KSEEB solutions for SSLC Class 10 Prose Chapter 5 The Concert Points To Ponder
The lesson is a touchy real-life incident in which a boy’s ambition was fulfilled by his sister which seemed to be impossible.
Anant was a fifteen-year-old boy suffering from cancer last stage. He was the best table tennis player in the school and was the fastest runner.
He was learning to play sitar lessons. He was able to compose his own tunes to the astonishment of his guru.
Then cancer struck him and the doctors had given up hope and he was on a life-supporting system.
Smita, his sister wanted to fulfill his ambition of attending the concert of Pandita Ravi Shankar at the Shanmukhananda Auditorium in Bombay where their family of four stayed in a small apartment for his treatment.
The words of Anant, I must hear him and see him, it’s the chance of a lifetime, were striking in the mind of his sister. She made her mind to attend the concert with some thought.
After the concert, Smita wriggled her way through the crowds towards the stage, with great hope she went before him, with folded hands she addressed him and told him the story of his brother and his ambition to hear his concert.
To her great astonishment, the great maestro agreed to perform in her house the next morning.
The next morning, the two great human beings, Pandit Ravi Shankar and Tabla master UstadAllah Rakha, and played for the boy in his house surrounding him with great and beautiful happiness as life went out of him, gently, very gently.

SSLC English Class 10 Chapter 5 The Concert Textual Exercises
Question 1. Which word in the first paragraph describes the manner of the girl when she saw the newspaper?
Answer: Excitedly.
Question2. Why do you think the mother cautioned the girl?
Answer: Because the ailing boy was asleep and needed sleep and rest. More than that it loo:s the mother did not want the boy to know about that news.
Question3. We mustn’t miss the chance.
a) What chance did the boy not like to miss?
Why? Do you think the boy Would get a chance in the future?
Answer: The boy did not want to miss the chance to listen to the concert of Pandit Ravi Shankar as he had always wished to hear and see Pandit Ravi Shankar. It was a chance of a lifetime as the boy was on the last stages of cancer and might not live to witness the same in the future.
Question4. Imagine you were the mother of the boy; would you have reacted differently In the situation? If so, how?
Answer: I would have reacted in a similar manner if I were to be the mother of the boy. The boy was ailing with cancer and had no strength even to get up so it was better for him to rest and not bother about other things. Since the boy liked music concerts but was not in a condition to attend them, I would not have liked the boy to know such news and feel sad and disgusted for not being able to fulfill his wish.
Question 5. Read the third paragraph. He raised himself up without any help. The mother murmured with a catch in her throat on seeing him. What does this suggest about the condition of the boy? Read the fourth paragraph and answer.
Answer: The condition of the boy was very serious. His condition had deteriorated to such an extent that even the slightest movement tired him and made him gasp for breath. He had to be given oxygen every now and then.
Class 10 English The Concert Share Your Responses
Question 1. For a moment, Smita had forgotten something. What was it?
Answer: Smita had forgotten that her brother was ill and would not be able to accompany her to the concert.
Question 2. In what way was the truly frightening to Smita?
Answer: The frightening truth to Smitha was that her brother was in the last stage of cancer and would die anytime.
Question 3. Do you consider Anant a talented boy? Justify with support from the text.
Answer: Anant was an extremely talented boy. He was the best table tennis player in the school at the young of just fifteen years. He was the fastest runner. He was learning to play sitar and was doing better than his elder sister. He had already composed his own tunes to the astonishment of his guru.
Question 4. ‘They had come with high hopes’.
a. What were their ‘high hopes’?
Answer: They hoped that Anant would be cured at the hospital, and he would again walk and run and even take part in the forthcoming table tennis tournament. And he would play the sitar and perhaps would be a great sitarist one day.
b. Do you think their hopes would be fulfilled? Support your
Answer: The condition of Anant was deteriorating day by day, so the chances of Anant’s recovery were very remote.
c. Doctors said something to the parents. Were those words of hope or words of despair? (Para.6)
Answer: The words of the doctors were despairing. They asked their parents of Anant to take him home and give him the things he liked. Thus these words were a proofthatAnant did not have many days to live.
Question 5. ‘Her eyes filled with tears’, were they tears of happiness or sorrow? Give reasons.
Answer: They were tears of sorrow because she knew that her brother was not in a condition to attend the concert and would not be alive to see the concert the next time. She was also feeling miserable and helpless as she was not in a position to fulfill her brother’s last wish.
