KSEEB Class 8 Maths Solutions For Chapter 13 Factorisation Points To Remember
When we factorize an expression, we write it as a product of factors. These factors may be numbers, algebraic variables, or algebraic expressions.
An irreducible factor is a factor that cannot be expressed further as a product of factors.
A systematic way of factorizing an expression is the common factor method. It consists of three steps:
1) Write each term of the expression as a product of irreducible factors.
2) Look for and separate the common factors and
3) Combine the remaining factors in each term in accordance with the distributive law.
Sometimes, all terms in a given expression do not have a common factor, but the terms can be grouped in such a way that all the terms in each group have a common factor across all the groups leading to the required factorization of the expression.
This is the method of regrouping
In factorisation by regrouping, we should remember that any regrouping (i.e., rearrangement) of the terms in the given expression may not lead to factorisation. We must observe the expression and come out with the desired regrouping by trail and error.
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Factorisation Solutions
A number of expressions to be factorised are of the form or can be put into the form: \(a^2+2 a b+b^2, a^2-2 a b+b^2, a^2-b^2 \text { and }\)\(x^2+(a+b)+a b\).
These expressions can be easily factorised using identities 1,2,3&4
⇒ \(a^2+2 a b+b^2=(a+b)^2\)
⇒ \(a^2-2 a b+b^2=(a-b)^2\)
⇒ \(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\)
⇒ \(x^2+(a+b) x+a b=(x+a)(x+b)\)
In expressions which have factors of the type (x+a)(x+b) remember the numerical term gives ab. Its factors a and b should be so chosen that their sum, with signs taken care of, is the coefficient of x.
We know that in the case of numbers, division is the inverse of multiplication. This idea is applicable also to the division of algebraic expressions.
In the case of division of a polynomial by a monomial we may carry out the division either by dividing each term of the polynomial by the monomial or by the common factor method.
In the case of division of a polynomial by a polynomial. We cannot proceed by dividing each term in the dividend polynomial by the divisor polynomial. Instead, we factorise both the polynomials and cancel their common factors.
In the case of divisions of algebraic expressions that we studied in this chapter, we have
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient
In general, however, the relation is
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
Thus, we have considered in the present chapter only those divisions in which the remainder is zero.
There are many errors students commonly make when solving algebra exercises. One should avoid making such errors.

Kseeb Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Pdf
Factorisation Solutions KSEEB Class 8 Maths Exercise 13.1
1. Find the common factors of the given terms.
1) 12x, 36
Solution: 12x = 2 x 2 x 3 x x
36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3
The common factors are 2,2,3
i.e., 2 x 2 x 3 = 12
2) 2y, 22xy
Solution: 2y = 2 x y
22xy = 2 x 11 x x x y
The C.F. are 2y
KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Maths Factorisation Exercises
3) \(14 p q, 28 p^2 q^2\)
Solution: 14pq = 2 x 7 x p q
\(28 p^2 q^2=2 \times 2 \times 7 \times p \times p \times q \times q\)The C.F. are = 2 x 7 x p x q
= 14pq
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Solutions For Chapter 13 Factorisation
4) \(2 x, 3 x^2, 4\)
Solution: 2x = 2 x x
⇒ \(3 x^2=3 \times x \times x\)
4 = 2 x 2
∴ C.F. are = 1
5) \( 6 a b c, 24 a b^2, 12 a^2 b\)
Solution: 6abc = 2 x 3 x a x b x c
⇒ \( 24 a b^2=2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times a \times b \times b\)
⇒ \( 12 a^2 b=2 \times 2 \times 3 \times a \times a \times b\)
The C.F. = 2 x 3 x a x b
= 6ab
6) \(16 x^3,-4 x^2, 32 x \)
Solution: \(16 x^3=2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times x \times x \times x\)
⇒ \(-4 x^2=-2 \times 2 \times x \times x\)
2x = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x x
The C.F. are = 2 x 2 x x
= 4x
Karnataka Board 8th Maths Chapter 13 Factorisation Solutions
7) 10pq, 20qr, 30rp
Solution: 10pq = 2 x 5 x p x q
20qr = 2 x 2 x 5 x q x r
30rp = 2 x 3 x 5 x r x p
The C.F. = 2 x 5 = 10
8) \(3 x^2 y^3, 10 x^3 y^2, 6 x^2 y^2 z\)
Solution: \(3 x^2 y^3=3 \times x \times x \times y \times y \times y\)
⇒ \(10 x^3 y^2=2 \times 5 \times x \times x \times x \times y \times y\)
⇒ \(6 x^2 y^2 z=2 \times 3 \times x \times x \times y \times y \times z\)
The C.F. are = x x x x y x y
= \(x^2 y^2\)
