KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Textbook Questions (Solved)
Question 1. Answer the Following Questions:
(a) What is Agriculture?
Answer. The word ‘agriculture’ is derived from two Latin words ‘agn’ and ‘cultura’. ‘Agn’ means soil and ‘cultura’ means cultivation or tilling of soil. Agriculture thus refers to the cultivation of soil for growing crops and rearing of livestocks.
(b) Name the factors influencing agriculture.
Answer. The factors which influence agriculture are:
(a) Relief
(b) Soil conditions
(c) Temperature
(d) Rainfall
(c) What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
Answer. Shifting cultivation is mainly practised in the thickly forested areas. In this cultivation, a plot of land is cleared by felling trees and burning them. The ashes of these trees are mixed with the soil and crops are grown. Maize, Yarn, Potatoes and Cassava are the main crops grown in this type of cultivation. When the soil loses its fertility, the land is abandoned and the cultivator moves toanewplot.Mainareasofthiscultivationare:
Amazon basin, North-East India, parts of Southern Asia and tropical Africa. This cultivation is also known as ‘Slash and burn’ cultivation.
Disadvantages:
(a) It is not eco-friendly.
(c) It causes deforestation.
(b) It is very destructive.
(d) It can be a cause of soil erosion.

Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Pdf
(d) What is plantation agriculture?
Answer. It is a special type of commercial farming which requires large amount of labour, technical efficiency, very large estates and capital. In this type of agriculture, a simple crop of tea, rubber, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, banana or cotton is grown. The produce may be processed on the farm itself or in nearby factories. A well-developed transport network is also required. Tropical regions of the world are major plantation areas. Rubber in Malayasia, coffee in Brazil, tea in India and Sri Lanka are some examples.
(e) Name the fibre crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
Answer. Jute and Cotton are the major fibre crops.
Cotton requires high temperature, light rainfall, two hundred and ten frost free days and bright sunshine for its growth. Black and alluvial soils are best for its cultivation. Jute is also known as the ‘Golden Fibre’. High temperature, heavy rainfall and humid climate is required for its growth.
Question.2. Tick the Correct Answerwer:
(a) Horticulture meAnswer:
(a) Growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) Primitive Farming
(c) Growing of wheat
Answer.(a) Growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) Golden fibre refers to:
(a) Tea
(b) Cotton
(c) jute
Answer.(c) Jute
(c) Leading producer of coffee:
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c)Russia
Answer.(a) Brazil
Kseeb Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Notes
Question.3. Give Reasons:
(a) In India, agriculture is a primary activity.
Answer.
Agriculture is a primary activity in India. More than 75% of India’s population is living in villages and two-thirds of India’s population is still dependent on agriculture. Agriculture provides raw material to many industries. It is the base of Indian economy. It has an important role in GDP.
(b) Different crops are grown in different regions.
Answer.
Different crops require different types of soil and climatic conditions for growth. These requirements cannot be met at one place for all types of crops. For example: cotton is grown in black soil while alluvial soil is good for rice. Different regions have black and alluvial soil. Some crops like tea and jute require heavy rainfall, while cotton requires light rainfall. These climatic conditions are not possible in same area. So, different crops are grown in different regions.
Class 8 Geography Agriculture KSEEB Notes
Question.4. Distinguish between the following:
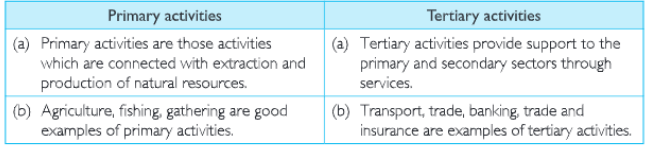
(a)Primary activities and Tertiary activities.