Question 6. ‘Suddenly a daring thought came to her’. Can you guess what thought Smita had?
Answer: Smitha had thought of meeting Pandit Ravi Shankar after the concert and tell him about his brother’s condition and plead him to come home and perform for his brother.
The Concert Summary For Class 10 SSLC English
Question 1. The word ‘gasp’, according to this dictionary, suggests- surprise or pain. Which meaning is relevant in this context? (Para.10).
Answer: Pain
Question 2. As Smita sat listening to music, she was spellbound. But all the while, her mind was echoing something else. What was that?
Answer: As Smitha sat listening to music, she was spellbound by the enchanting ragas. But all the while the plan she had decided to meet Pandit Ravi Shankar and talk to him about her brother remained firm in her mind. The words of her brother, ‘the chance of a life time’ kept on echoing in her mind.
Question 3. Why does the writer use the word ‘wriggled’ to describe Smita’s movement?
Answer: Smita’s movements were described as ‘wriggled’ may be to show the excitement and anxiety Smitha suffered in her as she hoped against hope. Her plan of meeting and talking to Pandit Ravi Shankar about his and requesting him to come to her house to perform for her brother was a very strange and uncertain plan that she had made in despair so she was full of anxiety.
Question 4. Samita’s nervousness is suggested by the phrase ‘her heart beating loudly’ in paragraph 12. Identify two more phrases that describe a similar state in the next paragraph.
Answer: felt weak, tongue dry
Question 5. Did Smita tell what she had in her mind to the musicians? Who responded to her request immediately. What was the response?
Answer: Yes, Smita told the musicians what she had in her mind. The mustachioed man who had made the long speech responded immediately. He told Smita that Pandit Ravi Shankar was a busy man so she should not bother him with such requests
Question 6. Do you think the response of the artists was unusual? If not, why?
Answer: Yes, the response of the artists was unusual. Pandit Ravi Shankar and Ustad Allah Rakha were the celebrities. They were very busy with commitments and it was very difficult to spare time for such reasons. But still, these personalities accepted the request of Smita and kept up their word. This shows that they are kind and compassionate human beings
Question 7. This neighbor could not believe their eyes. Why do you think they felt like this?
Answer: The neighbors could not believe their eyes because they saw two great celebrities visiting the house of Anant and Smita. They were more astonished when they saw these two great maestros perform for Anant. It was indeed an unusual sight for anybody.
Question 8. Can you say that the concert was entertaining to Samita? Justify your answer.
Answer: When the concert began, Smita felt as if the gates of enchantment and wonder were opening. Spellbound, she listened to the unfolding ragas, but all the while the plan she had decided the previous day remained firmly in her mind and the words of her brother kept on echoing in her mind. This shows that though she liked the concert very much, she could not enjoy it completely due to the tension and anxiety she had in her mind
Question 9. Samita was nervous as she stood before the wizard. Which sentence suggests this?
Answer: Her knees felt weak, and her tongue dry.
Question 10. Did Pandit Ravi Shankar and UstadAllah Raksha perform in the Boy’s house? Do you think this was an unusual incident? If yes, give reasons.
Answer: Yes, Pandit Ravi Shankar and UstadAllah Rakha did perform in the house of Anant. It was indeed an unusual incident because it is very rare to see the celebrities like these two maestros visit the house of common man for such reasons
KSEEB Class 10 English Prose Chapter 5 Question And Answers The Concert Think About The Text
Question 1. Do you like the story? Why
I like/don’t like, because. . ..(One reason in given.
You may give as many other reasons as you like)
A) This is a story about music
B) The story depicts love and affection ofa sister for her brother.
C) It shows how a sister can go to any extent to fulfil the ambition of her brother.
D) It depicts the humility and compassion shown by two great maestros.
E) It also depicts how cancer can be fatal and take toll ofthe children who are young and energetic
Question 2. In your opinion, which words in the list below The boy is….describe Anant’character or state? Write Yes/ No in the space given. (Refer to a dictionary for the words that you are not sure of)
a. Energetic -No
b. Robust -No
c. Aesthetic – Yes
d. Imaginative – Yes
e. Confident – Yes
3. Look at the following phrases in the lesson. They are descriptive.
Categorize them in columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ appropriately, {spellbound; unfolding the gate of enchantment; plaintive notes; fast twinkling ones;first notes; wonder, dream; unfolding ragas.