2. Factorize the following expressions.
1) 7x-42
Solution: 7x-42
= (7 x x)-(2x3x7)
= 7(x-6)
2) 6p-12q
Solution: 6p-12q
= 2 x 3 x p – 2 x 2 x 3 x q
= 2 x 3(p-2 x q)
= 6(p-2q)
3) \(7 a^2+14 a\)
Solution: 7 x a x a + 7 x 2 x a
= 7a(a+2)
4) \(-16 z+20 z^3\)
Solution: \(-16 z+20 z^3\)
= -4 x 4 x z + 4 x 5+z x z x z
= \(4 z\left(-4+5 z^2\right)\)
5) \(20 \ell^2 m+30 a \ell m\)
Solution: \(20 \ell^2 m+30 a \ell m\)
=\(10 \times 2 \times \ell \times \ell \times m+10 \times 3 \times a \times \ell \times m\)
=\(10 \ell m(2 \ell+3 a)\)
KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Maths Factorisation Exercises
6) \(5 x^2 y-15 x y^2\)
Solution: \(5 x^2 y-15 x y^2\)
=\(5 \times x \times x \times y-5 \times 3 \times x \times y \times y\)
=\(5 x y(x-3 y)\)
7) \(10 a^2-15 b^2+20 c^2\)
Solution: \(10 a^2-15 b^2+20 c^2\)
=\(5 \times 2 \times a \times a-5 \times 3 \times b \times b+4 \times 5 \times c \times c\)
=\(5\left(2 a^2-3 b^2+4 c^2\right)\)
8) \(-4 a^2+4 a b-4 c a\)
Solution: \(-4 a^2+4 a b-4 c a\)
=\(-4 a(a-b+c)\)
Kseeb 8th Standard Maths Chapter 13 Textbook Solutions
9) \(x^2 y z+x y^2 z+x y z^2\)
Solution: \(x^2 y z+x y^2 z+x y z^2\)
x y z(x+y+z)
10) \(a x^2 y+b x y^2+c x y z\)
Solution: \(x y(a x+b y+c z)\)
3. Factorize
1) \(x^2+x y+8 x+8 y\)
Solution: \(x \times x+x \times y+8 \times x+8 \times y\)
=x(x+y)+8(x+y)
=(x+y)(x+8)
2) 15 x y-6 x+5 y-2
Solution: \(5 \times 3 \times x y-2 \times 3 \times x \times+5 \times y-2\)
3 x(5 y-2)+1(5 y-2)
(5 y-2)(3 x+1)
3) a x+b x-a y-b y
Solution: x(a+b)-y(a+b)
(a+b)(x-y)
4) 15 p q+15+9 q+25 p
Solution: 15 p q+15+9 q+25 p
3 q(5 p+3)+5(3+5 p)
(5 p+3)(3 q+5)
5) z-7+7 x y-x y z
Solution: z-7+7 x y-x y z
z-x y z-7+7 x y
z(1-x y)-7(1-x y)
(1-x y)(z-7)
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Solved Problems Factorization Exercise 13.2
1. Factorize the following expressions.
1) \(a^2+8 a+16\)
Solution: \(a^2+8 a+16\)
=\((a)^2+2 \times a \times 4+(4)^2\)
=\((a+4)^2 \quad\left[(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right]\)
2) \(p^2-10 p+25\)
Solution: \(p^2-10 p+25\)
=\(p^2-2 \times p \times 5+5^2\)
=\((p-5)^2\)
∴ \([(a-b)^2=a^2-2ab+b^2]\)
3) \(25 m^2+30 m+9\)
Solution: \(25 m^2+30 m+9\)
=\((5 m)^2+2 \times 5 m \times 3+3^2\)
