KSEEB Solutions For Class 8 History Chapter 5 When People Rebel 1857 And After Questions
Question 1. What was the demand of Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansweri that was refused by the British?
Answer Rani Lakshmibai did not have a son who could succeed to the throne. She had adopted a son and wished that the Company would recognise him as the successor. The British did not accept this demand.
Question 2. What did the British do to protect the interests of those who converted to Christianity?
Answer. The British did a lot to protect the interests of those who converted to Christianity. In 1850, a new law was passed to make conversion to Christianity easier. This law allowed an Indian (who had converted to Christianity) to inherit the property of his ancestors. They were given additional rights as compared to other Indians.
Question 3. What objections did the sepoys have to the new cartridges that they were asked to use?
Answer. In 1856, the Indian soldiers were given greased cartridges which were to be bitten with one’s teeth before they could be fired. It was suspected that these cartridges were coated with the fat of cows and pigs. This enraged the Hindu and Muslim soldiers in the Indian army. The Indian soldiers got agitated and refused to use those cartridges. It also became the immediate cause of the revolt of 1857.
Question 4. How did the last Mughal emperor live the last years of his life?
Answer. The last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was captured and tried in the court. He was sentenced to life imprisonment. He and his wife, Begum Zeenat Mahal, were sent to prison at Rangoon in October, 1858. Bahadur Shah Zafar died in the jail in November 1862.

Kseeb Class 8 History Chapter 5 When People Rebel 1857 And After Solutions Pdf
Question 5. What could be the reasons for the confidence of the British rulers about their position in India before May 1857?
- The British made certain policies to strengthen their position in India. Policies like Subsidiary- Alliance and Doctrine of Lapse helped them to annex many Indian territories.
- The British put their Residents in the local courts. The armed forces of the local rulers were disbanded and the powers of the local rulers were reduced to minimum. Their revenues and territories were gradually overtaken by the British.
- The Company could boast of a strong and effective military.
- The Mughal emperor was so weak that he was unable to counter the influence of the British. Local rulers were also weak and they had no unity amongst themselves.
Thus, the British were very- confident about their position in India before May 1857.
Question 6. What impact did Bahadur Shah Zafar’s support to the rebellion have on the people and the ruling families?
Answer. The Indian sepoys captured Delhi and force Bahadur Shah Zafar to lead the rebels. The rebels stormed into the palace and proclaimed Bahadur Shah Zafar as their leader. The Mughals ruled over large areas headed by local chieftains. Since the British had captured most of these territories these rulers thought that their power would be restored once the Mughal emperor regained control. Bahadur Shah wrote letters to all the local rulers to form a confederacy of Indian states to fight against the British. Once people saw an alternative possibility, they were inspired. It gave them the courage, hope and confidence to act.
Sslc Class 8 History When People Rebel 1857 And After Question And Answers
Question 7. How did the British succeed in securing the submission of the rebellious landowners of Awadh?
Answer. The British tried to earn the loyalty of the people in every possible manner. They announced several rewards like restoring the landowners’ hereditary rights over their lands if they remained loyal to the British. The rebellious landowners could claim their lands if they surrendered and had not killed any white people. In this way, the British succeeded in securing the submission of the landowners of Awadh.
Question 8. In what ways did the British change their policies as a result of the rebellion of 1857?
Answer.
- After the revolt, the British changed the following policies:
- Powers of the East India Company were transferred to the British Crown. The Secretary of State for India was appointed in Britain to look after the administrative affairs in India.
- All the local ruling chiefs were assured that their kingdoms would not be annexed into the British Empire. They were also allowed to choose their own successors.
- The number of Indian soldiers n the army was reduced while the number of the European soldiers was increased.
- The British began to view Muslims with suspicion. The lard, property and other assets owned by the Muslims were confiscated.
- The British introduced several policies to protect the interests of the landlords. They were given security of rights over their lands.
Kseeb Class 8 History When People Rebel 1857 And After Textbook Solutions
When People Rebel 1857 And After Text Questions
Question 1. Imagine you are a sepoy in the Company army, advising your nephew not to take employment in the army. What reasons would you give?
