Karnataka Board Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Synopsis
Cell division is a process by which a cell duplicates for the growth and reproduction of an organism.
- Virchow proposed that new cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. This is called cell lineage theory
- Somatic cells divide by a process of mitosis while the germ cells divide by a process called meiosis (reduction division).
- In mitosis, daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Duplication of DNA molecules and doubling of chromosomal constituents are observed during the S – phase of interphase.
- Mitosis includes karyokinesis and cytokinesis. Karyokinesis occurs in four stages.
- During prophase nucleolus and nuclear membrane, disappear. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, each having two chromatids.
Karnataka Board Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle and Cell Division notes
During metaphase, spindle fibers are formed. Spindle fibers attach to the centromere of chromosomes. Chromosomes move to the center of the spindle.
- In Anaphase centromere divides. Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles.
- In Telophase nucleolus and nuclear membrane reappear. Chromosomes decondense into chromatin. Two daughter nuclei are formed.
- Cytokinesis is by cell plate method. Two daughter cells are formed.
- In meiosis, karyokinesis and cytokinesis occur two times.
- Meiosis I is a reductional division.
- Prophase I is the longest stage and is divided into 5 stages.
- In leptotene, chromosomes become distinct being quite long and uncoiled.
- In zygotene, pairing of homologous chromosomes – synapsis occurs.
- In pachytene, an exchange of genetic material (crossing over) occurs between non-sister chromatids of the bivalent.
- In diplotene, repulsion starts between homologous. Chiasmata show terminalisation process.
- In diakinesis, the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear.
- In metaphase 1, the bivalents come to lie at the equator
Class 11 Karnataka Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division Q&A
In anaphase 1, homologous chromosomes separate. Each chromosome of a pair moves to opposite poles of the spindle.
- Each chromosome of a pair moves to opposite poles of the spindle.
- Information Telophase 1 reappearance of nuclide and nuclear membrane results in the formation of two haploid nuclei.
- The events Four of meiosis 2 are similar to mitotic division. Thus it is an equational division. Four haploid cells are formed. The daughter cells produced are called gametes or spores
- Crossing and over evolution results in exchange species. of genetic information between individuals

Cell Cycle And Cell Division Very Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Between a prokaryote and a eukaryote, which cell has a shorter cell division time?
Answer:
- A prokaryotic cell has a shorter cell division time due to a shorter cell cycle.
- For instance, the bacterial cell cycle is 20 minutes as compared to 90 minutes of cell cycle in yeast.
Question 2. Among prokaryotes and eukaryotes, which one has a shorter duration of cell cycle?
Answer:
- Prokaryotes
- Bacteria (prokaryote) cell cycle is 20 minutes and in human cells (Eukaryote) it is 24 hours.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Karnataka Board Class 11 important questions
Question 3. Which of the phases of the cell cycle is of the longest duration?
Answer:
- Interphase
- In the human cell cycle of 24 hours, the interphase lasts for 23 hours (about 95% of the total duration).
Question 4. Which tissue of animals and plants exhibits meiosis?
Answer:
- Reproductive tissue – Gamete mother cells.
- Diploid cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid sex cells.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division For Class 11 Karnataka
Question 5. Given that the average duplication time of E.coli is 20 minutes. How much time will two E.coli cells take to become 32 cells?
Answer:
- 80 minutes.
- It takes 4 cell divisions to form 32 cells from the initial 2 cells.
Question 6. Which part of the human body should one use to demonstrate stages of mitosis?
Answer:
The cells of the upper layer of the epidermis, cells of the lining of the gut, and blood cells (bone marrow). The above cells of the human body are being constantly replaced.
Question 7. What attributes does a chromatid require to be classified chromosome?
Answer:
Two chromatids are attached to the centromere.
Question 8. Which of the four chromatids of a bivalent at prophase – 1 of meiosis can be involved in cross-over?
Answer:
- Nonsister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes (a bivalent).
- Crossing over occurs in the pachytene stage of Prophase – 1 in Meiosis
Question 9. If the tissue has at a given time 1024 cells, how many cycles of mitosis, had the original parental single cell undergone?
