KSEEB Class 8 Maths Solutions For Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Points To Remember
Expressions are formed from variables and constants
Constant: A symbol having a fixed numerical 2 value. Example: 2, 2/3, 2,1, etc.
Variable: A symbol that takes various numerical values.
Example: x, y, z, etc.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Kseeb Solutions For 8th Class Maths Chapter 6
Algebraic expression: A combination of constants and variables connected by the sign +, —, x, and ÷ is called Algebraic expression.
Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors.
Expressions that contain exactly one, two and three terms are called monomials, binomials, and trinomials respectively.
In general, any expression containing one or more terms with non-zero coefficients (and with variables having non-negative exponents) is called a polynomial.
Like terms are formed from the same variables and the powers of these variables are the same, too.
Co-efficient of like terms need not be the same.
While adding (or subtracting) polynomials, first look for like terms and add (or subtract) them, then handle the unlike terms.
There are number of situations in which we need to multiply algebraic expressions for example, in finding the area of a rectangle, the sides of which are given as expressions.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Monomial: An expression containing only one term Example: -3, 4x, 3xy, etc.
Binomial: An expression containing two terms
Example: 2x – 3, 4x + 3y, xy – 4 etc.
Trinomial: An expression containing three terms.
Example: \(2x^2\) + 3xy + 9, 3x + 2y + 5z etc.
Polynomial: In general, any expression containing one or more terms with non-zero coefficients (and with variables having non-negative exponents). A polynomial may contain any number of terms, one or more than one.
A monomial multiplied by a monomial always gives a monomial.
While multiplying a polynomial by a monomial, we multiply every term in the polynomial by the monomial.
In carrying out the multiplication of a polynomial by a binomial (or trinomial), we multiply term by term. i.e. every term of the polynomial is multiplied by every term in the binomial or (trinomial). Note that in such multiplication, we may get terms in the product which are like and have to be combined.
An identity is an equality, which is true for all values of the variables in the equality. On the other hand, an equation is true only for certain values of its variables. An equation is not an identity.
The following are the standard identities.
- \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2\)
- \((a – b)^2 = a^2 – 2ab + b^2\)
- \((a + b)(a – b) = a^2 – b^2\)
- \((x + a)(x + b) = x^2 +(a + b)x + ab\)
The above four identities are useful in carrying out squares and products of algebraic expressions, they also allow easy alternative methods to calculate products of numbers and so on.
Coefficients: In the term of an expression any of the factors with the sign of the term is called the coefficient of the product of the other factors.
Terms: Various parts of an algebraic expression that are separated by + and – signs.
Example : The expression 4x + 5 has two terms 4X and 5.
1) Constant term: A term of expression having no lateral factor.
2) Like term: The term having the same literal factors.
Example : 2xy and -4xy are like terms.
3) Unlike terms: The terms having different literal factors.
Example: \(4x^2\) and 3xy are unlike terms.