Answer. I would tell my nephew that the Indian sepoys are discriminated against the British soldiers. The Indian sepoys could not hope of promotions or high salaries. The British were biased towards their own soldiers.
Question 2. What were the important concerns in the minds of the people according to Sitaram and according to Vishnubhatt?
Answer. According to Sitaram and Vishnubhatt, the people were concerned about the British interferring in their religious beliefs. The British had introduced some laws which made the India discontented with British rule.
Question 3. What role did they think the rulers were playing? What role did the sepoys seem to play?
Answer. The local rulers were deposed by the British which hurt people’s sentiments. The rulers sent messages to the sepoys that the British are go ng to force India to change their religious beliefs. The sepoys were unhappy when Awadh was seized by the British. They aimed to resist the British rule.
Question 4. Why did the Mughal emperor agree to support the rebels?
Answer. The rebels agreed to restore the supremacy of the Mughal throne. The Mughal emperor, therefore, decided to side with the rebels.
Question 5. Write a paragraph on the assessment he may have made before accepting the offer of the sepoys.
Answer. The Mughal emperor must have imagined that if rebels won against the British, he will become a strong ruler. If the Indian soldiers would fight valiantly, he would regain his lost power and prestige. The Mughal dynasty was viewed with respect among the Indians and he could rule over vast territories in India if the India succeeded in their revolt.
Question 6. Make a list of places where the uprising took place in May June and July 1857.
Answer. The uprising began in Delhi, Meerut, Kanpur and Lucknow in the given months.
KSEEB Class 8 History Solutions For When People Rebel 1857 And After
When People Rebel 1857 And After Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. When did a major revolt take place against the British?
Answer. A major revolt broke out in India in 1857.
Question 2. From where did the Indian revolt of 1857 start?
Answer. The Indian revolt of 1857 started from Meerut
Queen 3. What was the immediate cause of the revolt of 1857?
Answer. New cartridges were introduced by the British which were smeared with grease made from fat of cows and pigs. This angered the Indian sepoys.
Question 4. When did the British occupy Jhansi?
Answer. The British occupied Jhansi in 1859.
When People Rebel 1857 And After Class 8 History Kseeb Important Questions
Question 5. India was discontented with the British. Give one reason.
Answer. Abolition of the custom of sat; was one the reasons of discontent among the India
Question 6. The Indian soldiers were discontented with the British. Give one reason.
Answer. One of the reasons of discontent among the soldiers was to go abroad for warfare.
Question 7. Who was proclaimed as the emperor of India at the time of the revolt of 1857?
Answer. Bahadur Shah Zafar was proclaimed as the emperor of India at the time of the revolt.
Question 8. Who was the first martyr of the revolt of 1857?
Answer. Mangal Pandey was the first martyr of the revolt of 1857.
Question 9. Who led the revolt of 1857 at Kanpur?
Answer. Nana Saheb led the revolt of 1857 at Kanpur.
Question 10. Where did Rani Lakshmibai breathe her last?
Answer. Rani Lakshmibai died fighting in the battlefield at Gwalior.
Question 11. What was the most important long-term result of the revolt?
Answer. The most important long-term result of the revolt was that it sowed the seeds of Indian nationalism which bore fruit subsequently in 1947.
Question 12. How did nawabs lose their power?
Answer. The British Residents were stationed in the local courts. The local armies were disbanded and the possessions of the rulers were reduced. In this way, the nawabs began to lose their power.
Karnataka Sslc Class 8 History Chapter 5 Solutions In English
Question 13. How was Awadh conquered by the British?
Answer. In 1801, the subsidiary alliance was enforced upon Awadh. Lord Dalhousie accused the Nawab of misgovernance and suggested that British rule was needed to ensure proper administration. Awadh was then annexed into the British Empire in 1856.
Question 14. Why were Indian sepoys not willing to go overseas?
Answer. In those days, many people believed that if they cross the sea, they would lose their religion and caste.
Question 15. Which reforms were introduced by the British?
