KSEEB Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Visualising Solid Shapes Points To Remember
There are three types of shapes
1) One-dimensional shapes: Shapes having length only, Example: aline
2) Two-dimensional shapes: Plane shapes having two measurements like length and breadth. Example: a polygon, a triangle, a rectangle etc., generally, two-dimensional figures are known as 2- D figures.
3) Three-dimensional shapes: Solid objects and shapes having length, breadth and height or depth. Example. cubes, cylinders, cone, cuboid, spheres etc.,
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths
4)Face: A flat surface of a three-dimensional figure.
5) Edge: line segment where two faces of solid meet.
Polyhedron: A 3 – D figure whose faces are all polygons.
Prism: Apolyhedron whose bottom and top faces (known as base) are congruent polygons and faces known as lateral faces are parallelograms. When the sides faces are rectangles. The shape is known as right prism.
Pyramid: Apolyhedron whose base is a polygon and lateral faces are triangles.
Vertex: Apoint where three or more edges meet.
Base: The face that is used to name a polyhedron
Euler’s Formula for any polyhedron is F + V – E= 2 where F stands for number of faces, V for number of vertices and E for number of edges.
3D objects have different views from different positions.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Practice Questions For KSEEB Class 8 Visualising Solid Shapes
Mapping: A map depicts the location of a particular object/place in relation to other objects/places.
A map is different from a picture.
Symbols are used to depict the different object places
There is no reference or perspective in a map.
Maps involve a scale which is fixed for a particular map.
Convex: The line segment joining any two points on the surface of a polyhedron entirely lies inside or on the polyhedron. Ex: Cube, cuboid tetrahedron, pyramid, prism etc.,

KSEEB Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Visualising Solid Shapes PDF
Class 8 Maths KSEEB Chapter 14 Solved Examples Visualizing Solid Shapes Exercise 14.1
1. For each of the given solid, the two views are given. Match for each solid the corresponding top and front views. The first one is done for you.

Solution:
Object side view Top view
a) A bottle 3 4
b) A weight 1 5
c) A flask 4 2
