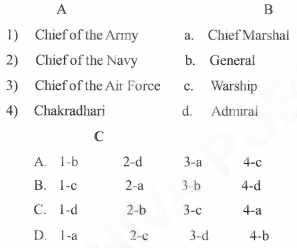
Karnataka Class 9 Social Science Model Question Papers 2023
Choose the correct alternative and Write the complete answer along with its alphabet in the sheet provided:
Question 1. The First woman to rule Delhi was
- Razia Sultana
- Lakshmi Bai
- Durgavathi
- Padmini
Answer: 1. Razia Sultana
Question 2. The main teaching of Shankaracharya is
- Path of knowledge is the way to attain moksha
- Atma and Paramatma are two different entities
- Upheld concept of Kayakave Kailasa
- Atma and Parmatma are like masters and servant
Answer: 1. Path of knowledge is the way to attain moksha
Question 3.One who among the following is not elected by elected members of the Legislative Assembly?
- The President of India
- The members of the Rajya Sabha
- The members of the Legislative Council
- The members of the Lok Sabha
Answer: 4. The members of the Lok Sabha

Question 4. The presence of innumerable castes and caste-based associations is leading to
- Communalism
- Nationalism
- Colonialism
- Regionalism
Answer: 1. Communalism
Question 5. Children learn many things from peers that he cannot learn from their parents because their peer is
- His age group
- More than his age group
- Neighbor of child
- Relative of child
Answer: 1. His age group
Class 9 Karnataka Social Science Sample Papers With Answers
Question 6.The person who believed in the motto of ‘Industrialize or perish’ was
- Sir M.Vtsveswaraiah
- Jawarhalal Nehru
- Gandhiji
- Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
Answer: 1.Sir M.Vtsveswaraiah
Question 7. Ibrahim Roza, a pilgrimage is located in
- Gulbarga
- Bidar
- Raichur
- Vijayapura
Answer: 4. Vijayapura
Question 8.4R strategy related to
- Automobile engine
- Conservation of resources
- Research in science and technology
- Software technology
Answer: 2. Conservation of resources
Question 9. The credit obtained by the suppliers of goods is
- Advance from customers
- Bank credit
- Trade credit
- The loan from indigenous bankers
Answer: 3. Trade credit
Question 10. The goods purchased at different places have to be collected at one central place It is known as
- Assembling
- Storage and warehousing
- Transportation
- Grading
Answer: 2. Storage and warehousing
Fill in the blanks:
- The retirement age of the High Court judges is 62 years.
- The Commander-in-Chief of our three Armed Forces is President.
- ‘Theory of evolution was presented by Darwin.
- The district which has more females is Udupi.
- Labour is a Human input in production.
Match the following
A B
GurjaraPratihars dynasty MoolarajaI
Garhwalas dynasty Dhanga
Parmar dynasty Chandradeva
Solankis dynasty Nagabhatta
Chandelas dynasty Prithviraj
Upendra Krishna Raja
Chand Bardai
Jayachandra
Answer:
GurjaraPratihars dynasty – Nagabhatta
Garhwalas dynasty – Chandradeva
Parmar dynasty – Upendra Krishna Raja
Solankis dynasty – MoolarajaI
Chandelas dynasty – Dhanga
Answer the following
Question 1. Why did Paigambar travel from Mecca to Medina in 622 AD?
Answer: Paigambar opposed polytheism strongly. The enraged people of Mecca conspired to murder him. So Paigambar traveled from Mecca to Medina to save his life in 622 AD.
Question 2.Why did Guru Nanak start ‘Langar’?
Answer: Guru Nanak started ‘Langar ’ a community kitchen where food is prepared and catered to all.
Question 3. What was the opinion of Robert Sewell on Krishnadevaraya?
Answer: Krishnadevaraya was an unparalleled warrior, shrewd commander, and political expert.
Karnataka Class 9 Social Science Model Papers Set 1 Solutions
Question 4. Which are the cases undertaken by Lok Adalats?