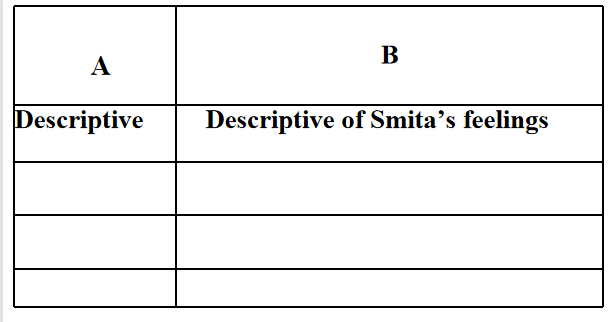
Answer: Descriptive of music- unfolding the gates of enchantment, plaintive notes, fast twinkling ones, first notes, unfolding ragas. Descriptive of Smita’s feeling – spellbound, wonder, dream
Question 4. Ustad Sahib and Pandit Ravi Shankar agreed to perform for the boy. What made them agreed to do so? What would have you done if you were the musician? The two maestros were touched by the story of Smita’s brother. The tears, anxiety, and boldness shown by Smita to convince them made them feel the condition of the boy and his love for their concert. They were great human beings who had compassion for consideration for others’ feelings. Therefore they agreed to perform
5. Suppose you are Smita and invite Pandit Ravi Shankar(PRS) to your home. Imagine the conversation that follows and write it. Some clues are given.
You (Samita): Good evening sir, May I have a word with you, please?
You (Smita) : Good evening sir, May I have a word with you, please?
PRS: Well?
My brother is a great a fan of yours
PRS: I’m glad to hear this,is he here?
you: No, he can’t come here, he is bedridden as he is suffering from cancer
PRS:I’m sorry to hear this. How Can I help you?
You: Would you kindly come with me to see him
PRS : (looking at others) What do you say?
You: Please, I beg you all to come and play for him
Mustachioed man: Are you joking? Do you know whom are you talking to?
Don’t bother them with your silly talk
PRS: Sh! (Silencing him) so What shall we do ustad?
Allah Raksha : (after some thought) Don’t weep, Don’t worry, child We’ll be there at your house tomorrow.
KSEEB SSLC English Chapter 5 The Concert Enrich Your Vocabulary
Task 1: Complete the crossword with the help of the following clues- Across and down. Refer to the dictionary for any help

Clue Across
1. To make a sound louder (7)- Amplify
7. A short unit in music, or part of pub (3)- Bar
8. A lot of musicians who play together (9)- Orchestra
11. A kind of dance popular in the 1950s (5)-given in the crossword)-Twist
13. To call off. To give up something that was planned (6)- Cancel
14. We’ll bring the work Thursday (preposition)(2)- On
15. Top rock stars lot of money (Verb) (4)- earn
16. A collective word used to describe trumpets, trombones etc (5)-Brass
17. Asong sung by two people (4)-Dute
18. If you want to record a song, you should make of a good studio. (3)- Use
Clue Down
1. Preposition (2)- At
2. It is stereo (4)-Mono
3. A long playing record (2)- (given in the crossword)-Lp
4. Music and painting are examples of this (3)-Art
5. The maestro keeps looking at it,as he conducts the orchestra(6)-Chart
6. Another name for the word ‘Instrument’ (5)- Organ
7. The most famous pop group of all time (7)- (given in the crossword) – Beatles
9. Musical entertainment to the audience (7)-Concert
10. It might a C.D., or else a ‘vinyl’. It repeats the voice when desired. (6)-Record
12. A flutist plays, but a vocalist-Signs
16. It has forms like – is, am, was etc.-Be

Task 2: Drafting a Wedding invitation. This is a Wedding Invitation card which is designed by the parents of the bride. Read Carefully

SSLC English Prose Chapter 5 The Concert Learn Grammar Through Communication Finite And Non Finite Verbs
Verbs can occur in sentences in a variety of shapes or forms. For example, if we take the verb ‘write’, this verb can be used in sentences in these five forms or shapes.
e.g,
a. Vinaywrites well.
b. Vinay and Vijay write to each other.
c. Vinay wrote to me about his tour.
d. Vinay is writing all the time.
e. Vmay Has written me a long letter.
f. Vinay has decided to write letter to the chairman.