=\((5 m+3)^2 \quad\left[(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right]\)
Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Kseeb Important Questions And Answers
4) \(49 y^2+84 y z+36 z^2\)
Solution: \((7 y)^2+2(7 y) \times(6 z)+(6 z)^2\)
=\((7 y+6 z)^2\left[(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right]\)
5) \(4 x^2-8 x+4\)
Solution: \((2 x)^2-2 \times(2 x) \times(2)+2^2\)
=\((2 x-2)^2 \quad\left[(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right]\)
Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 KSEEB Detailed Answers
6) \(121 b^2-88 b c+16 c^2\)
Solution: \((11 b)^2-2 \times(11 b)(4 c)+(4 c)^2\)
=\((11-4 c)^2 \quad\left[(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right]\)
7) \((\ell+m)^2-4 \ell m\)
Solution: \((\ell+m)^2-4 \ell m\)
⇒ \(\ell^2+2 \ell m+m^2-4 \ell m\)
⇒ \(\ell^2-2 \ell m+m^2\)
⇒ \((\ell-m)^2 \quad(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\)
8) \(a^4+2 a^2 b^2+b^4\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2\right)^2+2 \times a^2+b^2+\left(b^2\right)^2\)
= \(\left(a^2+b^2\right)^2 \quad\left[(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right]\)
2. Factorize
1) \(4 p^2-9 q^2\)
Solution: \((2 p)^2-(3 q)^2\)
⇒ \(\quad\left(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right)\)
=\((2 p+3 q)(2 p-3 q)\)
2) \(63 a^2-112 b^2\)
Solution: \(63 a^2-112 b^2\)
=\(7\left(9 a^2-16 b^2\right)\)
=\(7\left[(3 a)^2-(4 b)^2\right]\)
=\(7(3 a+4 b)(3 a-4 b)\)
3) \(49 x^2-36\left(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right)\)
Solution: \((7 x)^2-6^2\)
=\((7 x+6)(7 x-6)\)
4) \(16 x^5-144 x^3\)
Solution: \(16 x^3\left(x^2-9\right)\)
=\(16 x^3 \quad\left(x^2-3^2\right)\)
=\(16 x^3(x+3)(x-3)\)
⇒ \(\left(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right)\)
5) \((\ell+m)^2-(\ell-m)^2\)
Solution: \([(\ell+m)+(\ell-m)][(\ell+m)-(\ell-m)]\)
=\((\ell+\not{m}+\ell-\not{m})(\ell+m-\ell+m)\)
=\(2 \ell \times 2 \mathrm{~m}\)
= 4lm
KSEEB 8th Maths Factorisation Solutions
6) \(9 x^2 y^2-16\)
Solution: \((3 x y)^2-(4)^2\)
=\((3 x y+4)(3 x y-4)\)
7) \(\left(x^2-2 x y+y^2\right)-z^2\)
Solution: \(\left(x^2-2 x y+y^2\right)-z^2\)
= \((x-y)^2-z^2\)
= \((x-y+z)(x-y-z)\)
8) \(25 a^2-4 b^2+28 b c-49 c^2\)
Solution: \(25 a^2-\left(4 b^2-28 b c+49 c^2\right)\)