Answer:
- Cycles of mitosis,
- Mitosis Is equatorial cell division and the doubling of cell number occurs per cell division.
Question 10. An anther has 1200 pollen grains. How many pollen mother cells must have been there to produce them?
Answer:
- 300 pollen mother cells.
- Due to meiosis, each PMC produces 4 pollen grains.
Question 11. At what stage of the cell cycle does DNA synthesis occur?
Answer:
- S or Synthetic phase of Interphase.
- During S phase 2C DNA increases to 4C DNAnswer:
Question 12. One cycle of cell division in human cells (eukaryotic cells) takes 24 hours. Which phase of the cycle, do you think occupies the maximum part of the cell cycle?
Answer:
- Interphase occupies the maximum time i.e., 23 hours.
- It is about 95% of the total duration of the cell cycle in human cells.
Question 13. It is observed that heart cells do not exhibit cell division. Such cells do not divide further and exit phase to enter an inactive stage called
Answer:
- G phase
- Quiescent stage (Go)
Karnataka PUC 1 Biology Cell Cycle and Cell Division solved questions
Question 14. Identify the substages of prophase – 1 in Meiosis in which synapsis and desynapsis are formed.
Answer:
- Synopsis (pairing of homologous chromosomes) occurs in the zygotene substage of prophase – 1 in meiosis.
- Desynapsis (separation of homologous chromosomes) occurs in the Diplotene substage of prophase – 1 in meiosis. of cell cycle. Fill in the blanks.
Question 15. Name the stage of meiosis in which actual reduction in chromosome number occurs.
Answer:
- Anaphase – 1 in Meiosis I
- During this stage, homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles.
Question 16. Mitochondria and plastids have their DNA (genetic material). What is their fate during nuclear division like mitosis?
Answer:
- Mitochondria and plastids have no role during the nuclear division of mitosis.
- At the time of cytoplasmic division, mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the two daughter cells.
Question 17. A cell has 32 chromosomes. It undergoes mitotic division. What will be the chromosome number during metaphase? What would be the DNA content (C) during anaphase?
Answer:
- The chromosome number in the cell at the metaphase of mitosis is 32 only. But each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids.
- In anaphase, two sister (daughter) chromatids of a chromosome are separated and move to opposite poles. Each of the separated chromatids consists of 2C and DNA.
Question 18. While examining the mitotic tissue, one finds some cells with 16 chromosomes and some with 32 chromosomes. what possible reasons could you give for this difference in chromosomes that could have arisen from cells with 32 chromosomes or vice versa?
Answer:
- In mitosis cells at prophase and metaphase consist of basic sets of chromosomes, i.e., in this case, 2m = 16.
- But at anaphase splitting of two sister (daughter) chromatids of a chromosome leads to a doubling of number i.e., 32 that distribute equally (16 each) among two daughter cells formed from a mother cell.
Question 19. The following events occur during the various phases of the cell cycle. Fill in the blanks with a suitable answer against each.
- Disintegration of nuclear membrane _______________________
- Appearance of nucleolus _______________________
- Division of centromere _______________________
- Replication of DNA _______________________
Answer:
- Prophase
- Telophase and Interphase.
- Anaphase
- S (Synthesis) phase in Interphase.
Question 20. Two key events take place during the s-phase in animal cells – DNA replication and duplication of centriole. In which parts of the cell do these events occur?
Answer:
- DNA replication occurs in chromosomes present in the nucleus during the s-phase of Interphase.
- Centriole duplication occurs in the cytoplasm.
Question 21. Name a cell that is found arrested in the diplotene stage for months and years. Comment in two or three sentences, how it completes cell cycle.
Answer:
- Oocytes of some vertebrates, diplotene can last for months or years.
- Terminalizationofchiasmataoccursin diakinesis and homologous chromosomes separated. Subsequently, cell enters into other stages of MeiosisI for the reduction of chromosome number
- Meiosis 2 results in the formation of 4 daughter cells each with a haploid chromosome set.
Question 22. Name a stain commonly used to color chromosomes.
