KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Minerals And Power Resources Textbook Questions
Question 1 . Answer the following questions:
(a) Name any three common minerals used by you every day.
Answer . Three common minerals used by us everyday are:
(a) Iron ore for making steel
(b)Sand for constructing building
(c)Copper wires
(b) what is an ore? Where are the ores of metallic minerals generally located?
Answer. Rocks from which minerals are mined are known as ores.
Or
An ore is the natural accumulation of metals or minerals in a concentrated form. It has many impurities. Generally, ores of the metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations that form large plateaus.
(c)Name two regions rich in natural gas resources.
Answer. Russia and U.K are the major producers of natural gas iri the world. In India, Jaisalmer. Krishna- Godavari delta, have natural gas resources.
(d) Which sources of energy would you suggest for:
(a) Rural areas
(b) Coastal areas
(c) Arid areas
Answer. I would suggest
(a)Rural area: Energy sources for rural areas-Biogas
(b)Coastal areas: Hydel power, Wind energy, Tidal energy
(c)Arid areas: Solar energy

(e)Give five ways in which you can save energy at home.
Answer. Five ways in which we can save energy at hone are as follow:
(a)Switching off the appliances when not in use.
(b)Keeping the lights dust free.
(c)The appropriate maintenance and usage of appliances as per the given instructions.
(d) Maximising the use of natural breeze and light by keeping the windows open.
(e)Using CFL tube lights.
Class 8 Geography Minerals and Power Resources KSEEB Notes
Question 2. Tick the correct answer
(a)Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of minerals?
(a)They are created by natural processes.
(b) They have a definite chemical composition.
(c) They are inexhaustible.
(d) Their distribution is uneven.
Answer. (c) They are inexhaustible
(b)Which one of the following is NOT a producer of mica?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Karnataka
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Andhra Pradesh.
Answer. (c) Rajasthan
(c)Which one of the following is a leading producer of copper in the world?
(a) Bolivia
(b) Ghana
(c) Chile
(d) Zimbabwe.
Answer. (c) Chile
(d)Which one of the following practices wi I NOT conserve LPG in your kitchen?
(a) Soaking the dal for some time before cocking it.
(b)Cooking food in a pressure cooker.
(c)Keeping the vegetables chopped before lighting the gas for cooking.
(d)Cooking food in an open pan kept on low flame.
Answer. (d) Cooking food in an open pan kept on low flame.
Question 3. Give Reasons:
(a)Environmental aspects must be carefully looked into before building huge dams.
Answer.
Dams are built for developing canals and generating water power. But sometimes huge dams cause environmental problems. Many large dams produce environmental impacts upstream, downstream and in the vicinity of the reservoir and hence controversies surround such development. So, all these should be carefully looked.
(b)Most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
Answer.
Most industries are concentrated around coal mines because coal is an important source of energy. It is a key mineral and fuel for the industries. It is used as a power resource :n many industries. Many industries use it as a raw material. So, most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
(c)Petroleum is referred to as black gold.
Answer.
Now-a-days, petroleum is a major source of energy in the world. Many by-products such as kerosene, fuel, lubricating oils, etc. are obtained from L Petrochemical products have become very useful. Petroleum is used in agro-industry, paints, perfumes, trAnswerport, etc. So it is rightly called black gold.
(d)Quarrying can become a major environmental concern.
Answer.
Quarrying can become a major environmenta concern because this process is used to dig out those minerals that lie near the surface. It causes land degradation and soil erosion all over the world.
KSEEB Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Questions And Answers
Question 4 Distinguish between the following.
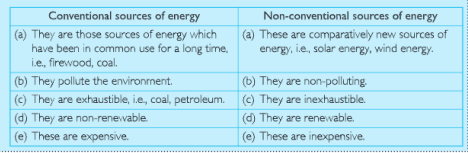
(a)Conventional and Non-conventional sources of energy.
(b) Biogas and natural gas.

(c) Ferrous and Non-ferrous minerals.
Answer.
(a) Ferrous minerals: These minerals contain iron. For example: Iron ore, manganese and chromite,
(b) Non-ferrous minerals: These minerals do not contain iron but may contain some other metal, i.e., gold, silver, etc.
(d) Metallic and Non-metallic minerals.

Minerals and Power Resources Activity
(a)Use pictures from old magazines to show different kinds of fuels used by us in our lives and display them on your bulletin board.
Answer. Students will do it. They can take help from their teacher.
(b)Design a poster highlighting energy conservation, tips you would take for your school.
Answer. Students will do it.
(c)Salma’s class took up an action campaign to do an energy audit of their school by surveying electricity consumption. They prepared survey sheets for the students of the school.
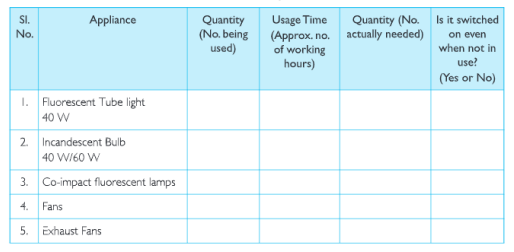
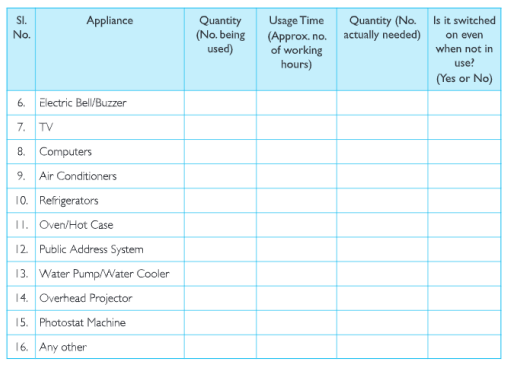
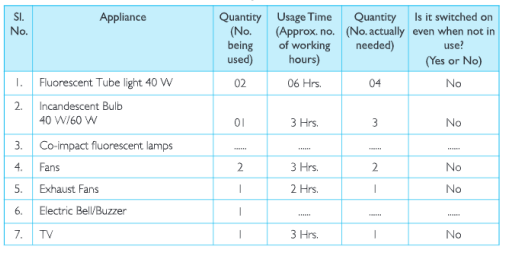
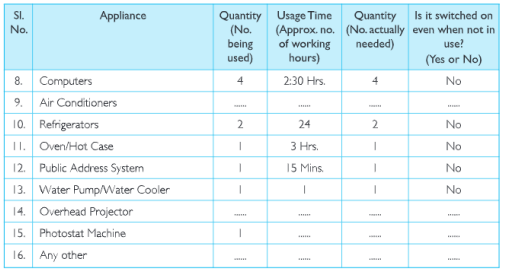
Using the data collected during the survey, students calculated the units consumed for one month and the approximate expenditure and compared it with the electricity bill of the previous month.
They also calculated the approximate cost of electricity consumed by fans, lights and other appliances not switched off. Thus they highlighted the amount that could be saved and suggested simple energy conservation habits like:
- Switching off the appliances when not in use.
- Minimal usage as per requirement.
- Maximising the use of natural breeze and light by keeping the windows open.
- Keeping the lights dust free.
- The appropriate maintenance and usage of appliances as per given instructions.
Can you add some more tips to this list?
You could conduct a similar survey at home and then extend it to your apartment and make your neighbours also energy wise.
Minerals and Power Resources Text Questions
Question 1. List uses of any five minerals Answer.
(a) Sand: used as building material
(b) Salt: used in food
(c)Gold: used for ornamental purposes
(d) Iron: used for making tools and machines
(e)Copper: used for making wires
Minerals And Power Resources KSEEB Class 8 Textbook Solutions
Minerals and Power Resources Activity
Question 1 With the help of an atlas, on an outline map of India, mark the distribution of iron, bauxite, manganese and magnesium.
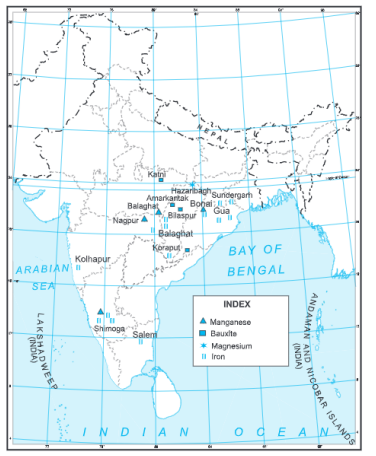
Minerals and Power Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1 By which properties we can identify minerals?
Answer. Minerals can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical properties such as solubility.
Question 2. Where do we find oldest rocks in the world?
Answer. The oldest rocks in the world are h western Australia.
Question 3. Why are Kolar mines famous?
Answer. Kolar gold mines are located in Karnataka, India. These mines are among the deepest in the world.
Question 4. Name three large producers of iron ore in the world.
Answer. Russia, U.S.A. and Brazil.
Question 5. Which energy is called geothermal energy?
Answer. Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal erergy.
Question 6. Mention two ways by which the reserves of minerals resources can be saved.
Answer. Reusing and the rec/cling of minerals can help to use the discarded materials once again.
Question 7. Which is the lowest quality of coal?
Answer. Peat is the lowest quality of coal, with 50-60% of carbon.
Question 8. What is an alloy?
Answer. A new mineral formed due to combination of minerals.
Question 9. Mention the two hydro-electric projects of India.
Answer. Bhakhra Nangal project, Nagarjuna sagar project.
Question 10. Name some chemical properties of two rocks.
Answer. Salt is soluble, quartz is insoluble.
Question 11. Name three ages based on minerals.
Answer. Copper age, Bronze age, Iron age.
Question 12. What is tidal energy?
Answer. Energy generated by tides is called tidal energy.
Question 13. Give two advantages of wind energy.
Answer.
(a) It is non-polluting
(b) It is clean and safe.
Question 14. What is thermal power?
Answer. Electricity generated from coal is called thermal power.
Question 15. Name the leading coal producers of the world.
Answer. China, U.S.A., Germany, Russia, South Africa and France.
Question 16. What are commercial sources of energy?
Answer. Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas, Hydro-electricity and Nuclear energy.
Question 17. How is coal formed?
Answer. Coal originated from wood. It is buried beneath the earth’s surface. Wood is changed to carbon after a long time. Thus, coal is formed.
Question 18. Name four important iron ore producing states of India.
Answer. Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Goa.
Question 19. What is a mineral?
Answer. A naturally occurring substance that has a def nrte chemical composition is called a mineral.
Question 20. Name two inaccessible areas where minerals are found.
Answer. Arctic ocean bed and Antarctica.
Important Questions For KSEEB Class 8 Geography Chapter 3
Question 21. What is an ore?
Answer. A rock from which mineral is mined.
Question 22. What is the importance of sources of energy?
Answer. Energy plays a vital role in our lives. We need erergy for industry, agriculture, trAnswerport, communication and defence.
Minerals and Power Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Distinguish between a mine and a quarry.
Answer. The process of mineral extraction is called mining. A mine is an excavation in the ground for digging out minerals. It may be deep. Surface mines are called open pit mines or quarries.
Question 2. Name the three types of energy and their sources.
Answer.
(a) Thermal power: From coal and natural gas;
(b) Nuclear energy: From uranium;
(b) Hydro-electricity: From falling water.
Question 3. What are the alternative sources of energy?
Answer. There are other sources of energy as well. They include hydropower, geothermal, nuclear, solar and wind. These are also referred to as alternative energy sources.
Question 4. Describe the different types of coal.
Answer.
(a) Peat: Peat is the first stage of coal development. It is dark brown in colour. It has about 35 per cent carbon content
(b)Lignite: Lignite is the next stage of coal formation, which has nearly 50 per cent carbon.
(c) Anthracite: Lignite becomes sub-bitumnous, bituminous and eventually anthracite coal.
Anthracite has more than 85 per cent carbon. It is the best quality of coal. It is very hard, compact, black in colour. It ignites slowly and bums with a short blue flame.
Question 5. List three basic ways through which energy s obtained.
Answer. Energy is the capacity to do work It car be obtained by:
(a)Direct heating like fire, sun, etc.,
(b) Electricity;
(c)Stored energy in the form of a battery.
Question 6. ‘Mineral conservation can delay a crisis.’ Explain.
Answer. Due to growing population, the use of minerals is increasing at an alarming rate Minerals will riot last long.
We need to find substitutes, reduce consumption and recycle mineral resources It can delay a mineral crisis.
Question 7. Classify metals.
Answer. Metals are classified as follows:
(a) Precious metals – gold and silver;
(b) Ferrous – iron and manganese;
(c) Non-ferrous – copper and lead;
(d) Light metal – aluminium;
(e) Rare metals – zirconium.
Question 8. What is an alloy? Give example.
Answer. Sometimes a metal is combined with another The new metal is called alloy.
Such as: Copper + tin = Bronze
Iron + nickel + chromium = Steel alloy.
Question 9. Name four main belts where iron ore is found.
Answer. The four main iron ore belts are:
(a) Odisha-Jharkhand belt;
(b) Durg-Bastar Chandarpur belt
(c) Bellary-Chikmagalur belt
(d) Maharashtra-Goa belt.
KSEEB Geography Chapter 3 Class 8 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 10. Describe the different methods of extracting minerals.
Answer. Taking out minerals from rocks is called mining.
(a) Open cast mining: Minerals at shallow deoths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
(b) Shaft mining: Minerals at depth are taken out by making deep bores.
(c) Drilling: Deep wells are bored to take out petroleum.
(d) Quarrying: Minerals at the surface are dug out
Question 11. Describe the uses of some important minerals.
Answer.
(a) Gems are used in jewellery.
(b)Copper is used in coins, pipes.
(c)Silicon is used in computer industry.
(d) Aluminium is used in automobiles and aeroplanes.
Question 12. Distinguish between the following:
(a)Thermal power and Hydel power.
Answer. (a) Thermal power and Hydel power.

(b)Anthracite coal and Bituminous coal.
Answer .(b)Anthracite coal and Bituminous coal.

Minerals and Power Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe the distribution of coal and mineral oil in the world.
Answer. Coal:
(a) Russia has about 1-3rd of the world’s coal reserves.
(b) U.S.A. has about 1-4th of the world’s coal reserves.
(c) It is also found in China, Australia, parts o’Western Europe, South Africa and India.
(d) 90% of the coal reserves of the world are found in these places and rest of it is scattered in different parts of the world.
Mineral Oil:
(a) The Persian Gulf and the surrounding areas have about 2/3rd supply of the total reserves of oil available.
(b) Saudi Arabia has the largest reserves.
(c) Oil reserves are also found in Russia, Venezuela, Mexico, Libya and Nigeria.
(d) 90% of the world’s reserves come from these countries.
(e) Germany, Norway, Denmark, U.S.A., U.K. also produce oil.
(f) India also has several oilfields.
Question 2. What are alternative sources of energy?
Answer. Alternative sources of energy are:
(a) They include hydropower, geothermal, nuclear, solar and wind power.
(b) All these resources are renewable.
(c) They are inexpensive in nature.
(d) They do not cause pollution.
(e) They can be developed in rural areas ard maintained at low costs.
Thus, because of their qualities, there is a possibility that they might replace fossil fuels in the future.
Question 3. Why is recycling of metals and minerals necessary?
Answer.
Mineral resources are limited. But man is using these at a fast rate. Developed countries with 16% of world population use 70% minerals (such as USA, Europe, Japan). The existing mineral resources will not last long. Thus, reducing consumption, reusing and recycling are ways to conserve these. Metals like aluminium can be recycled easily. Discarded metals can be recycled arid used again.
Question 4. Discuss distribution of iron, copper and bauxite in the world.
Answer.
(a) Iron: Iron is the most widely used metal. Because of its importance, it is taken as the symbol of modern civilisation. Iron-ore is found ir large amount in Ukraine, Kazakhstan, U.S.A., China, Brazil, Australia and India. In Europe, the best quality of iron-ore is found in Sweden. France and Germany also have iron ore deposits. Liberia and South Africa in Africa have iron ore deposits with over 60 per cent iron content. India has many important iron-ore fields. Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are major producers of iron-ore in our country.
(b)Copper: Copper is used largely in electrical industries because of its quality of electrical conductivity’. Its ore is found in Chile, U.S.A., Canada, Poland, Russia, Kazakhstan, Georgia, Armenia, Congo and Zambia. In India, re serves of copper are found in Jharkhand and Rajasthan.
(c)Bauxite: Aluminium is a light and versatile metal. It is used for making aeroplanes, machines tools, utensils, packaging, construction and electricals. It is extracted from bauxite using electrolysis smelting process, which requires large amount of electrical energy. For this reason, aluminium is manufactured mostly in developed countries, where abundant electric energy is available at a low cost. Australia, Guinea, Jamaica and Brazil are the main producers of bauxite in the world.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Guide On Minerals And Power Resources KSEEB
Question 5 .Discuss the potential of alternative sources of energy.
- Nuclear Power: Power is emitted by Uranium and Thorium, which are put into nuclear reactors where nuclear fission takes place. USA and Europe are large producers of nuclear power in the world. In India, the nuclear power stations are Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu), Tarapur (Maharashtra), Rana Partap Sagar (Rajasthan), Narora (U.P.) and Kaiga (Karnataka).
- Tidal Energy: It is generated from high tides. Russia, France and Gulf of Kachchh have huge tidal mills.
- Solar Energy: Solar energy can be trapped using solar collectors, which can heat water for homes. Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight directly into electricity. Experiments are going on to make it more efficient and less expensive. Some countries like Japan, France, Germany, U.S A, Canada and India are producing photovoltaic cells in small quantities. They are still in early stage of development.
- Wind Energy: More recently, wind has been used to generate electricity. The potential for wind energy is tremendous. Yet. there are problems in its use because it is highly variable in time, place and intensity. Regions with greatest potential for wind energy in North America are the Pacific north-west coastal area and the coastal region of north- eastern U.S.A. and southern California. Netherlands in Europe is using windmills for a long time. The Gujarat coast has few wind mill farms in India.
- Geothermal Energy: It is the useful conversion of natural heat from the interior of the Earth to heat buildings and generate electricity. As early as 1904, geothermal power was developed in Italy. Natural internal heat is now being used to generate electricity in Russia, Japan, New Zealand, Iceland, Mexico, Hawab and California.
Question 6. Describe the production of petroleum in India.
Answer.
Production: In about 10 lakh sq. km. oil bearirg rocks are found in India. The oil re serves in India are estimated to be 50 crore metric tons. The first oilfield in India was discovered in 1867 at Makum in Assam. At present, the production is as under
(a) Assam: In Assam, oil is produced in Digboi, Moran, Naharkatiya and Sibsagar regions.
(b )Gujarat: In Gujarat, oil is produced in Gulf of Khambat region at Kalol, Ankleshwer, Lunej, etc.
(c) Maharashtra: Oil has struck in offshore region at Mumbai High along the coast of Mumbai. It is the leading producer of crude oil in India. North Basin and South Basin and Albet islands are the important oil fields.
The product on of oil in India is increasing everywhere under the organization of Oil and Natural Gas Commission. The production of oil in India was estimated to be about 210 lakh tonnes in 2001.
Question 7. Describe the distribution of important minerals in India.
Answer.
(a) Iron-ore: Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra, Karnataka.
(b)Bauxite: Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu.
(c)Mica: Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan.
(d)Copper: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh.
(e) Manganese: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh.
(f)Limestone: Bihar, Jhar<hand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Rajasthan.
(g)Gold: Kolar (Karnataka).
Minerals and Power Resources Hots Corner
Question 1. . Describe the formation of coal.
Answer. Coal is a black or brown rock consisting mainly of carbon. Coal is formed by the decomposition of vegetation of last ages. Most of coal deposits were formed in carboniferous age about 300 million years ago.
Question 2. ‘Human civilisations are associated with discovery of minerals.’ Give example.
Answer. Mining is an age-old activity. The use of minerals is marked with different stages of human civilisation. During 5000 B.CE., Copper Age existed. During 3000 B.C.E., Bronze Age and during 1400 B.C.E., Iron Age started.
Question.3. On what factors does the commercial extraction of mineral depend?
Answer. Factors on which commercial extraction of mineral depends are:
(a) Sufficient ore content
(b) Easy structure
(c) Low cost of extraction
(d) Easy mining
Question 4. Describe the economic importance of minerals. Describe major types of minerals.
Answer.
Minerals: Mineral resources are of great use to man. Minerals have been called *the Gifts of Nature’. Mineral resources have been used since pre-historic times. Human civilisation has seen many ages like Stone Age, Copper Age and Iron Age. Modem industrial and economic development depends upon the production and utilisation of minerals.
Types of Minerals: There are 70 to 80 minerals found on the surface of the Earth. These can be divided into three types:
(a)Non-Metallic Minerals: These include salt, mica, limestone, graphite, potash, gypsum.
(b)Metallic Minerals: These include iron, copoer, aluminium, gold, silver. These can be melted into useful metals.
It also includes coal, oil and natural gas. These are called sources of power.
Importance of Minerals:
(a) Industries: Minerals form the Oasis of heavy industries like iron and steel. Minerals are called ‘vitamins’ of industry-.
(b)Machinery: Minerals provide machinery for modern manufacturing.
(c)TrAnswerport: Minerals are used in the making of different meAnswer of trAnswerportation.
(d)Sources of Energy: Minerals provide energy to the modem industries.
KSEEB Class 8 Minerals And Power Resources Study Materials
Minerals and Power Resources Map Based Questions
Question 1 .Show the distribution of important minerals in India.

Question.2. Show distribution of iron ore in India.
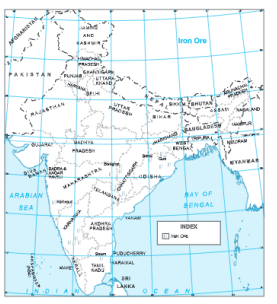
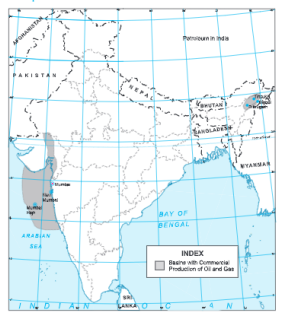
Question 3. Show the distribution of petroleum in India.
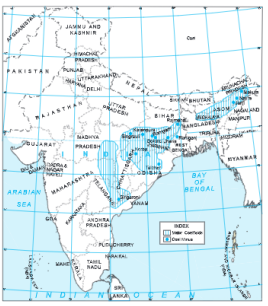
Question 4. Show the distribution of coal in India.
Minerals and Power Resources Miscellaneous Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Tick the correct option from the choices provided:
Question 1. A substance that has a definite chemical composition is called:
(a) Ore
(b) Mineral
(c) Rock
d) Energy
Ans.(b) Mineral
Question 2.Which of these is not a property of minerals?
(a) Colour
(b) Density
(c) Hardness
(d) None
Ans. (d) Luster
Question 3.Which of these is a metallic mineral?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Iron ore
(d) Luster
Ans.c) Iron ore
Question 4.Which of these is a non-metallic mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Manganese
(c) Chromite
(d) Lime stone
Ans.(d) Lime stone
Question 5.Which of these is a ferrous mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Gold
(c) Silver
(d) Gold
Ans.(a) Iron ore
Question 6.Which of these is a non-ferrous mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Manganese
(c) Chromite
(d) Copper
Ans.(d) Gold
Question 7.Mineral is mined at agreat depth using:
(a) Open cost mining
(b) Shaft mining
(c) Drilling
(d) Quarrying
Ans.(b) Shaft mining
Question 8.Which of these is a conventional source of energy?
(a) Wind energy
(b) Nuclear power
(c) Geothermal energy
(d) Coal
Ans.(d) Coal
Question 9.Which of these is a non-conventional sourceof energy?
(a) Coal
(b) Waterpower
(c) Petroleum
(d) Wind energy
Ans.(d) Wind energy
Question 10.Manikaran is located in the state of:
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) J&K
Ans.(c) Himachal Pradesh
Solutions for Minerals And Power Resources KSEEB Class 8 Geography
Minerals and Power Resources B.One Word-Sentence Answer
Answer the following questions in one word/sentence:
(a)Which is the leading producer of iron-ore in the world?
Answer. Europe.
(b)Who is the largest producer of bauxite in the world?
Answer. Australia.
(c)Which is the highest quality of coal?
Answer. Anthracite.
(d)Which is the most widely used metal?
Answer. Iron.
(e)What is the process of separating metals from their ores called?
Answer. Smelting.
(f)Which country has the largest reserves of oil?
Answer. Saudi Arabia.
(g)Where was the oil first found in India?
Answer. Assam.
(h) Which mineral is called ‘Black Gold’?
Answer. Petroleum.
(i)Which country is the leading producer of copper in the world?
Answer. Ghana.
(j) The largest Solar Plant in India is located at which place?
Answer. Madhapar.
Minerals and Power Resources Fill in the Blanks
Fill the blanks with appropriate terms in the following sentences:
(a)_________is the softest mineral.
Answer. Talc
(b)_________has no known mineral deposit in it.
Answer. Switzerland
(c)_________are two groups into which the minerals are classified.
Answer. Metallic and non-metallic minerals
(d)_________are two examples of metallic minerals.
Answer. Iron, and copper
(e)_________are examples of two precious metals.
Answer. Gold and silver
(f)_________The windmills are found at in India.
Answer. the Gujarat coast
(i)_________ is the alternative sources of energy.
Answer. Solar energy and wind power
(j)_________ are two countries producing solar energy.
Answer. japan, and U.SA
(k)_________Solar energy is produced at in India.
Answer. the Gujarat coast
(i)_________ is used for sparkle in tooth pastes.
Answer. Mica
(j)_________is the biggest source of non-traditional energy.
Answer. Nuclear power
Minerals and Power Resources Picture Interpretation
Look at the following picture and Answerwer the questions that follow:
- Carefully see the pictures given below and identify the use of these products shown in it.

Answer. The picture shows wind mills. Wind mills are sources of non-conventional and clean energy.
2.

Answer. The picture shows turbines near the shoreline. It is used in tapping tidal energy and is a source of non-conventional and clean energy.