Answer: Lok Adalats take up cases relating to vehicle accidents, land possession, banking, marriage and alimony, laborers’ problems, etc.
Question 5. Name the two Houses of Parliament.
Answer: Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha
Question 6. What is a ‘Nuclear Family’?
Answer: The family which consists of a father-mother and their unmarried children as members are called a Nuclear family.
Question 7. Define city.
Answer: A place that has more population and population density is called a City.
Question 8. There is an improvement in the yield production of cotton. Why?
Answer: As a result of the development of disease-tolerant and high-yield varieties of cotton by the Agricultural Research Institute.
Tie
Question 9. Why Tobacco is the most injurious to health?
Answer: Tobacco belongs to the nicotiana group. It contains an intoxicating substance called nicotine.
Question 10. Name the districts with the highest and the lowest density of population.
Answer: Bengaluru Urban district, has the first position with the largest population, and Kodagu district occupies the last position.
Question 11. What are District Roads?
Answer: Roads that link district headquarters with taluk headquarters, major towns, villages, railways, and major highways are called District roads.
Question 12. What is Global Hunger Index?
Answer: In order to measure the extent of hunger, the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) calculates the country-wide hunger index and publishes it in its annual publication ‘Global Hunger Index (GHI)’.
Question 13. Which two aspects consist of the food security system?
Answer:
- Buffer stock
- Public Distribution System
Question 14. What is a Double entry system?
Answer: While entering the two aspects of the business we enter two aspects on opposite sides. This system is called the Double entry system.
Answer the following
Question 1. How was Christianity expanded?
Answer: Various nations of Europe established colonies in various parts of the world with the help of Geographical discoveries. They slowly emerged as strong political forces. In order to ensure their continuation of authority, they also supported Christianity. These developments resulted in the growth of Christianity in India and various other countries of the world swiftly.
Question 2. What was the relationship between the Vassal and laborers?
Answer: The vassals took the help of laborers for agriculture. These laborers were given land sufficient for survival as long as they worked with the vassals. They were not given any monetary returns.
Question 3. Why did the French citizen angry at Queen Mary Antoinette?
Answer: Mary Antoinette was the princess of Austria. She was squandering money for her personal indulgences and festivals. She had no concern for the problems of the people. She was interfering in the administration of the nation. People hated her since she was a foreigner and had no love for the French people. The king could not control her. Eventually, the situation went beyond control and led to a revolution.
Karnataka 9th Class Social Science Exam Pattern 2023
Question 4. What was the condition of Germany before unification?
Answer: Germany was a cluster of independent states. Among them, the larger and more powerful states were Wittenberg, Bavaria, Baden, 1 lea, etc. The rest of them were small. They used to frequently attack each other. These states were politically weak and economically backward.
Question 5. The opposition leader of Lok Sabha is very important in a democratic system. Why?
Answer:
The opposition leader of Lok Sabha plays a very important role in the:
- Highlight the wrongdoings of the ruling government.
- Examine thoroughly the policies of the government.
- Keep the government, council of ministers and officials alert.
- Enjoys dignity in the legislature.
Question 6. Differentiate between regional and national parties.
Answer:
National Parties:
- These types of political parties have branches in many states of that particular nation.
- These are recognized nationwide.
- They have a respectable number of representatives in parliament and also in state legislatures.
- The national political parties are Indian National Congress, Bharatiya Janata Party, and Communist Party.
Regional parties:
- These have branches within that particular state in which it is recognized.
- Recognized within that particular state.
- They form their own government in the state. They also play a major role in making coalition government at the center or in the state.
- Some of the regional political parties are Shivasena (Maharashtra), Janata Dal (Secular) Karnataka, Samajwadi Party (UP), and many more.
Question 7. Which are the two important origins of social change?
Answer:
The two important origins of social change are:
- Natural reasons like earthquakes, natural calamities, floods, etc.
- Human mobility and creativity from his new inventions.
