KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Social Science Political Science Chapter 6 Defence Of The Nation Points To Remember
- Our country was under the imperial rule of foreigners and only after many protests, struggles and sacrifices we got our independence on 15th August 1947. Hence it is our bounded duty to ensure that our nation does not ever come under external aggression.
- India has nearly 15,200 km of land border and about 7,516.50 km of sea border to protect.
- The Indian Defence system consists of three wings -Army, Navy and Air Force.
- The headquarters of the Defence Ministry is in New Delhi. This Ministry has four sections:
1. Defence Section
2. Defence Production Section
3. Defence Research and Development Section
4. Retired Defence Personnel Welfare Section.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Political Science Chapter 6
- The headquarters of the Indian Army is in New Delhi. Its head is known as the Commander-in-Chief. He has a Deputy Commander-in-chief, General, Major General, Brigadier, Military Secretary and a Military Engineer to assist him in his work.
- The army consists of Infantry, Cavalry, Tank Regiments called the Armed Corps and the Gunners’ Regiment.
- The important training centres are the National Defence Academy in Khadakvasla near Pune, the Defence Personnel College in Wellington near Ooty, the National Defence College inNew Delhi, the Indian Military Academy in Dehradun and the Officers’ Training School in Chennai.
- The headquarters of the Navy is also in New Delhi. Its head is The Admiral, and under him, there are various officers like, Vice-Admiral, Rear Admiral, Commander,Captain, Lieutenant Commander, Lieutenant and Sublieutenant.
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
- Indian Navy is huge and to expand it further, Hindustan Ship Yard has been established at Vishakapatnam.
- Warships like INS Neelagiri, Himagiri, Devagiri, Taragiri, Vindhyagiri, Chakradhari (a recent addition in March 2012) and INS Godavari, survey ships and Coastguard forces have been contacted.
- Indian Navy has two training centres, one in Kerala INS Vanduvarti and the other in Maharashtra, INS Shivaji at Lonavala.
- The Indian Air Force is a modem unit, well-equipped with technologically advanced aircraft.
- The headquarters of the Air Force is in New Delhi. The head of the Air Force is Air Chief Marshall.
- The main types of aircraft are Canberra, Hunter, Ajeet, MiG 21, MiG 23, MiG 25, MiG 27, MiG 29, Mirage 2000, etc.,
- Those who desire to work in the Armed forces should be service-oriented, patriotic, ready to sacrifice their lives for the sake of the country and also be familiar with the multicultural fabric of the nation.
Class 9 Political Science Defence of the Nation KSEEB Notes
- The DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation) which was established in 1958, has developed advanced earth-to-earth rockets like Pruthvi, Trishul, Akash, Nag, Agni 1,2,3,4 and 5.
- The second line of defence is:
1. Territorial Army
2. N.C.C. -National Cadet Corps
3. Coastal Guard
4. Border Security Force
5. Civil DefenceHome Guards
6. Red Cross. - The territorial Army is a voluntary part-time force which was established in 1949 to provide services during emergencies like natural calamities.
- Every year, the third Saturday of November is celebrated as ‘Territorial Army Day.
- National Cadet Corp’s aim is to develop among the students a sense of discipline, leadership qualities, friendliness and service-mindedness.
- The ships of the Coastal Guard have been given names like Puthar, Vikram, Vijay, Veera etc.
- Coastal Guard has four regional headquarters at Mumbai, Chennai, Gandhinagar and Port Blair in Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- BSF which has a training centre in Yelahanka in Bangalore successfully prevented transgression of our borders and illegal entry of foreigners and smuggling.
- The main aim of the Civil Defence force is the protection of the life of the citizens.
- Home Guards great help to the local police in curbing communal clashes, and restoring peace in society and during elections.
- The Red Cross Society renders valuable service to people during natural calamities and other emergencies.
- It is in gratitude for their sacrifice, courage, and great achievement that they are honoured with awards like Param Vir Chakra, Vishisth Vir Chakra, Vir Chakra etc.
- The defence forces are also rendering invaluable service during natural calamities like floods, droughts, earthquakes, landslides, storms etc.]

Defence Of The Nation Textual Questions And Answers
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
1. The main objective of our defence policy is protecting Nation
2. The Commander-in-Chief of our three Armed Forces is The President
3. The Chief of the Army is called General
4. The headquarters of the Defence Ministry is in Delhi
5. The Hindustan Ship-building yard is at Vishakhapatnam
6. The border security force training centre is in Yelahanka, Bangalore.
7. The Indian Red Cross Society was established in 1920 AD.
KSEEB Class 9 Social Science Chapter 6 Question and Answers
Defence Of The Nation Answer The Following Questions After The Group Discussion.
Question 1. What is the Naval Base near Karwar known as?