Verbs – writes, write, and writing are finite verbs since they indicate tense-present past. A finite verb carries tense on its own.
If we take the other forms of write namely, writing, written, and to write they do not indicate the tense. Such forms of the verbs are called Non-finite verbs. The ANon-finite verb does not carry tense on its own.
e.g.: Some verbs are underlined in the passage given below. See how they are classified into finite and non-finite verbs
They were
(1) Waiting
(2) For the bus. After a long time, it came
(3) The bus was
(4) Heavilycrowded
(5) Anyway, they managed
(6) To push
(7) Through and they squeezed
(8) Themselves in. They felt
(9) Tired
(10) As they had
(ll) Been
(12) Waiting
(13) For a long, I wonder
(14) Who can
(15) Ever improve
(16) Our transport system.
Finite verbs and Non-finite verbs
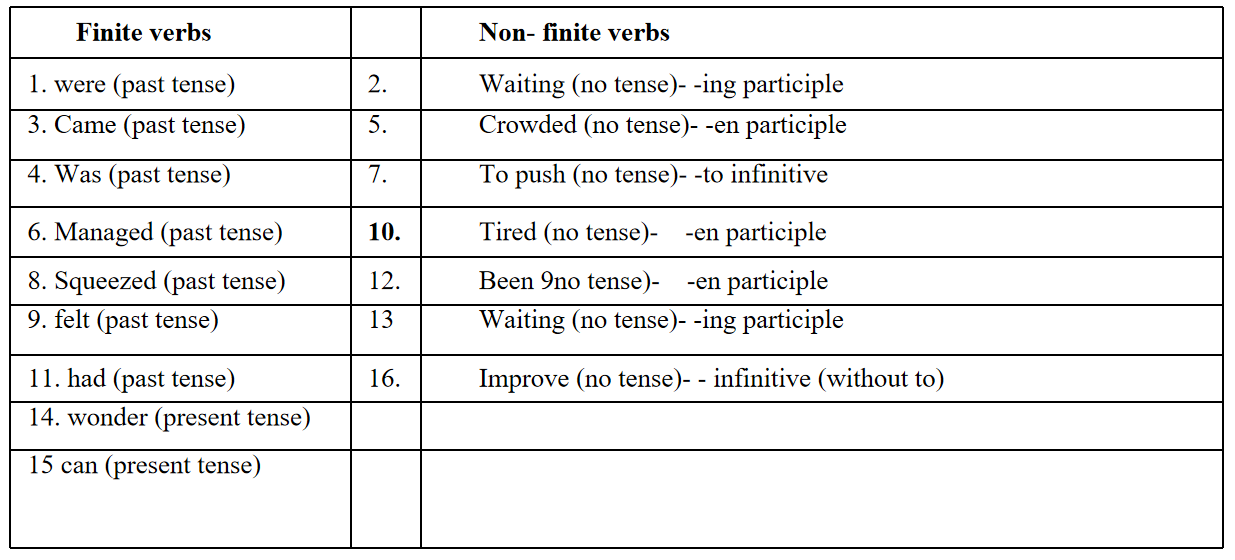
Task 1: Read the paragraph and classify the underlined verbs into Finite verbs and Nonfinite verbs. Write these of the finite verbs and the type of Non-finite verbs.
To examples are given. Smitabit her lip itself-reproach. She had been so excited at seeing the announcement that she had not remembered that her brother was very ill. She had seen how the doctors had shaken their heads gravely and spoken words that neither she nor even her parents could understand. But somewhere deep inside, Smita had known the frightening truth that Anant was going to die. The word cancer had hung in the air. Her brother was dying of cancer even though she pretended that all would be well and they would return together, a small family of four, to their home in Gangapur. And he was only fifteen, and the best table tennis player in the school and the faster runner. He was learning to play the sitar; they were both taking sitar lessons, but Anant was better than are as in many other things. He was already able to compose his own tunes to the astonishment of their guru. Then cancer had struck and they had come to Bombay so that he could be treated at the cancer hospital in they city
Finite verbs
had -past tense
Non-finite verbs
understand – infinitive without
Task 2: Look at the signs below. Frame appropriate sentences on each of them. First, identify the verbs. Then analyze each verb as in task 3 above. One example is done.
