KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work And Energy Important Concepts
Work: Work is said to be done if a body is displaced by a force. Mathematically, W= Force x displacement. Work is a scalar quantity.
S.I unit of work: newton-meter or joule
Positive and Negative work: If the angle between the directions of displacement and force is an acute angle(< 90°), then the work is said to be positive. If the angle between the directions of displacement and force is an obtuse angle (> 90), then the work is said to be a negative obtuse angle (> 90), then the work is said to be negative.
Zero work: Work is said to be zero if
1) The angle between the directions of displacement and force is 90° or displace is zero or no force acts on the body
Energy: Energy is defined as the capacity of a body to do work. It is a scalar quantity and its S.I unit is the joule.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
Types of energy: Mechanical energy (kinetic energy and potential energy), heat energy, chemical energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, light energy etc.
Kinetic energy: It is the energy of a body by the virtue of its motion
Potential energy: It is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position or configuration
Law of conservation of energy: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed
Power: Power is defined as the rate of doing work. It is a scalar quantity and the S.I unit is a watt.
Commercial unit of power: Commercial unit of power is a kilowatt hour (kWh). It is electrical energy used by a device of power 1000W in one hour, kilowatt hour (kWh) 1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Work And Energy Exercises
Question 1. A force of 7N acts on an object. The displacement is 8m along the direction of a force. What is work done?
Answer: Work = Force x displacement = 7 x 8 = 56 J
Question 2. When do we say that work is done?
Answer: Work is said to be done when a force displaces a body.
Question 3. Write an expression for the work done when a force is acting on an object in the direction of its displacement
Answer: Work = Force x displacement
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Question 4. Define 1J of work
Answer: One joule is defined as work done by a force of IN in displacing a body through lm in its direction
Question 5. A pair of bullocks exerts a force of HON on a plough. The field being ploughed is I5m long. How much work is done in ploughing the length of the field.
Answer: Work done = Force x displacement = 140 x 15 = 2100J
Question 6. What is the kinetic energy of an object?
Answer: The energy of an object by virtue of its motion is called kinetic energy.
Question 7. Write an expression for the kinetic energy of an object
Answer: K.E = 1/mv2 where m = mass of the object and v = velocity of the object
Question 8. The kinetic energy of an object of mass m moving with a velocity of 5m/s is 25J. What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is doubled? What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is increased 3 times?
Answer:
Initial kinetic energy=25J Since K.E is proportional to (velocity)2 when velocity is doubled, then
K.E =(2)2x Initial K.E = 4 x 100 = 400J
When the velocity is trebled, then K.E =(3)2x 25 = 225J.
Question 9. What is power?
Answer: Power is defined as the rate of doing work
Question 10.Define 1 watt of power
Answer: One watt is the power when the one-joule work is done in one second
Karnataka Board Class 9 Science Work and Energy Solutions PDF
Question 11. A lamp consumes 1000J of electrical energy in 10s. What is its power?
Answer: Power of he lamp = energy consumed / time = 1000/10= 100W
Work And Energy Textual Questions
Question 1. Look at the activities listed below. Reason out whether or not work is done in the light of your understanding of the term ‘work’.
1)Suma is swimming in a pond.
2)A donkey is carrying a load on its back.
3)A windmill is lifting water from a well.
4)A green plant is carrying out photosynthesis.
5)An engine is pulling a train.
6)Food grains are getting dried in the sun.
7)A sailboat is moving due to wind energy.
Answer:
1)Yes. Work is done by suma become she is moving forward by pushing water backward
2)No. Work is not done by the donkey. This is because the weight (Force) of the load acts perpendicular to its displacement
3)Yes. Work is done by the windmill by lifting water against the earth’s gravity
4)Yes. Work is not done by the green plant because neither a force nor a displacement is observed during the photosynthesis by leaves
5)Yes. The force exerted by the engine and the displacement of the train are in the same direction
6)No work is done since neither a force nor displacement is seen
7)Yes. Work is done by the wind in pushing the sailboat in the direction of the wind
Question 2. An object was thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the object?
Answer: Zero because the force of gravity and the displacement are perpendicular
Question 3.A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Answer: First chemical energy is converted into electrical energy and then electrical energy is converted into heat and light energy.