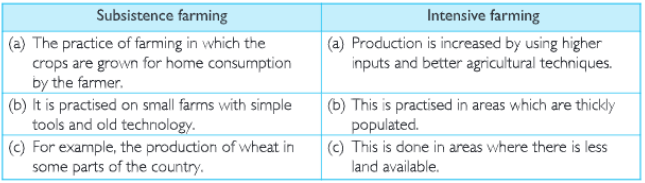
(b) Subsistence farming and Intensive farming.
Karnataka Board Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Solutions
Agriculture Additional Questions (Solved)
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1 . What was grown by the farmer?
Answer. Farmer was grow ing wheat
Question 2. What was he adding to the soil and why?
Answer. He was adding manure to the soil to make it more fertile.
Question 3. Name three types of economic activities.
Answer.
(a)Primary activity;
(b) Secondary activity;
(c) Tertiary activity.
Question 4. What is Primary activity?
Answer. All activities related to extracting natural resources and producing them to suit human needs are called primary- activities, i.e., agriculture, fishing and gathering food.
Question 5. What are Secondary activities?
Answer. Those activities which are connected with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities, i.e., manufacturing of steel, baking of bread, etc.
Question 6. What are Tertiary activities?
Answer. Activities which help in the extraction and production of primary and secondary activities are called tertiary activities, i.e., trasport, trade, banking, etc.
Question 7. What is arable land?
Answer. Arable land refers to a land which is fit for the cultivation of crops.
Question 8. In which areas nomadic herding is practised ?
Answer. The arid and semi-arid areas of Central Asia, regions of Sahara and some parts of India practice nomadic herding.
Question 9. What is commercial farming?
Answer. Commercial farming deals with growing crops and rearing animals for selling them in the market.
Question 10. Which grains are also known as coarse grains?
Answer. Millets are also known as coarse grains.
Question 11. From which continent did maize originate? Who is the largest producer of maize?
Answer. Maize originated from the U.SA U.S. A. is the largest producer of maize.
Question 12. For what product does India stand second in the world?
Answer. India stands second in the world in the production of rice, jute and jowar.
Question 13. Name some oil seeds.
Answer. Some oil seeds are mustard, groundnut, soyabean, rapseed, sunflower, linseed, castor seed and niger seed.
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Important Questions
Question 14. When does the Kharif season begin?
Answer. The Kharif season begins with the onset of the Monsoon.
Question 15. Why is India called an agricultural country?
Answer. Agriculture is a primary activity. About two-th rd of India’s population is employed in agriculture for its livelihood. India is, therefore, called an agricultural country.
Question 16. Name some important Robi crops.
Answer. Wheat, barley, peas, gram.
Question 17. Name some important Kharif crops.
Answer. Paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, pulses, cotton, jute groundnut.
Question 18. What is zaid cropping season?
Answer. It is a short season during the summer months between the robi and kharif seasons.
Question 19. What is Green Revolution?
Answer. It is an agricultural strategy used for increasing the yield of crops.
Question 20. Where does cotton grow?
Answer. In tropical and sub-tropical areas.
Question 21. What type of soil is required for wheat?
Answer. Well-drained fertile soil.
Question 22. What type of plant is rice?
Answer. Rice is a tropical plant
Question 23. What is the main base of the Indian Economy?
Answer. Agriculture is the main base of the Indian Economy.
Question 24. What is ‘Slash and Burn’ agriculture?
Answer. It is a type of agriculture where a piece of land is burnt or cleared for farming.
Question 25. What do you mean by agricultural development?
Answer. It refers to efforts made for increasing farm production to meet the growing demand of increasing population.
Question 26. Name three types of cotton on the basis of staple length.
Answer. Short staple, medium staple and long staple.
Question 27. Name three factors required for farming.
Answer. Three factors required for farming are land, water and seeds.
Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4
Question 28. Name three physical controls of agriculture.
Answer.
- Relief and soil
- Climate
- Temperature and rainfall
Question 29. What factors determine the classification of types of agriculture?
Answer.
- Agricultural practices
- Size of farms, tools and techniqnues used
- Livestock
Question 30. Name three types of traditional agriculture.