Analyses of verbs
1. Are – finite — present tense
2. Requested – non-finite participle
3. To keep off – non-finite -infinitive with to
Class 10 SSLC English Chapter 5 The Concert Make Reference
Decode the following sms into the sentences: (one has been done for you)
Question 1. ‘Tryitjst Is again,’he words Sentence: ‘Try it just
Answer: once again,’ he would say.
Question 2. Yday, i rot leaVletta 2 hm
Answer: Yesterday, I wrote a leave letter to him.
Question 3. My sis gt 8T% n mats n 2nd tst.
Answer: My sister got 80% in maths in the second test.
Question 4. bravo India Id match
Answer: Bravo! India won the match.
Question 5. w’rguna excursiononsatday2 historical places.
Answer: We are going on an excursion on Saturday to historical places.
Question 6. I’m ill, i do not attend today’s Skool so plagiary the notes intervening.
Answer: I am ill, I cannot attend today’s school so Please give your notes in the evening.
Question 7. do d mark quickly n zzzwel. Gudn8.
Answer: Do the homework quickly and sleep well. Good night.
Interesting language activities for formative assessment vocabulary and grammar
1. Anagram Square
In the following puzzle, all the words across have the same letters but in a different order. The placement of one letter is indicated. Find the words.
a)
M_ _ _ – MITE
_ M_ _ – EMIT
_ _M_ _- TIME
_ _ _M – ITEM
b)
N_ _ _ _ – NOTES
_N_ _ _ _ – ONSET
_ _N_ _ _ – TONES
_ _ _N_ _ – STONE
The Concert Notes for Class 10 SSLC Dictionary Work
Choose the words from box A and complete the sentences in box B
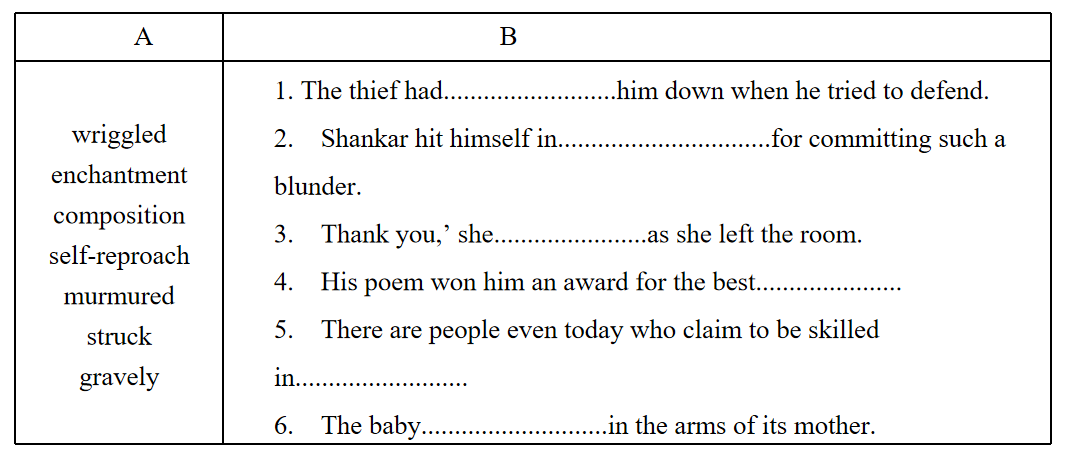
Answer: wriggled enchantment composition self-reproach murmured struck gravely
1. The thief had him down when he tried to defend.
2. Shankar hit himself in…………….for committing such a blunder.
3. ‘Thank you,’ she as she left the room.
4. His poem won him an award for the best
5. There are people even today who claim to be skilled in
6. The baby is in the arms of its mother.
Class 10 English The Concert KSEEB Solutions Interesting Activities on Comprehension And Composition
Get Into Pairs, Read The Lesson Carefully And Choose The Correct Option To Complete The Sentences.
Question 1. He raised himself up on his elbow for one second, then fell back
a) As he changed his mind not to raise further
b) Since he could not continue to do so
c) As it was his practice of doing so
d) As per the instruction of the doctors.