Question 4. A certain force acting on a 20 kg mass changes its velocity from 5m/s to 2 m/s. Calculate the work done by the force.
Answer:
Work done by the force = Change in the kinetic energy
= Initial kinetic energy – final kinetic energy
= 1/2 mu2– 1/2 mv2= 1/2 m(v2 – u2)
= 1/2 (20) (52-22) = 10 (25 – 4) = 210J
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy Notes
Question 5. A mass of 10kg is at point A on a table. It is moved to point B. If the line joining A and B is horizontal, what is the work done on the object by the gravitational force? Explain your answer.
Answer: Zero because the force of gravity and the displacement are perpendicular
Question 6. The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively. Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
Answer: No. This is because the loss in potential energy is equal to the gain of its kinetic energy such that the total energy of the object remains constant.
Question 7. What are the various energy transformations that occur when you are riding a bicycle?
Answer: Muscular energy is converted into mechanical energy (kinetic energy) of the bicycle and a part of the kinetic energy of the bicycle is converted into heat energy due to friction between the tires and the road.
Question 8. Does the transfer of energy take place when you push a huge rock with all your might and fail to move it? Where is the energy you spend going?
Answer: Yes. Muscular energy is used to overcome the friction between the rock and the ground
Question 9. A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month. How much energy is this in joules?
Answer: 1 unit = 1kwh = 3.6 x106J.
250 units = 250 x 3.6 x106J. = 9×106J.
Question 10. An object of mass 40 kg is raised to a height of 5 m above the ground. What is its potential energy? If the object is allowed to fall, find its kinetic energy when it is halfway down.
Answer:
Potential energy of the object = mgh
= 40 x 9.8 x 5 = 1960 J
Let v be the velocity of the object a the halfway mark ie when s = 2.5 m
We have v2= u2+2gs = 02 + 2 x 9.8 x 2.5 = 49 => v = 7m/s
The kinetic energy of the object = 1/2 mv2 = 1/2 x 40 x49 = 980J
Question 11. What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving around the earth? Justify your answer.
Answer: Zero. Because the force of gravity acts as the dentripetal force which is perpendicular to the displacement.
Question 12. Can there be displacement of an object in the absence of any force acting on it? Think. Discuss this question with your friends and teacher.
Answer: The net force acting on the falling raindrops is zero ie rain drops are displaced with no force acting on them.
Question 13. A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? Justify your answer.
Answer: No work was done because the displacement of the bundle of hay is zero.
Question 14. An electric heater is rated 1500 W. How much energy does it use in 10 hours?
Answer: Energy used = Power x time =1.5 kW x 10 hour =15 kWh
Question 15. Illustrate the law of conservation of energy by discussing the energy changes which occur when we draw a pendulum bob to one side and allow it to oscillate. Why does bob eventually come to rest? What happens to its energy eventually? Is it a violation of the law of conservation of energy?
Answer: When we draw a pendulum bob to one side, the work done against gravity is stored as potential energy in the bob. When the bob is released, this potential energy is gradually converted into kinetic energy such that at any position, the sum of kinetic and potential energies is always constant. When the bob is at the mean position, its potential becomes zero and kinetic energy will be maximum. As the bob reaches another extreme position the total energy will only be potential energy. Thus total energy is conserved. Du-friction, the energy of the bob is lost gradually in the form heat and the motion of the pendulum decreases with time and comes to rest after some time.
Question 16. An object of mass, m is moving with a constant velocity, v. How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
Answer: Work done = kinetic energy of the object = 1/2 mv2
Question 17. Calculate the work required to be done to stop a car of 1500 kg moving at a velocity of 60 km/h.
Answer:
Given mass(m) = 1500kg and velocity(v)
= 60km/h = 60 x 5/18 = 50/3 m/s
Work to be done = kintic energy of the car = 1/2 mv2 = 14 x 1500 x (50/3)2= 208,333.33J
Question 18. In each of the following a force, F is acting on an object of mass, m. The direction of displacement is from west to east shown by the longer arrow. Observe the diagrams carefully and state whether the work done by the force is negative, positive, or zero.
