KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Useful Microorganisms, Animals And Plants Notes
Many living organisms are present in soil, water, and air around us. Some of these organisms are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes. We need a magnifying instrument called a microscope to see these extremely small organisms. These extremely small organisms are known as microorganisms (micro = extremely small). We can now say that: Those organisms which are too small to be seen without a microscope are called microorganisms. The study of microorganisms is called microbiology.
Useful Microorganisms
Initially it was thought that all the micro-organisms are harmful and cause diseases. Later on scientists discovered that only a handful of microorganisms are harmful and cause diseases. Most of the microorganisms are harmless and some of the microorganisms are even beneficial to us (or useful to us).
Microorganisms play an important role in our lives. We will now describe the beneficial effects and harmful effects of micro-organisms in detail, one by one.
Useful Bacteria
Bacteria are very small, singlc-ccllcd microorganisms which have cell walls but do not have an organised nucleus and other structures. Bacteria are found in large numbers everywhere: in air; soil and water; every surface around us; on our bodies and even inside our bodies.They are invisible to the naked eye and can be only viewed under a microscope. The study of bacteria is bacteriology.
Class 8 Biology KSEEB Useful Microorganisms Animals and Plants Notes
Food
Some bacteria are useful to us. They can be used to make curd, cheese and vinegar. The milk changes lo curd due lo Lhe presence of a bacteria called Lactobacillus acidophilus. When a little of pre¬made curd is added to warm milk, then Lactobacilli bacteria present in curd multiply in milk and convert it into curd. This happens as follows: Milk contains a sugar called lactose. Lactobacilli bacteria convert llie lactose sugai into lactic acid. This lactic acid then converts milk into curd. Acetobacter bacteria convert alcohol into acetic acid (or vinegar).

Medicines Synthesising The Vitamin
The bacteria found in the human intestine synthesize the vitamin B-complcx which further helps in digestion and absorption of food in the human body.

Kseeb Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Useful Microorganisms Solutions Pdf
Antibiotics And Vaccines
A medicine which stops the growth of, or kills the disease-causing microorganisms is called an antibiotic. The source of antibiotic medicines are microorganisms. The antibiotics are manufactured by growing specific microorganisms (and used to cure a number of diseases). These days, a large number of antibiotics are being produced from microorganisms such as fungi and bacteria.
Some of the common antibiotics which are made from fungi and bacteria are: Penicillin, Streptomycin, Erythromycin and Tetracycline. Antibiotics are, however, not effective against diseases caused by viruses. For example, antibiotics cannot be used to cure diseases like common cold’, ‘flu’, and ‘viral fever* because these are caused by viruses.
Mircoorganisms are also used to make vaccines.
A vaccine is a special kind of preparation (or medicine) which provides immunity (or protection) against a particular disease. Vaccines are given to healthy persons so that they may not get certain diseases throughout their life (even if they are exposed to the pathogens of these diseases later on in life). The diseases which can be prevented by vaccination of children at proper age are: Polio, Smallpox, Cholera, Typhoid, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis (TB), Tetanus, Measles, Rabies, Diphtheria and Pertussis (Whooping cough).
Tanning Of Leather
Tanning is the process of treating animal skin to produce leather. Bacteria are also used in tanning process. The bacteria employed in the process of tanning are obtained from cowdung and the excreta of dogs and poultry.
Retting Of Fibres
The action of some bacteria like Clostridium, Pseudomonas, etc., help in fibre retting i.e. separation of stem and leaf fibre of plants from other softer tissue.
KSEEB Class 8 Biology Solutions For Useful Microorganisms
Production Of Biogas
Bacteria, while converting animal dung and other organic wastes to manure, help in production of fuel that is a must in gobar gas plant

