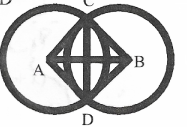KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement In Food Resources Important Concepts
Crop yields, crop variety, crop production manure and fertilizers, Irrigation, cropping patterns. Animal husbandry – cattle farming, poultry farming, Fish production, Beekeeping.
Crop production: Crops are plants cultivated by human beings for food, fodder, and other materials. The important types of crops are. Cereal crops – Wheat, rice, maize, Pulses – Pea, Greengram, Oil seed – Groundnut, soybean
Crop seasons:
1)Kharif season -These crops are grown in the rainy season.
Example: Paddy, soybean.
2)Rabi season – These crops are grown in the winter season.
Example: Wheat, peas.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Macronutrients: The essential elements utilized by plants relatively in large quantities.
Examples: Nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, and calcium.
Micronutrients: The essential elements utilized by plants in small quantities.
Examples: Manganese, Boron, Zinc, and Copper.
Manures: Manures are organic substances obtained through the decomposition of plant waste and animal excreta. Manure can be classified into
1)compost
2)Vermicompost
3)Green manure.
Fertilizers: Fertilisers are commercially produced plant nutrients.
Types of fertilizers:
1)Nitrogenous fertilizers
2)Phosphatic fertilizers
3)potassic fertilizers
Organic Farming: It is a farming system with minimal or no use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides, etc., and with a maximum input of organic manures, recycled farm wastes, etc.
Irrigation: It is the process of supplying water to crop plants in the fields by means of canals, reservoirs, wells, tube wells, etc.,
Mixed cropping: It is the practice of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land. Eg. Wheat + gram, ground nut T sunflower.
Intercropping: It involves growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of a second crop.
Example : soybean + maize + cowpea
Crop rotation: The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a preplanned succession is known as crop rotation.
Pest: Any destructive organism that causes great economic damage to crop plants.
Example: Insects, mites, etc.,
Pesticide: It refers to a chemical that is used to kill a pest organism.
- Insecticides – killing the insects
- Weedicides – killing the weeds
- Fungicides – killing the fungi
- Rodenticides – killing rodents
Weeds: They are small-sized unwanted plants that grow along with a cultivated crop in a field.
Livestock: It refers to the domestic animals kept in use for milk, and flesh and includes cattle, buffaloes, sheep, and goats.
Animal husbandry: Animal husbandry is the scientific management of animal livestock. It includes various aspects such as feeding, breeding, and disease control.
Cattle farming: Cattle husbandry is done for two purposes milk and drought labor. Milk-producing females are called milch animals. Draught animals are used for farm labor.
Breeding: It means ‘to reproduce’ and is done to obtain animals with desired characteristics.
Poultry: It is the branch of animal husbandry concerned with rearing birds for eggs and meat. Poultry practices required good care for food, shelter, and disease control.
Fish production: There are two ways of obtaining fish. One is from natural resources, which is called capture fishing. The other way is by fish farming, which is called culture fishery.
Bee-keeping: Bee-keeping or Apiculture is the rearing, care, and management of honey bees for obtaining honey, wax, and other substances.

Improvement In Food Resources Exercises
Question 1. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Answer: Intercropping is one of the methods of crop production which ensures high yield because it ensures maximum utilization of the nutrients supplied and also prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop infield. In this way, both crops can give better returns.
Question 2. Why are manures and fertilizers used in fields?
Answer: Manures add a great amount of organic matter in the form of humus in the soil. Fertilizers are very rich in plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium.
Improvement In Food Resources KSEEB Class 9 Question Answers
Question 3. What are the advantages of intercropping and crop rotation?
Answer:
Advantages of using intercropping:
1)It helps to maintain soil fertility.
2)Crops can easily be harvested and trashed separately.
Advantages of crop rotation:
1)It avoids the depletion of a particular nutrient from the soil.
2)It helps in weed control.
Question 4. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Answer: Genetic manipulation is a process of transferring genes or characteristics that are desirable from one plant to another plant for the production of varieties with desirable characteristics. Genetic manipulation is useful in increasing yield, better quality, and desirable characteristics.
Question 5. How do storage grain losses occur?
Answer:
There are mainly two types of factors
1)Biotic factors — Insects, rodents, birds & microorganisms.
2)Abiotic factors Moisture content, temperature, and humidity.
Question 6. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Answer:
Advantages of animal husbandry practices are.
1)Increasing the yield of foodstuffs such as milk, eggs, and meat.
2)It is beneficial for the farmers as increased yield brings more income to the farmer and raises his living standard.
Question 7. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Answer:
Cattle fanning is beneficial in the following ways
1)Good quality of meat, fiber can be obtained.
2) Milk-yielding animals and a good breed of draught animals can be obtained.
Question 8. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries, and bee-keeping?
Answer: Through cross-breeding, the production of poultry, fisheries, and beekeeping can be increased.
Question 9. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture, and aquaculture?
Answer:
Capture fishing:
It is the process of obtaining fish from natural resources such as rivers, ponds, canals, etc.
Mariculture:
It is a practice of a culture of marine fish varieties in the open sea.