Answer: The Naval Base near Karwar is known as Sea Bird.
Question 2. Which are the four divisions of our Defence Ministry?
Answer: The sections Defence Ministry four are
- Defence Section
- Defence Production Section
- Defence Research and Development Section
- Retired Defence Personnel Welfare Section.
Question 3. Explain the structure of the Indian Army.
Answer:
- Indian Army’s head is known as the Commander-in-Chief.
- He has a Deputy Commander in- in – chief, General, Major General, Brigadier, Military Secretary and a Military Engineer to assist him in his work.
- The army consists of Infantry, Cavalry, Tank Regiments called the Armed Corps and the Gunners’ Regiment. There is a Supply and Engineering branch too.
- The Indian Army has been divided into seven commands for administrative convenience
- Each command is under the charge of a general officer of the rank of a Lt. General.
- These army commands are divided into Areas and Sub-areas which are headed by Major Generals and Brigadiers respectively.
Question 4. Which are the Commands of the Army?
Answer: The seven commands of the Army are
1. Western Command – Chandimandir (Chandigarh)
2. Eastern Command – Kolkata (West Bengal)
3. Norther Command-Udhampur (Kashmir)
4. Southern Command-Pune (Maharashtra)
5. Central Command – Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)
6. Training Command – Mhow (Madhya Pradesh)
7. North-Western Command-Jaipur (Rajasthan)
Question 5. Explain the functions of the Indian Air Force.
Answer:
- The Indian Air Force works effectively and courageously both during war times and peace times.
- It has succeeded in ensuring safety, security and stability.
SSLC Class 9 Political Science Chapter 6 Solutions Karnataka Board
Question 6. What are the qualifications required for recruitment to the Army?
Answer: There are certain conditions with regard to physical requirements, mental health, general education and technical knowledge that have to be met.
Question 7. What are the aims of N.C.C.? What are its advantages?
Answer: The aims of N.C.C. are To develop a sense of discipline, leadership qualities, friendliness and service-mindedness among the students
The advantages of Joining N.C.C are
- Those who have received N.C.C. training can join the armed forces easily.
- Cadets who have earned distinction during training are given seats in professional colleges.
- Cadets are given training in handling weapons.
- During training, cadets go on adventures like hiking, trekking, gliding, scaling or mountaineering, sailing etc.
- Students who have received N.C.C. training can secure admission in any defence school.
Question 8. Explain the organization of the Indian Red Cross Society.
Answer:
- In 1920 Red Cross Society organisation was established in India.
- The Indian Red Cross is a humanitarian voluntary organization
- The Indian President is its Chairman and governor in the state branch.
- The Red Cross Society renders valuable service to people during natural calamities and other emergencies.
- Without any discrimination, it helps sick people and those wounded on the battlefield.
Defence Of The Nation Additional Questions And Answers
Choose the correct alternative and write the complete answer along with its alphabet in the sheet provided:
Question 1. Which one among the following statement is WRONG regarding Territorial Army?
- It is a voluntary part-time force.
- It has no professional soldiers.
- The Civilians who are eager to play a role in defence can join.
- Government pay them a salary and other Monthly allowance.
Answer: 4. Government pay them a salary and other Monthly allowance.
Question 2. The Headquarters of the Defense Ministry is in
- Kolkatta
- Karwar
- Vishakapatnam
- New Delhi
Answer: 4. New Delhi
Defence of the Nation Class 9 KSEEB Important Questions
Question 3. The Coromandel-in-chief of the three Armed forces is the
- Vice-President
- President
- Prime Minister
- Home Minister
Answer: 2. President
Class 9 Social Science Defence Of The Nation Answers
Question 4.‘INS Neelagiri, Himagiri, Devagiri, Taragiri, Vindhygiri,’ all these are
- Warships
- Aircrafts
- Rockets
- Submarines
Answer: 1. Warships
Question 5. In list ‘A’ group of officers’ names and in list ‘B’ their posts are given. Identify the group that matches from list ‘C’
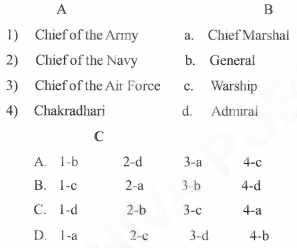
Answer: A. 1-b 2-d 3-a 4-c
Question 6. The correct statement regarding Seabird Naval is
- It is recently established at Karwar in Karnataka
- Many people in India do not like to join it
- It is a Para-military force of India
- It comes under the state home ministry
Answer: 1. It is recently established at Karwar in Karnataka
Defence Of The Nation Answer The Following Questions In A Sentence Each:
Question 1. It is our bounded duty to ensure that our nation does not ever come under external aggression. Why?