Sslc Class 8 Biology Useful Microorganisms Question And Answers
Scavenging
Saprophytic bacteria obtain food from organic remains such as animal excreta, fallen leaves, meat etc. They decompose these substances by action of digestive enzymes aerobically or anaerobically (known as fermentation). Thus they help in sanitation of nature, hence, also known as scavengers. An example is Pseudomonas.
Decomposition
Bacteria use the dead and decaying mailer as a source of nutrients, and in turn help in recycling the organic compounds trapped in the dead matter. Through this process, other organisms also get benefited, who can use the simpler forms of organic compounds/nutrients released from the dead matter by various bacteria.
Useful Fungi
Fungi are microorganisms that look like small plants but do not contain chlorophyll and do not photosynthesise. They can be unicellular or multicellular. The body of a fungi consists of many cotton-like threads that are called mycelium, and each of such single thread is called hypha. Fungi grow’ in damp and warm places and are often found on breads, pickles and rotting food items.
Food
Some species of fungi are edible. They are cooked with rice or eaten as vegetables or prepared in soups. Some examples are Morchella (morels), mushrooms, Ramaria, and so on. These are used for preparing mushroom soup, as pasta toppings or to add flavour to an omelette. Fungi are also used to process cheese with different flavours.
Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Useful Microorganisms Summary Kseeb
Bakery
Yeast is used in the baking industry for making bread. When yeast is mixed in dough for making bread, the yeast reproduces rapidly and gives out carbon dioxide gas during respiration. The bubbles of carbon dioxide gas fill the dough and increase its volume. This makes the bread ‘rise’.
Fermentation
Yeast is also used in breweries to make beverages such as wine and beer. These microorganisms convert the sugar to an acid or alcohol. This process in which microorganisms convert the sugar to alcohol is called fermentation. Wine is prepared by the fermentation of grapes whereas beer is obtained by the fermentation of barley.
Useful Microorganisms Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Manure
The seaweeds are also added as a manure in the agricultural fields which help in improving the soil quality and its fertility.
Medicines
The antibiotic penicillin is obtained from PeniciUium.
Useful Algae
Algae is a large group of simple, plan t-like organisms. They contain chlorophyll and produce food by photosynthesis just like plants. Algae, however differ from plants because they do not have proper roots, stems and leaves. Some of the examples of algae are: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Blue-green algae; Diatoms and Seaweeds.
Algae As A Food
A few red algae are good source of food. In Japan a popular dish is prepared from Laminaria, a brown algae. It contains a large amount of minerals. Algae are also used as food by animals. Many seaweeds make very useful fodder.

Useful Microorganisms Class 8 Biology Kseeb Important Questions
Medicines
Seaweeds also yield bromine, acetic acid, formic acid and acetone. An antibiotic called Chlorellin is prepared from Chlorella.
In Industries
Agar (also known as China grass) is obtained from red algae. This product is used in laboratory for various experiments. Diatoms are a kind of algae found in sea. They contain silica which is extensively used in making metal polish, porcelain and toothpaste. Iodine is extracted from Laminaria.
Useful Animals
The animals are useful to us in many ways. A number of domestic animals like cows, goats, ducks, and others provide us with milk, eggs, meat, and so on. This process of rearing of animals for a specific purpose is called domestication. All the domesticated animals which are useful in producing various products are called livestock. The taking care of this livestock such as their food, shelter and breeding along with rearing of animals at a large scale is known as animal husbandry. Animals are reared on the farm for food, milk, and other activities. Livestock can come under different categories. Let us discuss them here:
Milk Yielding (Milching) Animals
Cows, buffaloes, goats, camels and other animals provide us with milk that is nutritious and rich in calcium. Livestock raised as a source of milk are called milk animals. Milk is a good source of vitamins, proteins and minerals. In India, buffaloes are the major source of milk as compared to cows.
There are three types of breeds of dairy cows majorly found in India.
Karnataka Sslc Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Solutions In English
Indigenous breeds
These breeds are also known as desi breeds. For example. Red Sindhi, Gir and Sahiwal.
Exotic breeds
These breeds are imported from other countries. For example, Holstein-Friesian, Brown Swiss and Jersey
Crossbreed
These breeds are developed by mating exotic breeds with indigenous breeds. Their milk-yielding capacity is two to three times more than indigenous ones. For example, Karan Fries, Frieswal and Karan Swiss. The three breeds of buffaloes in India are as follows:
Murrah
The milk yield of this breed is about 12-16 litres of milk on daily basis during lactation time. It is considered as the best breed of buffalo in Haryana and Punjab.
Mehsana
Mehsana breed is commonly found in and around Gujarat. The average milk yield is around 10-12 liters per day.
Surti
The Surti is a breed of water buffalo found in a few districts of Gujarat. They can yield 7-9 liters of milk in a day.