Answer: Acetocarmine
Question 23. Name the pathological condition when uncontrolled cell division
Answer: Cancer
Karnataka Board Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 question and answers PDF
Question 24. Meiosis has events that lead to both gene recombinations as well as Mendelian recombinations! Discuss,
Answer:
Both chiasmata and crossing over occur between non-sister chromatids. Due to crossing over, genetic recombinations are caused. During Anaphase – 1 of meiosis – 1, Mendelian recombination takes place.
Question 25. Both unicellular and multicellular organisms undergo mitosis. What are the differences, if any, observed between the two processes?
Answer:
In unicellular organisms, a cell divides into two halves by binary fission. Stages like Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase are present in multicellular organisms. It’s not present in unicellular organisms
Karnataka Board Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Short Question And Answers
Question 1. In which phase of meiosis are the following forms? Choose the answers given below
- Synaptonemal complex ________________________
- Recombination nodules _______________________
- Appearance/activation of _______________________
- Termination of chiasmata _______________________
- Interkinesis _______________________
- Formation of dyad of cells. _______________________
Answer:
- Synaptonemal complex – Zygotene
- Recombination nodules- Pachytene
- Appearance/ activation of Pachytene Enzyme recombinase
- Termination of chiasmata – Diakinesis
- Interkinesis- After Telophase – 1 / Before Meiosis – II
- Formation of the dyad of cells – Telophase – 1 / After Meiosis – 1
Question 2. Mitosis results in the production of two cells that are similar to each other. What would be the consequence if each of the following irregularities occurs during mitosis?
- The nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate.
- Duplication of DNA does not occur.
- Centromeres do not divida.
- Cytokinesis does not occur.
Answer:
- If the nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate chromosomes cannot spread through the cytoplasm of the cell. Metaphase cannot take place.
- If Duplication of DNA does not occur equal number of chromosomes cannot enter into daughter cells, resulting in a variable number of chromosomes.
- If centromeres do not divide chromatids cannot move to opposite poles, then daughter cells have the same chromosome number with two chromatids.
- If cytokinesis does not occur then after cell division each cell contains two nuclei. Resulting in multinucleate condition.
Question 3. Comment on the statement “Meiosis enables the conservation of specific chromosome number of each species even though the process per second, results in a reduction of chromosome number.
Answer:
- Meiosis is the mechanism, by which chromosome number is reduced to half in sexually reproducing organisms.
- Enzyme recombinase
- Meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells (sex cells or gametes) from a diploid mother cell.
- Fertilization or union of sex cells again gives rise to diploid (2n) organisms.
- So, Meiosis is the mechanism, by which the conservation of the specific chromosome number of each species is achieved across generations.
- It also increases the genetic variability in the population of organisms from one generation to the next, which leads to evolution.
Question 4. How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer:
- Cytokinesis refers to the division of a mother cell into 2 daughter cells.
- This occurs after the Karyokinesis, the division of a mother nucleus into 2 daughter nuclei.
- In an animal cell, cytokinesis is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane.
- The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the center, dividing the cell cytoplasm into two.
- Plant cells are enclosed by a relatively inextensible (rigid) cell wall.
- So in those cells, wall formation starts in the center of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls.
Question 5. Which division is necessary to maintain constant chromosome number in all body cells of multicellular organisms and why?
Answer:
- Cell division Meiosis is necessary to maintain constant chromosome numbers in all body cells of multicellular organisms.
- The reason is mitosis divides and forms two daughter cells which are similar to the parent cell.
- The chromosome number remains constant in all the cells.
- Growth occurs due to mitosis.
- Mitosis also helps in cell repair and growth.
Question 6. Though redundantly described as a resting phase, the interphase does not involve rest. Comment.
Answer:
In the cell cycle, the stage at which the nucleus is not in a state of division is called interphase. It occurs between two successive divisions. During interphase, the cell prepares for division by undergoing growth as well as DNA replication in an orderly manner, though considered as the resting phase.
Based on biochemical studies, interphase is subdivided into 3 stages :
- G1: phase,
- S: phase, and
- G2 phase.
These are
- G1: phase: Cell increases in size, RNA and proteins are synthesized in large quantity
- S phase: DNA replication occurs and its content increases to 4c from 2c.