=\((5 a)^2-\left[(2 b)^2-2 \times 2 b \times 7 c+(7 c)^2\right]\)
=\((5 a)^2-(2 b-7 c)^2\)
=\([5 a+(2 b-7 c)][5 a-(2 b-7 c)]\)
= \([5 a+2 b-7 c][5 a-2 b+7 c]\)
⇒ \(\left[a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right]\)
3. Factorize the expressions.
1) \(a x^2+b x\)
Solution: x(ax+b)
2) \(7 p^2+21 q^2\)
Solution: \(7\left(p^2+3 q^2\right)\)
3) \(2 x^3+2 x y^2+2 x z^2\)
Solution: \(2 x\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)\)
4) \(a m^2+b m^2+b n^2+a n^2\)
Solution: \(\left(a m^2+b m^2\right)+\left(b n^2+a n^2\right)\)
=\(m^2(a+b)+n^2(b+a)\)
=\((a+b)\left(m^2+n^2\right)\)
5) (lm+l)+m+1
Solution: lm+l+m+1
= lm+m+l+1
= m(l+1)+1(l+1)
=(l+1)(m+1)
6) y(y+z)+9(y+z)
Solution: (y+z)(y+9)
7) \(5 y^2-20 y-8 z+2 y z\)
Solution: \(5 y^2-20 y-8 z+2 y z\)
=\(5 y(y-4)+2 z(y-4)\)
=\((y-4)(5 y+2 z)\)
Factorisation Class 8 Kseeb Notes Pdf
8) 10ab+4a+5b+2
Solution: 10ab+5b+4a+2
= 5b(2a+1)+2(2a+1)
= (2a+1)(5b+2)
9) 6xy-4y+6-9x
Solution: 6xy-9x-4y+6
3x(2y-3)-2(2y-3)
(2y-3)(3x-2)
4. Factorize
1) \(a^4-b^4\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2\right)^2-\left(b^2\right)^2\)
=\(\left(a^2-b^2\right)\left(a^2+b^2\right)\)
=\((a-b)(a+b)\left(a^2+b^2\right)\)
2) \(p^4-81\)
Solution: \(\left(p^2\right)^2-9^2\)
=\(\left(p^2+9\right)\left(p^2-9\right)\)
=\(\left(p^2+9\right)\left(p^2-3^2\right)\)
=\(\left(p^2+9\right)(p+3)(p-3)\)
3) \(x^4-(y+z)^4\)
Solution: \(\left(x^2\right)^2-\left[(y+z)^2\right]^2\)
\(\left(x^2+(y+z)^2\right)\left(x^2-(y+z)^2\right)\)=\(\left[x^2+(y+z)^2\right][x+(y+z)][x-(y+z)]\)
=\(\left[x^2+(y+z)^2\right][x+y+z][x-y-z]\)
4) \(x^4-(x-z)^4\)
Solution: =\(\left(x^2\right)^2-\left[(x-z)^2\right]^2\)
=\(\left[x^2+(x-z)^2\right]\left[x^2-(x-z)^2\right]\)
=\(\left[x^2+(x-z)^2\right][x+(x-z)][x-(x-z)]\)
=\(\left[x^2+(x-z)^2\right](x+x-z)(x-x+z)\)
=\(\left[x^2+(x-z)^2\right](2 x-z) \times z\)
=\(z(2 x-z)\left(x^2+(x-z)^2\right)\)
=\(z^2(2 x-z)\left(x^2+x^2-2 x z+z^2\right)\)
=\(z(2 x-z)\left(2 x^2-2 x z+z^2\right)\)
5) \(a^4-2 a^2 b^2+b^4\)
Solution: \(\left(a^2\right)^2-2 a^2b^2+\left(b^2\right)^2\)
=\(\left(a^2-b^2\right)^2\)
=\([(a+b)(a-b)]^2\)
=\((a+b)^2(a-b)^2\)
5. Factorize the following expressions.
1) \(p^2+6 p+8\)
Solution: It can be observed that