d) cup & saucer 5 3
e) container 2 1
2. For each of the given solid, the three views are given. Identify for each solid the corresponding top, front and side views.
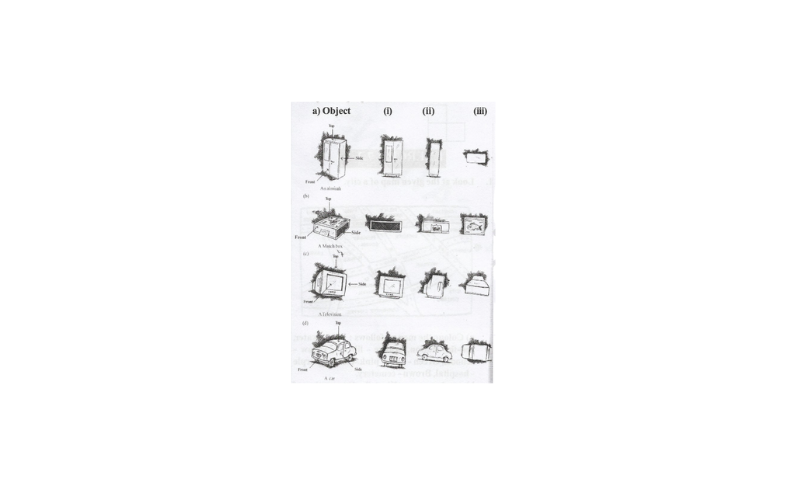
Solution:
Object 1 2 3
a) An almirah Front view Side view Top view
b) A matchbox Side view Front view Top view
c) A Television Front view Side view Top view
d) A car Front view Side view Top view
Karnataka Board Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Solutions
3. For each given solid, identify the top view, front view, and side view.
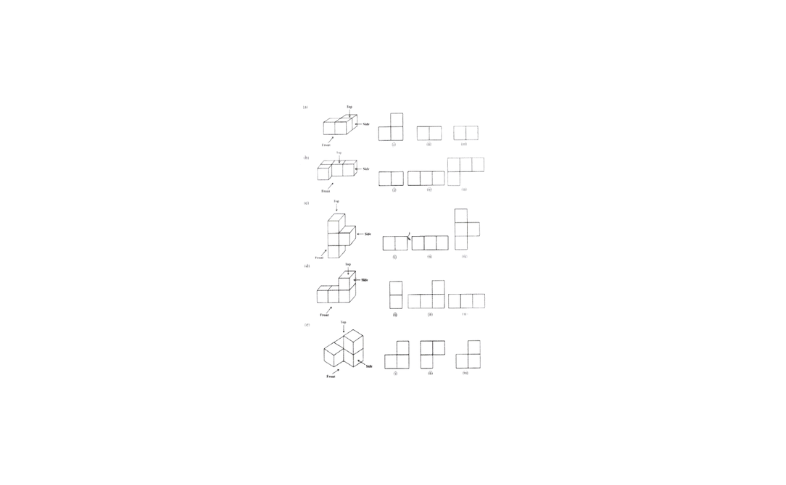
Solution:
Object 1 2 3
a) Top view Front view Side view
b) Side view Front view Top view
c) Top view Side view Front view
d) Side view Front view Top view
e) Front view Top view Side view
Simplified Guide For KSEEB 8th Maths Visualising Solid Shapes
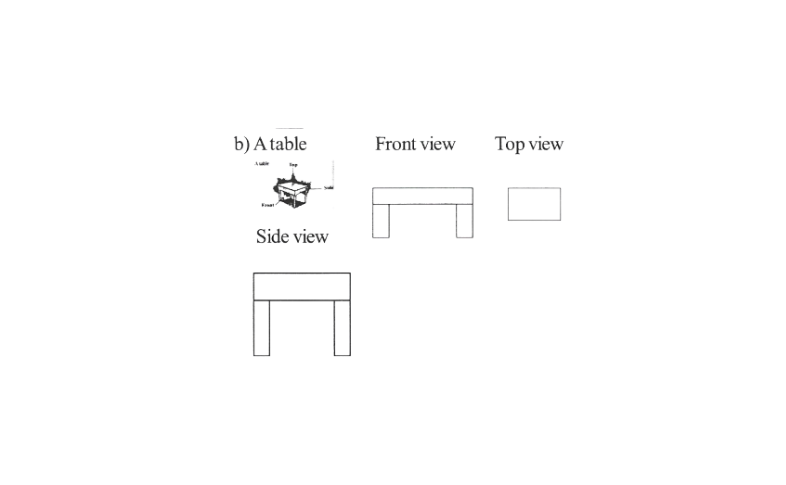
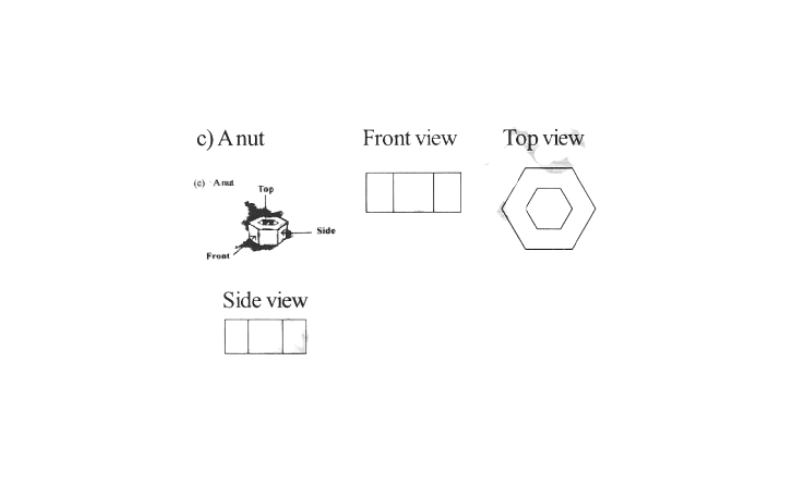
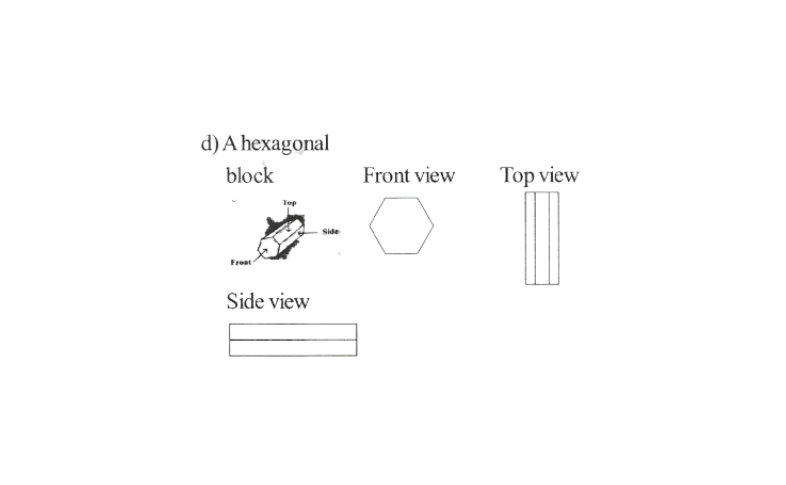
4. Draw the front view, side view, and top view of the given objects
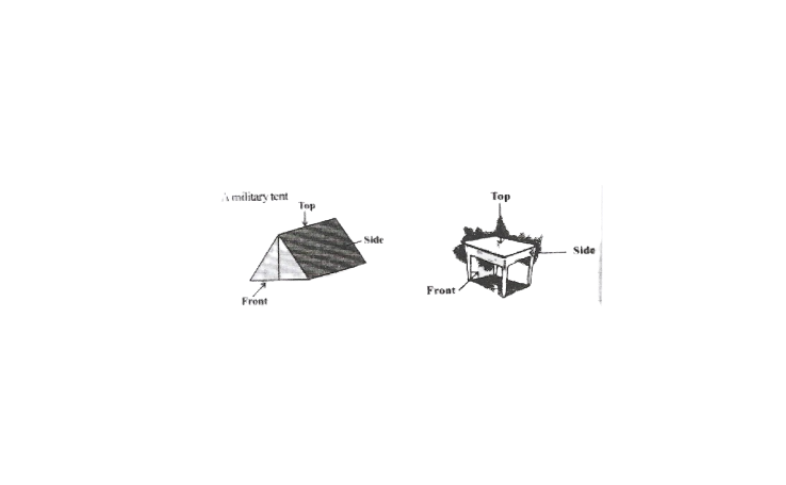
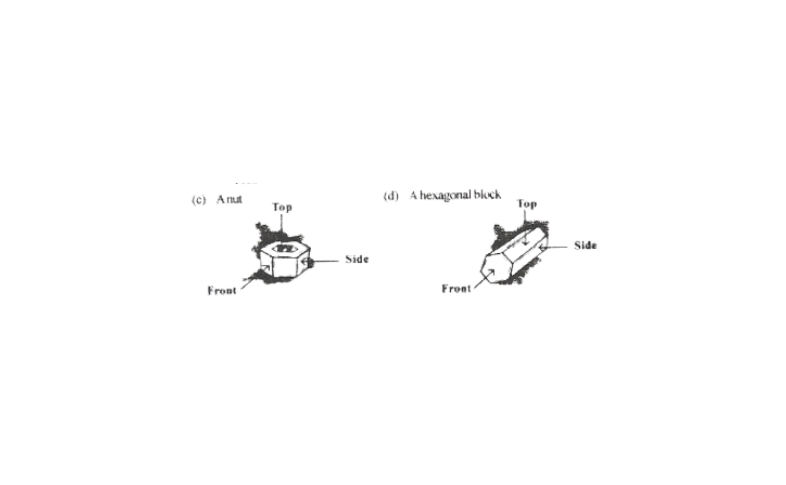
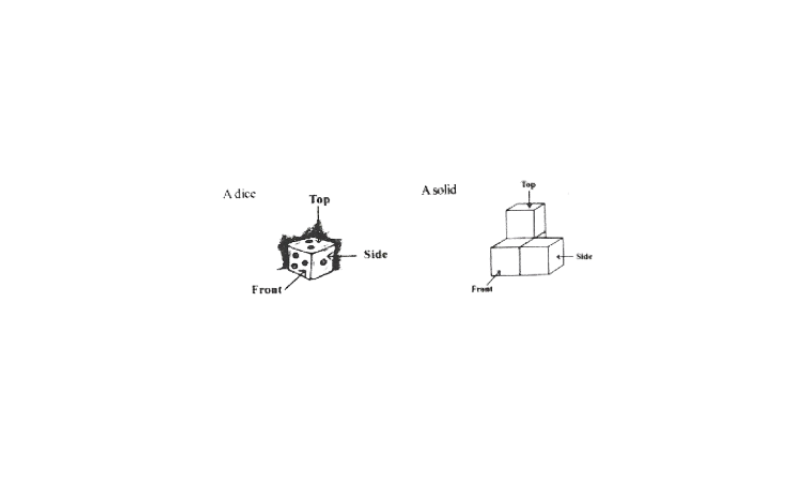
Solution:

Step-By-Step Solutions For Visualising Solid Shapes Class 8 Karnataka Board
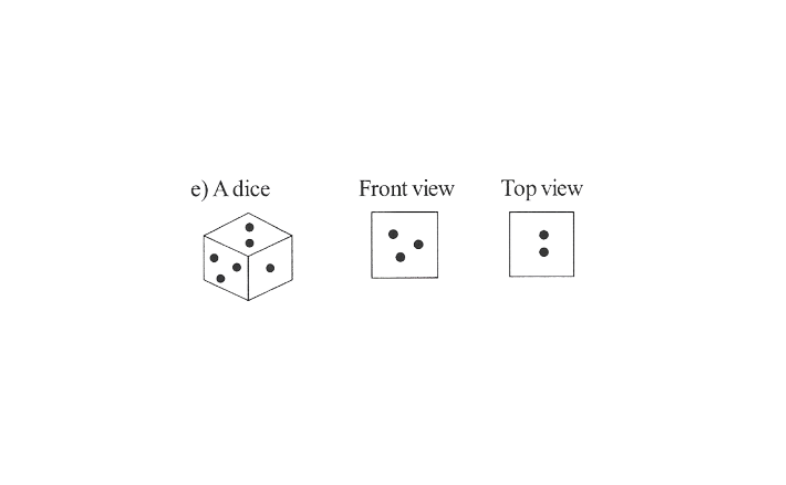
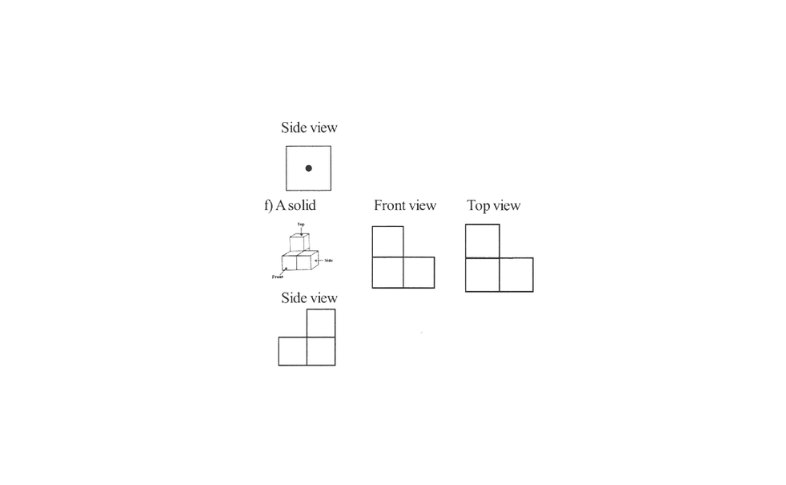
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Visualising Solid Shapes
Visualizing Solid Shapes Class 8 KSEEB Guide Exercise 14.2
1. Look at the given map of a city.
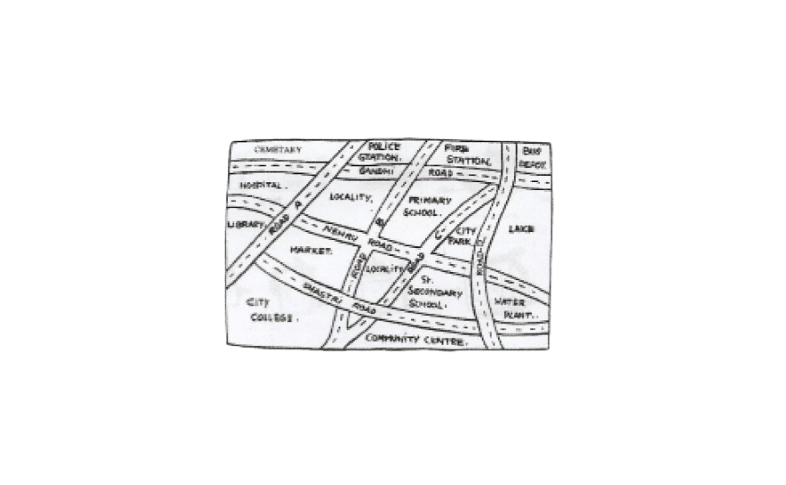
a)Colour the map as follows: Blue-water, red-fire station, orange – library, yellow – schools, Green – park, pink-college, purple – hospital, Brown – cemetery.
b)mark a green ‘X’ at the intersection of Road ‘C’ and Nehru road, Green ‘Y’ at the intersection of Gandhi Road and Road A.
c)In red, draw a short street route from library to the bus depot.
d)Which is further east, the city park or the market?
e)Which is further south, the primary school or the Sr. secondary school?
Solution:
a)
b) 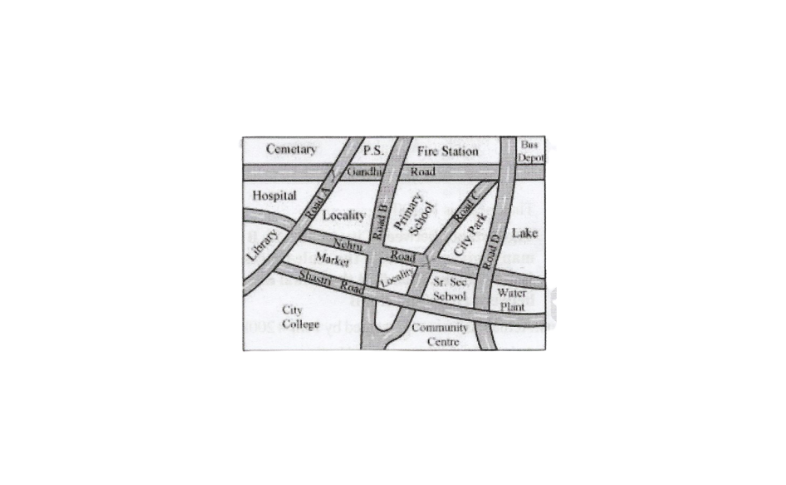
c) 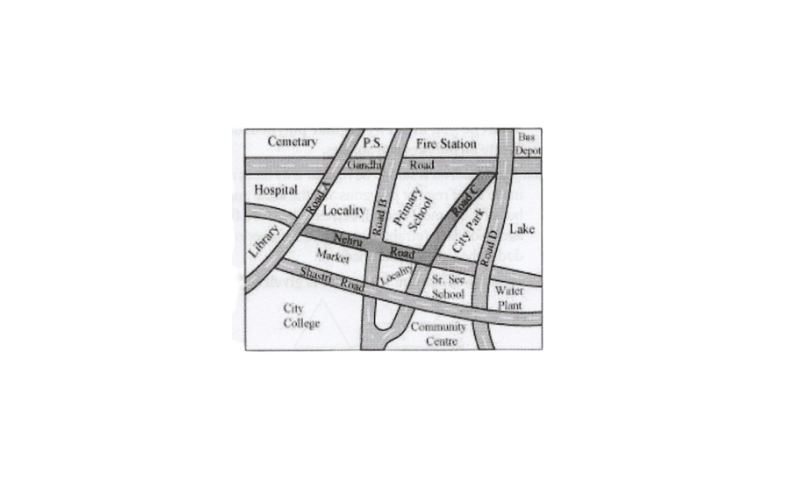
d) Between the market and the city park, the city park is further east.
e) Between the primary school and the Sr. secondary school. The Sr. secondary is further south.
Visualising Solid Shapes Class 8 KSEEB Solutions With Answers
KSEEB Class 8 Visualising Solid Shapes Solutions Exercise 14.3
1. Can a polyhedron have for a face?
1) 3 triangles?
2) 4 triangles?
3) a square and four triangles?
Solution: 1) No, such a polyhedron is not possible. A polyhedron has minimum 4 faces.
2)yes, a triangular pyramid has 4 triangular faces.