Answer.
- Nomadic herding
- Shifting cultivation
- Intensive agriculture
Question 31. Name three means of Shifting cultivation.
Answer.
- Forests of tropical Africa
- South-East Asia
- North-East India
Question 32. Name five areas where commercial farming is practised.
Answer.
(a) Canada and U.S.A .
(b) Ukraine
(c) Argentina
(d) Australia
(e) India
Question 33. What is the average size of farm in the U.S.A.?
Answer. The average size of farm in U.SA. is about 250 hectares.
Question 34. How does a farmer work in the U.S.A.?
Answer. The farmer in U.SA. w’orks like a businessman and not like a farmer.
Question 35. Why is agriculture called a system?
Answer. Seeas, fertilisers, machinery and labour are inputs for some operations. These provide crops, wool, dairy Droducts to make it a system.
Question 36. Name three types of commercial farming.
Answer.
(a) Commercial grain farming.
(b) Mixed farming,
(c) Plantation agriculture.
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Question Answers
Question 37. Why is a single crop grown in the grasslands of North America?
Answer. Due to restriction of severe winters.
Question 38. Name four areas of mixed farming.
Answer.
(a) Argentina
(b)S.E. Australia
(c) New Zealand
(d) South Africa.
Question 39. Name some plantation crops.
Answer. Tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew and rubber.
Question 40. Name three areas where agriculture is concentrated due to favourable factors.
Answer.
(a) India
(b)China
(c) Prairies of U.S.A.
Question 41. Name two types of subsistence farming.
Answer.
(a) Intensive
(b) Primitive.
Question 42. Name two factors favouring subsistence farming.
Answer.
(a) Sunn/weather
(b) Fertile soils.
Question 43. Name two types of farms in U.S.A.
Answer.
(a) Mixed farms
(b) Specialised farms.
Question 44. Classify tea on the basis of its preparation.
Answer. Black tea, green tea and brick tea.
Question 45. Name two varieties of coffee.
Answer. Coffee Arabica and Coffee Robusta.
Question 46. What is Plantation agriculture?
Answer. Bush or tree farming.
Question 47. How much rain is required by the millet crop?
Answer. 30 to 60 cm.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Summary Kseeb
Question.48. How much time is required by jute to mature?
Answer. 8 to 10 months.
Question 49. Which are the beverage crops?
Answer. Tea and Coffee.
Agriculture Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What do you mean by farm system?
Answer.
Farming or agriculture is like a system. Seeds, fertilisers, machinery and labour are its inputs. Ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding and harvesting are the operations involved in it The outputs from the system include crops, wool, dairy and poultry- products.
Question 2. What are the physical conditions required for the cultivation of rice?
Answer. The conditions required for the cultivation of rice are:
(a)Temperature: It requires 16°C to 20°C for the early growing stage.
(b)Rainfall: 150-300 cm. rainfall is required.
(c)Soil: Alluvial soil with clayey sub-soil.
Kseeb 8th Class Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Textbook Solutions
Question 3. Why is agriculture called the mainstream of the Indian Economy?
Answer.
India’s main occupation is agriculture. Two-thirds of India’s population is engaged in agriculture. It is the main stream of the Indian economy. Agriculture provides food to the teeming millions in India. It provides raw material to agro-based industries. Agriculture along with forests and fisheries form 5% of our total national income. Our industrial structure is being built on the broad foundation of Indian agriculture. It is also a great earner of foreign exchange.
Question 4. Name three important wheat producing states of India.
Answer.
Wheat and rice are the two main food crops of India. India is second largest producer of wheat in the world. It is mainly grown in Uttar Pradesh Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Bihar.
Question 5. What type of labour is required for tea cultivation?
Answer. Tea is a plantation agriculture. It is a labour intensive crop, therefore sufficient, cheap and skilled labour is required for its cultivation.
Question 6. Which are the intensely cultivated areas in India?