8 = 4 x 2 and 4 + 2 = 6
∴ \(p^2+6 p+8\)
=\(p^2+2 p+4 p+8\)
=\(p(p+2)+4(p+2)\)
=\((p+2)(p+4)\)
KSEEB Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Factorisation
2) \(q^2-10 q+21\)
Solution: It can be observed that
⇒ \(21=(-7) \times(-3) \text { and }(-7)+(-3)=-10\)
∴ \(q^2-10 q+21\)
=\(q^2-7 q-3 q+21\)
=\(q(q-7)-3(q-7)\)
∴ \((q-7)(q-3)\)
3) \(p^2+6 p-16\)
Solution: It can be observed that
-16 = \((-2) \times 8 \& 8+(-2)=6\)
∴ \(p^2+6 p-16\)
=\(p^2+8 p-2 p-16\)
=\(p(p+8)-2(p+8)\)
=\((p+8)(p-2)\)
KSEEB Maths Class 8 Factorization Exercise 13.3
1. Carry out the following divisions.
1) \(28 x^4 \div 56 x\)
Solution: ![]()
=\(\frac{x^3}{2}=\frac{1}{2} x^3\)
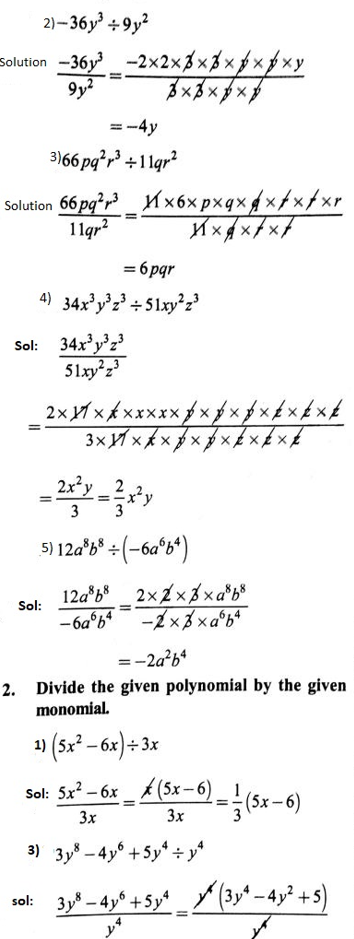


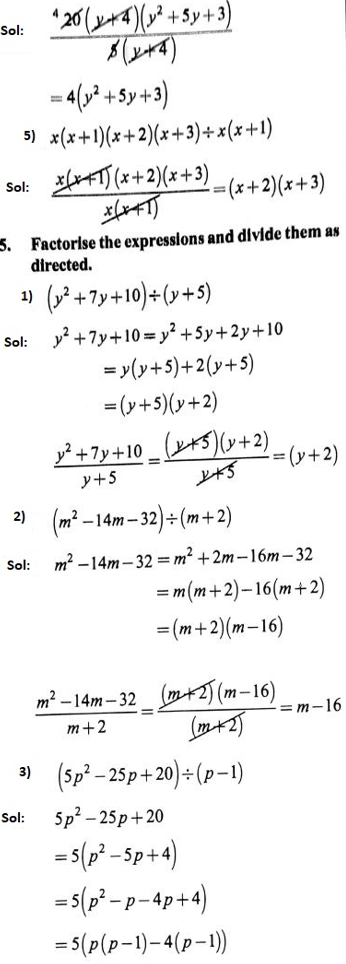
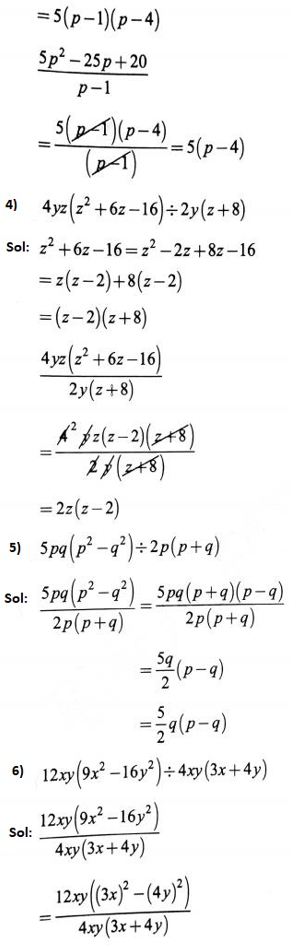
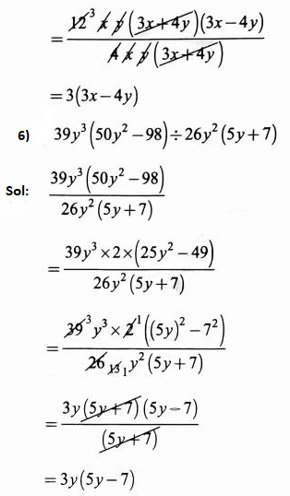
Kseeb 8th Maths Chapter 13 Exercise Solutions Step By Step
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Key Concepts Of Factorization Exercise 13.4
1. Find and correct the errors in the following mathematical statements.
1. 4(x-5)=4x-5
Solution: LHS = 4(x-5)=4×20 ≠ RHS
∴ The correct statement is
4(x-5)=4×20
2. \(x(3 x+2)=3 x^2+2\)
Solution: LHS = x(3x+2)
= \(x \times 3 x+x \times 2\)
=\(3 x^2+2 x\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is
∴ \(x(3 x+2)=3 x^2+2 x\)
3. 2x+3y=5xy
Solution: LHS = 2x+3y ≠ RHS
The correct statement is
2x + 3y = 2x + 3y
4. x + 2x + 3x = 5x
Solution: LHS = x + 2x + 3x
= x(1+2+3)
= 6x ≠ RHS
The correct statement is x + 2x + 3x = 6x
5. 5y + 2y + y – 7y = 0
Solution: LHS = 5y + 2y + y – 7y
= 8y – 7y
= y ≠ RHS
The correct statement is
5y + 2y + y – 7y = y
6. \(3 x+2 x=5 x^2\)
Solution: LHS = 3x + 2x
= 5x
≠ RHS
∴ The CS is 3x + 2x = 5x
KSEEB Maths Class 8 Factorisation Examples Explained
7. \((2 x)^2+4(2 x)+7=2 x^2+8 x+7\)
Solution: LHS = \((2 x)^2+4(2 x)+7\)
=\(4 x^2+8 x+7\)
≠ RHS
∴ The CS is \((2 x)^2+4(2 x)+7\)
=\(4 x^2+8 x+7\)
8. \((2 x)^2+5 x=4 x+5 x=9 x\)
Solution: LHS = \((2 x)^2+5 x\)
=\(4 x^2+5 x\)
≠ RHS
The CS is \((2 x)^2+5 x\)
=\(4 x^2+5 x\)
9. \((3 x+2)^2=3 x^2+6 x+4\)
Solution: LHS = \((3 x+2)^2\)
=\((3 x)^2+2(3 x)(2)+2^2\)
=\(9 x^2+12 x+4\)
≠ RHS
∴ \((a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\)
The CS is \((3 x+2)^2=9 x^2+12 x+4\).