Factors: Each term in an algebraic expression is a product of one or more number (S) and / or literals. These numbers (S) and/or literal (S) are known as the factor of that term. A constant factor is called numerical factor, while a variable factor is known as a literal factor. The term 4x is the product of its factors 4 and x.
Algebraic Expressions And Identities Solutions KSEEB Class 8 Maths Exercise 6.1
1. Identify the terms, their co-efficients for each of the following expressions.
1) \(5xyz^2 —3zy\)
Solution:
Terms : \(5xyz^2\) ,—3zy
Co – efficients : 5, -3
2) \(1 + x + x^2\)
Solution:
Terms : 1, x, \( x^2\)
Co-efficients: 1,1,1
3) \( 4x^2y^2 – 4x^2 y^2 z^2 + z^2\)
Solution:
Terms : \(4x^2y^2\) , \(-4x^2 y^2 z^2\) , \(z^2\)
Co – efficients : 4, -4, 1
4) 3 – pq + qr – rp
Solution:
Terms : 3 — pq, qr, rp
Co – efficients : 3, -1, 1,-1
5)\( \frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{2}-x y\)
Solution:
Terms: x/2, y/2, -xy
Coefficients: 1/2, 1/2, -1
6) 0.3a -0.6ab + 0.5/)
Solution:
Terms : 0.3a, — 0.6ab, 0.5b
Coefficient : 0.3, — 0.6, 0.5
2. Classify the following polynomials as monomials, binomials, or trinomials, which polynomials do not fit in any of these three categories?
x+y, 1000, \(x+x^2+x^3+x^4\) , 7+y+5x, \( 2y-3y^2+4y^3\) ,5x-4y+3xy, \( 4z-15z^2\) , ab+bc+cd+da, pqr, \( p^2q+pq^2\) , 2p+2q
Solution:
MonomiaLs: 1000, QPR
Binomials: x + y, \(2y-3y^2\), \(4z-15z^2\),\(p^2q+pq^2\), 2P + 2q
Trinomials : 7 + y + 5x, \(2y-3y^2+4y^3\), 5x – 4y + 3xy
Polynomials that do not fit in any of these categories are: \(x + x^2+x^3+x^4\), ab + bc + cd + da
3. Add the following
1) ab – bc, bc – ca, ca – ab
2) a – b + ab, b – c + bc, c – a + ac
Solution:
1) 
2) a -b + ab, b -c + bc,c – a + ac
Solution:
\(a-\not b+a b+b-c+b c+\not c-a c+a c\)
= ab+bc+ac
3) \(2p^2q^2 -3pq + 4,5 + 7pq -3p^2q^2\)
Solution: \(2p^2q^2 — 3pq + 4 + 5+ 7pq— 3p^2q^2\)
= \(-p^2q^2 +4pq + 9\)
4)\(l^2+m^2\), \(m^2+n^2\), 2lm+2mn+2nl
Solution: \(\begin{aligned}
& \ell^2+m^2+m^2+n^2+n^2+\ell^2 \\
&+2 \ell m+2 m n+2 n \ell
\end{aligned}\)
= \(2 \ell^2+2 m^2+2 n^2+2 \ell m+2 m n+2 n \ell\)
Karnataka Board 8th Maths Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions Solutions
4. 1) Subtract 4a-7ab+3b+12 from 12a-9ab+5b-3
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}
& 12 a-9 a b+5 b-3 \\
& (-) 4 a-7 a b+3 b+12 \\
& 8 a-2 a b+2 b-15 \\
&
\end{aligned}\)
b) Subtract 3xy + 5yz — 7zx from 5 xy — 2 yz — 2 zx +10 xyz
Solution:
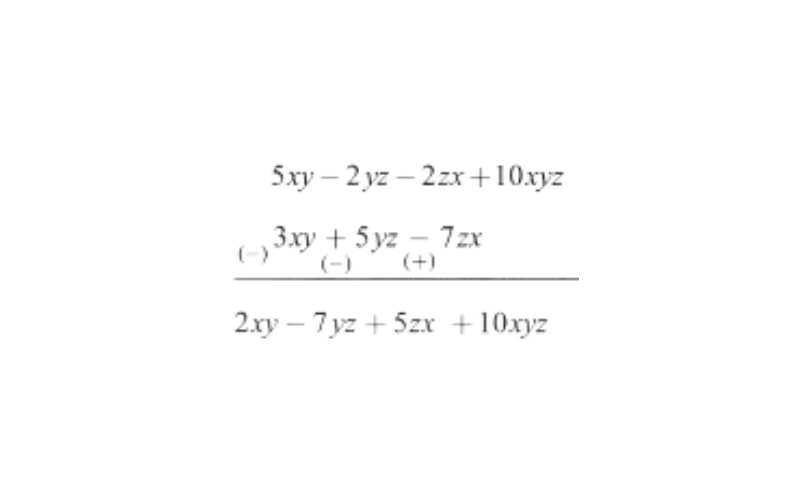
c) Subtract \(4 p^2 q-3 p q+5 p q^2-8 p+7 q-10\) from \(18-3 p-11 q+5 p q-2 p q^2+5 p^2 q\)
Solution:
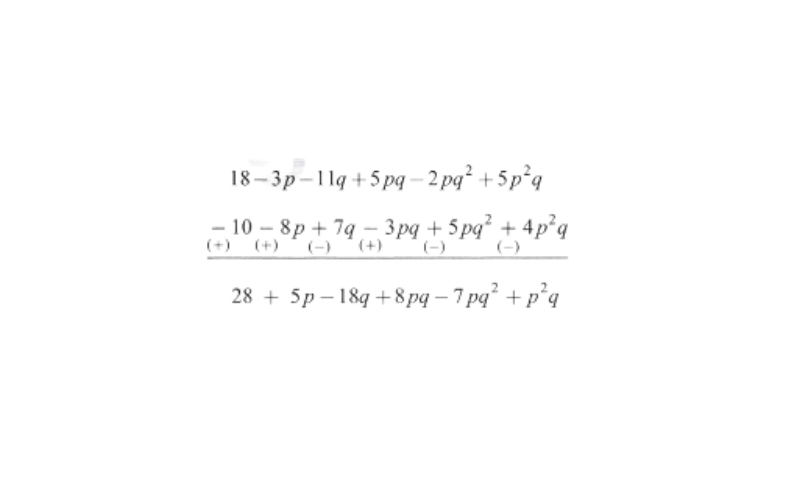
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Exercise 6.2
1. Find the product of the following pairs of monomials.
1) 4,7p
2) -4p,7p
3) -4p,7pq
4) \(4 p^3\), -3p
5) 4p,0
Solution:
1) \(4 \times 7 \times p=28 p\)
2) \(-4 p \times 7 p=-28 p^2\)
3)\(-4 p \times 7 p q=-28 p^2 q\)
4) \(4 p^3 \times-3 p=-12 p^4\)
5)\(4 p \times 0=0\)
Kseeb 8th Standard Maths Chapter 6 Textbook Solutions
2. Find the areas of rectangles with the following pairs of monomials as their lengths and breadths respectively.
1)(p,q)
2) (10m, 5n)
3) \(\left(20 x^2, 5 y^2\right)\)
4) \(\left(4 x, 3 x^2\right)\)
5) (3mn,4np)
Solution:
1) (p, q)
Area of rectangle = length x breadth
= pxq = pq
2) (10m, 5n)
Area of rectangle = l x b = 10m x 5n
= 50 mn
3) \(\left(20 x^2, 5 y^2\right)\)
Area of reactangle = l x b = \(20x^2 x 5y^2\)
= \(100x^2y^2\)
4) \(\left(4 x, 3 x^2\right)\)
Solution: Area of rectangle = l x b = \(4x x 3x^2\)
=\(12x^3\)
v) 3mn x 4np
Solution: Area ofrectangle = l x b = 3mn x 4np
=\(12mn^2p\)
3. Complete the table of products
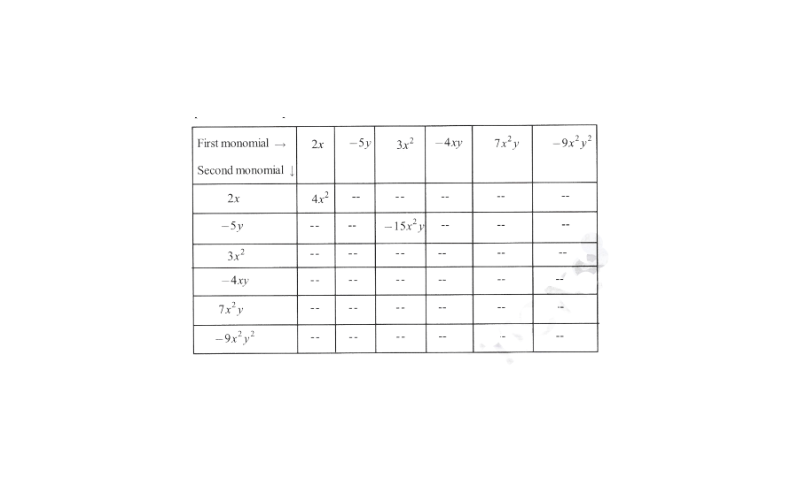
Solution:
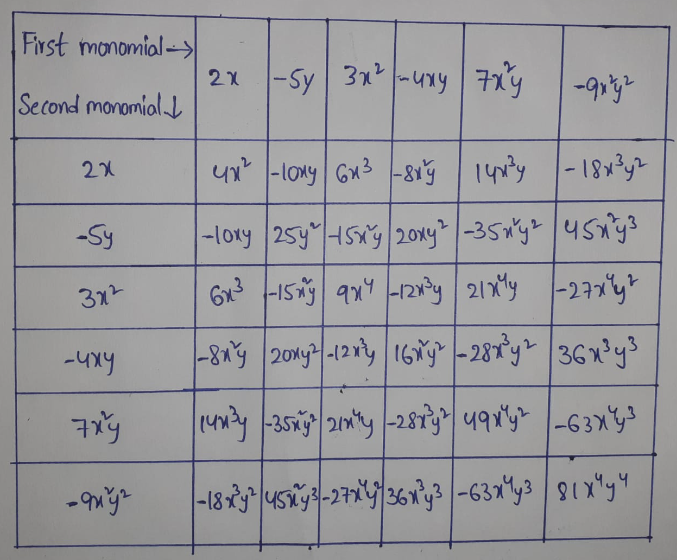
Class 8 Maths Chapter 6 Kseeb Important Questions And Answers
4. Obtain the volume of rectangular boxes with the following length, breadth and height respectively.
1) \(5 a, 3 a^2, 7 a^4\)
2) \(2 p, 4 q, 8 r\)
3) \(x y, 2 x^2 y, 2 x y^2\)
4) \(a, 2 b, 3 c\)
Solution: Volume = Length x Breadth x Height
1) \(\vartheta=5 a \times 3 a^2 \times 7 a^4=5 \times 3 \times 7 \times a \times a^2 \times a^4=105 a^7\)
2) \(\vartheta=2 p \times 4 q \times 8 r=2 \times 4 \times 8 \times p \times q \times r=64 p q r\)
3) \(\vartheta=x y \times 2 x^2 y \times 2 x y^2=2 \times 2 \times x \times x^2 \times x \times y \times y \times y^2=4 x^4 y^4\)
4)\(\vartheta=a \times 2 b \times 3 c=2 \times 3 \times a \times b \times c=6 a b c\)
5) Obtain the product of
1) xy, yz, zx
Solution: \(x \times y \times y \times z \times z \times x==x^2 y^2 z^2\)
2) \(a,-a^2, a^3\)
Solution: \(a \times\left(-a^2\right) \times a^3=-a^6\)
3) \( 2,4 y, 8 y^2, 16 y^3\)
Solution: \(2 \times 4 y \times 8 y^2 \times 16 y^3=1024 y^6\)
4) \(a \times 2 b \times 3 c \times 6 a b c=36 a^2 b^2 c^2\)
Solution: \(a \times 2 b \times 3 c \times 6 a b c=36 a^2 b^2 c^2\)
5) \(m,-m n, m n p\)
Solution: \(m \times(-m n) \times(m n p)=-m^3 n^2 p\)
KSEEB Maths Class 8 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Exercise 6.3
1. Carry out the multiplication of the expression in each of the following pairs.
1) \(4 p, q+r\)
2) \(a b, a-b\)
3) \(a+b, 7 a^2 b^2\)
4) \(a^2-9,4 a\)
5) \(p q+q r+r p, 0\)
Solution:
1) \((4 p) \times(q+r)\)
=\((4 p \times q)+(4 p \times r)\)
= \(4 p q+4 p r\)
2) \((a b) \times(a-b)\)
=\(a b \times a-a b(b)\)
=\(a^2 b-a b^2\)
3)\((a+b)\left(7 a^2 b^2\right)\)
=\(a \times 7 a^2 b^2+b \times 7 a^2 b^2\)
=\(7 a^3 b^2+7 a^2 b^3\)
4) \( \left(a^2-9\right)(4 a)\)
=\(a^2 \times 4 a-9 \times 4 a\)
=\(4 a^3-36 a\)
5) \((p q+q r+r p)(0)\)
=\((p q \times 0)+(q r \times 0)+(r p \times 0)\)
=\(0+0+0=0\)
Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Kseeb Notes Pdf
2. Complete the table
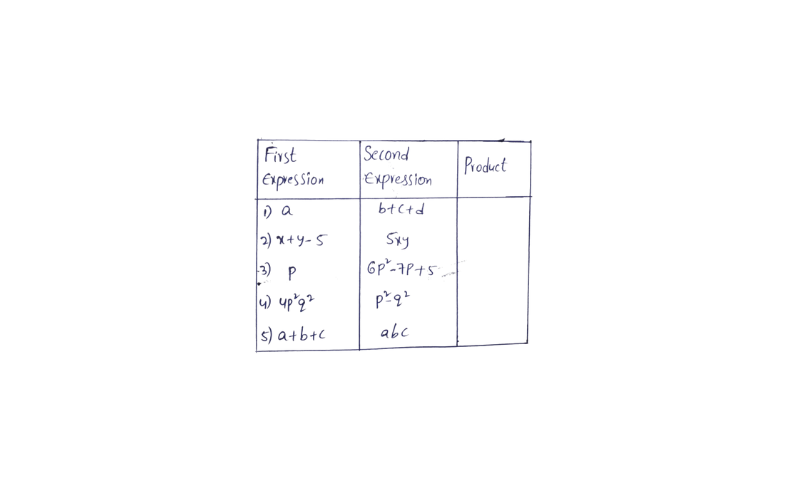
Solution:
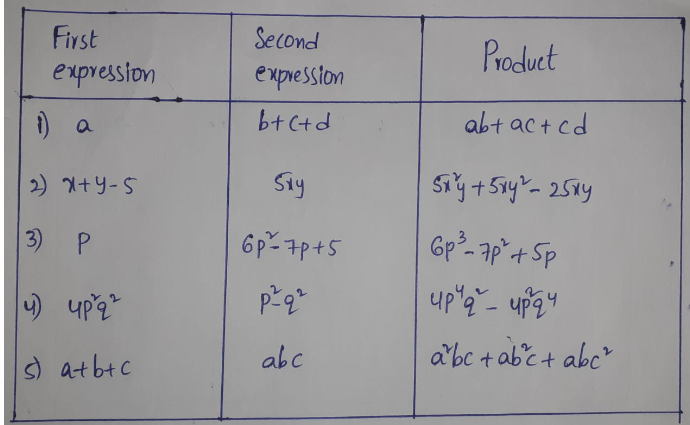
3. Find the product
1) \(\left(a^2\right) \times\left(2 a^{22}\right) \times\left(4 a^{26}\right)\)
Solution: \(2 \times 4 \times a^2 \times a^{22} \times a^{26}\)
=\(8 a^{50}\)
2) \(\left(\frac{2}{3} x y\right) \times\left(\frac{-9}{10} x^2 y^2\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(\frac{2}{3}\right) \times\left(\frac{-9}{10}\right) \times x \times y \times x^2 \times y^2\)
=\(\frac{-3}{5} x^3 y^3\)
3) \(\left(\frac{-10}{3} p q^3\right) \times\left(\frac{6}{5} p^3 q\right)\)
Solution: \(\frac{-10}{3} \times \frac{6}{5} \times p \times q^3 \times p^3 \times q\)
=\(-4 p^4 q^4\)
4) \(x \times x^2 \times x^3 \times x^4\)
Solution: \(x^{10}\)
4. a) Simplify 3x(4x-5)+3 and find its values for
1) x=3
2) \(x=\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution: \(3 x(4 x-5)+3\)
=\(
= [latex]12 x^2-15 x+3\)
1) For x=3,\(12 x^2-15 x+3\)
=\(12(3)^2-15(3)+3\)
=\(12 \times 9-15 \times 3+3\)
=\(108-45+3\)
= 66
2) For \(x=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(12 x^2-15 x+3\)= \(12 \times\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-15 \times \frac{1}{2}+3\)=\(12^3\times\frac{1}{4}-\frac{15}{2}+3\)
= \(3-\frac{15}{2}+3\)
= \(6-\frac{15}{2}=\frac{12-15}{2}\)
= \(\frac{-3}{2}\)
Kseeb 8th Maths Chapter 6 Exercise Solutions Step By Step
b) Simplify \(a\left(a^2+a+1\right)+5\) and find its value for
1) a=0
2) a=1
3) a= -1
Solution:
\( a\left(a^2+a+1\right)+5=a^3+a^2+a+5\)For a=1, \( a^3+a^2+a+5\)
⇒ \( 1^3+1^2+1+5=1+1+1+5=8\)
For a= -1, \( a^3+a^2+a+5\)
⇒ \( (-1)^3+(-1)^2+(-1)+5\)
= \( -1+1-1+5=4\)
5. a) Add: p(p-q), q(q-r) and r(r-p)
Solution: p(p-q)+q(q-r)+r(r-p)
= \(p^2-p q+q^2-q r+r^2-r p\)
= \(p^2+q^2+r^2-p q-q r-r p\)
b) Add: 2x(z-x-y) and 2y(z-y-x)
Solution: 2x(z-x-y)+2y(z-y-x)
= \(2 x z-2 x^2-2 x y+2 y z-2 y^2-2 x y\)
= \(-2 x^2-2 y^2-4 x y+2 y z+2 z x\)
c) 3l(l-4m+5n) from 4l(10n-3m+5n)
Solution: 4l(10n-3m+2l)-3l(l-4m+5n)
= \(40ln-12ml+8l^2-3l^2+12ml-15ln\)
= \(25ln+5l^2\)
d) Subtract: 3a(a+b+c)-2b(a-b+c) from 4c(-a+b+c)
Solution: \(4 c(a+b+c)-3 a(a+b+c)+2 b(a-b+c)\)
= \(-4 a c+4 b c+4 c^2-3 a^2-3 a b-3 a c+2 a b-2 b^2+2 b c\)
= \(-4 a c-3 a c+4 b c+2 b c-3 a b+2 a b+4 c^2-3 a^2-2 b^2\)
= \(-7 a c+6 b c-a b+4 c^2-3 a^2-2 b^2\)
Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities In KSEEB Maths Exercise 6.4