Answer: b) since he could not continue to do so
Question 2. She murmured with a catch in her throat. The underlined phrase means
a) With a choke in the throat
b) With something to hide from revealing
c) In order to draw the attention of others
d) With a feeling of great sorrow
Answer: d) with a feeling of great sorrow
Question 3.‘It’s the chance of a lifetime, said Anant because he knew that
a) He would not be alive to see it next time
b) He might not get another chance to see the concert
c) The maestros would not visit his city the next time
d) That was the last concert of the maestros
Answer: a) he would not be alive to see it next time
Question 4. In the park, Smitafelt is alone in the midst of so many things and people around her. This shows
a) That she did not like going there
b) That she was feeling very sad and helpless for her brother
c) Her anxiety to meet the two maestros
d) That she did not like the company of her aunt.
Answer: b) that she was feeling very sad and helpless for her brother
Question 5. Smita wriggled her way through the crowds toward the stage
a) To greet the two maestros
b) To help carry bouquets for the maestros
c) To meet and talk to the two maestros about her brother’s wish
d) As she had an appointment with the maestros
Answer: c) To meet and talk to the two maestros about her brother’s wish
Question 6. They could not believe their eyes when they saw
a)The two maestros entered the apartment of aunt Sushila
b) Anant began to raise to meet Pandit Ravi Shankar
c) Smita went on the stage to meet the two maestros
d) Anant breathing his last
Answer: a) The two maestros entered the apartment of aunt Sushila
Question 7. Finally, he agreed to coach him daily for two hours. The finite verb in the sentence is
a) Coach
b) Daily
c) Finally
d) Agreed
Answer: d) Agreed
Class 10 English The Concert Read The Extracts Carefully And Answer The Questions That Follow
Question 1 . ‘I must hear him and see him’.
a) Who is the T and ‘him’?
Answer: ‘Prefers to Anant and ‘him’ refers to Pandit Ravi Shankar.
b) Why did the person say so?
Answer: Anant was a great fan of Pandit Ravi Shankar.
c) What does the words of the speaker show about him?
Answer: His words show his longing for attending the concert.
Question 2. ‘But they did not voice their fears’.
a) Who are the ‘they’?
Answer: The parents of Anant.
b) What was their fear?
Answer: Their fear was that Anant would die anytime.
c) Why did they not voice their fears?
Answer: They did not want Anant to know that he would die anytime.
Question 3. ‘She was lost in her thought’.
a) Who is the ‘she’?
Answer: Smita
b) Where was she and what was she doing?
Answer: She was in a park for a walk.
c) What were her thoughts?
Answer: She was thinking about her brother’s wish to attend Pandit Ravi Shankar’s concert
The Concert Class 10 English Question And Answers The Concert Finite And Non Finite Verbs
Complete The Sentences With An Infinitive Using The Words In Brackets.
Question 1. “I’ll send you to China.”
His boss to China (promise, him)
Answer: promised to send him
Question 2.“All right, I’ll give you a ten percent discount.”
The shopkeeper (agreed, me)
Answer: Agreed to give me a ten percent discount.
Question 3.“We’re moving out of this town next year.”
They are out of this town next year, (plan, move)
Answer: They are planning to move
Question 4.“Show me all the dresses on that shelf, please.”
The customer all the dresses on the shelf, (asked, the salesman)
Answer: Asked the salesman to show
Question 5. Don’t tell anyone what I just told you.”
My friend anyone what she told me. (asked, me)
Answer: Asked me not to tell
The Concert Answer The Correct Words From Those Given In Brackets.
1. My watch has stopped (to work/working)- Working
2. I would like (to buy / buying) a better one.- To buy
3.T don’t know where (to go/going) for one. – To go
4. lam not very interested in (to shop/shopping) – Shopping
5. Thank you for (take /taking) me to the cinema. – Taking
KSEEB Guide For SSLC Class 10 Prose Chapter 5 The Concert Fill In The Blanks With The Correct Form Of The Verb In The Brackets
Question 1.S alma decided Some lime juice, (make)
Answer: To make
Question 2. After the limes, she removed the seeds, (cut)
Answer: Cutting
Question 3. She added sugar after the juice of the limes in a bowl, (squeeze)
Answer: Squeezing
Question 4. After that, Salma added a little warm water to the sugar, (dissolve)
Answer: To dissolve
Question 5. She also stirred the sugar well sure that all of it had dissolved, (make)
Answer: To make
Question 6. Then a strainer, she strained the juice the juice into a glass, (use)
Answer: Using
Question 7 that, she added ice and some cold water, (have)
Answer: Having
Question 8. Finally, she added a pinch of salt out the flavor, (bring)
Answer: To bring