Question 8. Name the important East Flowing river of Karnataka.
Answer: The Krishna, Cauvery, Pennar, and Palar Rivers flow eastwards.
Question 9. Explain the geographical location of Karnataka in India.
Answer: It is situated in the Southern part of India, in the Western Central area of the peninsular region. It extends from 11°-31′ North to 18°~45′ North latitude and 740°-12′ East to 78°-40′ East longitude. Its length is 750 km., stretching from Aurad taluk in Bidar district in the northernmost tip of the State to Chamarajnagar district in the south. Its width is 400 km. from west to east. Karwar in Uttar Kannada district is at the western end whereas Mulbagal taluk in Kolar district is at the eastern end. Karnataka state has both land and water frontiers too.
Question 10. Why does the Malnad region get heavy rainfall?
Answer: Malnad region gets heavy rainfall because the height ranges from 900 to 1500 meters from sea level. These hills obstruct the rain-bearing winds from the Arabian Sea and cause heavy rains often more than 200 cm.
Question 11.Why Karnataka is called the ‘Land of Gold’?
Answer: Karnataka occupies the first position in the production of gold in India. It produces 80% of the total gold in India. Hence Karnataka is known as the ‘Land of Gold’.
Question 12. Which are the major tourist attractions of Mysuru.?
Answer: Mysuru is the City of Palaces. Millions of people visit Mysuru during the Dasara festival. Chamundi Hills, K.R. Sagar Dam, and Brindavan, etc., are the other major tourist attractions of Mysuru.
Question 13. Write short notes on National highways.
Answer: Roads that link important cities, capitals of states, and ports are called National highways.
- These are well-planned wide roads and are two-lane, four-lane, and six-lane roads.
- They are under the authority of the Central Government and are managed by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- There are 14 national highways in Karnataka.
- National highways NH-4 and NH-7 come under the National Highway Authority’s Golden Quadrilateral Highway Project as well as ‘Corridor Project’.
- They have six lanes.
Question 14. The quantity and quality of the labor force in a country are crucial factors. Why?
Answer: Labour is a productive factor of production. It activates the other factors and makes them useful for production purposes. Therefore the quantity and quality of the labor force in a country are crucial factors, in accelerating the development of that country. The higher the labor force, the larger the economic activity and development.
Class 9 Karnataka Social Science Model Questions 2023 Set 1
Question 15. What are the types of Accounts? Give examples.
Answer:
Accounts are classified into three types. They are:
- Personal Accounts: banka/c,
- Real Accounts: Cash a/c furniture a/c
- Nominal Accounts: interest a/c commission a/c
Answer the following
Question 1. What were the administrative reforms implemented by Mohammad bin Tughlaq?
Answer:
Administrative Reforms:
Revenue Reforms: An official record that had all the details of the lands of the empire was implemented by him. He established the department of agriculture. The uncultivated lands were made cultivable. Various schemes were implemented to provide financial assistance to the farmers. But, the farmers of Do-ab had to pay higher land taxes during his time.
Shifting of his Capital: Mohammed bin Tughlaq shifted his capital from Delhi to Devagiri in central India. There are two main reasons behind this move: to establish the capital city at the center of the vast empire and to protect the capital city from foreign invasions. Though the plan was good, proper precautions were not taken to implement this. As a result, innumerable common people suffered severely.