Karnataka Board Class 8 Maths Factorisation Problems And Answers
10. Substituting x = -3 in.
a) \(x^2+5 x+4 \)gives
\((-3)^2+5(-3)+4=9+2+4=15\)Solution: For x = -3
∴ \(x^2+5 x+4=(-3)^2+5(-3)+4=9-15+4\)
= 13 – 15 = -2
b) \(x^2-5 x+4\) gives \((-3)^2-5(-3)+4 = 9 – 15 + 4 = -2\)
Solution: \(x^2-5 x+4=(-3)^2-5(-3)+4\)
= 9 + 15 + 4 = 28
c) \(x^2+5 x gives (-3)^2+5(-3)=-9-15=-24\)
Solution: \(x^2+5 x=(-3)^2+5(-3)=+9-15=-6\)
11. \((y-3)^2=y^2-9\)
Solution: LHS = \((y-3)^2=y^2-2(y)(3)+3^2\)
\(\left[(a-b)^2=a^2-2 a b+b^2\right]\)=\(y^2-6 y+9\)
≠ RHS
The correct statement is \((y-3)^2=y^2-6 y+9\)
12. \((z+5)^2=z^2+25\)
Solution: LHS = \((z+5)^2=z^2+25=z^2+2 \times z \times 5+5^2\)
=\(z^2+10 z+25\)
≠ RHS
The correct statement is \((z+5)^2=z^2+10 z+25\)
13. \((2 a+3 b)(a-b)=2 a^2-3 b^2\)
Solution: LHS = (2a+3b)(a-b)
= \(2 a \times a+3 b \times a-2 a \times b-3 b \times b\)
=\(2 a^2+3 a b-2 a b-3 b^2\)
=\(2 a^2+a b-3 b^2 \neq \text { RHS }\)
The correct statement is (2a+3b)(a-b)
=\(2 a^2+a b-3 b^2\)
14. \((a+4)(a+2)=a^2+8\)
Solution: LHS = (a+4)(a+2)
∴ \((x+a)(x+b)=x^2+x(a+b)+a b\)
=\(a^2+(4+2)(a)+4 \times \)
=\(a^2+6 a+8\)
≠ RHS
The correct statement is
∴ \((a+4)(a+2)=a^2+6 a+8\)
How To Solve Factorisation Problems In Class 8 Kseeb Maths
15. \((a-4)(a-2)=a^2-8\)
Solution: LHS = (a-4)(a+2)
=\(a^2+[(-4)+(-2)] a+(-4)(-2)\)
=\(a^2-6 a+8 \neq \text { RHS }\)
The correct statement is
∴ \((a-4)(a-2)=a^2-6 a+8\)
16. \(\frac{3 x^2}{3 x^2}=0\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{3 x^2}{3 x^2}=\frac{3 \times x \times x}{3 \times x \times x}=1\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is \(\frac{3 x^2}{3 x^2}=1\)
17. \(\frac{3 x^2+1}{3 x^2}=1+1=2\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{3 x^2+1}{3 x^2}=\frac{3 x^2}{3 x^2}+\frac{1}{3 x^2}\)
=\(1+\frac{1}{3 x^2}\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is \(\frac{3 x^2+1}{3 x^2}=1+\frac{1}{3 x^2}\)
KSEEB 8th Class Maths Factorisation Solutions
18. \(\frac{3 x}{3 x+2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{3 x}{3 x+2}\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is \(\frac{3 x}{3 x+2}=\frac{3 x}{3 x+2}\)
19. \(\frac{3}{4 x+3}=\frac{1}{4 x}\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{3}{4 x+3}\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is \(\frac{3}{4 x+3}=\frac{3}{4 x+3}\)
20. \(\frac{7 x+5}{5}=7 x\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{7 x+5}{5}=\frac{7 x}{5}+\frac{5}{5}=\frac{7 x}{5}+1\) ≠ RHS
∴ The correct statement is \(\frac{7 x+5}{5}=\frac{7 x}{5}+1\)
21. \(\frac{4 x+5}{4 x}=5\)
Solution: LHS = \(\frac{4 x+5}{4 x}=\frac{4 x}{4 x}+\frac{5}{4 x}=1+\frac{5}{4 x}\) ≠ RHS
The correct statement is \(\frac{4 x+5}{4 x}=1+\frac{5}{4 x}\)
Factorization Chapter 13 KSEEB Maths Additional Problems
1. Find the common factor of \(7 p^3 q\) and 5pq
Solution: \(7 p^3 q=7 \times p \times p \times p \times q\)
5pq = 5 x p x q
common factor of \(7 p^3 q\) and 5pq is pq.