1. Multiply the binomials.
1) (2x+5) and (4x-3)
Solution: (2x+5)x(4x-3)
=2 x(4 x-3)+5(4 x-3)
=\(2 x \times 4 x-2 x \times 3+5 \times 4 x-5 \times 3\)
=\(8 x^2-6 x+20 x-15\)
=\(8 x^2+14 x-15\)
2) (y-8) and (3y-4)
Solution: (y-8)x(3y-4)
=\(y \times(3 y-4)-8(3 y-4)\)
=\(y \times 3 y-y \times 4-8 \times 3 y-8 \times(-4)\)
=\(3 y^2-4 y-24 y+32\)
=\(3 y^2-28 y+32\)
3) (2.5l-0.5m) and (2.5l+0.5m)
Solution: (2.5l-0.5m)x(2.5l+0.5m)
=2.5l(2.5l+0.5m)-0.5m(2.5l+0.5m)
=2.5l x 2.5l + 2.5l x 0.5m -0.5m x 2.5
= \(6.25l^2+1.25lm-1.25lm-0.25m^2\)
=\(6.25l^2-0.25m^2\)
4) (a+3b) and (x+5)
Solution: \((a+3 b) \times(x+5)\)
=\(a(x+5)+3 b(x+5)\)
=\(a x+a 5+3 b x+15 b\)
=\(a x+5 a+3 b x+15 b\)
5) \(\left(2 p q+3 q^2\right) \text { and }\left(3 p q-2 q^2\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(2 p q+3 q^2\right) \text { and }\left(3 p q-2 q^2\right)\)
= \(2 p q \times 3 p q-2 p q \times 2 q^2+3 q^2\times 3 p q-3 q^2 \times 2 q^2\)
= \(6 p^2 q^2-4 p q^3+9 p q^3-6 q^4\)
6) \(\left(\frac{3}{4} a^2+3 b^2\right) \text { and } 4\left(a^2-\frac{2}{3} b^2\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(2 p q+3 q^2\right) \times\left(3 p q-2 q^2\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{3}{4} a^2+3 b^2\right) \times\left(4 a^2-\frac{8}{3} b^2\right)\)
= \(\frac{3}{4} a^2\left(4 a^2-\frac{8 b^2}{3}\right)+3 b^2\left(4 a^2-\frac{8 b^2}{3}\right)\)
= \(\frac{3}{4} a^2 \times 4 a^2-\frac{\not \beta}{4} a^2 \times \frac{8^2}{\not 8} b^2+3 b^2\times 4 a^2-\frac{8}{3} b^2 \times \not 3 b^2\)
= \(3 a^4-2 a^2 b^2+12 a^2 b^2-8 b^4\)
= \(3 a^4+10 a^2 b^2-8 b^4\)
2. Find the Product
1) (5-2x)(3+x)
Solution: (5-2x)(3+x)
= 5(3+x)-2x(3+x)
= \(15+5 x-6 x-2 x^2\)
= \(15-x-2 x^2\)
2) (x+7y)(7x-y)
Solution: (x+7y)x(7x-y)
= x(7 x-y)+7 y(7 x-y)
= \(7 x^2-x y+49 x y-7 y^2\)
= \(7 x^2+48 x y-7 y^2\)
3) \(\left(a^2+b\right)\left(a+b^2\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2+b\right)\left(a+b^2\right)\)
= \(a^2\left(a+b^2\right)+b\left(a+b^2\right)\)
= \(a^3+a^2 b^2+a b+b^3\)
4) \(\left(p^2-q^2\right)(2 p+q)\)
Solution: \(\left(p^2-q^2\right) \times(2 p+q)\)
= \(p^2(2 p+q)-q^2(2 p+q)\)
= \(2 p^3+p^2 q-2 p q^2-q^3\)
3. Simplify
1) \(\left(x^2-5\right)(x+5)+25\)
Solution: \(\left(x^2-5\right)(x+5)+25\)
= \(x^2(x+5)-5(x+5)+25\)
= \(x^3+5 x^2-5 x-25+25\)
= \(x^3+5 x^2-5 x\)
2) \(\left(a^2+5\right)\left(b^3+3\right)+5\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2+5\right)\left(b^3+3\right)+5\)
=\(a^2\left(b^3+3\right)+5\left(b^3+3\right)+5\)
= \(a^2 b^3+3 a^2+5 b^3+15+5\)
= \(a^2 b^3+3 a^2+5 b^3+20\)
3) \(\left(t+s^2\right)\left(t^2-s\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(t+s^2\right) \times\left(t^2-s\right)\)
= \(t\left(t^2-s\right)+s^2\left(t^2-s\right)\)
= \(t^3-s t+s^2 t^2-s^3\)
4) \((a+b)(c-d)+(a-b)(c+d)+2(a c+b d)\)
Solution: \((a+b) \times(c-d)+(a-b) \times(c+d)+2(a c+b d)\)
= \(a(c-d)+b(c-d)+a(c+d)-b(c+d)+2(a c+b d)\)
= \(a c-a a+b c-b a+a c+a d-b c-b a+2 a c+2 b a\)
= 4ac
5) (x+y)(2 x+y)+(x+2 y)(x-y)
Solution: \((x+y) \times(2 x+y)+(x+2 y) \times(x-y)\)
= \(x(2 x+y)+y(2 x+y)+x(x-y)+2 y(x-y)\)
= \(2 x^2+y y+2 x y+y^2+x^2-y y+2 x y-2 y^2\)
= \(3 x^2-y^2+4 x y\)
6) \((x+y)\left(x^2-x y+y^2\right)\)
Solution: \((x+y)\left(x^2-x y+y^2\right)\)
= \(x\left(x^2-x y+y^2\right)+y\left(x^2-x y+y^2\right)\)
= \(x^3-y^2 y+y y^2+y^2 y-y y^2+y^3\)
= \(x^3+y^3\)
7) (1.5 x-4 y)(1.5 x+4 y+3)-4.5 x+12 y
Solution: (1.5 x-4 y)(1.5 x+4 y+3)-4.5 x+12 y
= 1.5 x(1.5 x+4 y+3)-4 y(1.5 x+4 y+3)-4.5 x+12 y
= \(2.25 x^2+6 x y+4.5 x-6 x y-16 y^2-12 y-4.5 x+12 y\)
= \(2.25 x^2-16 y^2\)
8) (a+b+c)(a+b-c)
Solution:(a+b+c)x(a+b-c)
= a(a+b-c)+b(a+b-c)+c(a+b-c)
= \(a^2+a b-\not c c+a b+b^2-b c+\not c c+b c-c^2\)
= \(a^2+b^2-c^2+2 a b\)
