KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Biology Chapter 7 Nervous System Learning Objectives
Types of nerves: sensory, motor, mixed, cranial and spinal nerves Structure of motor neuron Central nervous system, its parts and functions Reflex actions—definitions and basic terms used to describe reflex actions, stimulus, response, impulse, receptor, effector; common examples of reflex actions.
Nervous System
- All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The living organisms show response to stimuli such as light, heal, cold, sound, smell, lasle, touch, pressure, pain, water, and force of gravity, etc. The response of organisms to a stimulus is usually in the form of some movement of their body part. For example, if a man touches tip of the needle or a pin accidently, he quickly pulls his hand away from the needle.
- Here, the man reacts by moving his hand away from the hot needle. Similarly, when the sun is bright, we close our eyes. In this case, light is the stimulus and we react by closing the eyes.
- Human body perform various processes such as, respiration, digestion, excretion, growth, circulation, etc. These processes are being carried out by specialised organs that are interrelated and interdependent on each other. There is usually coordination between these organ systems because of which they are able to function smoothly.
- Coordination is defined as the interaction and interrelation between the various activities in the body of a living being that takes place internally and externally.
- Coordination is important in simple activities such as eating food, where there has to be coordination between hand movements, the eye and mouth so that food goes to the right place and is consumed.

Kseeb Class 8 Biology Chapter 7 Nervous System Solutions Pdf
Types Of Coordination
Coordination can be of two types—nervous coordination and chemical coordination. Let us understand them one by one.
Nervous Coordination
- The coordination of the nerves and the brain is part of the nervous coordination. For example, we withdraw our hand immediately on touching a hot pan or getting pricked; some games such as cricket and tennis require visual, muscular and mental coordination.
- The actions of the body could be voluntary or reflex. Voluntary actions are those that are under our control or we are conscious of such actions. Reflex or involuntary actions are those that are in response to external or internal stimuli.
Chemical Coordination
- This coordination takes place when the endocrine glands are involved and they produce the chemicals that are essential and vital in controlling various processes in the human body. The endocrine glands are also known as ductless glands. Chemicals are secreted from these glands which are known as hormones. Hormones are chemicals that are secreted directly into the blood steam by the endocrine glands which regulate certain processes in the human body.
Functions Of Nervous System
- The function of nervous system is to coordinate the activities of our body. It is the control system for all our actions, thinking and behaviour.
- The nervous system helps all other systems of our body to work together. The nervous system is like a manager inside our body. Its job is to control and coordinate the parts of our body so that they work together, doing their job at the right time.
- Our nervous system coordinates muscles so that we can do things which need thinking like reading, writing, cycling or dancing. The nervous system also coordinates things which we don’t have to think about, like heart beat and breathing. The human nervous system receives information from the surroundings, processes it, interprets it and then responds accordingly. The nervous system also passes information from one internal system to another.
- For example, as soon as we put food in our mouth, it immediately causes the release of saliva from the salivary glands.
Sslc Class 8 Biology Nervous System Question And Answers
Nervous System in Higher Organisms
- Vertebrates have a well-developed nervous system. It is made up of nerve cells or neurons. Messages are transferred through the nerve cells in the form of electrical impulse. There are about 30,000 million nerves in human body.
The Neuron
Neurons or nerve cells are the smallest structural and functional units of the nervous system. A neuron consists of the following three parts:
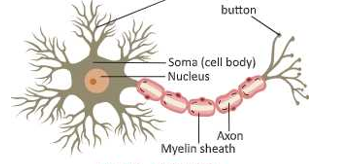
Cyton
Each neuron consists of a main cell as the body which is known as a cyton. It contains nucleus and cytoplasm.
Dendrite
There are a number of processes or finger-like extensions known as dendrites that emanate from ihe cell body. Dendrons further divide and form dendrites. They receive messages from other neurons.
Kseeb Class 8 Biology Nervous System Textbook Solutions
Axons
Axon is a long specialised process arising from the other side of cyton. It may be from few mm up to more than one metre in length. Axon is surrounded by a sheath called myelin sheath.
It carries messages from the cell body of one neuron to the cell body of other neuron.
Types of Nerves
Nerves are of three kinds as discussed here.
- Sensory nerves: These contain sensory fibres that carry impulses from the sense organs to the brain or the spinal cord.
- Motor nerves: These contain motor fibres that carry impulses from the muscles or glands from the brain to the spinal cord.
- Mixed nerves: These contain both sensory as well as motor fibres.

Nervous System Class 8 Biology Kseeb Important Questions
Places where one neuron communicates with another neuron are called synapses. A synapse is a junction where the axon terminal of one neuron lies in a close contact to the dendrite of other neuron.
Nervous System In Human Beings
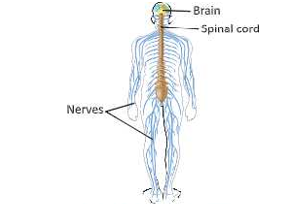
- The human nervous system is the centre of communication and control in the human body. It comprises of the following three parts: the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
The Central Nervous System
- The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is enclosed within the skull and the spinal cord lies within the vertebral column. The major decisions and control functions are carried out by the brain and hence, it becomes the most critical part of the body organ system.