Class 8 Biology Useful Microorganisms Notes Karnataka Board
Management of Milch Animals
The management of milk-yielding animals include appropriate shelter and feeding requirements.
Shelter
The animals’ shelter should have the following characteristics:
- Animals’ shelters should be clean and well-ventilated.
- Their sheds should be well-covered to protect them from rain, heat and cold.
- The shelter should be big enough to provide sufficient space to the animal for stay.
- It should have clear drinking water.
- The shelter should be protected from predators.
Feeding
The animal food containing essential nutrients needed for the growth and development is called feed.
Cattle feed is of two types:
- Roughage: Roughage has more fibre content. It includes feed such as hay, straw, fodder, legumes, silage, coco pea and so on.
- Concentrates: Concentrates have very low fibrous matter. They are rich in nutrients.
They include grains such as bajra, jowar, rice, barley, gram, chaff, wheat bran, husk, oilseeds, molasses, etc.
Proper breeding
Animals with specific and desired characters are selected for breeding. This is important for propagating only those specific desired species of livestock.
KSEEB Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Important Questions
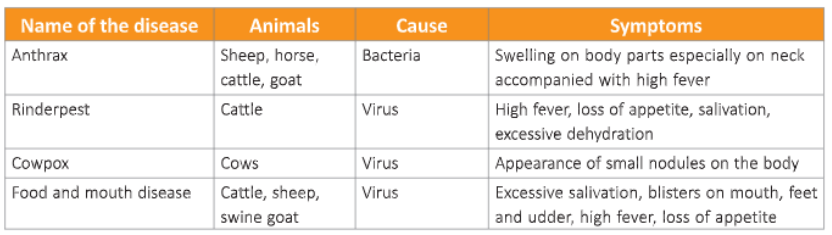
Diseases of Cattle
Like humans, cattle also sutler from diseases by bacteria and viruses. Dairy animals should be vaccinated regularly to be protected from diseases Some of the diseases in cattle are listed in the table shown here
Useful Microorganisms Class 8 Biology Summary And Explanation Kseeb
White Revolution
Operation Flood (OF), commonly referred to as ‘white revolution, refers to rapid development in milk production that took place in India from 1970-1996 . This project transformed India from a milk deficient country to the world’s largest milk producer in 1998. The main architect of this successful project was Dr. Verghese Kurien, also known as the ‘Father of White Revolution’. ‘Operation flood’ is a program started by National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
Operation flood was completed in three phases. During the first phase of its starting (1970-1980), the country’s 18 main milk sheds were connected to the consumers of the four metros, that is, Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai and Kolkata. During the second phase (1981-1985), the management increased the milk sheds from 18 to 136; 290 urban markets expanded the outlets for milk. By the end of 1985, a self-sustaining system of43,000 village cooperatives with 42.5 lakh milk producers were covered.
In the third and last stage (1986-1996) of white revolution, the dairy cooperatives were enabled to expand and strengthen the infrastructure required to procure and market increasing volumes of milk. Veterinary first aid, health care sendees, feed and artificial insemination sendees for cooperative members were extended, along with intensified member education.
Meat and Egg-yielding Animals
Goat, sheep, hen and other poultry birds provide us with meal. Fish is also a source of food. These animals are reared on a commercial scale for their meat. Hen meat is called chicken. Sheep and goat meat is called mutton.
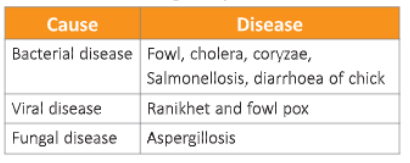
Poultry farming
Poultry is the rearing of birds like fowl (cock and hen), goose, turkey and duck for their meat and eggs. The eggs from these birds are a rich source of proteins. The chicken used for laying eggs are called layers, and chicken used for rearing meat is called broiler. In India, there arc three types of breeds of chickens: indigenous, exotic and cross-breed.
The most popular indigenous breed is Aseel. Exotic breeds such as White rock. Black Minorcha, Rhode Island Red arc produced outside India. They are excellent egg layer and good meat producers. In India, some cross breeds of chicken such as ILS-82, HH-260, B-77 have been raised. They have high egg laying capacity.