Answer. The alluvial tracts of Northern India extending from Punjab to West Bengal and Assam and the Coastal Plains from Gujarat in the West to Odisha in the East are intensely cultivated.
Question 7. Name the different varieties of crops in India.
Answer.
(a) Cereals
(b) Pulses and Oilseeds
(c) Fibre crops
(d)Beverage crops
(c) Cash crops.
Question 8. What are the main features of agricultural development in India?
(a)India is a vast country. More than 70% of its population is dependent upon agriculture for its livelihood.
(b)The major foodgrains produced in India a*e rice and wheat
(c)Most of the farms are not more than one hectare of land.
(d)India is self-sufficient in the production offoodgrairs.
(e)In India, half of the total cultivable land is irrigated.
Question 9. Discuss the different types of fibres.
Vegetable fibres are obtained from seeds, barks, leaves and fruit cases. Animal fibres are produced from insects such as silkworm and animals such as camels, sheep, goats, yaks, Hamas, rabbits, guanacos, alpacas, vicunas and reindeers. Mineral fibres such as glass is made from silica sand. Synthetic fibres are derived from chemical treatment of natural cellulose, which is made from wood pulp.
Question. 10. What do you know about commercial agriculture?
Answer.
In this type of agriculture, the main aim is to produce the c-x>p for sale in the market. It can be intensive or extensive agriculture. The farmers try to keep the cost of production low. The framework is done by machines. This type of agriculture is practised in the prair es of North America, Pampas of South America, Steppes of Russia, Western Europe and in some parts of India
Karnataka 8th Standard Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Solutions
Question. 11. What has been the impact of mechanisation on agriculture?
Answer.
The earlier farmers used simple tools. Gradually ox-driven ploughs were introduced. But now in modern times, the techniques have been charged. Now, in developed countries, all farm operations have been mechanised. It has reduced the number of people engaged in agricultural work Many people can now work in industries and services.
Question. 12. State three features of nomadic herding. In which part of India and by what tribes was it practised?
Answer.
(a) The herdsmen move from place to place w’ith their animals and fodder.
(b)Sheep, camel, yak, goats are reared.
(c)These provide milk, meat and wool hides.
In India, Gjjars and Sakarwals (in Kashmir) practise nomadic herding.
Question. 13. What are the uses of crops?
Answer.
(a) These meet the food requirement of the population.
(b)These are basis of agro-basea industries.
(c)These are fibre crops.
(d)These are used as fodder for animals.
Question. 14. Name four countries where rice is grown.
Answer. China (leader in production) India, Japan and Sri Lanka.
Important Questions For KSEEB Class 8 Geography Chapter 4
Question. 15. Name five wheat producing countries.
Answer. Canada, U.S.A., Russia, Argentina and Australia.
Agriculture Long Answer Type Questions
Question. I. Describe the geographical conditions, soil and the distribution of the following crops:
(a)Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Cotton
(d)Jute
(e) Tea
(f) Coffee.
Answer.
(a) Wheat: It is one of the oldest cereal crops cultivated in the world. It is one of the three largest produced crop in the world, other two being rice and maize (com). The wheat plant grows to a height between 0.5 and 1.5 metres.
(a)Geographical Conditions: Wheat is grown in temperate regions with rainfall ranging between 30 cm to 80 cm. Different climatic conditions and sowing seasons across the world have led to harvesting of wheat in every month of the year in one or the other part of the world.
(b)Soil: Wheat cultivation is mainly carried on in fertile soil or loamy soil.
(c)Distribution: In the world, America, Russia and China are the major producers of wheat China is the world’s largest producer. India France. Ukraine, Canada are Argentina are the other leading producers.
In India it is grown in Punjab, Haryana Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Bihar.