 Answer:
Answer:
(1) Since the force(F) is perpendicular to the displacement(s), work done is zero
(2)Since the force(F) and displacement(s) are in the same direction, work done = Fs joule and positive
(3)Since the force(F) and displacement(s) are opposite directions, work done = – Fs joule and negative.
Question 19. Soni says that the acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. Do you agree with her? Why?
Answer: Yes. I do agree with her. Acceleration can be zero if the resultant of several forces acting on the object is zero.
Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy Important Questions Karnataka Board
Question 20. Find the energy in kW h consumed in 10 hours by four devices of power 500 W each.
Answer: The power of each device = 500W = 0.5kW
Therefore, Energy consumed by the 4 devices = 4xPxt = 4x 0.5 x 10 = 20kWh
Question 21. A freely falling object eventually stops on reaching the ground. What happens to its kinetic energy?
Answer: On reaching the ground, the kinetic energy of the falling body is converted into heat energy and sound energy.
Work And Energy Additional Questions
One Mark Questions
Question 1. Write an expression for the work when force and displacement are inclined with an angle Q.
Answer:
W = FS cos Q
where F = force
S = displacement
Question 2.Define the term energy
Answer: The energy of a body is defined as the capacity of the body to do the work.
Question 3. Name the largest natural sources of energy
Answer: The sun is the largest natural source of energy.
Question 4. Both work and energy has the same unit joule. Why
Answer: The energy possessed by an object is measured in terms of the capacity of doing work. Hence energy and work have the same unit joule.
Question 5. Give an account for the kinetic energy of a flying arrow.
Answer: The work done in stretching the string is stored as P.E. in the string. When the string is released the P.E. is converted into K.E. of the flying arrow.
Question 6. How do plants produce food?
Answer: Plants produce food through a process called photosynthesis with the help of solar energy.
Question 7. How are fuels such as coal and petroleum formed?
Answer: Millions of years ago plants and animals were buried deep inside the crust of the earth under temperature and pressure. They got converted into coal and petroleum.
Question 8. Calculate the speed of a body of mass 1kg having a kinetic energy of 1J
Answer: 1/2 mv2 = kinetic energy => 1/2 x 1 x v2 = 1 =>v2= 2 and v = \(\sqrt{2} \)m/s
Question 9. What happened to the potential energy and kinetic energy of a stone on reaching at the highest position?
Answer: Potential energy will be maximum and kinetic energy will be zero.
Question 10. How much work is done by a weight lifter when he holds a weight of 80kg on his shoulders for 2 minutes?
Answer: zero
Karnataka State Board 9th Science Work and Energy Exercise Solutions
Question 11. Identify the energy possed by
(1)A running horse
(2)A raised hammer
(3)Compressed spring
(4)Water stored in a dam
(5)Book kept on a table
(6)A man climbing a hill
(7)A flying bird
Answer:
(1) Kinetic energy
(2) Potential energy
(3) Potential energy
(4) Potential energy
(5) Potential energy
(6) Both kinetic and potential energies
(7) Both K.E and P.E
Question 12. Write the energy transformation at
(1) Thermal power station
(2) Nuclear Power plant
(3) Hydroelectric power station
Answer:
(1) Chemical energy of coal —> heat —> kinetic energy —> electrical energy
(2)nuclear energy —> heat —> mechanical energy —> electrical energy
(3)kinetic energy of water —> electrical energy
Question 13. If the speed of a car is increased 3 times, what is the increase in kinetic energy?
Answer: Since K.E ∞ v2, the kinetic energy of the car increases 9 times
Question 14. A stone is thrown vertically upwards. The kinetic energy of the stone decreases gradually. Is the law of conservation of momentum violated? Justify your answer.
Answer: No. The law of conservation of energy is not violated because the decrease in the kinetic of the stone will be equal to the increase in its potential energy.
Question 15. What will be the power of a body when a force ION moves it with a constant velocity of 2m/s?
Answer: Power = Force x velocity =10 x 2 = 20W
Question 16.Mention the two conditions that need to be satisfied for work to be done
Answer:
1) A force should act on the object
2) The object must be displaced
Question 17. We apply a force to lift an object upwards against the gravity of the earth. Mention which force does positive work and which force does negative work.
Answer: The applied force does positive work since force and displacement are in the same direction. The force of gravity does negative work since the displacement is opposite to the force.
