KSEEB Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Physical World Synopsis
Physics: Physics is the study of nature and natural phenomena.
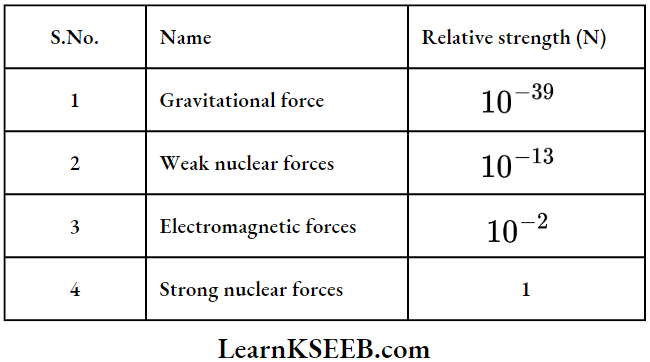
Fundamental Forces In Nature: In physics
- Gravitational Force
- Electromagnetic Force
- Strong nuclear Force
- Weak nuclear Force.
Gravitational Force: It is the force of attraction between any two objects by virtue of their masses.
- These are very weak forces. They are very long-distance forces. For heavy bodies like planets and stars etc., the magnitude of these forces is high.
- These forces are very important in planetary motion and in the formation of Stars and Galaxies.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Class 11 Physics Solutions
Electromagnetic Forces: It is the force between two charged particles.
- Between like charges they are “repulsive forces” and between unlike charges, they are “attractive forces”.
- These forces are very strong forces. These are long-distance forces.
Strong Nuclear Forces: Strong nuclear forces bind protons and neutrons in a nucleus.
These are very strong attractive forces. They are 100 times stronger than electromagnetic forces. They are short-range forces. Their effect is up to very few fermi.
Weak Nuclear Forces: Weak nuclear forces will appear only in certain nuclear processes such as β-the decay of the nucleus where the nucleus emits electrons and neutrino.
These are weak forces, their range is up to a few fermi.
KSEEB Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Solved Examples
Conserved Quantities: In physics, any physical phenomenon is governed by certain forces. Several physical quantities will change with time blit some special physical quantities will remain constant with time. Such physical quantities are called conserved quantities of nature.
Conserved Quantities Example: For motion under an external conservative force such as a gravitational field the total mechanical energy (i.e., P.+K.E) is constant or energy is conserved.

Physical World Solutions KSEEB Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. What is Physics?
Answer:
Physics is a branch of science that deals with the study of nature and natural phenomena.
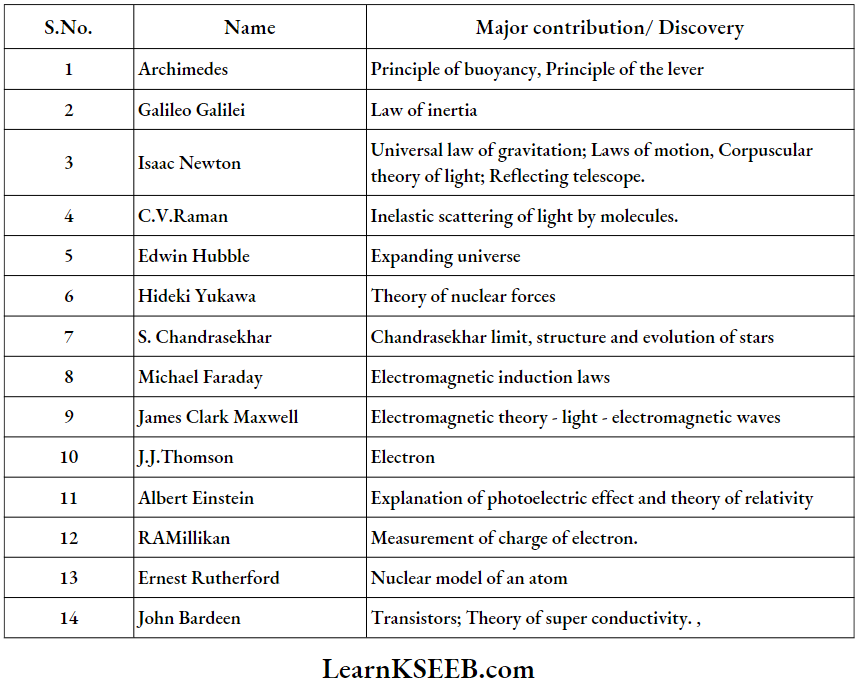
Question 2. What is the discovery of C.V. Raman?
Answer:
C.V. Raman’s contribution to physics is the Raman effect. It deals with the scattering of light by molecules of a medium when they] are excited to vibrational energy levels.
Question 3. What are the fundamental forces in nature?
Answer:
There Are Four Fundamental Forces In Nature
- Gravitational force
- Electromagnetic force
- Strong nuclear force
- Weak nuclear force
Question 4. Which of the following has symmetry?
- Acceleration due to gravity.
- Law of gravitation.
Answer:
- Acceleration due to gravity varies from place to place. So it has no symmetry.
- The law of gravitation has symmetry because it does not depend on any physical quantity.
Question 5. What is S. Chandra Seklmi’s contribution to physics?
Answer:
S. ChandraSekhnrdlsoovorod Hit-slniclurn and evolutIon ol stars. I defined the “Chandra Sekhar limit” which Is used In the study of black holes.
Question 6. What Is beta (β) decay? Which force is a function of it?
Answer:
In β-decay, the nucleus emits an electron and an uncharged particle called neutrino.
β – decay is due to weak nuclear forces.
Some Physicists And Their Major Contributions
Fundamental Forces Of Nature
Fundamental Constants Of Physics
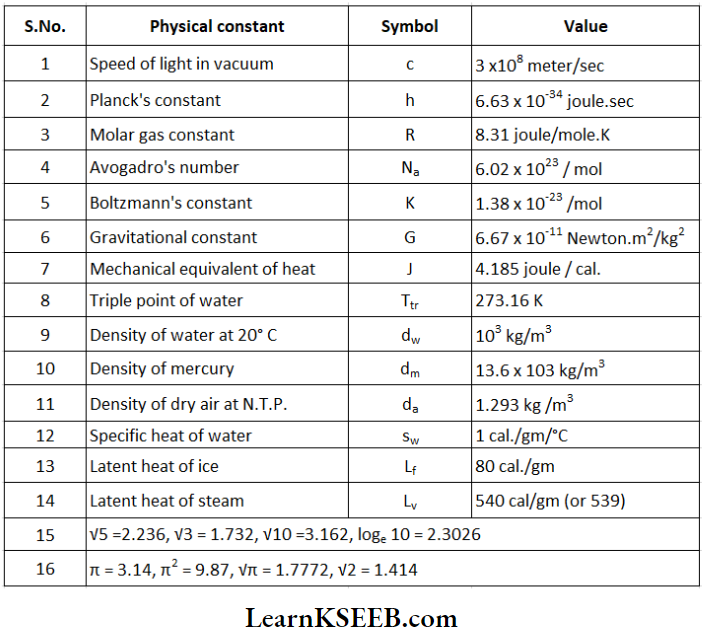
KSEEB Class 11 Physics Physical World Notes And Solutions
Conversion Factors:
- 1 metre 100 cm
- 1 millimeter 10-3 m
- 1 inch 2.54 x 10-2 m
- 1 micron (μ) 10-4 cm
- 1 Angstrom (A°) 10-8 cm
- 1 fermi (f) 10-13 cm
- 1 kilometer 103 m
- 1 light year 9.46 x 1015 m
- 1 litre 10³ cm³
- 1 kilogram 1000 gm
- 1 metric ton 1000 kg
- 1 pound 453.6 gm
- 1 atomic mass
- unit (a.m.u) 1.66 x 10-27 kg
- 1 a.m.u 931 MeV
- 1 day 8.640 x 104 seconds
- 1 km/hour \(\frac{5}{8} m/sec or 0.2778 meter/sec
- 1 Newton 105 dynes
- 1 gm wt 980.7 dynes
- 1 kg. wt 9.807 Newton
- 1 Newton/meter² 1 Pascal
- 1 atmospheric pressure 1.0133 x 105 pascal (N/m²) or, 76 cm of Hg
- 1 Pascal 10 dyne/cm²
- 1 Joule 107 erg
- 1 kilo watt hour 3.6 x 106 joule
- 1 electron volt (ev) 1.602 x 10-19 joule
- 1 watt 1 joule/sec
- 1 horsepower (HP) 746 watt
- 1 degree (°) 60 minute (‘)
- 1 Radian 57.3 degree (° )
- 1 Poise 1 dyne. sec / cm²
- 1 Poiseuille 10 poise (Newton, sec/m2² (or) Pascal sec.)
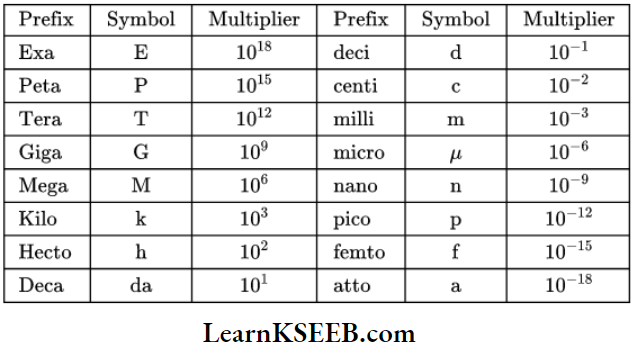
Important Prefixes:
The Greek Alphabet:
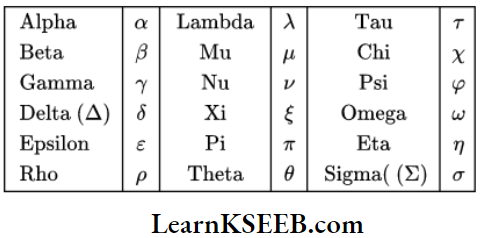
Formulae Of Geometry:
- Area of triangle = 1/2 x base x height
- Area of parallelogram = base x height
- Area of square = (length of one side)²
- Area of rectangle = length x breadth
- Area of circle = πr² (r = radius of circle)
- Surface area of sphere = 4πr² (r = radius of sphere)
- The volume of cube = (length of one side of the cube)³
- The volume of parallelopiped = length x breadth x height
- Volume of cylinder = πr²l
- Volume of sphere = [latex]\frac{4}{3}\) πr³and Circumference of square = 4l
- Volume of cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\) πr²h
- Circumference of circle = 2πr
Formulae Of Algebra:
- (a + b)² = a² + b² + 2ab
- (a-b)² = a² + b² -2ab
- (a² – b²) = (a + b) (a – b)
- (a + b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3ab (a + b)
- (a – b)³ = a³ – b³ – 3ab (a – b)
- (a + b)² – (a – b)² = 4ab
- (a + b)² + (a – b)² = 2(a² + b²)
Formulae Of Differentiation:
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (constant) = 0 dx; Differentiation with respect to x = \(\frac{d}{d x}\)
- \(\frac{d}{d x}\left(x^m\right)=n x^{n-1}\)
- \(\frac{d}{d x}(\sin x)=\cos x\)
- \(\frac{d}{d x}(\cos x)=-\sin x\)
KSEEB Class 11 Physics Physical World Key Concepts
Formulae of Integration: Integration with respect to x = dx
- \(\int d x=x\)
- \(\int x^n d x=\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}\)
- \(\int \sin x d x=\cos x+c\)
- \(\int \cos x d x=\sin x+c\)
Formulae Of Logarithm:
- log mn = (log m + log n)
- log(\(\frac{m}{n}\)) = (log m – log n)
- log mn = n log m
Value Of Trigonometric Functions:
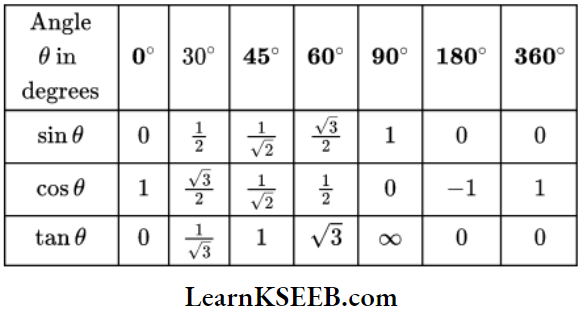
Signs Of Trigonometrical Ratios:
sin (90° – θ) = cos θ; sin (180° – θ) = sin θ
cos (90° – θ) = sin θ ; cos (180° – θ) = – cos θ
tan (90° – θ) = cot θ ; tan (180° – θ) = _-tanθ
According To Binomial Theorem: (1 + x)n ≈(1 + nx) if x < < 1
Quadratic Equation: ax² + bx + c = 0
x = \(\left(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4 a c}}{2 a}\right)\)