(b)Rice: Rice is the seed of paddy plant. It is a major fooa crop of the world. There are many varieties of rice, cultivated in different sols and under different climatic conditions. It is one of the crops for which a lot of human labour is required. All operations including the preparation of seedling beds, ploughing, planting, weeding, harvesting and separation of grain are done by human labour
(a)Geographical Conditions: Paddy requires high temperature of over 20°C to germinate, bloom and mature. Rainfall of 100 cm to 150 cm is required. Paddy is grown in deltas, flood-plains and coastal-plains, and some terraced fields in the mountainous areas as well.
(b)Soil: Rice grows best in clayey alluvial soil, which can hold water.
(c)Distribution: Paddy is cultivated mainly in India, China, Japan, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Thailand and Myanmar. In India, paddy is cultivated most widely in Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh. Other producers are .Assam, Tamil Nadu, Odisha and Punjab.
(c)Cotton: It has been cultivated in India for the last 5,000 years.
(a)Geographical Conditions: Cotton requires cloud-free sunny days and uniformly high temperature. It grows best in areas where the temperature is between 30°C to 40″C. Cotton plants require rainfall of 60 to 100 cm.
(b)Soil: Alluvial and black soils are best suited for cotton plants.
(c)Distribution: The leading cotton producers are China, the U.S.A., Russia, India, Pakistan and Brazil. In India, cotton is produced to a large extent in Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Haryana
(d)Jute: Jute fibre is obtained from the bark of the jute plant. The jute plant originated in the Indian subcontinent. It is a major fibre crop grown intensively in the South-Eastern Asia. Bangladesh is the world leader in the international jute market.
(a)Geographical Conditions: It requires warm and humid climate. Jute plant requires temperature of more than 25°C and rainfall of over 150 cm per year.
(b)Soil: It grows best in well-drained sandy loam.
(c)Distribution: India, Bangladesh and China produce 85 per cent of the world’s production. Jute is also produced on a small scale in Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand and Brazil. In India, jute is cultivated on the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta in West Bengal and Assam. Some of the minor producers of jute are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Tripura and Meghalaya.
(e)Tea: Tea is another beverage crop, popular for its stress bursting quality. It is the largest consumed beverage in the world.
(a)Geographical Conditions: Tea plants require moderate temperature up to 25°C and rainfall about 200 cm per year. Climatic requirements restrict the commercial cultivation of tea to rainy tropical and humid sub-tropical regions.
(b)Soil: Tea requires well-drained alluvial soil.
(c)Distribution: Apart from India, other major tea producers are Sri Lanka, China, Japan and Indonesia. More than three-fourth of world production of tea is contributed by these four countries. In India, tea is produced in Assam, West Bengal, Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Assam alone accounts for half of the amount of tea produced in the country.
(f) Coffee: One-third of the world population drinks coffee, the second largest beverage after tea. There are two types of coffee plants. Coffee Arabica or Mocha and Coffee Robusta. Robusta is the main variety produced in the world.
(a) Geographical Conditions: The coffee plant requires warm climate and moderate rainfall. Both strong sunshine and snow-fell are harmful to the plant. During its growth, coffee plant requires rainfall of 100 cm to 150 cm and temperatures between 15°C and 25 °C. Irrigation is required where the annual rainfall is less than 100 cm.
(b) Soil: Coffee requires well-drained loamy soil.
(c) Distribution: The important coffee producers are Brazil, Columbia and Cote d’Ivoire. These three countries meet more than half the world’s demand for coffee. In India, coffee is largely grown on the eastern sheltered slopes of Western Ghats in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Kseeb Class 8 Social Science Chapter 4 Agriculture Exercise Answers
Question.2. Describe the different types of Farming.
Answer.
(a) Shifting Agriculture: This farming method is practiced by primitive people liv ing in dense forests. The land is prepared by felling trees and burning them. People move from one area to another when the soil loses its fertility.
(b)Subsistence Farming: In this method, feme’s use primitive tools to cultivate their lands. Farmers in these regions produce agricultural goods, which are sufficient enough to satisfy- their own needs.