Practice For Algebraic Expressions and Identities KSEEB Maths Exercise 6.5
1. Use a suitable identity to get each of the following products.
1) (x+3)(x+3)
Solution: (x+3)(x+3)
\((x+3)^2\)a=x, b=3
\((a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\) \((x+3)^2=x^2+2 x \times 3+b^2\) \((x+3)^2=x^2+6 x+b^2\)2) (2y+5)(2y+5)
Solution: (2y+5)(2y+5)
= \((2y+5)^2\)
\((a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\) \((2 y+5)^2=(2 y)^2+2 \times 2 y \times 5+5^2\)= \(4 y^2+20 y+25\)
3) (2a-7)(2a-7)
Solution: (2a-7)(2a-7)
\((2 a-7)^2\) \((a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\) \((2 a-7)^2=(2 a)^2-2 \times 2 a \times 7+7^2\)=\(4 a^2-28 a+49\)
Karnataka Board Class 8 Maths Algebraic Expressions Problems And Answers
4) \(\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\) \((a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\) \(\left(3 a-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=(3 a)^2-2 \times 3 a \times \frac{1}{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)=\(9 a^2-3 a+\frac{1}{4}\)
5) (1.1 m-0.4)(1.1 m+0.4)
solution: (1.1 m-0.4)(1.1 m+0.4)
\((a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2\)(1.1 m-0.4)(1.1 m+0.4)
= \((1.1 m)^2-(0.4)^2\)
= \(1.21 m^2-0.16\)
6) \(\left(a^2+b^2\right)\left(-a^2+b^2\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2+b^2\right)\left(-a^2+b^2\right)\)
= \(\left(a^2+b^2\right)\left(b^2-a^2\right)\)
= \(\left(b^2+a^2\right)\left(b^2-a^2\right)\)
=\(\left(b^2\right)^2-\left(a^2\right)^2\left\{(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2\right\}\)
= \(b^4-a^4\)
7) (6x-7)(6x+7)
Solution: (6x-7)(6x+7)
= \((6 x)^2-7^2 \quad\left\{(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2\right\}\)
= \(36 x^2-49\)
8) (-a+c)(-a+c)
Solution: (-a+c)(-a+c)
= (c-a)(c-a)
= \((c-a)^2 \quad\left\{(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \(c^2-2 \times c \times a+a^2\)
= \(c^2-2 a c+a^2\)
9) \(\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)^2 \quad\left\{(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \(\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)^2+\not 2\left(\frac{x}{\not 2}\right)\left(\frac{3 y}{4}\right)+\left(\frac{3 y}{4}\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{x^2}{4}+\frac{3 x y}{4}+\frac{9 y^2}{16}\)
10) (7a-9b)(7a-9b)
Solution: (7a-9b)(7a-9b)
\((7 a-9 b)^2 \quad\left\{(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \((7 a)^2-2 \times 7 a \times 9 b+(9 b)^2\)
= \(49 a^2-126 a b+81 b^2\)
2. Use the identity \((x+a)(x+b) = x^2+(a+b) x+a b\) to find the following products.
1) (x+3)(x+7)
Solution: (x+3)(x+7)
\((x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b) x+a b\)
a=3 b=7
\((x+3)(x+7)=x^2+(3+7) x+3 \times 7\)
= \(x^2+10 x+21\)
2) (4x+5)(4x+1)
Solution: (4x+5)(4x+1)
x=4x, a=5, b=1
\((x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b) x+a b\)
\((4 x+5)(4 x+1)=(4 x)^2+(5+1)(4 x)+5 \times 1\)
= \(16 x^2+24 x+5\)
3) (4x-5)(4x-1)
Solution: (4x-5)(4x-1)
= \((4 x)^2+(5-1)(4 x)+5(-1)\)
= \(16 x^2+16 x-5\)
4)(4x+5)(4x-1)
Solution: (4x+5)(4x-1)
= \((4 x)^2+(5-1)(4 x)+5(-1)\)
= \(16 x^2+16 x-5\)
5) (2x+5y)(2x+3y)
Solution: \((2x+5y)(2x+3y)\)
= \(2 x)^2+(5 y+3 y)(2 x)+(5 y)(3 y)\)
= \(4 x^2+(8 y)(2 x)+15 y^2\)
= \(4 x^2+16 x y+15 y^2\)
6) \(\left(2 a^2+9\right)\left(2 a^2+5\right)\)
Solution: \(\left(2 a^2+9\right)\left(2 a^2+5\right)\)
= \(\left(2 a^2\right)^2+(9+5)\left(2 a^2\right)+9 \times 5\)
= \(4 a^4+28 a^2+45\)
7) (xyz-4)(xyz-2)
Solution: (xyz-4)(xyz-2)
= \((x y z)^2+(-4-2)(x y z)+(-4)(-2)\)
= \(x^2 y^2 z^2-6 x y z+8\)