Answer. The British banned the practice of sati in 1829. They passed an Act in 1856 which permitted widow remarriage. They also promoted English language as the primary medium of education.
Question 16. Name any four major centres of 1857 revolt.
Answer. Meerut, Delhi, Lucknow and Kanpur were some important centres of the revolt
When People Rebel 1857 And After Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
When People Rebel 1857 And After Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. List some Indian rulers who attempted to negotiate with the Company in their interest? What was the British response?
Answer
- Rani Lakshmibai requested the Company to recognise her adopted son as the heir to the kingdom after the death of her husband.
- Nana Saheb, the adopted son of Peshwa Baji Rao II, also urged the British to give his due pension after his father died.
- The Company was sure that it was superior to the Indian rulers in every way. The British did not accept any of the demands.
Kseeb Class 8 History When People Rebel 1857 And After Solved Exercises
Question 2. How did the Company deal with the Mughal dynasty?
Answer
- The Company planned to bring about an end to the Mughal dynasty. The name of the Mughal Emperor was removed from the coins minted by the Company.
- In 1849, Lord Dalhousie announced that the family of Bahadur Shah Zafar would be shifted to another place from Red Fort after he died.
- In 1856, Lord Canning declared that Bahadur Shah Zafar would be the last Mughal Emperor and his descendants would be called princes, and not kings. Thus, the Company put an end to the Mughal dynasty.
Question 3. Why were the Indian sepoys angry with the British Government?
Answer
The Indian sepoys in the British army were angry with the British Government?
- The Indian sepoys were not satisfied with their pay, allowances and conditions of service. They were given less pay and allowances as compared to the British soldiers.
- The British made it compulsory for the sepoys to travel overseas. This angered the Indian sepoys.
- Many Indian states like Awadh were annexed by the British. It led to resentment among the Indian sepoys.
- The Indian sepoys were aware of the poor conditions of the farmers in the countryside. This made them resentful of the British.
Queen 4. What was Indian response to reforms introduced by the British?
Answer. The British believed that the Indian society needed reform. Therefore, they introduced some laws like ban on sot’ and permitting widow remarriage. They also promoted the English language as the medium of instruction. They allowed the Christian missionaries to propagate their religion within their territories. Likewise, many incentives were given to the converted India
Question 5. How did the Sepoy Mutiny turn into a popular rebellion?
Answer. A large number of people realised that they should unite against the British at the same time. The revolt spread to northern parts of the country. It had been a century that the East India Company was governing most of India. The Sepoy Mutiny turned into a popular rebellion because many princes and common people took part in it
Question 6. Narrate the events that took place in Meerut.
Answer. The rebellion began in Meerut on 10th May, 1857. The public and soldiers of Meerut openly revolted against the British. The whole city echoed with slogans like ‘Maro Firang’Ko’.Soldiers broke the gates of jails and released their companions. They then marched to Delhi.
Question 7. Narrate the events that took place in Barrackpore.
Answer. Greased cartridges were supplied to the soldiers at Barrackpore on 29th March, 1857. Barrackpore was a cantonment station in Bengal. A soldier named Mangal Pandey refused to use them. In a fit of anger, he shot an English officer and asked his companions to attack other British officers. Manga! Pandey was sentenced to death. All the soldiers of Barrackpore cantonment got enraged by this incident Mangal Pandey was the first martyr of the revolt of 1857
Class 8 History When People Rebel 1857 And After Notes Karnataka Board
Question 8. State the events that occurred in Delhi during the revolt of 1857.
Answer. The English officers tried to check rebels at Delhi, but failed to do so. The rebels declared Bahadur Shah Zafar as their king and Delhi came under their control in four days. On 19th September, 1857
some differences arose among the rebel soldiers in Delhi. The British took advantage of the rift andre- established their control.
Terror was let loose on the citizens. Bahadur Shah was arrested. Two of his sons were shot dead in front of him. He was then sent to Rangoon where he died in November 1862.
Question 9.Describe the main events of the uprising at Lucknow.