2. Factorize: \(3 x-15 x^2\)
Solution: \(3 x-15 x^2=3 \times x-3 \times 5 \times x \times x\)
= 3x(1-5x)
3. Factorize: \(5 p(2 q-3 r)^2+2 p(2 q-3 r)\)
Solution: \(5 p(2 q-3 r)^2+2 p(2 q-3 r)\)
=\(p\left[5(2 q-3 r)^2+2(2 q-3 r)\right]\)
=\(p(2 q-3 r)[5(2 q-3 r)+2]\)
=\(p(2 q-3 r)(10 q-15 r+2)\)
4. Factorize: \(36 x^2-\frac{1}{169}\)
Solution: \(36 x^2-\frac{1}{169}\)
=\((6x)^2-\left(\frac{1}{13}\right)^2\left[\left(a^2-b^2\right)=(a+b)(a-b)\right]\)
=\(\left(6 x+\frac{1}{13}\right)\left(6 x-\frac{1}{13}\right)\)
5. Factorize: \(9 p^2+24 p+16\)
Solution: \(9 p^2+24 p+16\)
=\((3 p)^2+2 \times 3 p \times 4+4^2\)
∴ \(\left[a^2+2 a b+b^2=(a+b)^2\right]\)
=\((3 p+4)^2\)
6. If x=16 and y=5 find the value of \(\frac{x^2+y^2+x y}{x^2-y^2}\)
Solution: \(\frac{x^2+y^2+x y}{x^2-y^2}=\frac{16^2+5^2+16 \times 5}{16^2-5^2}\)
=\(\frac{256+25+80}{(16+5)(16-5)}=\frac{361}{21 \times 1}=\frac{361}{21}\)
7. Factorise: \(x^3 y^2+x^2 y^3-x y^4+x y\)
Solution: \(x^3 y^2+x^2 y^3-x y^4+x y\)
⇒ \(x y\left(x^2 y+x y^2-y^3+1\right)\)
8. Factorize: \(a^2 x^2+2 a x+1\)
Solution: \(a^2 x^2+2 a x+1\)
=\((a x)^2+2(a x)(1)+1^2\)
using identities \(\left[(a+b)^2=a^2+2 a b+b^2\right]\)
Here a=ax, b=1
=\((a x+1)^2\)
=(ax+1)(ax+1)
9. Factorize: \(9 y^2-4 x y+\frac{4 x^2}{9}\)
Solution: \(9 y^2-4 x y+\frac{4 x^2}{9}\)
=\(4\left(\frac{9}{4} y^2-x y+\frac{x^2}{9}\right)\)
=\(4\left(\left(\frac{3}{2} y\right)^2-x y+\left(\frac{x}{3}\right)^2\right)\)
=\(4\left(\left(\frac{3}{2} y\right)^2-2\left(\frac{3}{2} y\right)\left(\frac{x}{3}\right)+\left(\frac{x}{3}\right)^2\right)\)
=\(4\left(\frac{3}{2} y-\frac{x}{3}\right)^2\)
10. Factorize: \(y^2+7 y+12\)
Solution: Here 12 = 4 x 3 and 4 + 3 = 7
∴ \(y^2+7 y+12=y^2+4 y+3 y+12\)
=y(y+4)+3(y+4)
∴ \(y^2+7 y+12=(y+4)(y+3)\)
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Practice Questions
11. Divide \(24\left(x^2 y z+x y^2 z+x y z^2\right) \text { by } 8 x y z\)
Solution: \(\frac{24\left(x^2 y z+x y^2 z+x y z^2\right)}{8 x y z}\)
=\(\frac{3 x^2 y z+3 x y^2 z+3 y z^2}{x y z}\)
=\(\frac{3 x^2 y z}{x y z}+\frac{3 x y^2 z}{x y z}+\frac{+3 x y z^2}{x y z}\)
=\(3 x+3 y+3 z=3(x+y+z)\)
12. Divide \((-q r x y+p r y z-r x y z) \div(-x y z)\)
Solution: \(\frac{-q r x y+p r y z-r x y z}{-x y z}\)
∴ \(\frac{-q r x y}{-x y z}+\frac{p r y z}{-x y z}-\frac{r x y z}{-x y z}\)
=\(\frac{q r}{z}-\frac{p r}{x}+r\)
13. Factorize: \(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2-3 x-\frac{3}{x}\)
Solution: \(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2-3 x-\frac{3}{x}\)
=\(\left[x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2\right]-3\left[x+\frac{1}{x}\right]\)
=\(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^2-3\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
=\(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}-3\right)\)