Answer: As you have already known, our country was under the imperial rule of foreigners and only after many protests, struggles and sacrifices we got our independence on 15th August 1947.
Question 2. The role of our defence forces assumes great significance. Why?
Answer: Although India has made sincere efforts to solve all problems in an amicable manner through peace talks, our efforts have not met with success.
Question 3. Which are the three wings of the Indian Defence system?
Answer: The Indian Defence system consists of three wings -Army, Navy and Air Force.
Question 4. Name the important wings of the Indian Army.
Answer: The army consists of Infantry, Cavalry, and Tank Regiments called the Armed Corps and the Gunners’ Regiment.
KSEEB Class 9 Political Science Defence of the Nation Summary
Question 5. Which are the fleets of the Indian Navy?
Answer: The fleets of the Indian Navy are
- The Western Fleet and the Eastern Fleet.
Question 6. Where do we find the training centres of the Indian Navy?
Answer: Indian Navy has two training centres. They are:
- Kerala – INS Vanduvarti.
- Maharashtra -INS Shivaji at Lonavala.
Question 7. How are the women soldiers recruited to defence forces?
Answer: Recruitment of women to the three armed forces takes place through the Women Special Entry Scheme (WSES).
Defence Of The Nation Answer The Following Questions In 4-6 Sentences Each:
Question 1. What are the main responsibilities of the army?
Answer: The main responsibility of the army is to protect the land and its sovereignty against attacks by foreign nations. The defence has a great influence on our geographical, political, social and technical environments. It also plays an important role in guarding border areas and in tackling natural calamities.
Question 2. Name the three naval commands of the Indian Navy.
Answer: The three naval commands of the Indian Navy are
1. Western Naval Command (Mumbai)
2. Eastern Naval command (Vishakhapatnam)
3. Southern Command (Cochin).
Question 3. Indian Air Force is considered one of the most powerful Air forces in the world. Why?
Answer:
- The Indian Air Force is a modem unit, well-equipped with technologically advanced aircraft.
- It has good defence equipment, a well-developed communication network, the latest spying technology, capability to confront the enemy and defend the nation.
- It also has a sufficient number of warplanes, helicopters and assault aircraft.
Question 4. Name the important Operational Commands of the Indian Air Force.
Answer: The important Operational Commands of the Indian Air Force are
1. Western Command – New Delhi
2. Eastern Command – Shillong (Meghalaya)
3. Central Command – Allahabad (Uttar Pradesh)
4. North Western Command – Gandhinagar (Gujarat)
5. Southern Command – Thiruvananthapuram (Kerala)
SSLC Class 9 Political Science Defence of the Nation Notes PDF
Question 5. Mention the names of the Second line of defence forces in India.
Answer: The Second line of defence forces of India are
- Territorial Army
- N.C.C. – National Cadet Corps
- Coastal Guard
- Border Security Force
- Civil Defence
- Home Guards
- Red Cross
Question 6. What are the characteristics of TerritorialArmy?
Answer: The characteristics of the Territorial Army are
- It is a voluntary part-time force. Its services are used only during emergencies like natural calamities.
- It was established by a Parliament Act in 1949.
- It has no professional soldiers, but only civilians who are eager to play a role in defence and are given military training in their spare time. ,.
- Only a person who is gainfully employed and in the age group of 18 to 42 is eligible to join the force.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Karnataka State Syllabus
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science History
- Chapter 1 Christianity and Islam
- Chapter 2 Medieval India and Political Transition
- Chapter 3 Religious Promoters and Social Kingdoms
- Chapter 4 Vijayanagara and Bahamani Kingdoms
- Chapter 5 The Moghuls and the Marathas
- Chapter 6 Bhakti Panth
- Chapter 7 Europe in the Middle Ages
- Chapter 8 Modern Europe
- Chapter 9 Revolution and Unification of Nations
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Political Science
- Chapter 1 Our Constitution
- Chapter 2 The Union Government
- Chapter 3 State Government
- Chapter 4 Judicial System
- Chapter 5 Indian Election System
- Chapter 7 National Integration
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Sociology
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography
- Chapter 1 Our State – Karnataka
- Chapter 2 Physiographic Divisions of Karnataka
- Chapter 3 Climate,Soil, Natural Vegetation and Animals of Karnataka
- Chapter 4 Water Resources of Karnataka
- Chapter 5 Land Resources of Karnataka
- Chapter 6 Mineral Resources
- Chapter 7 Transport
- Chapter 8 Industries of Karnataka
- Chapter 9 Major Tourist Centers of Karnataka
- Chapter 10 Population of Karnataka
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics
- Chapter 1 Natural Resources
- Chapter 2 Human Resoruces of Inda
- Chapter 3 Poverty and Hunger
- Chapter 4 Labour and Employment
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Business Studies