Class 8 Biology Kseeb Useful Microorganisms Short And Long Answer Questions
Management of poultry birds
It is very important that the chickens are kept with care in the poultry sheds. The birds should not be kept in the open as there is always a danger of the birds being attacked by other animals. Care should be taken while feeding the birds. Bird food generally include cereals like bajra, maize, wheat, ragi, etc.
Sheep and Goat
Animals such as goat, hen and sheep are reared for their flesh or meat. Sheep provides us mutton, wool and hide (leather). Goat provides us milk, meat, and skin. The process of removal of wool from sheep is called shearing. Wool is produced from the fleece of sheep. Power shears arc used for shearing. The quality of wool varies from breed to breed. For example, Pashmina wool is very soft and warm.
It is obtained from Indian breed called Pashmina, which is found in Kashmir and Himalayan areas. Important breeds of sheep in our country are Nellore, Mandya, Dorset, Marwari, Bikaneri, Rampuri, and Deccani. Important breeds of goat include Gaddi, Jamnapuri, Black Bengal, Assam hill, Decanny, Kashmiri and many more.

Management of sheep and goat
Sheep do not require a well-structured shelter. They live under natural shades of trees and hills. Goats require a clean, dry and safe home. Goals should be protected from heat and cold.
Sheep and goat are given grains, gram chaff, oil cakes, and mineral mixtures along with grass, foliage, herbs, etc.
Detailed Notes On Useful Microorganisms In KSEEB Biology
Diseases in sheep and goat
Sheep and goat suffer from bacterial and viral diseases. Regular immunisation and proper sanitation help in the prevention of diseases.
Draught Animals
Animals which arc used to carry loads and doing labour in fields such as carting, tilling and ploughing are called draught animals. Animals are being used as a means of transportation since ancient times. We have all seen bullock carts, horse carts and camel carts. Elephants, mules, donkeys and horses also help in carrying load and transporting goods from one place to another.
Bullocks are used extensively by farmers in ploughing and irrigating, hi desert areas, the main form of transportation of human beings and goods is the camel. The camel is hence known as the ship of the desert.

Apiculture
The rearing of bees for honey is called apiculture. The scientific name for honeybee is Apis. In the process of rearing the bees, special wooden boxes are placed in the orchards. At the doors of these boxes, there are pores from which the bees can move in or out. The boxes are used as a hive by the bees and arc called apiaries. Generally, there are thousands of bees in one hive along with one queen bee. Most of the bees are workers or drones. These bees collect nectar from flowers which they turn into honey. Honey is rich in carbohydrates, and is thus, very good for health. Beeswax, also produced from apiculture, is used in the manufacturing of candles, cosmetics items, etc.
Class 8 Kseeb Biology Useful Microorganisms Examples In Plants And Animals
Pisciculture
Raising fish commercially in tanks or enclosures such as fish ponds, usually for food or business is called fish farming or pisciculture. It is the principal form of aquaculture. The fish may be reared in small and large rivers, lakes, canals, etc. Hatcheries are developed wherein fish seeds or fish eggs are pul. Later, when they grow and are nursed, the young fishes are finally harvested. Culturing fish can be done in various processes and classifying them can be done based on the way they are grown in the ponds.