14. The sum of the square of n natural number is \(\frac{2 n^3+3 n^2+n}{6}\). Factorize this expression.
Solution: \(\frac{2 n^3+3 n^2+n}{6}=\frac{n\left(2 n^2+3 n+1\right)}{6}\)
=\(\frac{n\left(2 n^2+2 n+n+1\right)}{6}\)
[we know 3 = 2 + 1 & 2 x 1 = 2]
⇒ \(\frac{n[2 n(n+1)+(n+1)]}{6} \Rightarrow \frac{n(2 n+1)(n+1)}{6}\)
15. Using factorization, find the positive square root of \(\frac{(a+b)^2-(c+d)^2}{(a+b)^2-(c-d)^2} \times \frac{(a+b+c)^2-d^2}{(a+b-c)^2-d^2}\)
Solution: \(\frac{(a+b)^2-(c+d)^2}{(a+b)^2-(c-d)^2} \times \frac{(a+b+c)^2-d^2}{(a+b-c)^2-d^2}\)
using identity \(a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\)
⇒ \((a+b)^2-(c+d)^2 =[(a+b+c+d)(a+b-c-d)]\)
⇒ \((a+b+c)^2-d^2 =(a+b+c+d)(a+b+c-d)\)
⇒ \((a+b)^2-(c-d)^2 =(a+b+c-d)(a+b-c+d)\)
⇒ \((a+b-c)^2-d^2 =(a+b-c+d)(a+b-c-d)\)
putting the identities together, we get
=\(\frac{(a+b+c+d)(a+b-c-d)}{(a+b+c-d)(a+b+d-c)}\times \frac{(a+b+c+d)(a+b+c-d)}{(a+b+c-d)(a+b-c+d)}\)
=\(\frac{(a+b+c+d)(a+b+c+d)}{(a+b-c+d)(a+b-c+d)}\)
=\(\frac{(a+b+c+d)^2}{(a+b-c+d)^2}\)
16. Evaluate \((205)^2-(195)^2\)
Solution: \((205)^2-(195)^2\)
= (205+195)(205-195)
⇒ \(\left\{a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right\}\)
= 400 x 10
= 4000
17. Factorize: \(x^2+x y+9 x+9 y\)
Solution: \(x^2+x y+9 x+9 y\)
= x(x+y)+9(x+y)
= (x+y)(x+9)
18. Factorize: \(2 a^2\left(b^2-c^2\right)+b^2\left(2 c^2-2 a^2\right)+2 c^2\left(a^2-b^2\right)\)
Solution: \(2 a^2\left(b^2-c^2\right)+b^2\left(2 c^2-2 a^2\right)+2 c^2\left(a^2-b^2\right)\)
=\(2\left(a^2 b^2-a^2 c^2\right)+2\left(b^2 c^2-b^2 a^2\right)+2\left(c^2 a^2-c^2 b^2\right)\)
= 2 x 0
= 0
19. Divide: \(\left(4 x^2-100\right) \div 6(x+5)\)
Solution: \(\frac{4 x^2-100}{6(x+5)}=\frac{4\left(x^2-25\right)}{6(x+5)}\)
= \(\frac{4_2(x+5)(x-5)}{6_3(x+5)}=\frac{2}{3}(x-5)\)
20. Find two numbers A and B so that A+B=12 and AB=27.
Solution: Given A+B=12 and AB=27
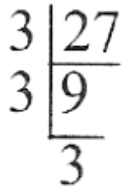
A x B = 27 = 9 x 3
A + B = 12 = 9 + 3
Such that A=9 and B=3
21. If \(a^2+b^2=74 \& a b=35 \text {, }\) then find a+b?
Solution: Given \(a^2+b^2=74 \& a b=35\)
since, \((a+b)^2=a^2+b^2+2 a b\)
⇒ \((a+b)^2=74+2 \times 35=74+70=144\)
⇒ \(a+b=\sqrt{144}\)
⇒ a+b=12
22. If m-n=16 & \(m^2+n^2=400\), then find mn.
Solution: \(m-n=16 \& m^2+n^2=400\)
⇒ \((m-n)^2=m^2+n^2-2 m n\)
⇒ \((16)^2=400-2 m n\)
⇒ \(2 m n=400-(16)^2=400-256\)
⇒ \(m n=\frac{144}{2}=72\)
23. The height of a Δle is \(x^4+y^4\) and its base is 14xy. Find the area of the Δle.
Solution: Given, the height of a Δle and its base are \(x^4+y^4\) and 14xy respectively
wkt, the area of a Δle =\(\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\)
=\(\frac{1}{2} \times 14 x y \times\left(x^4+y^4\right)\)
=\(7 x y\left(x^4+y^4\right)\)
24. The area of a square is given by \(4 x^2+12 x y+9 y^2\). find the side of the square.
Solution: We have
Area of square = \(4 x^2+12 x y+9 y^2\)
so, we factorize the given expression
∴ \(4 x^2+12 x y+9 y^2\)
=\((2 x)^2+2 \times 2 x \times 3 y+(3 y)^2\)
=\((2 x+3 y)^2\)
Since the area of a square having side length a is \(a^2\), hence, side of the given square is 2x+3y.