(c) Commercial Farming: When farmers use modem tools and equipments such as tractors, threshers, winnowers, etc, and produce crops mainly to sell them in the market t is called commercial farming.
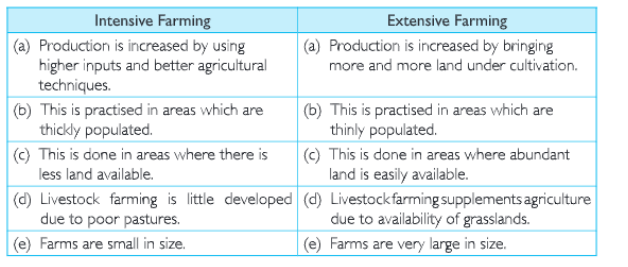
(d) Extensive Farming: This method is practised in countries where the population is sparse and availability of land is more. Farmers use machines to a great extent as the size of land holdings is large.
(e) Intensive Farming: In this method of farming, the same piece of land is used throughout the year continuously. The soil is also very fertile. Farmers use more labourers, seeds that can yield more, better manures and ensure regular water supply.
(f) Irrigation Farming: It is the type of farming, which mainly depends on irrigation through canals, wells and tanks. Farmers cultivate their lards throughout the year.
Some of the important river valleys of the world where this method is followed are, the Ganga valley and the Indus valley in India, the Nile valley in Egypt, the Xi Jiang valley in China, the Missouri and San Joaquin valley in the United States of America.
(b) Rainfed Farming: In those regions where the rainfall is not only seasonal but also scanty, farmers use different measures to cultivate their lands and use the scarce amount of rain water efficiently. This is known as rainfed farming.
(g) Mono-crop Farming: When the farmers specialise in the production of a single crop or if the soil and other natural factors allow farmers to cultivate only one crop that farming is known as one-crop or mono-crop farming.
(h) Double and Multi-crop Farming: When two or more crops are cultivated in a plot of land, it is known as double or multi-crop farming. In this method, farmers apply scientific methods-use seeds that can give high yield and apply manures in an appropriate manner. and invention of farm equipments brought remari<able changes in the development of agriculture in the world. There has been a progressve growth in agr culture during the twentieth century as well.
(c)With high yielding varieties of seeds and application of fertilisers, pesticides, insecticides and weedicides, agricultural production has increased worldwide.
(d)Now genetically modified crops to get higher yield with less Droblems of pests and weeds have also been developed by some countries.
Question.4. Describe the various steps taken by the Government of India to improve agriculture.
Answer. The Indian Government took several steps to improve the agricultural conditions in the world:
(a)Modem methods of cultivation were introduced in the country.
(b)The government provided better infrastructure facilities such as irrigation, electricity and transportation.
(c)Land reforms were introduced. Under this, the government took lands of big landow ners away and redistributed to landless labourers.
(d)Most of the farmers in India have small farms. Even this land is fragmented over the years with the growing population. As a result, a large number of people tend to stay in farming. The government has encouraged consolidation of land holdings to promote use of farm machines.
(e)Agricultural equipments such as tractors, threshers and harvesters, high yielding varieties of seeds, fertilisers, pesticides and electricity-‘ were made available to farmers at less than the actual price. This led to tremendous increase in the production of crops especially food grains.
Question.5. Distinguish between:
(a)Subsistence farming and Commercial farming

(b) Intensive farming and Extensive farming.
Agriculture Hots Corner
Question 1. Where are the following plantation crops grown?
(i) Tea
(ii) Rubber
(iii) Coffee.
Answer.
(i) Tea in India
(ii) Rubber in Malayasia
(iii) Coffee in Brazil.
Question.2. Name the major crops grown in the U.S.A..
Answer. Com, soyabean, wheat, cotton, and sugarbeet
Question 3. Why are land holdings small in subsistence farming?
Answer. Due to right of inheritance.
Question.4. Which are the two agricultural seasons in India?