- Monoculture is a type where a single type of fish is grown in a particular water body.
- Polyculture involves growing more than one type of fishes in a single water body.
- Integrated fish culture is an entirely different type where fishes are grown with agricultural crops/animals.
Pisciculture is done in various types of ponds based on stages of growth of fish. The types of ponds include—breeding ponds, hatchery ponds, nursery ponds, rearing ponds and stocking ponds.
Simplified Notes For KSEEB Class 8 Useful Microorganisms
Sericulture
Sericulture refers to the process of the breeding and management of silkworms for the production of silk. In the process of sericulture, the eggs of the silkworms are kept together in trays. They are kept there until the eggs hatch. The small larvae called silkworms have a short life cycle, divided into four stages.
 Eggs
Eggs
The time when a female silk moth lays eggs is the beginning stage of the life cycle of silkworm, and they hatch to form worms. To speed up the time of hatching the eggs, they are incubated.
Larva
After about 20 days, the larvae or caterpillars start hatching from these eggs. After hatching, these larvae that come out are known as silkworms or caterpillars. These silkworms eat voraciously.
Pupa
These silkworms feed on fresh mulberry leaves and grow in size. They secrete fine filaments from two glands on their heads, which is made up of protein that hardens to form silk fibres when exposed to air. The silkworm deposits filaments in a number of concentric layers around its body, through the movements of the head, forming a structure, called the cocoon.
Adult
Inside the cocoon, the silkworm enters the next stage of its life called the pupa and then into a moth. It then breaks open the cocoon emerging as an adult and again lays eggs and the cycle continues again. To extract silk from silkworms, the cocoons are put in water to extract the soft silk threads. These threads are then purified and spun into yarns.
USEFUL PLANTS
Plants are the primary producers, all other living organisms directly or indirectly depend on them for food. They fulfill almost all our basic needs for food and also release life sustaining oxygen in atmosphere. We get different products from plants as discussed here:
Food Crops
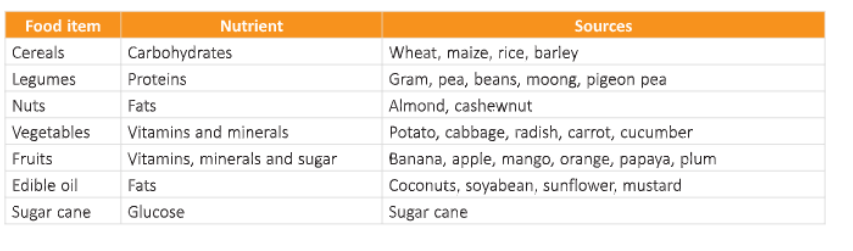
A food crop is any cultivated plant that is harvested to be consumed by both human beings and animals. They are grown with the primary intention of being consumed and thus, require special care throughout the cultivation period. The plants which are grown to produce crops are known as the crop plants. Main crops include cereals, pulses, etc.
Such crops are a part of our food along with the oils and beverages that are produced through them. The production of food is not limited to cereals and pulses but also extends to vegetables and fruits. Some of the food crops grown in India are discussed here.
Karnataka Board Class 8 Biology Useful Microorganisms Experiment Notes
Cereals And Pulses
The cereals like corn, wheat and paddy provide us starch, fibre and minerals. They also give us proteins.
Oilseeds
The seeds which are the source of oils are called oilseeds. Important oilseeds are mustard, groundnut, sesame (til j, soya bean, sunflower, and so on. The oil cake is the residue left after the extraction of oil.
Vegetables
The vegetables are soft, seasonal and herbaceous plants. They give us nutrients, and are rich in minerals, vitamins, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Cash Crops
Cash crops are the ones which are produced in order to further sell the produce rather than consumption. These are exported to foreign countries. These crops are grown on large estates called plantations.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Biology Chapter 9 Useful Microorganisms Notes
Spices
India produces a wide range of spices and spice products, such as pepper, cardamom, cinnamon,ginger, turmeric, chilli, coriander, cumin, clove, saffron,garlic, mustard, and so on.
Rubber
Rubber plantation in India started in 1895 on the hills of Kerala. Rubber is produced from the latex of different plants but majorly, the rubber plant is used to produce it.
Fibre-yielding crops
Fibre-yielding crops are the ones which produce- fibres and are used for manufacturing fibre goods. These crops include jute, hemp, cotton, milkweed, etc.
Medicinal plants
India produces numerous medicinal and herbal plants such as amla, brahmi, ashok, calihari, neem, makoi, sandalwood, tulsi, Aloe vera, and many more.
Keywords
Germs: Microorganisms which cause diseases
Antibiotics: The chemicals carry antibodies to fight against diseases
Vaccines: The injections with antigens to fight against diseases
Animal husbandry: Rearing of animals on a large scale at or in a farm and taking care of their shelter, food, breeding and health
Apiculture: Rearing of bees for production of honey
Sericulture: The process of breeding, rearing and management of silkworms for the production of silk
Pisciculture: Raising fish commercially in tanks or enclosures, usually for food or business
Food crop: Any cultivated plant that is harvested to be consumed by both human beings and animals
Summary
- Bacteria turns the lactose present in the milk and converts it into lactic acid. This acid helps in turning milk into curd.
- Cash crops are the ones which are produced in order to further sell the produce rather than consumption.
- All the domesticated animals which are useful in producing various products are called livestock.
- Poultry is the rearing of birds like fowl (cock and hen), goose, turkey and duck for their meat and eggs.
- Draught animals are used to carry loads and are used for carting, tilling, ploughing, etc.
- Rearing of honeybees for commercial purposes and to obtain honey is called apiculture.
- Rearing of silkworm to obtain silk is called sericulture.
- A food crop is any cultivated plant that is harvested to be consumed by both human beings and animals.