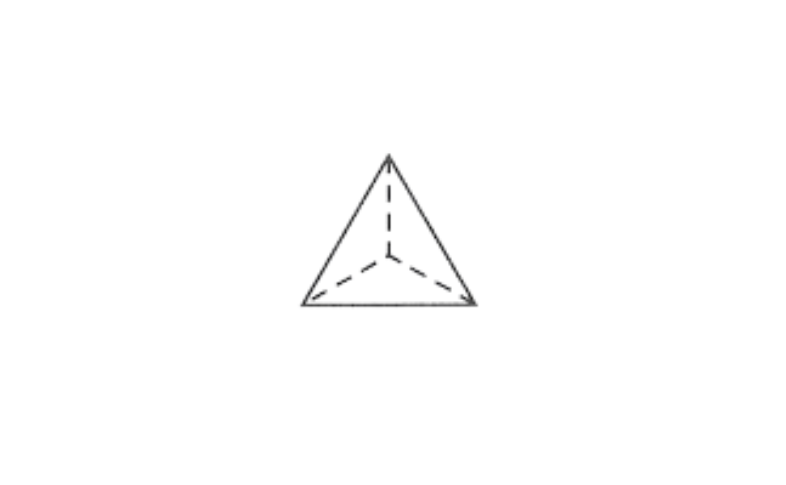

3) yes, a square pyramid has a square face and 4 triangular faces.
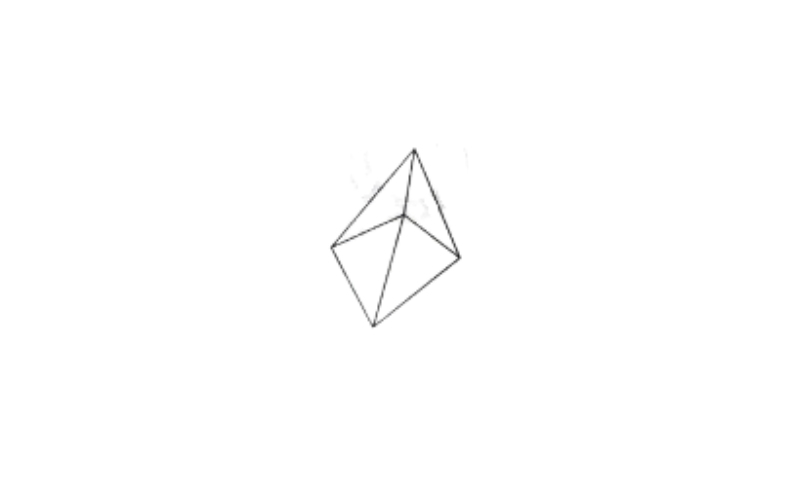

KSEEB Class 8 Maths Visualising Solid Shapes Exercise 14.1 Solutions
2. Is it possible to have a polyhedron with any given number of faces?
Solution: A polyhedron has a minimum of 4 faces.
3. Which are prisms among the following?
1) 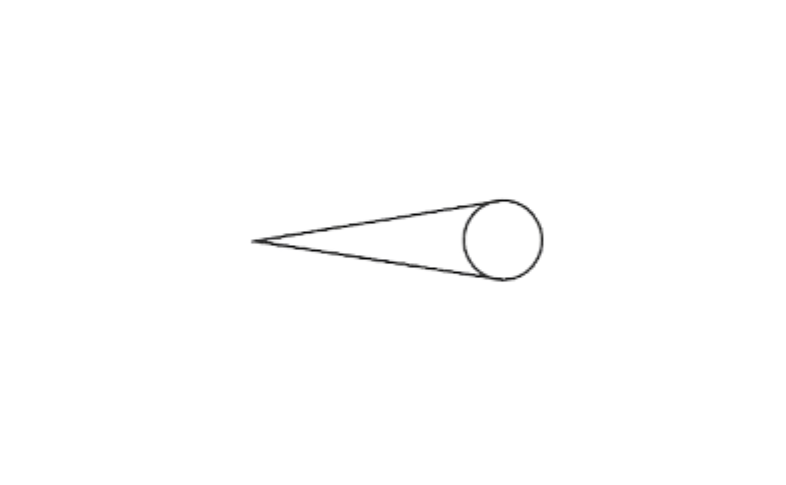
Solution: It is not a polyhedron as it has a curved surface.
∴ it will not be a prism also.
2) 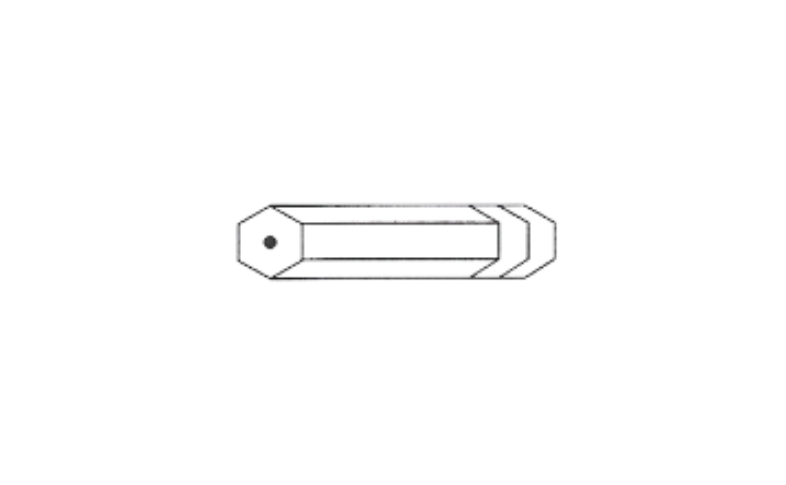
un-sharpened pencil.