Answer. The two agricultural seasons in India are Khorif and Rabi.
Question.5. Who is the largest producer of rice in the world?
Answer. China is the largest producer of rice. India is cr second place.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Guide KSEEB
Question.6. How much population of India is still engaged in agricultural activities?
Answer. Two-thirds of India’s population.
Question 7. Describe the main features of an agricultura farm in India.
Answer. The following are the main features of a farm located in Adalibad village in Ghazipur district of Uttar Pardesh in India:
(a) The size of farm is about 1.5 hectares.
(b) The farm includes the residence of the owner.
(c)The farmer uses a well and pump set for mgation.
(d)Rice is the main crop.
(e)Government officials provide advice to the farmer.
(f)Different crops are grown in different plots.
(g)The farmer sells milk in co-operative store.
(h) Mobile labourers are employed.
(i)The farmer has a few cows, buffaloes, buls, hens, roosters and chickens.
(j)Moneylenders, banks, societies give loan,
(k) The farmer sells his produce in the market
Question.8. What are the main features of agricultural farms in the U.S.A.?
Answer. In the U.SA two types of farms functioned (i) Specialised farms (ii) Mixed farms.
(a)Specialised farms: A specialised farm concentrates on a particular type of livestock or crop. About 95 per cert of farms in the U.SA are specialised farms. Mostly cereal grains such as com, wheat, sorghum, rice, barley, oats and rye are grown in specialised farms. These farms also produce crops such as cotton, groundnut sugarcane, tobacco, vegetables and foiits. Nearly half of the specialised farms in the U.SA are livestock farms. These livestock farms rear meat animals, raise milk cows, chickens and turkeys.
(b)Mixed farms: These farms raise a variety of crops. In these farms, farmers produce a variety of crops and rear livestock The United States is the world’s leader in international agricultural goods Market.
Agriculture Map Based Question
Question. I. Study the map given below and Answer the following Question:
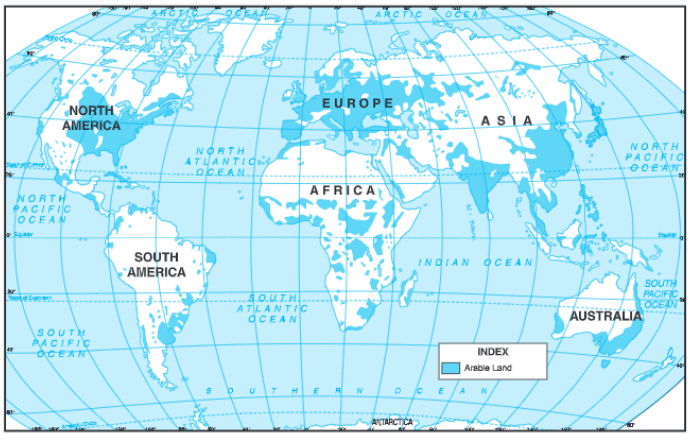
(a)Name three countries having large arable land. Give one reason.
(b)Name three continents having low arable land. Give reasons.
Answer.
(i) India China and the U.SA have large araole land. This is due to the presence of large alluvial plains,
(ii) South America, Australia and Africa have low arable land. This is due to dense forests, hilly areas and deserts.
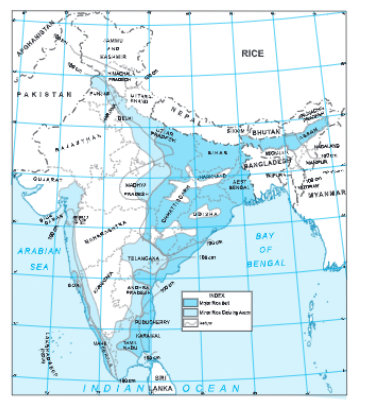
Question.2. Show the distribution of rice on the map of India
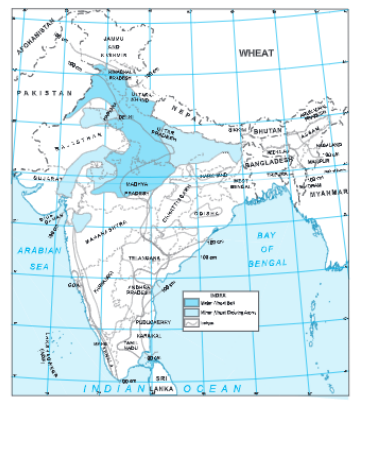
Question.3. Show the distribution of wheat on the map of India.