Question 18.
1) How is kinetic energy related to
- Mass of the body
- the velocity of the body
Answer:
1) Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the body.
2) Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of velocity.
Question 19. A bullet of mass 5g is fired with a velocity of lOOm/s. What is its kinetic energy?
Answer:
M = 5g = 5 x 10-3kg
v= 100 m/s
K.E. = 1/2 Mv2
= 1/2 x 5 x 10-3 x (100)2 = 25J
Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy Summary KSEEB
Question 20. An object of mass 5kg is dropped from a height of 10m. What will be the kinetic energy? When it is 5m from the ground (g = 10m/s)
Answer: W.K.T.
v2=u2 + 2gh
= ( 0 )2 + 2 x 10×5
v2= 100
v = \(\sqrt{100}=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}\)
K.E. = 1/2 Mv2= 1/2 x 5 x 100 = 250 J
Question 21. Does a stretched rubber possess energy from where does it set energy?
Answer: Work done to stretch the rubber is converted into the potential energy of the rubber band.
Question 22. What kinds of energy conversions sustain the water cycle?
Answer: Solar energy converts water from water bodies into water varpus which get cooled and pour as rains. When the rainwater flows with K.E. and reaches the water bodies and its K.E. is converted into P.E.
Question 23. Define mechanical energy. Mention two forms of mechanical energy. State the law of conservation of energy
Answer: Energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position of motion is called mechanical energy. The two forms of mechanical energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed
Question 24. Name the following devices which convert
1)Chemical energy into electrical energy
2)Electrical energy into mechanical energy
3)Mechanical energy into electrical energy
4)Light energy into electrical energy
5)Nuclear energy into electrical energy
6)Heat energy into mechanical energy
7)Wind energy into electrical energy
Answer:
1) Electric cell
2) Electric motor
3) Generator
4) Photocell
5) Nuclear power reactor
6) Turbine
7) Wind-mill
Question 25. Define work. When the work is said to be
(1) positive and
(2) negative
Answer:
Work is said to be done if a body moves under the action of a force
(1)If the force and displacement of a body are in the same direction, then work is said to be positive
(2)If the force and displacement of the body are in opposite directions, then work is said to be negative
Question 26. Write an expression for the work when force and displacement are
(1) in the same direction
(2) opposite directions
Answer:
(1) Fs
(2) – Fs where F = force and s = displacement
Question 27. Sharma tried to push a heavy rock of mass 120kg for 2 minutes with a force of 50N but could not move it. What will be the work done by Sharma at the end of 2 minutes?
Answer: Zero because there is no displacement of rock
Question 28. What is kinetic energy? Derive an expression for the kinetic energy of a body
Answer:
Kinetic energy:
The energy of an object by virtue of its motion is called as its kinetic energy. Consider an object of mass ‘m’ moving with uniform velocity ‘u’. Let a constant force F acts on the object and displaces it through a distance ‘s’
Work done by the force W = Fs
Let ‘v’ be the final velocity of the object and ‘a’ be the acceleration of the object.
Using the equation v2= u2 + 2as, we get
\(\mathrm{s}=\frac{v^2-u^2}{2 a}\)According to Newton’s 2nd law of motion F = ma
Hence W = mas =ma x ( v2– u2 )/2a
\(=1 / 2 m\left(v^2-u^2\right)\)If the object were at rest before the application of the force, then u = 0, and kinetic energy Ek = 1/2 m(v2 – u2)
Work and Energy Class 9 KSEEB Textbook Solutions Free PDF
Question 29.
1) Define gravitational potential energy.
2)Derive an expression for the gravitational potential energy of an object of mass ‘m’ kept a height ‘h from the ground
3)Find the energy possessed by an object of mass 10kg when it is at a height of 6m above the ground (given g = 9.8m/s2)
Answer:
1) The gravitational potential energy of an object at a point above the ground is defined as the work done in raising it from the ground to that point against gravity.
2) 
Consider an object of mass ‘nT is raised through a height ‘h’ from the ground. The force required to do this is F = mg where g = acceleration due to gravity
Thus work done (W) = F x h = mgh
This work is stored as the gravitational potential energy of the object. Thus gravitational potential energy (Ep) = mgh
3) Given m= 10kg, h = 6m and g = 9.8m/ s2 Potential energy of the body = mgh
= 10 x 9.8 x 6 = 588 joule
Question 30.