3. Find the following squares by using the identities.
1) \((b-7)^2\)
Solution: \((b-7)^2\)
= \(b^2-2 \times b \times 7+7^2\)
\((a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\)
= \(b^2-14 b+49\)
2) \((x y+3 z)^2\)
Solution: \((x y+3 z)^2\)
\(\left\{(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \((x y)^2+2(x y)(3 z)+(3 z)^2\)
= \(x^2 y^2 z^2+6 x y z+9 z^2\)
3)\(\left(6 x^2-5 y\right)^2\)
Solution: \(\left(6 x^2-5 y\right)^2\)
\((a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\)
= \(\left(6 x^2\right)^2-2\left(6 x^2\right)(5 y)+(5 y)^2\)
= \(36 x^4-60 x^2 y+25 y^2\)
4) \(\left(\frac{2}{3} m+\frac{3}{2} n\right)^2\)
Solution: \(\left(\frac{2}{3} m+\frac{3}{2} n\right)^2\)
\(\left\{(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \(\frac{4}{9} m^2+2 m n+\frac{9}{4} n^2\)
5) \((0.4 p-0.5 q)^2\)
Solution: \((0.4 p-0.5 q)^2\)
\((a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\)
= \((0.4 p)^2-2 \times 0.4 p \times 0.5 q+(0.5 q)^2\)
= \(0.16 p^2-0.4 p q+0.25 q^2\)
6) \((2 x y+5 y)^2\)
Solution: \((2 x y+5 y)^2\)
\(\left\{(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \((2 x y)^2+2(2 x y)(5 y)+(5 y)^2\)
= \(4 x^2 y^2+20 x y^2+25 y^2\)
4. Simplify
1) \(\left(a^2-b^2\right)^2\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2-b^2\right)^2\)
\((a-b)^2=a^2-2b+b^2\)
= \(\left(a^2\right)^2-2 \times a^2 \times b^2+\left(b^2\right)^2\)
= \(a^4-2 a^2 b^2+b^4\)
2) \((2 x+5)^2-(2 x-5)^2\)
Solution: \((2 x+5)^2-(2 x-5)^2\)
\(\begin{aligned}
& (a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2 \\
& (a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2
\end{aligned}\)
\(\left\{(2 x)^2+2 \times 2 x \times 5+5^2\right\}-\left\{(2 x)^2-2 \times 2 x \times 5+5^2\right\}\)
= \(\left(4 x^2+20 x+25\right)-\left(4 x^2-20 x+25\right)\)
= \(4 x^2+20 x+25-4 x^2+20 x-25\)
= 40x
3) \((7 m-8 n)^2+(7 m+8 n)^2\)
Solution: \((7 m-8 n)^2+(7 m+8 n)^2\)
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2 \\
(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
\(\left\{(7 m)^2-2 \times 7 m \times 8 n+(8 n)^2\right\}+\left\{(7 m)^2+2(7 m)(8 n)+(8 n)^2\right\}\)
= \(49 m^2-112 m n+64 n^2+49 m^2+112 m n+64 n^2\)
= \(98 m^2+128 n^2\)
4) \((4 m+5 n)^2+(5 m+4 n)^2\)
Solution: \((4 m+5 n)^2+(5 m+4 n)^2\)
=\(\left\{(4 m)^2+2 \times 4 m \times 5 n+(5 n)^2\right\}+\left\{(5 m)^2+2(5 m)(4 n)+(4 n)^2\right\}\)
= \(16 m^2+40 m n+25 n^2+25 m^2+40 m n+16 n^2\)
= \(41 m^2+80 m n+41 n^2\)
5) \((2.5 p-1.5 q)^2-(1.5 p-2.5 q)^2\)
Solution: \((2.5 p-1.5 q)^2-(1.5 p-2.5 q)^2\)
\(\left\{(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
= \(\left\{(2.5) p^2-2(2.5 p)(1.5 q)+(1.5 q)^2\right\}-\left\{(1.5 p)^2-2(1.5 p)(2.5 q)+(2.5 q)^2\right\}\)
= \(\left(6.25 p^2-7.5 p q+2.25 q^2\right)-\left(2.25 p^2-7.5 p q+6.25 q^2\right)\)
= \(6.25 p^2-7.5 p q+2.25 q^2-2.25 p^2+75 p q-6.25 q^2\)
= \(4 p^2-4 q^2\)
6) \((a b+b c)^2-2 a b^2 c\)
Solution: \((a b+b c)^2-2 a b^2 c\)
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((a b)^2+2(a b)(b c)+(b c)^2-2 a b^2 c\)
= \(a^2 b^2+2 a b^2 c+b^2 c^2-2 a b^2 c\)
= \(a^2 b^2+b^2 c^2\)
7) \(\left(m^2-n^2 m\right)^2+2 m^3 n^2\)
Solution: \(\left(m^2-n^2 m\right)^2+2 m^3 n^2\)
\(\left\{(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right\}\)
=\(\left(m^2\right)^2-2 \times m^2 \times n^2 m+\left(n^2 m\right)^2+2 m^3 n^2\)
= \(m^4-2 m^3 n^2+n^4 m^2+2 m^3 n^2\)
= \(m^4+n^4 m^2\)
5. Show that
1) \((3 x+7)^2-84 x=(3 x-7)^2\)
Solution: LHS = \((3 x+7)^2-84 x\)
= \((3 x)^2+2 \times 3 x \times 7+7^2-84 x\)
= \(9 x^2+42 x+49-84 x\)
= \(9 x^2-42 x+49\)
RHS = \((3 x-7)^2\)
= \((3 x)^2-2 \times(3 x)(7)+7^2\)
= \(9 x^2-42 x+49\)
∴ LHS=RHS
2) \((9 p-5 q)^2+180 p q=(9 p+5 q)^2\)
Solution: LHS = \((9 p-5 q)^2+180 p q\)
= \((9 p)^2-2 \times 9 p(5 q)+(5 q)^2+180 p q\)
= \(81 p^2-90 p q+25 q^2+180 p q\)
= \(81 p^2+90 p q+25 q^2\)
RHS = \((9 p+5 q)^2\)
= \((9 p)^2+2 \times 9 p \times 5 q+(5 q)^2\)
= \(81 p^2+90 p q+25 q^2\)
∴LHS=RHS
3) \(\left(\frac{4}{3} m-\frac{3}{4} n\right)^2+2 m n=\frac{16}{9} m^2+\frac{9}{16} n^2\)
Solution: LHS = \(\left(\frac{4}{3} m-\frac{3}{4} n\right)^2+2 m n\)
= \(\frac{16}{9} m^2-2 m n+\frac{9 n^2}{16}+2 m n\)
= \(\frac{16}{9} m^2+\frac{9 n^2}{16}\)
RHS = \(\frac{16}{9} m^2+\frac{9}{16} n^2\)
∴ LHS = RHS
4) \((4 p q+3 q)^2-(4 p q-3 q)^2=48 p q^2\)
Solution: LHS =\((4 p q+3 q)^2-(4 p q-3 q)^2\)
= \(\left\{(4 p q)^2+2(4 p q)(3 q)+(3 q)^2\right\}-\left\{(4 p q)^2-2(4 p q)(3 q)+(3 q)^2\right\}\)