Answer. Awadh region was one of the main centres of the revolt Lucknow was the capital of Awadh. The general public of Awadh sided with the rebels. The British were driven away from Lucknow by the Indian soldiers. The British, however, re-occupied the city on 31st March, 1858. After some time, the toluqdars of Awadh withdrew from the struggle. The revolt in Awadh was easily suppressed by the British.
Question 10. What happened at Jhanswesi during the revolt of 1857?
Answer. Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi led the revolt from jhansi. The British commander attempted to suppress the revolt, but failed. Jhansi was invaded in April 1858. This time, a few companions of Rani Lakshmibai deserted her and joined the British. She, however, bravely faced the aggressors. The fort of Jhansi came under the control other British and Rani Lakshmibai was killed in a battle near Gwalior.
Explanation Of The 1857 Revolt In KSEEB History
When People Rebel 1857 And After Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What were the political causes of the revolt of 1857?
Answer.
The political causes of the revolt of 1857 are given below;
- Expansionist policy of Dalhousie: Lord Dalhousie wanted to expand the dominions of British Empire in India. He, therefore, adopted the policy of annexation through Doctrine of Lapse. According to this policy’, a ruler who had no male heir was not allowed to adopt a son who might inherit his kingdom. He annexed several states like Nagpur and Satara to the British Empire with the help of this doctrine.
- Injustice with Nana Saheb: Nana Saheb was the adopted son of the last Maratha ruler, Peshwa Baji Rao II. After the death of Baji Rao, the British refused to pay his annual pension to Nana Saheb. So, he turned against the British.
- (Insult of Bahadur Shah: In 1856, the Governor-General told the Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah, that, he would be the last emperor of India. After his death, his princes will have to vacate the Red Fort and stay in a rented house near Qutub Minar. This decision of the British
annoyed Begum Zeenat Mahal, the queen of Bahadur Shah. She started planning to destroy the British rule in India - Unjustified Annexation of Awadh: Nawab wajid Ali Shah of Awadh was a faithful friend of the British. His ancestors had also helped the British several times. Even then, the British levelled the charges of maladministration against the Nawab and annexed his kingdom to the British Empire. They gave a fixed pension to Wajid Ali Shah and sent him to Calcutta. The people of Awadh were annoyed. There were about 60,000 Awadh soldiers in the Bengal army. They could not tolerate this injustice done to their king and decided to rise in revolt against the British.
When People Rebel 1857 And After Class 8 History Summary And Explanation Kseeb
Question 2. What were the military causes of the revolt of 1857?
Answer.
The military causes of the revolt of 1857 are as follows:
- Low salaries: The salaries of Indian soldiers were very low. They were not given higher salaries and the chances of their promotion were very low.
- Misbehaviour of the Europeans: The Indian soldiers were considered inferior to the Europeans and were not treated well.
- The Enlistment Act of 1856: An Act was passed in 1856 by which it was made obligatory for the soldiers to go overseas, if ordered. The Indian soldiers were extremely dissatisfied.
- Annexation of Awadh: The British annexed Awadh on the pretext of maladministration. The Nawab was deposed and his army was disbanded.
- Issue of greased cartridges: In 1856, the Indian soldiers were given greased cartridges which were to be bitten before they could be fired. It was believed that these cartridges contained fat of cows and pigs. This enraged the Hindu and Muslim soldiers in the British army.
Question 3. Describe the main events of the revolt of 1857 in brief.
Answer. The Indians rose against the British for the first time in 1857. The message of the rebellion was sent to the soldiers and the public by circulation of roses and choodatis. 31st May, 1857 was fixed as the date for the revolt but the incident of greased cartridges at Meerut led to the outbreak of rising on 10th May. An account of the events of this uprising is given below:
- Barrackpore: Greased cartridges were supplied to the soldiers stationed at Barrackpore, a cantonment in Bengal, in March 1857. A soldier named Mangal Pandey refused to use them and shot an English officer. Mangal Pandey was sentenced to death. All the soldiers of Bamackpore cantonment got enraged by this incident. Mangal Pandey became the first martyr of the revolt of 1857.