- G2 phase: Synthesis of proteins and RNA is continued. Various cell Organelles are newly synthesized. The proteins and energy pools associated with the structure and movement of chromosomes are established.
Important Long Answer Questions On Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Karnataka Board
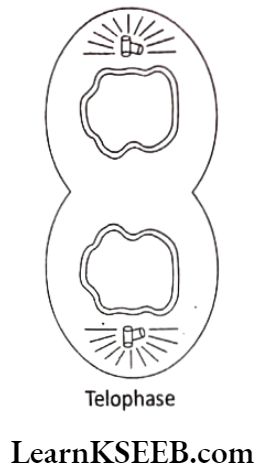
Question 1. Discuss the statement – Telophase is the reverse of prophase.
Answer:
- The changes occurring in telophase are almost reversed to those that take place in prophase.
- The daughter chromosomes reach opposite poles.
- These daughter chromosomes lengthen and their visibility decreases due to decondensation of chromatin. The kinetochore fibers disappear.
- The nuclear membrane reappears. Nucleolus, Golgi complex, and ER reform.
- Thus at the end of telophase, two independent daughter nuclei are organized in the same mother cell.
Telephone:
Class 11 Biology Karnataka Board Cell Cycle and Cell Division summary
Question 2. What are the various stages of meiotic prophase – 1 ? Enumerate the chromosomal events during each stage.
Answer:
Meiotic prophase I is longer and more complex when compared to the prophase of mitosis.
Prophase 1 is divided into 5 substages. They are
- Leptotene
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
- Diplotene
- Diakinesis.
1. Leptotene
: Nucleus enlarges in size. Chromosomes are visible. They are long and slender.
2. Zygotene:
- Homologous chromosomes attract each other and form pairs. These are called bivalents.
- The process of pairing is called synapsis.
- Electron micrographs of this stage indicate that chromosome synapsis is accompanied by the formation of a complex structure called synaptonemal complex
3. Pachytene: It is the most significant substage of Meiosis I.
- Each chromosome divides into two chromatids. Thus in each bivalent, 4 chromatids can be seen. These are called pachytene tetrads.
- In a bivalent, chromatids of the same chromosome are called sister chromatids and those of two different chromosomes are called non-sister chromatids.
- The Pachytene stage Is characterized by the appearance of recombination nodules, the sites at which crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids,
- The non-sister chromatids exchange their parts mutually at one or two or more places. Such points where the non-sister chromatids physically contact each other are called chiasmatAnswer: Chiasmata appear as X – shaped structures
- Crossing over is also an enzyme-mediated process and the enzyme involved is called recombinase.’
- By the end of pachytene, recombination between homologous chromosomes is completed leaving the chromosome linked at the side of crossing one.
4. Diplotene:
The beginning of diplotene is recognized by the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex and the tendency of the homologous chromosomes of the bivalent to separate from each other except at the site of charismata.
5. Diakinesis:
- Charismata moves toward the ends of chromosomes. This is called terminalisation.
- Bivalents become very thick and short.
- The nucleolus begins to disappear.
- The nuclear membrane disappears.
- Chromosomes are released into the cytoplasm.