= \(16 p^2 q^2+24 p q^2+9 q^2-16 p^2 q^2+24 p q^2-9 q^2\)
= \(48 p q^2\)
RHS = \(48 p q^2\)
∴ LHS = RHS
5) (a-b)(a+b)+(b-c)(b+c)+(c-a)(c+a)=0
Solution: LHS = (a-b)(a+b)+(b-c)(b+c)+(c-a)(c+a)=0
= \(\left(a^2-b^2\right)+\left(b^2-c^2\right)+\left(c^2-a^2\right)\)
= \(a^2-b^2+b^2-c^2+c^2-a^2\)
=0
=RHS =0
∴ LHS = RHS
6. Using identities, evaluate
1) \(71^2\)
Solution: \(71^2=(70+1)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((70)^2+2 \times 70 \times 1+1^2\)
= 4900+140+1
= 5041
2) \(99^2\)
Solution: \((99)^2=(100-1)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((100)^2-2 \times 100 \times 1+1^2\)
= 10000-200+1
= 9801
3)\(102^2\)
Solution: \((102)^2=(100+2)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((100)^2+2 \times 100 \times 2+2^2\)
= 10000+400+4
= 10404
4) \(998^2\)
Solution: \((998)^2=(1000-2)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((1000)^2-2 \times 1000 \times 2+2^2\)
= 1000000-4000+4
= 996004
5) \(5.2^2\)
Solution: \((5.2)^2=(5.0+0.2)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((5.0)^2+2 \times 5.0 \times 0.2+(0.2)^2\)
= 25+2+0.04
= 27.04
How To Solve Algebraic Expressions In Class 8 Kseeb Maths
6) 297 x 303
Solution: 297 x 303
= (300-3)(300+3)
= \((300)^2-(3)^2\)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= 90000-9
= 89991
7) 78 x 82
Solution: 78 x 82
= (80-2)(80+2)
=\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((80)^2-2^2\)
= 6400-4
= 6396
8) \(8.9^2\)
Solution: \((8.9)^2=(9.0-0.1)^2\)
= \((9.0)^2-2 \times(9.0)(0.1)+(0.1)^2\)
= 81-1.8+0.01
= 79.21
9) 10.5 x 9.5
Solution: (10.5)(9.5)
= (10+0.5)(10-0.5)
= \((10)^2-(0.5)^2\)
= 100-0.25
= 99.75
7. Using \(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\) find
1) \(51^2-49^2\)
Solution: \((51)^2-(49)^2\)
= (51+49)(51-49)
= 100 x 2
= 200
2) \((1.02)^2-(0.98)^2\)
Solution: \((1.02)^2-(0.98)^2\)
= (1.02+0.98)(1.02-0.98)
= 2 x 0.04
= 0.08
3) \(153^2-147^2\)
Solution: (153+147)(153-147)
= 300 x 6
= 1800
4) \((12.1)^2-(7.9)^2\)
Solution: \((12.1)^2-(7.9)^2\)
= (12.1+7.9)(12.1-7.9)
= 20 x 4.2
= 84
8. Using \((x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b) x+a b\), find
1) 103 x 104
Solution: 103 x 104
= (100+3)(100+4)
= \(100^2+(3+4)(100)+3 \times 4\)
= 10000+700+12
= 10712
2) 5.1 x 5.2
Solution: \((5.1) \times(5.2)=(5+0.1)(5+0.2)\)
= \(5^2+(0.1+0.2) 5+(0.1 \times 0.2)\)
= 25+1.5+0.02
= 26.52
3)103 x 98
Solution: \((103) \times(98)\)
= (100+3)(100-2)
= \(100^2+(3-2) \times 100+(3)(-2)\)
= 10000+100-6
= 10094
4) 9.7 x 9.8
Solution: 9.7 x 9.8
= (10-0.3)(10-0.2)
= \(10^2+(-0.3-0.2) 10+(-0.3)(-0.2)\)
= 100 – (0.5 x 10) + 0.06
= 100 – 5 + 0.06
= 95.06
Algebraic Expressions And Identities Questions And Answers KSEEB Maths Additional Problems
1. Subtract \(6 x^2-4 x y+5 y^2\) from \(8 y^2+6 x y-3 x^2\)
Solution:

2. Using suitable identity, evaluate
\((69.3)^2-(30.7)^2\)
Solution: \((69.3)^2-(30.7)^2\)
= (69.3+30.7)(69.3-30.7)
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
a^2-b^2 \\
=(a+b)(a-b)
\end{array}\right\}\)
= 100 x 38.6
= 3860
3. Add: 9ax, 3by-cz and -5by+ax+3cz
Solution: 9ax+3by-cz-5by7+ax+3cz
= 10ax-2by+2cz
4. Expand the following, using suitable identities
1) \(\left(\frac{4 x}{5}+\frac{y}{4}\right)\left(\frac{4 x}{5}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\)
Solution: \((x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b) x+a b\)
\(\left(\frac{4 x}{5}+\frac{y}{4}\right)\left(\frac{4 x}{5}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{4 x}{5}\right)^2+\left(\frac{y}{4}+\frac{3 y}{4}\right)\left(\frac{4 x}{5}\right)+\frac{y}{4} \times \frac{3 y}{4}\)
= \(\frac{16 x^2}{25}+\frac{16^4 x y}{4 \times 5}+\frac{3 y^2}{16}\)
= \(\frac{16 x^2}{25}+\frac{4 x y}{5}+\frac{5}{16} y^2\)
2) \((0.9 p-0.5 q)^2\)
Solution: \((0.9 p)^2-2 \times 0.9 p \times 0.5 q+(0.5 q)^2\)
= \(0.81 p^2-0.90 p q+0.25 q^2\)
5. Evaluate \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\right)^2\) using identity
Solution: \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\right)^2=\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^2+2 \times \frac{a}{b} \times \frac{b}{a}+\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)^2\)
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a+b)^2 \\
=a^2+2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
=\(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+2+\frac{b^2}{a^2}\)