- Meerut: The public and soldiers of Meerut came out in an open revolt against the British on 10th May, 1857. The whole city echoed with sloganswer like “Maro Firong’ Ko*. Soldiers broke open the gates of jails and released their compatriots. From there, they marched to Delhi.
- Delhi: The English officers tried to control the rebels at Delhi, but they failed. The rebels declared Bahadur Shah as their king, and Delhi came under their control in four days. On 19th September. 1857 differences arose among the rebel soldiers at Delhi. The British took advantage of this rift and re-established their control over Delhi. Bahadur Shah was arrested and sent to Rangoon.
- Kanpur: Nana Saheb declared himself as the Peshwa at Kanpur. The British Commander, Havelock defeated Nana Saheb and the control of Kanpur came back in the hands of the British. Tarrtia Tope tried to re-establish his control there but failed.
- Lucknow: Lucknow was the capital of Awadh. The British Commander, Havelock invaded Lucknow with a large army and established his control over the city on 31st March, 1858. After some time, the taljqdars of Awadh also laid down their arms and the fire of revolt in Awadh was extinguished.
- Jhansi: Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi led the uprising at Jhansi. The British officials attempted to suppress the revolt but failed. Jhansi was again invaded in April 1858. A few companions of Rani Lakshmibai deserted her and she became weak. The fort of Jhansi was captured by the British. The Rani was finally killed in a battle with the British near Gwalior.
- Central India: In Central India, Tantia Tope fought man/ battles with the British but was defeated. He was captured and hanged on April 18th, 1858.
Question 4. Describe the political and constitutional effects of the revolt of 1857.
Answer. The 1857 uprising failed but it had far-reaching effects. It brought political awakening among the masses which took the form of national struggle. The main political changes which took place after this revolt are given below:
- End of the Company’s rule: The most important result of the revolt of 1857 was the end of Company’s rule in India. The whole administration of India came under the control of the British Government in England. The Secretary of State for India was appointed to control the British Government in India. He had to submit a report every year on the moral and material progress in India. He was assisted by a council of 15 members.
- Change of designation of the Governor-General: With the end of Company’s rule, the designation of Governor-General was changed. He was now a representative of the British Crown. Keeping in view his new position, he was now designated as the Viceroy of India.
- Policy towards the Indian rulers: The British Government adopted a liberal policy towards the Indian rulers. They were assured that their states would not be annexed into the British Empire. The Indian rulers could now choose their own successors. Those who would support the British would be rewarded. At the same time, some restrictions were also imposed on the rulers. They were not allowed to establish relations with any internal or external power. The British could intervene in case of misrule or maladministration.
- End of the Mughal dynasty and rule of the Peshwas: Nana Saheb took an active part in the revolt, but when he become unsure of victory, he ran away to Nepal. In the absence of any heir, the title of Peshwa was discontinued. The Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah had revolted against the British too. He was sentenced to life imprisonment and sent to Rangoon. The title of the Mughal emperor was also abolished after his death.
KSEEB Notes For Class 8 History 1857 Rebellion
Question 5. Write down the main causes of the revolt of 1857.
Answer. The main causes of the revolt of 1857 were:
- Political discontentment: The Indians resented the British due to their political policies. Lord Dalhousie annexed several Indian states on the basis of Doctrine of Lapse. The British did not support local administration in villages. Cottage industries were discouraged by the British ; which also made the villagers unhappy.
- Administrative defects: Corruption was rampant in British administration. Justice was very costly, j Land tax system was extremely unfair. The British rule in India was, therefore, very unpopular.
- Economic exploitation: To promote industries in England, the British ruined the Indian industries. Now, only British-made goods were sold in the markets. Farmers too were greatly exploited by the Company. All highly paid jobs were given to the British who got their salaries from the Indian exchequer. The Indians felt that the British were exploiting them.
- Interference in religious matters: The British took many steps to convert the Indians into Christianity. They also tried to change the religious customs of the India As a result, Indian belonging to all religions turned against the English.