Aquaculture:
It is the production of fish from freshwater resources.
Improvement In Food Resource Textual Questions
Question 1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits, and vegetables?
Answer: Cereals give carbohydrates which provide energy. Pulses give proteins that build our bodies. Vegetables and fruits provide all essential minerals.
Question 2. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Answer:
Biotic and abiotic factors affect poor crop production by the following factors.
1)Weight loss
2)Poor germination ability
3)Infestation of insects.
4)Degradation in quality.
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 KSEEB Textbook Solutions
Question 3. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
Answer:
Desirable agronomic characteristics are.
1)Tallness and profuse branching are desirable characteristics for fodder crops.
2)Dwarfness is desired in cereals so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Question 4. What are macronutrients and why are they called macronutrients?
Answer: Macronutrients are essential elements utilized by plants relatively in large quantities. They require for the plants in greater amounts for proper growth and development.
Question 5. How do plants get nutrients?
Answer: The nutrients which are found in the soil get dissolved in the water and is absorbed by the roots of a plant
Question 6. Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Answer:
Manure:
1)Manure is a natural substance
2)It adds a great amount of organic matter
3)It is not nutrient specific
Fertilizers:
1)A fertilizer is a man-made substance.
2)It does not add any humus to the soil.
3)It is nutrient specific
Question 7. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
1)Farmers who use high-quality seeds do not adopt irrigation or use fertilizers.
2)Farmers use ordinary seeds, adopt irrigation and use fertilizers.
3)Farmers use quality seeds adopt irrigation use fertilizers and use crop protection measures.
Answer: Option (c) is the right answer.
The use of only quality seeds and irrigation and fertilizers are not sufficient for better yield, but also crop should be protected by biotic and abiotic factors.
Question 8. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops?
Answer: Diseases are spread by pathogens so to get rid of pathogens some preventive measures, as well as biological methods, are preferred.
Example: To kill the pathogen biological method will be used without affecting the plant or soil quality.
Question 9. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Answer:
1) Biotic factors – Insects, birds, and rodents
2) Abiotic factors — moisture content, temperature, and humidity.
Question 10. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer:
Cross-breeding of cattle is commonly used for improving cattle breeds because.
1)It helps in getting the desired traits.
2)To get disease-resistant and high-yielding cattle breeds.
Question 11. Discuss the implications of the following statement. “It is interesting to note that poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low-fiber food stuff (which is unfit for human consumption) into highly nutritious animal protein food.
Answer: Poultry farming is to raise domestic fowl for egg production and chicken meat. The poultry birds are also efficient converters of agricultural byproducts.
Question 12. What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming?
Answer:
- Providing proper shelter.
- Feeding
- Caring for animal health.
Question 13. What are the differences between broilers and layers and in their management?
Answer: The poultry bird groomed for obtaining meat is called a broiler. The egg-laying poultry bird is called a layer. The proper nutrition and environmental requirements of broilers are somewhat different from those of egg layers.
Question 14. How are fish obtained?
Answer: The fish can be obtained by
1)Capturing
2)Culturing
KSEEB Solutions For Improvement In Food Resources Short Notes
Question 15. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Answer: The composite fish culture is a combination of five or six fish species is used in a single pond.
Advantages
1. They do not compete for food among themselves.
2. The (fishes) have different types of food habits
3. Fishes feed in different zones.
Question 16. What are the desirable characteristics of the varieties suitable for honey production?
Answer:
1)The variety of bees should be able to collect a large amount of honey.
2)They (Bee) should stay in a given beehive for a long period.
Question 17. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Answer: Pasturage means the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. In addition to an adequate quantity of pasturage, the kind of flowers available will determine the taste of the honey.
Improvement In Food Resources Additional Questions
Question 1. Name the crop whose production has increased by
1)blue revolution
2) yellow revolution
Answer:
1) Blue revolution—Fish production
2)Yellow revolution—Oil production
Question 2. Is organic farming beneficial and why?
Answer: Yes organic fanning is very beneficial because it is a farming system with no use of chemicals with a maximum input of organic manures, recycled from waste.
Question 3. Why removal of weeds is necessary?
Answer: Weeds should be removed because it takes up nutrients from soil and reduce the growth of crops.
Question 4. Which is the most advantageous fish culture system?
Answer: Composite fish culture because fishes do not compete for food among them.
Question 5. How genetically modified crops can be obtained?
Answer: Genetically modified crops can be obtained by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristics.
Question 6. How does catla differ from mrigal?
Answer: Catla is a surface feeder, while mrigal is a bottom-feeding fish.
Improvement In Food Resources High Order Thinking Questions
Question 1. On what factors does the growth of plants and flowering are dependent?
Answer: Temperature and photoperiod (duration of sunlight)
Question 2. Neem and turmeric powders are often used in grain storage.
1)What are they called?
2)What is the purpose of using need and turmeric?
Answer:
1) Neem and turmeric powders are biopesticides,
2) Neem and turmeric keep away insects rodents, fungi, bacteria, etc from the stored foods.
Question 3. A farmer had a plot just beside the bank of a river. Each time be planted Kharif crops, crops got damaged due to floods. He consulted the agricultural scientist who gave him a special variety of seeds and also advised him to practice fish farming.