Solution: It is a prism
3) 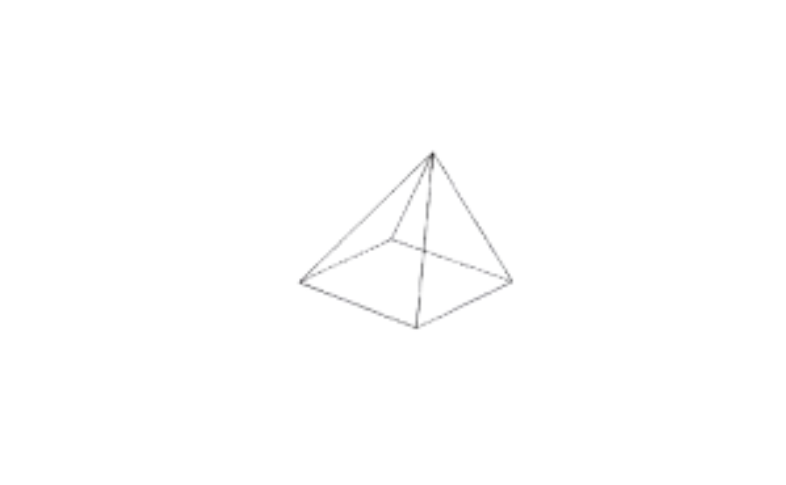
a table weight.
Solution: It is not a prism, it is a pyramid
4) 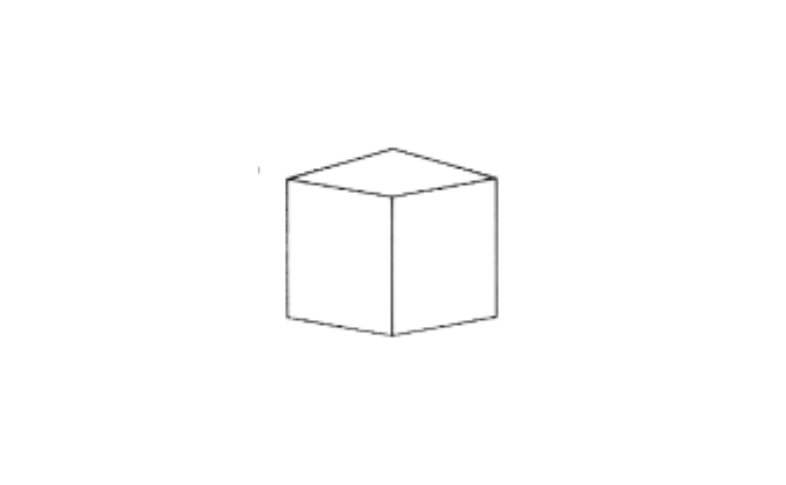
A box
Solution: it is a prism
4. 1) How are prisms and cylinder alike?
Solution: A cylinder can be thought of as a circular prism. i.e., a prism that has a circle as its base.
2) How are pyramids and cones alike?
Solution: A cone be thought of as a circular pyramid, i.e., a pyramid that has a circle as its base.
5. Is a square prism same as a cube? Explain.
Solution: A square prism has a square as its base. However, its height is not necessarily same as the side of the square. Thus, a square prism can also be a cuboid.
Class 8 Maths KSEEB Chapter 14 Solved Examples
6. Verify Euler’s formula for these solids.
1) 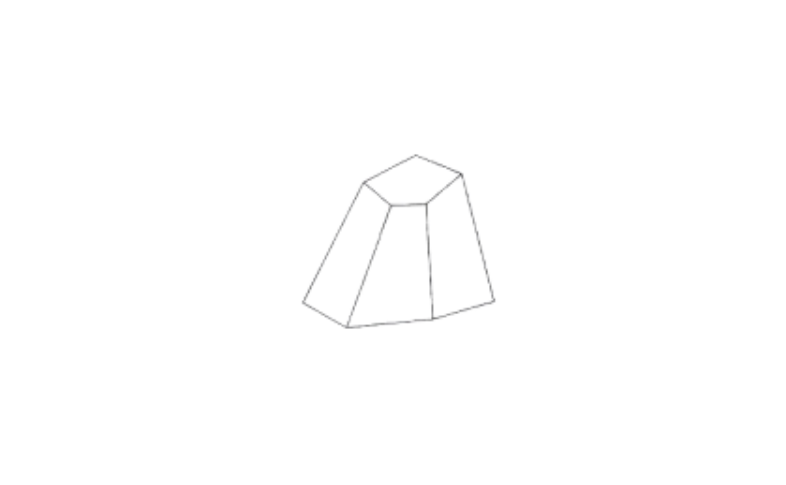
Faces = 7
Vertices = 10
Edges = 15
2) 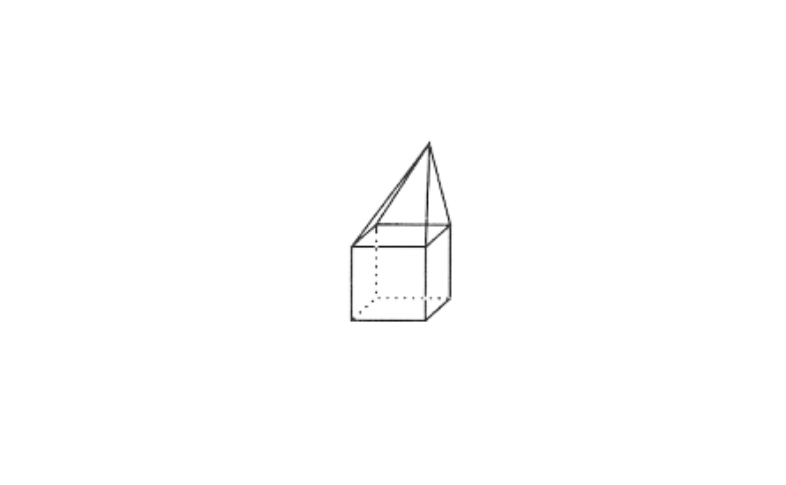
F = 9, V = 9, E = 16
F + V – E = 9 + 9 -16
= 18 – 16 = 2
F + V – E = 7 + 10 – 15 = 2
Hence, Euler’s formula is verified
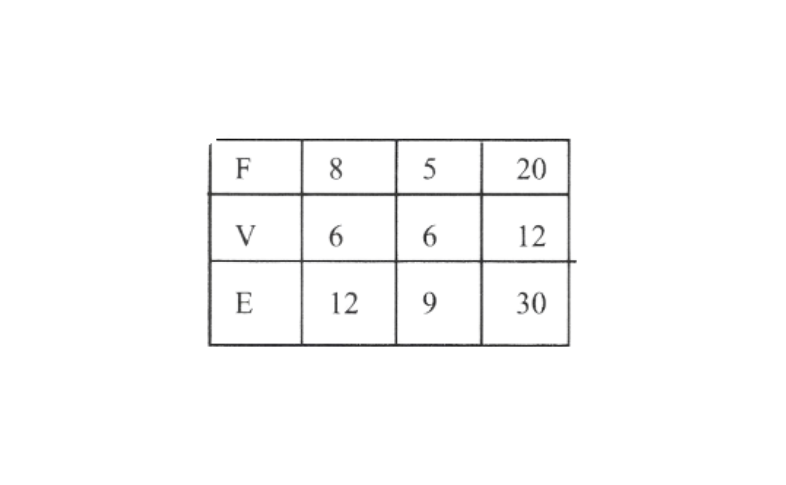
7. Using Euler’s formula find the unknown
Faces 7 5 20
Vertices 6 ? 12
Edges 12 9 ?
Solution: By Euler’s formula, we have F + V – E = 2
1) F + 6 – 12 = 2
F – 6 = 2
F = 2 + 6 = 8
2) 5 + V – 9 = 2
V – 4 = 2
V = 2 + 4 = 6
3) 20 + 12 – E = 2
32 – E = 2
32 – 2 = E
E = 30
Thus, the table can be written as
Karnataka Board 8th Maths Chapter 14 Important Questions And Answers