1) Define power. What is its S.I. unit?
2) Two girls A and B each of weight 400N climb up a rope through a height of 8m. Girl A takes the 20s while B takes the 50s to accomplish this task. What is the power expended by each girl?
Answer: Power is defined as the time rate of doing work.
ie P = work/time.
S.I unit power is a watt
Power extended by the girl A=mgh /1 = 400 x 8/20= 160W
Power extended by the girl B = 400 x 8 / 50 = 64W Self-test
Question 31. Define K.E. of a body. Prove that the change in K.E. of the body is equal to work done on it.
Answer:
K.E. of a body is defined as energy possessed by the body by virtue of its motion.
Consider an object of mass ‘m’ moving with uniform acceleration ‘a’.
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
s = displacement, then we have v2= u2+ 2as => s = \( \frac{\left(v^2-u^2\right)}{2 a}\)
If the object moves from rest, then u = o.
Hence w = 1/2 M V2
Thus work done = change in K.E. of the body.
Question 32.
1)An expression for K.E. of a body.
2)How much work has to be done by the engine of the car to increase the velocity of car from 30kmh-1 to 60kmh-1 Most of car is 1500kg.
Answer:
1)K.E. = 1/2 M V2
Where m = mass of the body v = velocity of the body
2) Mass of the car (m) = 1500kg Initial velocity of the car (u) = 30 x
Final velocity of the car (v) = \(60 \times \frac{5}{18}=\frac{50}{3} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}\)
work done by the engine [/latex]=\frac{1}{2} m\left(v^2-u^2\right)[/latex]
\( =1 / 2 \times 1500\left(\frac{50}{3}\right)^2-\left(\frac{25}{3}\right)^2\) \( =750 \times\left(\frac{2500}{9}-\frac{625}{9}\right)\) \(=\frac{750 \times 1875}{9}=156250 \mathrm{~J}\)KSEEB Class 9 Science Work and Energy Extra Questions with Answers
Question 33. The gravitational potential energy of a body does not depend on the path on which the body is moved. Illustrate your answer with the example.
Answer:
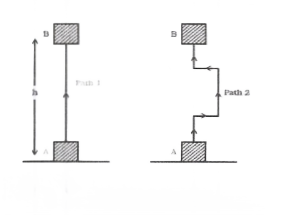 Case (1):
Case (1):
consider a block is taken from initial position A to B along the path -1 work done (W1) = Force x displacement
= mg x AB
ie Gravitation P.E. = mg x h
Case (2):
Now consider the block is taken along path 2 ie APQRSB
work done to raise from A to P = mg * AP work done to move from P to Q = 0 (since the displacement is perpendicular to the force of gravity)
work done to move from Q to R = mg x QR
work done to move from R to S=0 work done to move from S to B=mg x SB
thus total work done to raise the block along path 2 = mg (AP + QR + SB)
=mg x AB
Gravitational P.E. = mgh
Thus gravitational potential energy does not de- pend on the path through which the body is raised.
Work And Energy Application Questions
Question 1. A man pushes a wall but fails to displace it. Is work done? Justify your answer.
Answer: No work is done because there is no displacement of the wall.
Question 2. How much work done in moving an object around a circular path of radius 5m by a force of 10N?
Answer: zero. No work is done because the displacement and the centripetal force are perpendicular to each other.
Question 3. A 35kg boy runs along a circular path of radius 10m with uniform speed 5m/s. How much word is done by the in completing one circle. Justify your answer.
Answer: Zero. The displacement of the boy after one circle is zero. Hence work done is zero.
Question 4.
1) When does an object
- Lose energy
- gain energy
Answer:
1) When work is done by the object, the body loss energy
2) When work is done on the object, the body gains energy
Question 5. Can kinetic energy be negative?
Answer: because K.E. = 1/2 mv2
where mass (m) = positive quantity
and V2=positive quantity
Question 6. Why does the air move from place to place?
Answer: Due to solar energy the air is heated and becomes light. Hence it moves up and cooler air reaches its place.