The experiment of Symbolic Coins: the copper and brass coins were also brought into circulation symbolically. Then, minting coins was not vested with the government alone. Families who had traditional rights to mint coins were also there. The coins were minted more than the required number without the permission of the Sultan. This resulted in chaos. The state treasury became empty due to costly administrative experiments, severe drought, the shifting of the capital city, the process of relocating the capital back, and other measures. (OR)
Question 1. Explain the military achievements of Akbar
Answer: Akbar emerged victorious in the second battle of Panipat. His Prime Minister and royal representative, Bairamkhan came to Akbar’s assistance during the war. With the help of the mighty army, Akbar conquered Malwa, Jaipur, Gondavan, Chittor, Ranathambhor, Kalinjar, Gujarat, and Bengal. The Battle of Haldighat is the most significant battle in the history of medieval India, After the death of the Chittor king, Rana Uday Sing, his son Rana Pratapsingh came to power. Akbar sent his powerful army under the leadership of Generals Mansion and Asaf Khan to fight against Rana Pratap. In the battle at Haldighat, the Moghul army was victorious. The remaining states of Kashmir, Sindh, Orissa, Baluchistan, Khandhar, and Ahmednagar came under Akbar. Thus, he laid the firm foundation for the Moghuls to emerge as a powerful Kingdom in medieval India.
Question 2. Explain the salient features of our Constitution.
Answer:
The salient features of our Constitution are:
- Written and Lengthy Constitution
- Flexible and Rigid Constitution
- Parliamentary Form of Government
- Federal System
- Fundamental Rights
- Fundamental Duties
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Independent and Centralized Judiciary System
- Single Citizenship y Adult Franchise
- Bicameral Legislature y Party System (OR)
Question 2. Explain the structure of the Legislative Assembly.
Answer:
- The strength of the Vidhana Sabha depends on the population of the State.
- The maximum number of seats in any Vidhana Sabha should not exceed 500 or be below 60.
- The Governor can nominate one member from Anglo Indian community if he feels that they are not represented properly.
- However, the number of seats in small States is less. Example: In Mizoram and Goa, there are 40 members each.
- The Vidhana Sabha in Karnataka has 225 members. 224 members are elected whereas one Anglo-Indian is nominated by the Governor.
Karnataka Class 9 SSLC Social Science Model Paper 2023 Details
Question 3. Explain the role of the family in socialization.
Answer: Family plays a very important role in the socialization process of a child. Father-mother is direct blood relatives of the child. The idiom Mother is the first teacher of the child is literally true. The behavior, custom, practices, activities, the interaction of father and mother will extremely influence the emotional development of the child. The child learns the first lesson of life values such as love, concern, faith, patience, cooperation, coordination, etc., at home itself. The appreciation from the family always encourages the activities of the child. Children are obedient to their parents because they are old enough in their age, experience, and authority. Due to the socialization process, the hearts of the children blossom, and family is the basic foundation for all these processes. (OR)
Question 3. Differentiate between nomadic communities and rural communities.
Answer:
Characteristics of a nomadic community:
- Nomadism for life: Nomadic people wander for hunting, taming and exhibition of animals, animal husbandry, the practice of native medicine, exhibiting folk arts, etc., for their livelihood.
- Temporary Shelters: Since they have no permanent residence, and lack education and a fixed source of income, they live in temporary shelters erected outside the villages under some trees or in public places.
- Zero or no investment jobs: These communities do not have any economic security. Many of them earn money through rag picking, bucket repairing, fishing, hunting, selling small fancy products, etc.
- Universal Beings: They have immense knowledge of nature. They have a strong belief in nature’s invisible forces and worship them.
- Different Mother tongue: Nomadic community includes many races and every race has its own mother tongue.
Characteristics of rural community:
- Small in size: Generally, the size of the village is small and the population density is low.
- Agriculture and agriculture-related economy: Rural life is more simple. Here agriculture and agriculture-related activities are prominent.
- Community life: Rural people have strong faith in nature. They worship rain. They collectively celebrate festivals and other rituals of local deities. Generally, people live in harmony. Villages evolved on the basis of “One for all and all for one”. Here competition, cheating, superficialness, and exploitation have less or no space at all.
- Democratic Ideals: The Indian villages are being bulk on the basis of democracy these days. In many villages, all the members of the village participate in a few activities. The participation of villagers in the functioning of Gram Panchayats is another good example.
- Lack of Civic Infrastructure: The lack of basic infrastructure that is needed to ensure basic civic facilities like health, education, civic protection, and the judiciary are more prevalent in rural communities.
Question 4. Explain the condition of Karnataka during the summer season.
Answer: During the Summer season, it is very hot, dry, and sultry. After March, the temperature rises uniformly all over the state and reaches the maximum during April and May. Raichur has recorded a temperature of 45.60 Celsius and it is the hottest place in Karnataka. The temperature is high even in the other districts of northern maidan. In general, the whole of Karnataka experiences hot climatic conditions during this time. The humidity is lower in the Northern maidan than in the Southern maidan. In summer, due to great evaporation, rain-bearing clouds are produced and they bring conventional rain along with lightning and thunder. The Hailstones fall in some places. This generally takes place for a short time during the afternoon. Since these showers enable the flowering of coffee plants, they are called ‘Cherry Blossoms’, and since they help the mango crop, they are also known as ‘Mango showers’. About. 7% of the annual rainfall of the state occurs during this season. (OR)
Question 4. What are the geographical factors required for the cultivation of Cotton?
Answer: Cotton is a fiber crop. Cotton is a crop of the tropics and the sub-tropics. Moderate rainfall, high temperature, and black soil are suitable for its growth. Cotton is akhariferop. It is sown in August-September. It is a rain-fed crop. It can also be grown with the help of an irrigation facility.
Question 5. What steps would you take to conserve energy use in school and at home?
Answer:
The steps taken to conserve energy use in school and at home are:
- Put off all lights when not in use
- Turn the air conditioner and heater off at night
- Get outside! Outside activities are fun and take less energy
- Keep door and winds shut when heating and cooling the house/car (OR)
Question 5. Both the birth rate and the death rate are high, and the population growth rate also remains very low in the backward stage. Why?
Answer: Backward stage: In a backward economy health facilities are lagging and people lack awareness about the advantages and means of birth control. People are also superstitious and bound by customs and traditions. Due to this, both the birth rate and the death rate are high resulting in lower population growth.
Social Science Class 9 Model Paper Set 1 Marking Scheme
Question 6. Differentiate between Short term finance and Long term finance
Answer:
Short-Term Finance: Finance that is required for day-to-day working is called Short term finance,
- It is required to meet the working capital needs, i.e. to purchase raw materials, pay wages and salaries, meet the marketing and administrative expenses,
- There is always a time gap between sales and receipt of sale proceeds. To fill the financial gap between these two processes namely sales and receipt of sale proceeds sufficient funds are required. Hence there is a need for short-term finance.
- Long-term finance refers to finance required for the development programs such as an expansion of the level of production, modernization of production methods, etc., This type of finance is also required for financing the fixed capital of an undertaking. Example: To procure fixed assets, establish new undertaking, etc. raised against securities. It is raised by Joint Stock Companies, through the issue of shares and debentures. Also raised through term loans from financial institutions. (OR)
Question 6.“Directing and co-ordinations are very important functions in business management” how?
Answer:
- Directing is the area of functional management where instructing, guiding, supervising, and leading the people of an organization towards the accomplishment of the organizational goals. It is issuing orders or instructions to the sub-ordinates and making certain that the instructions are properly carried out and the operations are successfully planned.
- Coordination is the harmonious blending of the activities of the different departments for the achievement of the desired goals. It is the arrangement of group efforts to provide unity of actions in the pursuit of a common purpose.
Answer the following.
Question 1. Explain the art and architecture of the Vijayanagar period.
Answer: The excellent work done by Vijayanagar kings in the fields of art and architecture is memorable.
- Temples, palaces, forts, towers, huge halls (maha mandapa), public buildings, tanks, bunds, canals, and dams were constructed.
- The Vijayanagar kings continued the architectural style of Chalukyas, Cholas, and Hoysalas.
- The unique feature of their architecture was the construction of huge auditorium and marriage halls.
- Temples had huge towers (rayagopura), leaf-shaped arches, and platforms.
- Ornamentation, the qualities of grandeur, awe, and elegance were given importance.
- Rough granite stone (kanashile) was used for the construction of these structures.