- Discontentment in the army: There was discontentment among the Indian soldiers. They were given very low salaries. The British soldiers mistreated them. In 1856, the Indian soldiers were asked to use cartridges which attacked their religious sentiments. The soldiers then decided to unite against the British.
Sslc Class 8 History Chapter 5 Workbook Answers
Question 6. What were the causes of the failure of the revolt of 1857?
Answer. Following were the main causes of failure of tie uprising of 1857:
- Beginning of the revolt Before time: The rebellion started before it was planned because of some incidents at Berrampur, Barrackpore and Meerut. The revolutionaries were not organised and the British got sufficient time to suppress the revolt.
- No common aim: The leaders participating in the struggle did not have any common goal. Some were fighting for the cause of religion, some for the safety of their states, while others wanted to free the nation.
- Revolt was unorganised: The rebels had no able leader who could keep them united. They were unorganised and indisciplined.
- Untrained soldiers: The rebels lacked trained soldiers. They had no modem weapons of war. Most of the people who participated in the rising were disbanded soldiers and had little experience.
- The Rising did not spread in the whole country: The struggle remained restricted only to no-them India. People of South India did not take active part in it Had the w hole of India stood united against the British, the First War of Indian Independence would not have failed.
- Control of the British over me answer of transportation: All the meanswer of tsanswer port and communication like railways, post and telegraph, etc., were in the hands of the British. They were in a position to send soldiers and weapons of war from one place to another.
- Harsh methods of the British to suppress the revolt: The British dealt with the revolutionaries very’ cruelly. Cities were looted and burnt. Many people were hanged. The people got frightened and did not take part in the uprising.
- Economic difficulties: The rebels did not have enough money. They were not in a position to purchase good weapons. As a result, they failed in their mission.
When People Rebel 1857 And After Hots Corner
Question 1. Why did some Indian rulers join the rebels in the uprising of 1857?
Answer. Most of the Indian rulers participated in the revolt due to their selfish reasons. Their kingdoms were taken over by the British, so they wanted to take revenge and restore their power. Avvadh, Satara, Nagpur and Jhansweri were some such states.
Question 2. What is the importance of Indian War of Independence of 1857 in our history?
Answer. The First War of Independence proved to be a turning-point in the history of India Its significance
can be explained as follows:
- It was the first attempt by the Indians to get independence. Both the Indian public and the soldiers joined hands to face the enemy. It was the first example of Indian unity.
- This revolt gave a jolt to the British Government. In order to appease the Indianswer, they introduced many administrative reforms.
- Most of the Indianswer had laid down their lives in this war. The coming generations would get inspired from the sacrifices made by these people.
Question 3. What was the immediate cause of the outbreak of the revolt of 1857? Where did it start?
Answer. The immediate cause for the outbreak of the revolt was that the Indian sepoys were asked to use a new type of greased cartridges. A rumour spread that the grease was made of fat from cows and pigs.
The clip of the cartridge had to be pulled out with teeth b efore use. The Hindus and Muslim soldiers thought that this was a deliberate insult to their religions. This acted like a spark and resulted in the outbreak of the revolt It started in Meerut or 29th March, 1857.
Question 4. Why did the British Government stop the policy of annexing Indian states into the British Empire after the uprising of 1857?
Answer. After the 1857 uprising, India came directly under the control of the British Crown. The Queen, in order to win over the hearts of Indian rulers and the public, declared that the states of Indian rulers will not be annexed into the British Empire, t was also declared that the British Government will abide by the treaties made with the Indian rulers.
Class 8 Kseeb History Causes And Effects Of The 1857 Revolt
When People Rebel 1857 And After A. Multiple Choice Questions
Tick the correct option from the choices provided:
Question 1. When did the First War of Independence take place?
(a)1857
(b)1897
(c)1925
(d)1865
Answer. (a) 1857
Question 2. What did Rani Lakshmibai demand from the British?
(a) To adopt a daughter
(b)To adopt a son
(c)To give her back her kingdom
(d)To give her pension
Answer. (b) To adopt a son
Question 3. Who was the last Mughal emperor?