1)What was the specialty of seed grains?
2)What name can be given to this type of fish farming?
Answer:
1) The special variety of seed grains are genetically modified to protect them from the damaging effect of floods,
2)Composite fish culture.
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Important Questions
Question 4. What determines the quality of honey?
Answer:
1) The pasturage, i.e, the kind of flowers available.
2) Apiary location.
Question 5. Name one indigenous and one exotic breed of poultry.
Answer:
1) Indigenous—Aseel
2) Exotic—Leghorn.
Question 6. What are the desired agronomic characteristics for fodder and cereal crops?
Answer: Tallness and profuse branching are desirable characteristics for fodder crops. Dwarfhess is desired in cereals so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Question 7. Excessive use of chemicals, such as insecticides and pesticides causes a threat to ecology.” Explain with reason.
Answer:
1) Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides when washed away courses water pollution,
2) The pesticides accumulate in the soil for a long period.
3)They may lead to eutrophication,
4)They may result in biological magnification.
Improvement In Food Resources Unit Test
Question 1. To solve the food problem of the country, which among the following is necessary
1)Increased production and storage of food grains.
2)Easy access of people to the food grains
3)Proper storage of food grains.
4)All of these
Answer: (1) Increased production and storage of food grains.
Question 2. The place where bees are reared for commercial honey production is called
1)Beehive
2)Aviary
3)Apiary
4)collection unit
Answer: (3) Apiary
Question 3. The process of crossing genetically dissimilar plants of a species is called
1)Intervarietal cross
2) Interspecific cross
3)Intergeneric cross
4) Ail of these
Answer: (1) Intervarietal cross
Improvement In Food Resources Give One Word For The Following
1. Planting soybean and maize in alternative rows in the same field is called as Intercropping
2. Parthenium is commonly known as weed
3. Growing different crops on a piece of land in pre-planned succession is known as Crop rotation
Improvement In Food Resources Answer The Following Questions
one mark
Question 1. Why do organisms need food?
Answer: Food is required for body development, growth, and good health.
Question 2. Which technique is incorporated to obtain crop varieties?
Answer: Hybridisation.
Question 3. Which species of honey bee is used for the commercial production of honey?
Answer: Apis mellifera
Question 4. What is Aquaculture?
Answer: The production and management of fish is called aquaculture.
Question 5. Define the term hybridization.
Answer: Hybridisation refers to crossing between genetically dissimilar organisms.
Question 6. Give two examples of milch animals.
Answer: The cow and buffalo are milk animals.
Question 7. What is the advantage of green manure?
Answer: Green manure helps in enriching the soil with nitrogen and phosphorus.
Two And Four Marks
Question 1. Write any two methods of weed control.
Answer:
1) Weeds can be controlled by using pesticides.
2)Weeds can be removed by using a harrow, hoe or by cutting them.
3)The biological method involves growing crops like mustard along with the main crops which do not allow weeds to grow.
Question 2.What are th e ad vantages of hybridisation ?
Answer:
1) It makes crops disease resistant and a good response to fertilizers.
2) It gives a higher yield and improves product quality.
Question 3. Write any two characteristics of a storage structure for grains.
Answer:
1)Storage structures should be cleaned dried and airtight.
2)Storage structures should have inbuilt arrangements for aeration, temperature control, protection from pests, etc.
KSEEB Solutions Chapter 15 Agricultural Techniques Class 9
Question 4. State three ways by which pests attack the plants and name the chemical used to control pests.
Answer:
1) The pests cut the root, stem, and leaf,
2)They suck the cell sap from plants.
3)They bore into the stem, root, and fruit. Pesticides should be used to control pests.
Question 5. How can poultry farming be integrated with crop production?
Answer:
1) Poultry birds can be fed with farm wastes like degraded grains and certain parts of a plant as food.
2) Bird wastes or excreta can be used as manures to the plants.
Question 6. How is fumigant different from pesticides?
Answer: Fumigant is used before grains are stored for future use. Pesticide is used after the germination of seed and it is sprayed over the crop plant.
Question 7. List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield depends.
Answer:
The cultivation practices and crop yield depends upon the following factors.
1)Availability of high-quality seeds.
2)Availability of waters
3)Availability of fertile soil
4)Access to new information and technologies.


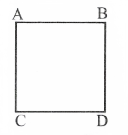 Answer: Consider the square field ABCD as shown in the figure. Given that fanner covers the boundary ABCD in 40 s. If he walks for 2 minutes and 20 seconds, he will be at point C.
Answer: Consider the square field ABCD as shown in the figure. Given that fanner covers the boundary ABCD in 40 s. If he walks for 2 minutes and 20 seconds, he will be at point C.
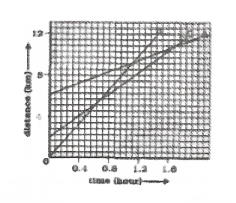 (1) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
(1) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?









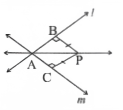

 Two circles with centres A and B intersect at C and D to join CD.
Two circles with centres A and B intersect at C and D to join CD.