6. Evaluate: \((\sqrt{5} a+\sqrt{3} b)^2\)
Solution: =\((\sqrt{5} a)^2+(\sqrt{3} b)^2+2 \times \sqrt{5} \times a \times \sqrt{3} \times b\)
= \(5 a^2+3 b^2+2 \sqrt{15} a b\)
= \(5 a^2+3 b^2+2 \sqrt{15} a b\)
\((\sqrt{5} a+\sqrt{3} b)^2=5 a^2+3 b^2+2 \sqrt{15} a b\)
7. Subtract the sum of \( 3l-4m-7n^2 and 2l+3m-4n^2 from the sum of 9l+2m-3n^2 and -3l+m+4n^2\)
Solution:
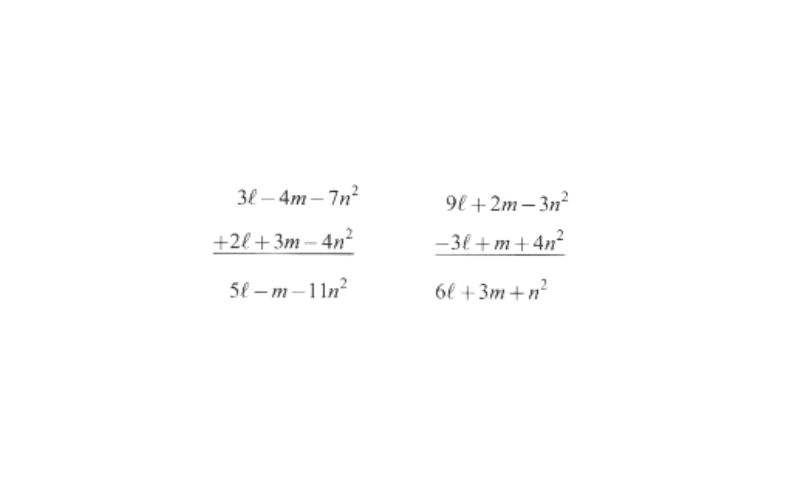
Subtracting \(5l-m-11n^2 from 6l+3m+n^2 we get\)
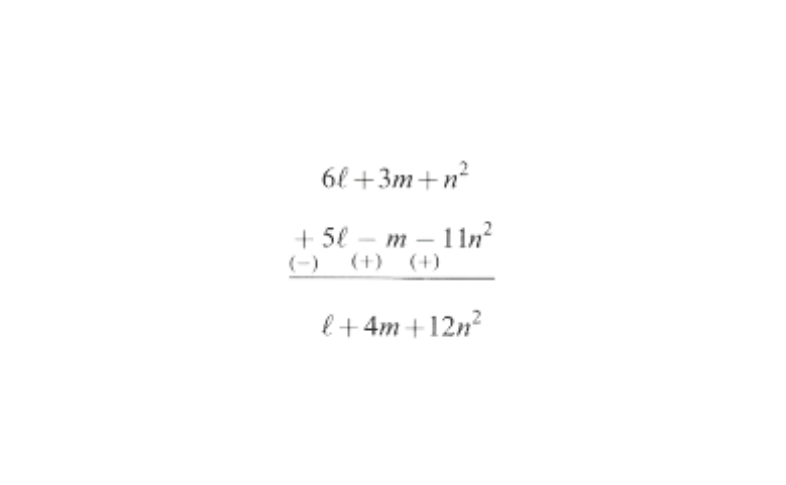
8. Subtract 7p(3q+7p) from 8p(2p-7q)
Solution: 8p(2p-7p)-7p(3q+7p)
= \(16 p^2-56 p q-21 p q-49 p^2\)
= \(-33 p^2-77 p q\)
9. Simplify \((ab-c)^2\)
Solution: \((ab-c)^2+2abc\)
= \((a b)^2-2 \times a b \times c+c^2+2 a b c\)
= \(a^2 b^2-2 a b c+c^2+2 a b c\)
= \(a^2 b^2+c^2\)
10. Expand (2x+9)(2x-7) using identity
Solution: (2x+9)(2x-7)
= \((2 x)^2+(9-7)(2 x)+(9)(-7)\)
= \(4 x^2+4 x-63\)
11. Expand: \((49)^2\)
Solution: \((49)^2=(50-1)^2\)
\(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
(a-b)^2 \\
=a^2-2 a b+b^2
\end{array}\right\}\)
= \((50)^2-2 \times 50 \times 1+1^2\)
= 2500-100+1
= 2400+1
= 2401
12. Write the greatest common factor in each of the following.
1) \(2 x y,-y^2, 2 x^2 y\)
Solution: \(2 x y,-y^2, 2 x^2 y\)
\(2 x y=2 \times x \times y\) \(-y^2 = -y x y\) \(2 x^2 y=2 \times x \times x \times y\)G.C.F = y-16
2) \(3 x^3 y^2 z,-6 x y^3 z^2, 12 x^2 y z^3\)
Solution: \(3 x^3 y^2 z,-6 x y^3 z^2, 12 x^2 y z^3\)
\(3 x^3 y^2 z=3 \times x \times x \times x \times y \times y \times z\) \(-6 x y^3 z^2=-3 \times 2 \times x \times y \times y \times y \times z \times z\) \(12 x^2 y z^3=2 \times 2 \times 3 \times x \times x \times y \times z \times z \times z\)G.C.F = 3xyz
13. Multiply the binomials
a) (2x+5)(4x-3)
Solution: (2x+5)(4x-3)
= 2x(4x-3)+5(4x-3)
= 2x x 4x +2x(-3)+5 x 4x + 5(-3)
= \(8 x^2-6 x+20 x-15\)
= \(8 x^2+14 x-15\)
14. Find the areas of rectangles with the following pairs of monomials as their lenghts and breadths respectively.
Solution: W.K.T. Area of rectangle = Length x Breadth
Area of 1st rectangle = \(3mn x 4np = 12mn^2p\)
Area of 2nd reactangle =\(4 x \times 3 x^2=12 x^3\)
15. If \(a+\frac{1}{a}=7, find a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\)
Solution: Consider \(a+\frac{1}{a}=7\) square bothside, we get
\(\left(a+\frac{1}{a}\right)^2=7^2\) \(a^2+2 \times a+\frac{1}{a}+\left(\frac{1}{a}\right)^2=49\) \(a^2+2+\frac{1}{a^2}=49\) \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}=49-2=47\) \(\text { ie } a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}=47\)16. Multiply \(x^2+2 y \text { by } x^3-2 x y+y^3 and find the value of the product for x=1 and y= -1\)
Solution: \(\left(x^2+2 y\right)\left(x^3-2 x y+y^3\right)\)
= \(x^2\left(x^3-2 x y+y^3\right)+2 y\left(x^3-2 x y+y^3\right)\)
= \(x^5-2 x^3 y+x^2 y^3+2 x^3 y-4 x y^2+2 y^4\)
= \(x^5+x^2 y^3-4 x y^2+2 y^4\)
put x=1 & y= -1
= \((1)^5+(1)^2(-1)^3-4(1)(-1)^2+2(-1)^4\)
= 1+(1)(-1)-4(1)(1)+2(1)
= 1-1-4+2 = -2
17. If \(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=38\), find the values of
1) \(x-\frac{1}{x}\)
2) \(x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}\)
Solution:
1)\(\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)^2=x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}-2 \times x \times \frac{1}{x}\)
= \(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}-2=38-2=36\)
∴ \(x-\frac{1}{x}=\sqrt{36}=6\)
2)\(\left(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\right)^2=x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}+2 \times x^2 \times \frac{1}{x^2}\)
\((38)^2=x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}+2\)= \(1444-2=x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}\)
∴ \(x^4+\frac{1}{x^4}=1442\)
18. Find the area of the reactangle whose length and breadths are \(3 x^2 y m and 5 x y^2 m\) respectively.
Solution: Length = \(3 x^2 y m\), breadth = \(5 x y^2m\)
Area of rectangle = length x breadth
= \(3 x^2 y \times 5 x y^2 \text { sq m }\)
= \(15 x^3 y^3 \text { sq } \mathrm{m}\)
19. Find the value of the expression \(\left(81 x^2+16 y^2-72 x y\right) \text {, when } x=\frac{2}{3} \& y=\frac{3}{4}\)
Solution: \(\left(81 x^2+16 y^2-72 x y\right)\)
= \((9 x)^2+(4 y)^2-2 \times 9 x+4 y\)
= \((9 x-4 y)^2\)
= \(\left(9 \times \frac{2}{3}-4 \times \frac{3}{4}\right)^2 \text {, when } x=\frac{2}{3} \& y=\frac{3}{4}\)
= \((6-3)^2=3^2=9\)