8. Can a polyhedron have 10 faces, 20 edges, and 15 vertices?
Solution: F=10, E=20, V=15
Any polyhedron satisfies Euler’s formula
According to which F+V-E=2
For the given polygon F+V-E
⇒ 10+15-20=25-20=5≠2
Since Euler’s formula is not satisfied, such a polyhedron is not possible.
KSEEB Maths Class 8 Chapter 14 Visualising Solid Shapes Additional Problems
1. Height of a building is 9m and this building is represented by 9cm on a map. What is the scale used for the map?
Solution: Scale of map = Size drawn/Actual size = 9cm/900cm = 1/100
[∵ 9m = 900cm]
Thus, scale is 1:100
2. The distance between city A and city B on a map is given as 6cm. If the scale represents 1cm=200km, then find the actual distance between city A and city B
Solution: Actual distance represented by 1cm = 200km
Actual distance represented by 6cm
So, actual distance between city A and city B is 1200km.
3. What do you mean by regular polyhedron? Write all polyhedron shapes.
Solution: A polyhedron is said to be regular if its faces are made up of regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are five such solids: tetrahedron cube octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron.
4. Identify the shape whose net is given below
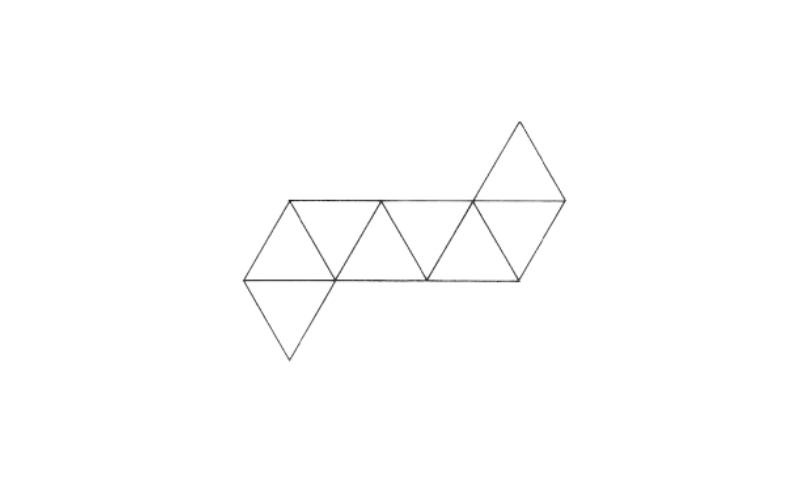
Solution: This shape is entirely made of equilateral triangles. When folded, it results in a regular octahedron. Note that since these are all equilateral and congruent faces, it is a regular polyhedron.