- The nerves that are found all over the body receive information from internal as well as external sources. The information is then processed and appropriate action is directed. The brain filters out information that is important and discards what is not important. The body is then directed to convey and carry out an appropriate response.
KSEEB Class 8 Biology Solutions For Nervous System
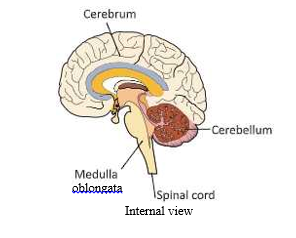
Brain
- The brain is round in shape and has many ridges and groves on its surface. It is found inside the skull or the cranium and is covered by membranes having fluid in between known as the cerebrospinal.
Karnataka Sslc Class 8 Biology Chapter 7 Solutions In English
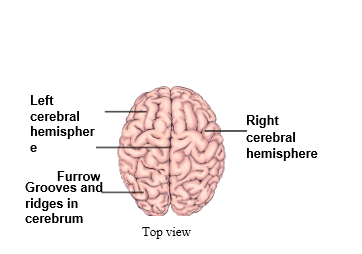
- Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest and most complex part of the brain. It is divided into two similar halves, right and left halves which are called cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere has four lobes, frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal and they are involved with specific functions.
- Both the cerebral hemispheres are hollow from inside and the walls have an inner and outer part. The outer part is known as grey matter and contains the neurons. It is made up of several groves and ridges since it has a large number of neurons. The inner part known as white matter consists of the axons.
- The cerebrum is the main control centre and is the seat of intelligence, willpower and consciousness. It controls the various voluntary activities and functions such as memory, thought, language, speech and perception.
- Cerebellum: The cerebellum is positioned behind and below the cerebrum. It is much smaller in size. It is responsible for maintaining a balance in the body and in coordinating muscles and itsfluid The brain is made up of three main parts— cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Each of these main parts further has sub-parts. The brain is connected with the body through the spinal cord.
- activities. While the decisions are being taken by the cerebrum, it is the responsibility of the cerebellum to ensure that they are implemented. Thus if the cerebrum has taken a decision to blow the nose, it is the cerebellum that directs the muscles of the hand to relax or contract, in order for the action to occur.
- Medulla Oblongata: This is the lowest part and continues till the spinal cord. Medulla oblongata controls the activities of the internal organs such as beating of the heart, breathing, etc. These are also known as involuntary actions. It is a critical part and injury to the medulla oblongata may lead to fatality.
Spinal Cord
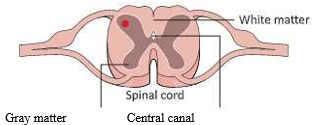
- The spinal cord begins at the medulla oblongata of the brain and extends inside the vertebral column or back bone almost till the end. It is made up of nerve tissue and remains protected by the vertebrae that make up the back bone. The inner part of the spinal cord is darker and makes up the grey matter comprising of nerve cell bodies.
- The outer part is white and comprises of axons or nerve fibres. The main function of the spinal cord is to assist in transfer of information between the brain and the various parts of the body and control reflexes below the neck. It is the focus for reflex actions.
Kseeb Class 8 Biology Nervous System Solved Exercises
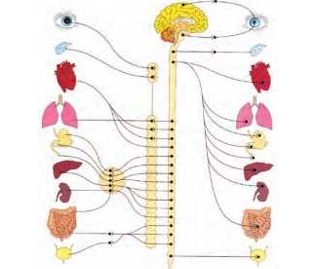
Peripheral Nervous System
All the nerves of the body together make up the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They all enter or leave the central nervous system. Depending on where they arise, the nerves those arise from the brain are known as cranial nerves and those from the spinal cord are known as spinal nerves. The peripheral nervous system consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves arise from the brain and spread throughout the head. They also carry both sensory and motor neurons.
Class 8 Kseeb Biology Structure Of Brain And Spinal Cord Notes
Spinal Nerves
Spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord along most of the length of the spinal cord and spread throughout the body (except the head).
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system consists of nerve fibres and mass of nervous tissue (ganglia) which are located on either side of the backbone. These control the involuntary actions of the internal organs of the body. The involuntary actions that take place due to external or internal stimuli are termed as reflex actions.
The autonomic nervous system has two parts: the sympathetic system and the parasympathetic system, both of which have opposing actions.
Nervous System Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is often called the fight or flight division. It results in increased alertness and metabolic activities to prepare the body for an emergency situation. It regulates responses during physical activity or emotional stress such as mcreased heart rate, dry mouth, cold skin and blood supply to arteries.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) is also called the rest and digest division. It conserve and restore body energies during rest or during the time when we take meals. The main nerves involved in the parasympathetic nervous system are vagus nerve and pelvic nerve.
Class 8 Biology Nervous System Notes Karnataka Board
Some Important Terms Related To Nervous System
- Following are some important terms related to the functioning of nervous system:
- Stimulus: This means the change that happens outside the body in the environment and which causes a change in the body. For example, heated cooker.
