabha are elected for a fixed tenure of five years.
Answer.
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
Why Do We Need a Parliament? C. Match the Following
Find and write the correct options from the given below columns:
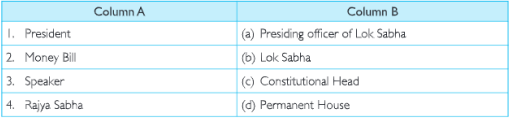
Answer.
1. (c)
2. (b)
3. (a)
4. (d).
Why Do We Need a Parliament? D.Picture Interpretation
Look at the following picture and answer the questions that follow:

- What does the following picture depict?
Answer. The following picture is of the Indian parliament. - How many houses does it have?
Answer. It consists of 2 houses, the lower house or the Lok Sabha, and the Upper House or the Rajya Sabha. - How many members does it have?
Answer. The Lok Sabha consists of 552 members and the Rajyasabha consists of 250 members.