Question 3. Differentiate between the events of mitosis and meiosis
Answer:

Differentiate between the events of mitosis and meiosis:
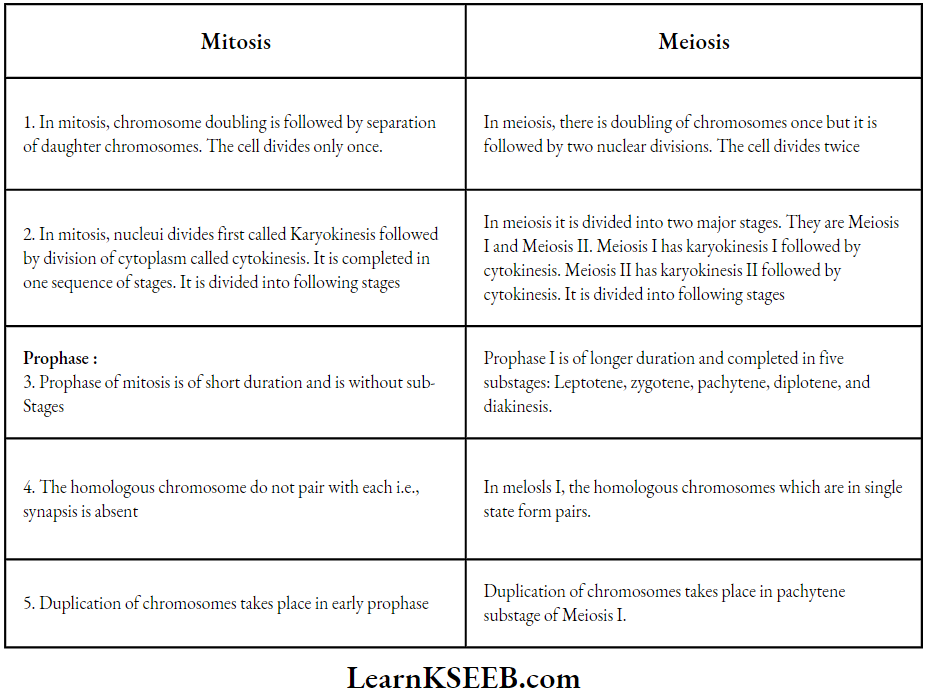

Karnataka Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle and Cell Division previous year questions
Question 4. Write a brief note on the following :
- Synaptonemal complex
- Metaphase plate
Answer:
1. Synaptonemal complex:
During the heptotene of prophase I, chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association is called synapsis.
- Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
- Electron micrographs of this stage indicate that chromosome synapsis is accompanied by the formation of a complex structure called synaptonemal complex.
- The complex formed by a pair of homologous synapsed homologous chromosomes is called a bivalent or a tetrad of chromatids.
2. Metaphase plate:
In Metaphase two important changes take place.
- Formation of bipolar spindle fibers and attach the same to the kinetochores of chromosomes.
- All the chromosomes lie at the equator.
- The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase is referred to as the metaphase plate or equatorial plate.
Karnataka Board Class 11 Cell Cycle and Cell Division MCQs with answers
Question 5. Write briefly the significance of mitosis and meiosis in multicellular organisms.
Answer:
Significance of mitosis:
- Growth in organisms is caused by mitosis and it restores the surface or volume ratio of the cell.
- The daughter cells formed by mitosis are identical to the mother cell. Hence it is important in conserving the genetic integrity of the organism.
- In unicellular organisms, mitosis helps in reproduction.
- Mitosis helps in wound healing and regeneration of lost plant parts.
- Mitosis helps with grafting in vegetative reproduction.
- It maintains a constant number of chromosomes in all the cells of the body.
Significance of meiosis:
- It helps in the maintenance of a constant chromosome number from one generation to the next.
- Due to crossing over, genetic recombinations are caused which help in genetic variation and origin of new species and leads to evolution.
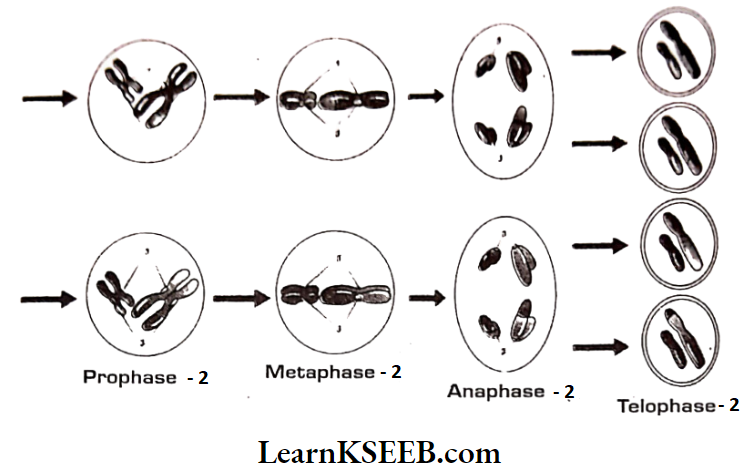
Question 6. An organism has two pairs of chromosomes (i.o., chromosome number = 4). Diagrammatically represent the chromosomal arrangement during different phases of meiosis – 2
Answer: