KSEEB Solutions For SSLC Class 10 English Chapter 1 Summary A Hero Points to Remember
Swami and Friends is the first of a trilogy of novels written by R.K. Narayan. This lesson ‘A Hero’ is an excerpt taken from the novel. The lesson, though presented in a comic manner, teaches the values of courage, a fight against superstition and the use of presence of mind in a right mariner. Swami doesn’t believe his father when he reads an incident from the newspaper of bravery of a boy fighting with a tiger. Father says that courage is everything, strength and age are not important. Swami disputes the theory saying that how can he fight a tiger with courage.
Father gives Swami a challenge to sleep alone that night in his office room and prove his courage. Swami tries to distract his father from the challenge through a number of excuses, lie tried to get excuses with the help of his mother and granny but the father wouldn’t agree.
Swami pretentiously slept in his place with granny but his father wakes him and forces him sleep in his office room on a bench in the dark with the door open. At night he is so scared that he remembers all the stories of devils and ghosts he had heard in his life. He gets up and crouches under the bench and after some time falls asleep. He sees a dream of a tiger chasing him and attacking him He tries to escape but couldn’t move a little.
When he opens his eyes he finds himself alone in the dark. He felt something moving down. He thought it to be a devil, he crawls out of the bench, hugs it with all his might, and uses his teeth on it like a mortal weapon It was a burglar whom Swami had caught. The next day he was congratulated by all his friends and even his headmaster or his brave act. The policemen were grateful for nabbing a notorious housebreaker of the district.

SSLC English Chapter 1 A Hero Textual Exercises To Check Your Understanding
Question1. Swarm’s father drew his attention to a report in the newspaper. What was the report about?
Answer: The newspaper report was that a brave village lad who while returning home by the jungle path came face to face with a tiger. He had a fight with the tiger and climbed up a tree and stayed there for half a day till some people came that way and killed the tiger.
Question2. The report said that the boy (who fought with the tiger) stayed on the tree for half a day. Why did he do so?
Answer: He wanted someone to kill the tiger.
Question3. Swami said that a very strong and grown up person might have fought with a tiger. Do you think he made this remark out of his (choose the most appropriate word)
Answer: belief
Question4. “Can you prove you have courage?” Swami’s father said.
1) Was he joking? Or, serious?
Answer: Serious.
Question 2) Was it a challenge? Or, a command?
Answer: a command.
Question5. The place where Swami usually slept was_______(Fill in the blank)
Answer: beside his granny.
Question6. What is disgraceful, according to Swami’s father?
Answer: According to Swami’s father, it is disgraceful to sleep beside granny or mother like a baby.
KSEEB Solutions SSLC English A Hero Share Your Responses
Question 1. What do you think was the practice of granny before she went to bed?
Answer: Granny used to tell stories to Swami before she went to bed.
Question 2. Was Swami really sleeping? Or was he pretending?
Answer: Swami was pretending to sleep.
Question 3. To Swami, his father looked like an
Answer: apparition.
Question 4. Why do you think Swami looked at his granny and his mother while following his father to the room?
Answer: Swami looked at his granny and his mother while following his father to the room with the hope that they would come forward to help him escape from the orders of his father.
Question 5. “There might be scorpions before your law books,” said Swami.
1) Had he seen them earlier? Or were there scorpions really?
Answer: In real there were no scorpions behind the books,
2) Was it a trick to escape from his father?
Answer: Yes, it was a trick to escape from his father
KSEEB SSLC English Class 10 Prose Chapter 1 A Hero Share Your Responses
Question 1. Swami wished that the tiger hadn’t spared the boy, which means…
Answer: he didn’t want the boy to be alive.
Question 2. As silence deepened in the room, what was Did swami remind of?
Answer: As silence deepened in the room, Swami was reminded of all the stories of devils and ghosts he had heard in his life
Question 3. Which place in the room did Swami think was safe, compact and reassuring?
Answer: The safe, compact and reassuring place in the room was under the bench.
Question 4. Swami touched _______in the room instead of granny, (fill in the blank appropriately)
Answer: the wooden leg of the bench
Question 5. Swami saw a moving creature in the room. Was it
Answer: a man
SSLC Class 10 English A Hero Share Your Responses
Question 1. Who cried, “Aiyo! Something has bitten me?”
Answer: The burglar cried.
Question 2. Who did father, cook and a servant stumble upon?
Answer: Father, cook and a servant stumble upon the burglar.
Question 3. Why were congratulations showered on Swami?
Answer: Congratulations were showered on Swami as he had grabbed a burglar who had been the most notorious house-breaker of the district.
Question 4. Do you think Swami really wanted to join the police? If not, what did he want to be?
Answer: No, Swami did not want to join the police. He wanted to be an engine driver, a railway guard, or a bus conductor.
Question 5. Did Swam muster up the courage to sleep alone after the burglar’s incident?
Answer: No, he did not muster up the courage to sleep alone after the burglar’s incident.
Question 6. Who supported Swami? His mother or his granny?
Answer: Swami’s mother supported him
Class 10 SSLC English Chapter 1 A Hero Think About The Text
Question 1. A report about a boy in the newspaper was an unexpected event in Swami’s life. Justify.
Answer: A report about a boy in the newspaper was an unexpected event in Swami’s life. The newspaper report read by his father about the courage of a boy made Swami and his father in an argument in which the father tells him that courage is everything, strength and age are not important. Swami disputes the theory ofhis father. In order to prove his theory, Swami father challenged him to sleep alone that night in his office and prove that he had courage to sleep alone in darkness. The father did not listen to any excuse and made him to sleep there.
Question 2. Swami made a comment on the newspaper report. Was he right? How did his view differ from that of his father?
Answer: Swami made a comment that the person who faced the tiger boldly must be a very strong grownup person, not a boy at all because a boy cannot fight a tiger. Swami was wrong in thinking so because his father was of the opinion that a man may have the strength of an elephant and yet be a coward: where as another may have the strength of the straw, but if he has courage, he can do anything.
Question 3. What desperate attempts did Swami make to escape from his father?
Answer: Swami made desperate attempts to escape from his father’s challenge to him. First he told that he would sleep alone from the next month. Next he slowly went to his bed and slept covering himself completely with a blanket and began to snore.
Question 4. Why did Swami conclude that his father’s proposition was frightful?
Answer: Swami concluded that his father’s proposition was frightful because he had always slept beside his granny in the passage, and any change in that arrangement, kept him trembling and awake all night.
Question5. As the night advanced, S wami felt that something terrible would happen to him. What would it be? How would it happen?
Answer: As the night advanced and the silence in the house deepened, his heart beat faster. He remembered all the stories of devils and ghosts he had heard in his life. He remembered how often his friend, Mani had seen the devil in the banyan tree at his street end. He also remembered Muni swami’s father, who had spat out blood because the devil near the river’s edge had slapped his cheek when he was returning home late one night. His thoughts continued with many more such fears.
Question 6. There was absolute silence in the room. In spite of it, some noises reached Swami’s ears. What were they?
Answer: The noises that reached his ears were the ticking off the clock, rustle of trees, snoring sounds, and some vague night insects humming.
Question 7. Narrate Swami’s dreadful experience when he was lying under the bench.
Answer: After sleeping under the bench, Swami began to dream of being chased by a tiger. He desperately tried to escape but his feet would not move, the tiger was at his back, and he could hear its claws scratch the ground. Then he heard a loud thud but he could open his eyes. With a desperate effort he opened his eyes and found himself under the bench. And his lonely state came back to him. He sweated with fright. He saw something rustling and moving down. He lay gazing at it in horror. He realized that the devil would presently pull him out and tear him. AS it came nearer he crawled out from the bench, hugged it with all his might, and used his teeth on it like a mortal weapon.
Question 8. How was Swami honoured by his classmates, teacher, and the headmaster?
Answer: Swami was showered with congratulations. His classmates at him with respect and his teacher patted his back. The headmaster said that he was a true scout. Swami had bitten into the flesh of one of the most notorious house-breakers of the district and the police were grateful to him for it.
Question 9. Why did father want Swami to sleep alone in the office room?
Answer: Swami was very dependent and was pampered by his mother and granny. Swami’s father wanted Swami to be self-dependent, bold and courageous. When Swami’s father read the news of a boy lacing a tiger boldly, Swami argued that one has to be a grown-up in order to be courageous. His father tried to convince him by saying that a man may have strength of an elephant yet be a crowd: where as another may have the strength of a straw, but if he has courage, he can do anything. Courage is everything, strength and age are not important. Swami disputed the theory of his father. Swami’s father wanted to show him how lacked courage so he wanted Swami to sleep alone in the office room.
Question 10. Who do you think was wiser, Swami or his father? Justify your preference.
Answer: Swami’s father was obviously wiser due to age and experience. He had seen and experienced the world where as Swami was still a small boy who was pampered and well protected by his mother and granny.
Question 11. Why did Swami feel relieved at the end?
Answer: Swami felt relieved when his father agreed to allow Swami sleep in his original place beside his granny.
Question 12. Suppose you are Swami of the story. Write a brief letter to your friend describing how you helped to catch a burglar in your house.
Answer: Students to answer.
Question 13. Some words describing the characters of the story A Hero’ are given in brackets. Put them in these columns appropriately.
Answer: Swami’s father: tricky, authoritative, disciplined. Mother: caring, protective.
Granny: caring, protective.
Swami: innocent, helpless, nervous.
KSEEB English Class 10 Chapter 1 A Hero Enrich Your Vocabulary
Task 1: Homophones. Fill in the blanks with appropriate word.
1. We had______ many apples to carry.
Answer: too
2. I_______ a horse at the Marirma Beach.
Answer: rode
3. Did you have a ______for lunch?
Answer: pare
4. The books are over on the shelf
Answer: there
Task 2: Fill in the blanks choosing the appropriate word and complete the story.
This is a __I_______told by a__2_____Once he received a letter. When he .3 ______it___4 ____he could not believe his own eyes. ___5____ it was written ____6 _____none other than the queen of the land. She asked him to meet her___ 7 _______a secret place. The knight was in a fix. But he thought ___8_____ a plan to tide over this problem. He_____9 to the meeting place, not alone, but along with his ___10 _______wife. Can you guess what happened then?
Answers:
1) Story
2) Knight,
3) Read
4) Through
5) For
6) By
7) At
8) Of
9) Went
10)Fair
Task 3: Scramble the letters to form words. See the meaning clues in brackets.
1. a t r t e f 1______ (praise)
Answer: Flatter
2. b o u d t______ (suspect)
Answer: Doubt
3. r a g g e d y _______(unhappy ending)
Answer: Tragedy
4. r a g f e n m t _____(apiece)
Answer: Fragment
5. r a e t l ____(careful)
Answer: Alert
6. c a c s r l y t_____(short supply)
Answer: Scarcity
7. y m t a s t h p e i c (not cruel)
Answer: Sympathetic
KSEEB Solutions For SSLC Class 10 English Chapter 1 A Hero Practice Writing
Briefly explain what is funny about each of these signs given in italics. (Reframe them to read appropriately
Answer:
1. Our best homemade pies for you.
2. Wanted two waiters and a young dish washer (maid) for the restaurant.
3. Fast haircut while you wait.
4. We sell lawnmowers here.
5. Instant soft drinks are sold here.
Learn grammar through communication.
1) Rewrite the sentences beginning with the ‘clue’ given in brackets.
2) Identify the language function.
Question 1. Please return my library books.
Answer:
1) Will you please return my library books?
2) Making request
Question 2. The files are heavy I’ll carry them for you.
Answer:
1) Would I carry these files for you?
2) Offering help.
Question 3. That’s your essay. Perhaps you have no objection if I see it.
Answer:
1)May 1 see your essay?
2) Seeking permission.
Question 4. Let me switch on the fan, OK?
Answer:
1) Do you mind if I switch on the fan? OR – Do you mind me switching on the fan?
2) Making offers or preferences.
Question5. Bring the books to my office.
Answer:
1) Would you please bring the books to my office? OR – Would you mind bringing books to my office?
2) Making request.
KSEEB SSLC English Class 10 Prose Chapter 1 A Hero Dictionary work
The box contains the words that have their synonyms in the lesson. Find them out and write them along with the sentences in which they are used.
Shameful lose conscious proposal or suggestion murmured unclear or indefinite covered moan or grumble extremely in the middle of accused shake with fear
Answers:
1. shameful – disgraceful
2. lose conscious – faint
3. proposal or suggestion- proposition
4) murmured – mumbled
5) unclear or indefinite – vague
6) covered-encased
7) moan, grumble – groan
8) extremely- tremendously
9) in the middle of- amidst
10) accuse -blame
11) tremble – shake with fear
SSLC Class 10 English A Hero Derogatory Terms
Text Box A has the derogatory terms and Text box B has their synonyms. Match them and write them together.
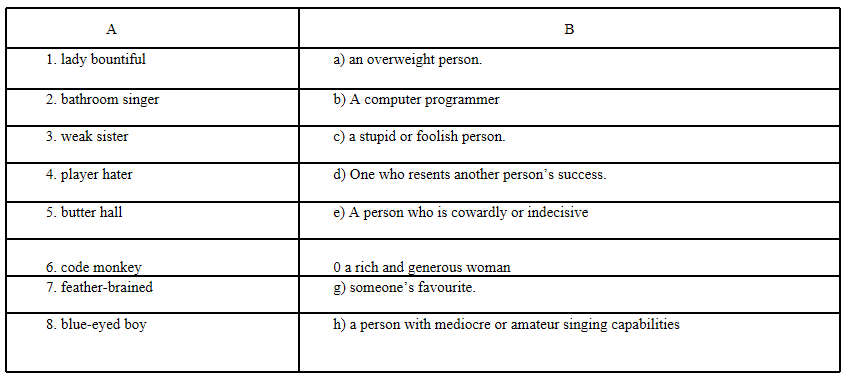
Answers:
1-f
2-h
3-e
4-d
5-a
6-b
7-c
8-g
Homophones: There are many words in the lesson for which homophones can be added. Read the lesson in pairs and find them out and add the other word to make pairs of homophones and find out their synonyms. One example is done for you.
Example: groan – grown
Answers:
1) By-buy
2) Face-phase
3) New-knew
4) Know-no-now
5) Night-knight
6) Weak-week
7) Once-ones
8) Leave-live
9) Feet-feat
10) Eyes-ice
11) Way-weigh
12)Forth-fourth
13) Break-brake
14) Peace-piece
15) Whole-hole
16) Hear-here
17) Claws-clause
Use the following words in sentences first as verbs and then as nouns:
1. trouble
Answer: trouble (v): Children should not trouble their parents.
trouble (n): The boy was in trouble due to his mischief.
2. produce
Answer: produce (v): Modem refrigerators do not produce
much sound.
produce (n): The agricultural produce has increased credibly due to scientific methods.
3. Pay
Answer: pay (v) Students should pay attention to their studies.
pay (n): Employees get their salaries on the first of every month.
4. Ride
Answer: ride (v): Raju likes to ride his bike very fast.
ride (n): We had a jolly ride on the elephant in Bandipur National Park.
5. Thought
Answer: thought (v): I have thought of visiting my native place
this weekend.
thought (n): The thought of visiting my Kashmir thrills me.
6. slap
Answer: slap (v): Children should never be slapped on the
face.
Slap (n): Ravi had a slap on his cheeks by his brother for telling lies
KSEEB SSLC English Class 10 Prose Chapter 1 A Hero Interesting Activities On Comprehension And Composition
Question 1. The report about the boy was that the boy
1) Had killed a tiger
2) Had saved a tiger
3) Faced the tiger boldly
4) Called the people to kill the tiger
Answer: 3) Faced the tiger boldly
Question2. Swami disputed the theory of his father because Swami believed that
1) Only strong and grown-ups can face the danger
2) Strength grows with age
3) Courage is nothing to do with age
4) One cannot face the danger only with courage
Answer: 1) Only strong and grown-ups can face the danger
Question 3. ‘Any change in this arrangement kept him trembling… ’ The arrangement refers to
1) Swami used to sleep alone in his room
2) Swami used to sleep beside his granny in the passage
3) Swami slept beside his mother in her room
4) Swami had to sleep in the office room of his father
Answer: 2) Swami used to sleep beside his granny in the passage
Question 4. He knew his father’s tenacity at such moments. The word ‘tenacity’ means
1) Confusion
2) Commands
3) Mood
4) Determination
Answer: 4) Determination
Question 5. ‘Don’t talk to me, and don’t let anyone call me… ’, Swami said so
1) Because he was feeling very sleepy
2) In order to show his anger to his father
3) Because he didn’t want his father know about his sleeping there
4) Because he didn ’ t want to sleep with his granny
Answer: 3) Because he didn’t want his father know about his sleeping there
Question 6. ‘It seemed to be a much safer place, more compact and reassuring’. The place was
1) Under the bench in office room
2) The office room with lights on
3) Beside his granny in the passage
4) Outside the office room
Answer: 1) Under the bench in office room
Question 7. He looked like an apparition in the semi-darkness of the passage. The figure of speech used here is
1) Synecdoche
2) Metaphor
3) Personification
4) Simile
Answer: 4) Simile
Question 8. As it came nearer he crawled out from the bench, and hugged it with all his might. Swami had hugged
1) His father
2) The devil
3) His granny
4) Burglar
Answer: 4) Burglar
Class 10 SSLC English Chapter 1 A Hero Read The Following Answer The Questions That Follow
You think you are wiser than the Newspaper?’
Question 1) Who is the ‘you’?
Answer: Swami
Question 2) What was the news report?
Answer: The news report was about the boy who faced a tiger boldly.
Question 3) Why did the speaker say so?
Answer: Because Swami refused to believe the news report.
‘Can you prove you have courage?’
Question 1) Name the speaker and who is the ‘you’?
Answer: The speaker was Swarm’s father. ‘You’ refers to Swami.
Question 2) How was the listener supposed to prove his courage?
Answer: He was supposed to prove his courage by sleeping alone in his father’s office room at night.
Question 3) What was the reply of the listener?
Answer: Swami unwillingly said ‘yes’ and tried to change the topic of their conversation.
‘If you do it, I’ll make you the laughing stock of your school’.
Question 1) What is the ‘it’ refers to?
Answer: ‘It’ refers to Swami sleeping beside his granny at night.
Question 2) Why was the person not supposed to do it?
Answer: Swami was not supposed to do it because he had taken the challenge of sleeping alone in the office room of his father that night.
Question 3) Give the meaning of‘laughing stock’.
Answer: an object of ridicule.
‘Aiyo! Something has bitten me’.
Question 1) Name the speaker.
Answer: The burglar.
Question2) What had bitten the speaker?
Answer: Swami had bitten him.
Question3) Why was the speaker bitten?
Answer: Swami bit him in defense thinking that it was a ghost.
Class 10 SSLC English Chapter 1 A Hero Gap Filling
Choose the best word from the options given below to complete the following letter.
Dear Daddy
I hope all’s well with you. Everything is fine here. I am sorry I (1)_____ write earlier. I was busy with my coaching camp (2)______ is now over. After the annual examination, most of (3)______ boarders have left for their homes. Only a few like me (4)_______ left behind. I can’t express how badly I miss you all. I don’t
know (v)_____ I’ll be able to join you. Dad, I hate (vi)_____ a border. How lonely
it is to stay here during the vacation! The few inmates left are not only boring but also nasty. I hope you will come to my rescue soon.
Options:
1) (a) couldn’t) hasn’t c) have not d) hadn’t
2) (a) which b) being c) to d) only
3) (a) which b) the c) are d) when
4) (a) couldn’t b) which c) when d) are
5) a) the b) being c) when d) am
6) a) being b) which c) to d) couldn’t
(1) a
(2) a
(3) b
(4) d
(5) c
(6) a