(a) Akbar
(b)Aurangzeb
(c)Jahangir
(d)Bahadur Shah Zafar
Answer. (d) Bahadur Shah Zafar
Class 8 History Kseeb When People Rebel 1857 And After Short And Long Answer Questions
Question 4. Where was Bahadur Shah Zafar exiled to?
(a) New Delhi
(b)Kanpur
(c)Rangoon
(d)Nepal
Answer. (c) Rangoon
Queen 5. From where did the revolt of 1857 start?
(a) Delhi
(b)Meerut
(c)Kanpur
(d)Jhanswsri
Answer. (b) Meerut
Question 6. ______was the first martyr of the revolt of 1857.
(a) NanaSaheb
(b) Mangal Pandey
(c) Rani Lakshmibai
(d)Tantia Tope
Answer. (b) Mangal Pandey
Question 7. ______led the revolt at Kanpur.
(a) Tantia Tope
(b) Rani Lakshmibai
(c)NanaSaheb
(d)Kunwar Singh
Answer. (c) Nana Saheb
Detailed Notes On 1857 Revolt KSEEB
When People Rebel 1857 And After B. Match The Following
Find and write the correct options from the given below columns:
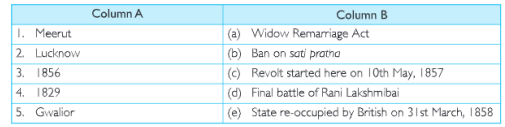
Answer. I.(c) 2. (e) 3. (a) 4. (b) 5. (d)
When People Rebel 1857 And After C. Picture Interpretation
Question 1. Study the given picture and Answer the following questions:

- What does the picture depict?
- From where did the Indian revolt of 1857 start?
- Describe the events that occurred at Meerut
Answer.
- It depicts the First War of Independence n India.
- The revolt of 1857 started from Meerut.
- The revolt broke out in Meenjt on I Oth May, 1857. The public and soldiers of Meerut came out in an open revolt against the British. The whole city echoed with slogAnswer like VVIaro Frangi Ko\ Soldiers broke open the gates of jails and released their compatriots. Then, they marched on to Delhi.
Kseeb Class 8 History When People Rebel 1857 And After Mcqs With Answers
Q.2. Study the given picture and Answer the following questions:

- Which famous fort is shown in the picture?
- How did the British re-capture Delhi?
Answer.
- This picture shows the famous Red Fort of Delhi.
- The rebel soldiers of Meerut killed the British and then marched towards Delhi. The English officers tried to check rebels at Delhi but the failed to do so. The rebels declared Bahadur Shah as their Icing and Delhi came under their control for four days. Some differences arose among the rebel soldiers and the British took advantage to re-establish their control over Delhi. The British attacked the rebellious India. Bahadur Shah was arrested and sent to Rangoon where aied in 1862.
Part A – Our PASTS – III (History)
- Chapter 1 How, When and Where
- Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory The Company Establishes Power
- Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside
- Chapter 4 Tribals Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age
- chapter 5 When People Rebel 1857 And After
- Chapter 6 Colonialism and the City: The Story of an Imperial Capital
- Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
- Chapter 8 Civilising the “Native” Educating the Nation
- Chapter 9 Women, Caste and Reform
- Chapter 10 The Changing World of Visual Arts
- Chapter 11 The Making of the National Movement 1870s -1947
- Chapter 12 India After Independence
Part B – Resources and Development (Geography)
- Chapter 1 Resources
- Chapter 2 Land,Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and A wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Industries
- Chapter 6 Human Resources
Part C: Social and Political Life -III (Civics)
- Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution
- Chapter 2 Understanding Secularism
- Chapter 3 Why Do We Need a Parliament ?
- Chapter 4 Understanding Laws
- Chapter 5 Judiciary
- Chapter 6 Understanding Our Criminal Justice System
- Chapter 7 Understanding Marignalisation
- Chapter 8 Confronting Marginalisation
- Chapter 9 Public Facilities
- Chapter 10 Law and Social Justice