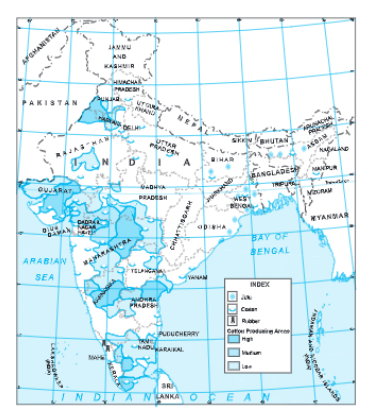
 Question.4. Show the distribution of cotton, jute and rubber on the map of India. Answer
Question.4. Show the distribution of cotton, jute and rubber on the map of India. Answer
Question 5. Show the distribution of tea and coffee on the map of India.

Agriculture Miscellaneous Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Tick the correct option from the choices provided:
Question 1 Agriculture is an activity of the type:
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quartemary
Answer . (a) Primary
Question 2 Which of the following is not a primary activity?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Fishing
(c) Forestry
(d)Manufacturing
Answer. (d)Manufacturing
Question 3 What percentage of people of the world are engaged in agriculture?
(a)0
(b)5
(c)50
(d) 55
Answer. (c) 50
Solutions For Agriculture KSEEB Class 8 Geography
Question 4 Which of the following is a tertiary activity?
(a)Transport
(b)Agriculture
(c)Manufacturing
(d) Fishing
Answer .(a) Transport
Question 5 Breeding of fish is called:
(a)Sericulture
(b)Viticulture
(c)Pisiculture
(d) Horticulture
Answer . (c) Pisiculture
Question 6 What is growing of grapes?
(a) Sericulture
(b) Pisiculture
(c) Viticulture
(d) Horticulture
Answer .(c) Viticulture
Question 7. Which country is the leading producer of rice?
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Japan
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer. (b) China
Question 8. Which country is the largest producer of wheat?
(a) India
(b) Pakistan
(c) Canada
(d) U.SA.
Answer. (d) U.SA
Question 9. Which country is the leading producer of coffee?
(a) Brazil
(b) Columbia
(c) India
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer. (a) Brazil
Question 10. Which country is the leading producer of tea?
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Japan
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer. (a) India
Agriculture One Word-Sentence Answer
Answer the following Questions in one word-sentence:
(a)Which is the most suitable soil for wheat cultivation?
Answer. Loamy soil.
(b)Mention two crops grown under intensive agriculture.
Answer. Rice and wheat
(c)Which crops are grown on large plantations in plantation agriculture?
Answer. Rubber, tea and coffee.
(d)Which crop is staple diet of about one-half of the world population?
Answer. Rice.
(e)How many frost free days are required for cotton?
Answer. 210 days.
(f)Which cultivation is also called ‘Slash and Burn’ agriculture?
Answer. Shifting cultivation.
(g)How much percentage of world population is engaged in agriculture?
Answer. 50%
(h) Which place accounts for half the amount of tea produced in India?
Answer. Assam.
(i) Which country is the world leader in jute production?
Answer. Bangladesh.
(j) What is golden- fibre ?
Answer. Jute.
Agriculture Picture Interpretation
Look at the following picture and Answer the Questions that follow:
What kind of agricultural practices are shown by the following pictures:
(a)

(b)

Answer.
(a) Subsistence farming
(b) Slash and burn agriculture