- Receptor: It is that sensory organ in the body that receives the stimulus. For example, on touching the heated cooker, the nerve cell in the skin will receive the stimulus and is called the receptor.
- Impulse: It is the sudden electrical disturbance which runs through the nerves. For example, on touching the heated cooker, the sensation that runs through the nerves is impulse.
- Effector: It is the muscle, gland or the body part which receives the response from the brain. For example, the hand muscle which is the effector will receive a command from the brain to remove the hand away.
- Response: The response is the change in body due to die stimulus. For example, the jerking away of the hand from the hot cooker is the response.
Reflex Action
- The simplest form of response in the nervous system is reflex action. This is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus which is not under the voluntary control of the brain. It is described as an involuntary action. Thus, a reflex action is one which we perform automatically. It is a comparatively simple form of behavior in which the same stimulus produces the same response every time.
- If we unknowingly touch a hot plate, we immediately move our hand away from it. So, moving our hand away on touching a hot plate is an example of reflex action. Similarly, moving our foot away when we step on something sharp, is also an example of reflex action.
Explanation of Nervous System in KSEEB Class 8 Biology
Pathway of Reflex Action
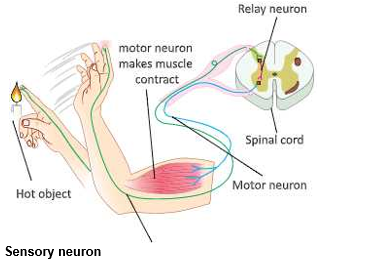
- The pathway (or route) taken by nerve impulses in a reflex action is called the reflex arc. Reflex arcs allow rapid response. We wall explain the meaning of a reflex arc by taking an example.
- A reflex action is an automatic response to a stimulus. An example of the way in which we respond to a stimulus is our reaction to touching a hot object (like a hot plate). Very quickly, and without thinking about it, we pull our hand away. This sort of very fast, automatic response is called the reflex action. shows the pathway taken by the nerve impulses in this reflex action. The stimulus here is the heat which we feel in our hand on touching the hot plate.
- This heat is sensed by a heat receptor (or thermoreceptor) in our hand. The receptor triggers an impulse in a sensory neuron, which transmits the message to the spinal cord. Here, the impulse is passed on to a relay neuron, which in turn, passes it to a motor neuron.
- The motor neuron passes the impulse to a muscle in our arm. The muscle then contracts and pulls our hand away from the hot plate. The muscle of arm is an effector because it responds to the stimulus. This pathway along which the impulse travels is called the reflex arc.
- The reflexes of this type which involve only the spinal cord are called spinal reflexes. Though spinal reflexes are produced in the spinal cord but the message of reflex action taken also goes on to reach the brain.
- Most of the reflex actions involve only the spinal cord. They are called spinal reflexes.
- Those reflex actions which involve brain are called cerebral reflexes. Cerebral reflexes occur in the organs present in the head because these organs are directly connected to the brain. This will become clear from the following example. Our eyes are present in the head.
- In dim light, the pupil (a hole in the front of eye) is large so that more light can enter into the eye and make us see properly even in dim light Now, when a bright light shines into our eye, then the pupil of our eye automatically becomes smaller (and prevents the damage to the retina of eye from too much light). The contraction of pupil of our eye automatically in the presence of bright light is an example of cerebral reflex.
Nervous System Class 8 Biology Summary And Explanation Kseeb
Summary
- Nervous system is the main coordinating and integrating system of the body. It is made up of nerve cells or neurons.
- Neurons are special cells that make up the nervous system.
- A bundle of axons or nerve fibres which are enclosed in an elongated sheath or casing form the nerve.
- There are three kinds of nerves: sensory, motor and mixed nerves.
- The human nervous system is the centre of communication and control in the human body. It comprises of the following three parts: the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
- The central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord. The brain is made up of three main parts: cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
- Reflex actions are the reactions that take place n a split second and do not involve any major effort.
- The autonomic nervous system consists of a pair of chains of nerves and ganglia on either side of the backbone.
Part A – Our PASTS – III (History)
- Chapter 1 How, When and Where
- Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory The Company Establishes Power
- Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside
- Chapter 4 Tribals Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age
- chapter 5 When People Rebel 1857 And After
- Chapter 6 Colonialism and the City: The Story of an Imperial Capital
- Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
- Chapter 8 Civilising the “Native” Educating the Nation
- Chapter 9 Women, Caste and Reform
- Chapter 10 The Changing World of Visual Arts
- Chapter 11 The Making of the National Movement 1870s -1947
- Chapter 12 India After Independence
Part B – Resources and Development (Geography)
- Chapter 1 Resources
- Chapter 2 Land,Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and A wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Industries
- Chapter 6 Human Resources
Part C: Social and Political Life -III (Civics)
- Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution
- Chapter 2 Understanding Secularism
- Chapter 3 Why Do We Need a Parliament ?
- Chapter 4 Understanding Laws
- Chapter 5 Judiciary
- Chapter 6 Understanding Our Criminal Justice System
- Chapter 7 Understanding Marignalisation
- Chapter 8 Confronting Marginalisation
- Chapter 9 Public Facilities
- Chapter 10 Law and Social Justice
