KSEEB Class 11 Chemistry Notes For Heat And Work In Thermodynamics
A system can interact with its surroundings by exchanging energy either in the form of heat or work or both. The interaction brings about changes in the properties ofthe system
Heat Definition
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the energy flowing across the boundary of a system by the temperature difference between the system and its surroundings.
KSEEB Class 11 Chemistry Notes for Thermodynamics
Work Definition
In thermodynamics, work is defined as the energy transferred between the system and its surroundings due to the existence of unbalanced forces between the two.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Class 11 Chemistry Notes
Some important features of heat and work:
Transfer of heat, work occurs only at the boundary of a system.Both heat and work are the forms of energy in transit. Heat or work appears only when a system undergoes a process. There is no existence of heat or work before or after the process.
- This means that heat and work are the forms ofenergy that are not stored within a system. Therefore, heat and work are not the properties of a system.
- Heat flows from a region of high temperature to a low temperature. If the temperature of a system is higher or lower than that of its surroundings, then heat flows from the system to the surroundings or vice-versa.
- A system can do work on its surroundings. When it occurs, we say that work is done by the system on its surroundings. Conversely, work can be done on the system by its surroundings.
- When heat flows from the surroundings to the system, the internal energy of the system increases. On the contrary, when heat flows from the system to its surroundings, then the internal energy ofthe system decreases.
- If work is done by the system on its surroundings, the internal energy of the system decreases. Conversely, if work is done on the system by its surroundings, the internal energy ofthe system increases.
- Heat and work are not the state functions of a system: When a system changes its state, the amount of heat transferred between the system and its surroundings or the amount of work involved in the change depends not only on the initial and the final states ofthe system but also on the path the system follows during the change.
- So, heat and work are not the state functions of a system. These are called path-dependent quantities.
Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Notes KSEEB PDF
Heat And Work Explanation:
In the following example it can be shown that the work and heat are not the state functions ofa system. Let us consider, that 1 mol ofice at (0°C and 1atm) is to be converted into water at the same temperature and pressure.
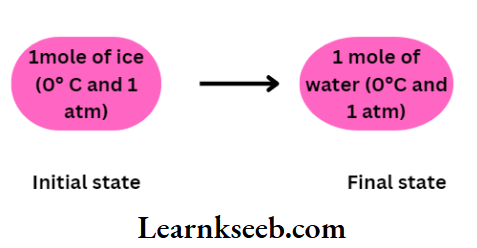
This transformation can be carried out by following the two alternative ways given below.
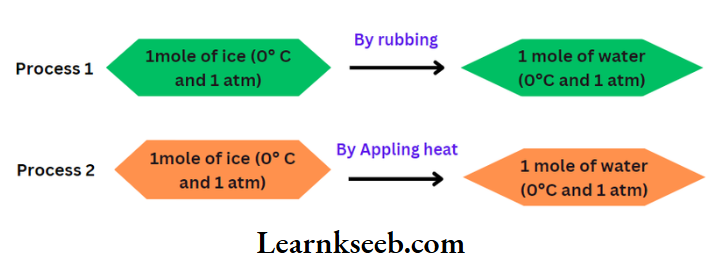
In Work is done during rubbing but no heat is transferred. But in heat is transferred but no work is done. Although the initial and final states of the system are the same in both processes, the amount of work or heat involved in these processes is different. Thus, work done or heat transferred in a process depends on the route followed to carry out the process.
In a process, the change in a property of a system is calculated by subtracting the final value from the initial value. Generally, this difference is denoted by the symbol ‘A’. Heat and work are not the properties of the system. Heat and work are the energies in transit. There is no existence of heat and work before or after a process. Thus, we can write AP or AV, but not Aq or Aw.
Sign of heat and work in thermodynamics:
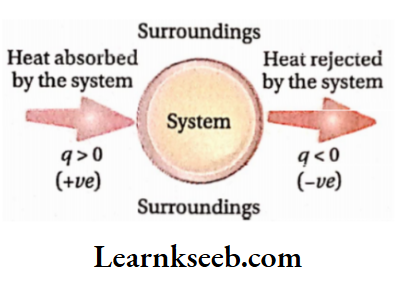
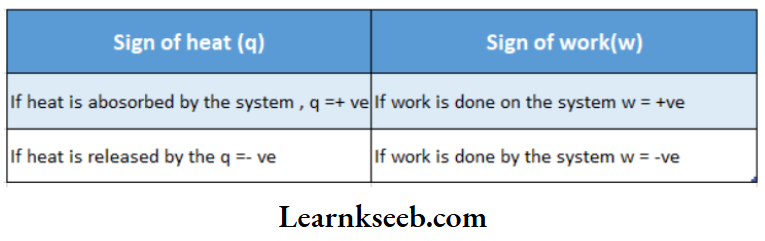
Sign of heat:
The amount of heat transferred is expressed by Q If heat is transferred from the surroundings to the system, the system gains energy. The gain of heat by the system is represented by the +ve sign. For example, if a system absorbs local heat from the surroundings, then q =+10 cal.
KSEEB Chemistry Class 11 Thermodynamics Chapter Notes
If heat is transferred from the system to the surroundings, the system loses energy. The heat rejected by the system is represented by the -ve sign. For example, if a system rejects 10 cal of heat to the surroundings, then q = -10 cal.
Thermodynamics Notes For KSEEB Class 11 Chemistry
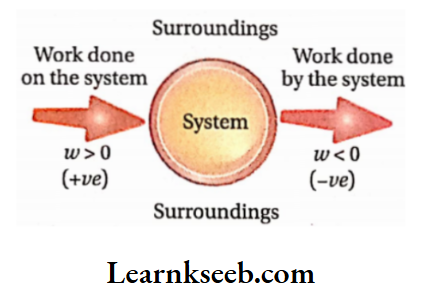
Sign of work:
Work done on the system or by the system is denoted by w. According to the IUPAC convention, the energy ofthe system decreases when work is done by it. So, w is negative. On the other hand, the energy ofthe system increases if work is done on it. So it is positive, Example if 10 kj of work is performed by a system, then w = -10 kl. On the other hand, if 10 kj of work is performed on a system, w = +10 kj
Important Thermodynamics Formulas Class 11 KSEEB
Sign conventions for heat (?) and work (m):
Units of heat and work:
Units of heat: The CGS unit of heat is calorie. The SI unit of heat is joule. [1 cal = 4.184 joule]
Units of work: The traditional unit of work is erg. lerg =1 dyn. cm. SI unit of work is joule. 1 joule =1 N. m = 107 erg.