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Textbook Solutions PDF
5. Using Euler’s formula find the unknown
1) F=? v=5 E=18
Solution: F+V-E=2
F+5-18=2
F-13=2
F=2+13=15
2) F=6 V=? E=12
Solution: F+V-E=2
6+V-12=2
V-6=2
V=2+6=8
6. The side of a square board is 50cm. A student has to draw its image in her notebook. If the drawing of the square board in the notebook has perimeter of 40cm, then by which scale the figure has been drawn?
Solution: Given, the side of a square board is 50cm. So, perimeter of thr square board = 4 x side = 4 x 50 = 200cm
On drawing in the notebook, the perimeter of a square board = 40cm.
∴ Scale
Size of actual square board/Size in notebook = 200/40 = 5 : 1
Hence, the used scale is 5 : 1.
7. A polyhedron has 60 edges and 40 vertices. Find the number of its faces.
Solution: By using Euler’s formula for polyhedron.
F+V-E=2
F+40-60=2
F-20=2
F=2+20=22
Hence, the number of faces are 22
8. The distance school and house of a girl is given by 5cm in a picture, using the scale 1cm : 5km. Find the actual distance between the two places?
Solution: Given scale = 1cm: 5km.
i.e., 1cm in picture =5km of actual distance
∴ 5cm in picture = 5 x 5km of actual distance.
Hence, the actual distance between the two places is 25km.
So 5cm represent = 5 x 5 = 25km distance.
KSEEB 8th Standard Maths Chapter 14 Notes And Solutions
9. What do you mean by regular polyhedra? Write all polyhedron shapes.
Solution: A polyhedron is said to be regular if its faces are made up of regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex.
There are five such solids: tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron and icosahedron.
10. Name the polyhedron that can be made by folding each net.
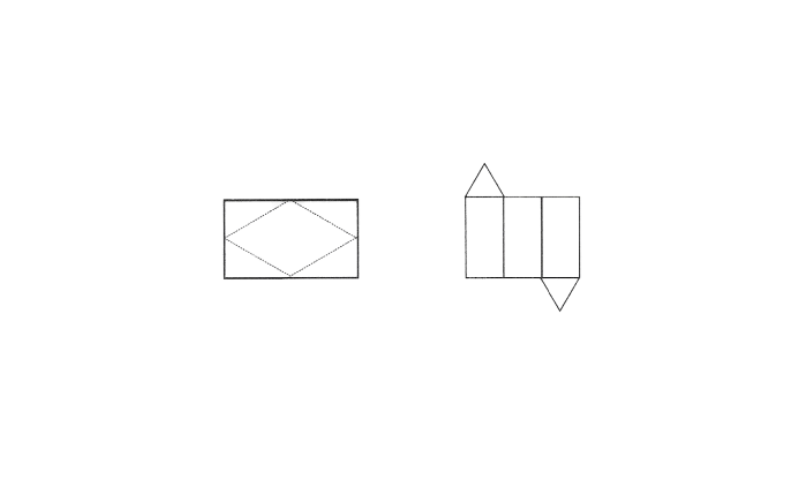
Solution: 1) Square pyramid
2) Triangular prism.
11. Name the following polyhedrons and verify Euler’s formula for each of them.
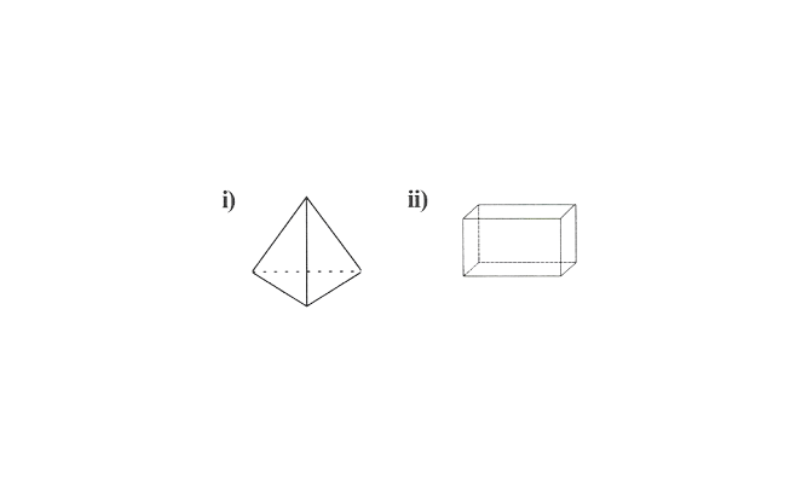
Solution: 1) Tetrahedron, F=4, V=4, E=6
Euler’s formula
F+V-E=2
LHS = 4+4-6
= 8-6=2 = RHS
Hence verified.
2) Cuboid, F=6, V=8, E=12
F+V-E=2
LHS = F+V-E = 6+8-12 = 14-12=2 = RHS
Hence Verified.
12. What figure is formed if only the height of a cube is increased or decreased?
Solution: If we only increase on decrease the height of a cube, the obtained figure is cuboid.
13. In a town, an icecream parlour has displalyed an ice-cream sculpture of height 360cm, the parlour claims that the ice-creams and the sculpture are in the scale 1:30. What is the height of the icecream served? hence, the height of the ice-cream served is 12cm.
Solution: Given, height of icecream sculpture = 360cm
Scale used for ice-cream sculpture & sculpture = 1:30
the height of the ice-creams served = scale x Actual size
=\(\frac{1 \times 360}{30}=12 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Hence, the height of the ice-cream served is 12cm.
