KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
Heron’s Formula Points to Remember
- Area of a triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x base x corresponding height
- For an equilateral Δle of side ‘a’
Area = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2\)
→ Perimeter = 3a
→ Altitude → \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a\) - For an isosceles Δle with length of two equal sides as ‘a ’ & base ‘b’
1) Area= \(\frac{b}{4} \sqrt{4 a^2-b^2}\)
2) Perimeter = 2 a + b
3) Altitude = \(\frac{1}{2} \sqrt{4 a^2-b^2}\) - For right angled Δle with a & b are the sides that includes to the right angle.
Area= \(\frac{1}{2} \times a \times b\)
Altitude = a
Perimeter = \(a+b+\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\)
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Heron’s Formula
consider a Δle with sides a, b&c so, perimeter = a + b + c
semi perimeter (s) = \(\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)

Area of triangle = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
This formula is applicable to all type a triangles whether it is a right triangle or isosceles or an equilateral triangle.
Heron’s Formula EXERCISES 12.1
1. A traffic signal board, indicating ‘SCHOOL AHEAD’, is an equilateral triangle with side ‘a’. Find the area of the signal board using Heron’s Formula. If its perimeter is 180cm, what will be the area of the signal board? OR Using Heron’s Formula, find the area of the equilateral Δle of side ‘a’ units.
Solution: ‘a’ = a, ‘b’ = a, ‘c’ = a
∴ \(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{a+a+a}{2}=\frac{3 a}{2}\)
Area ofthe signal board = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{\frac{3 a}{2}\left(\frac{3 a}{2}-a\right)\left(\frac{3 a}{2}-a\right)\left(\frac{3 a}{2}-a\right)} \\
& =\sqrt{\frac{3 a}{2} \times \frac{a}{2} \times \frac{a}{2} \times \frac{a}{2}}=\sqrt{\frac{3 a^4}{16}}=\frac{\sqrt{3} a^2}{4}
\end{aligned}\)
Perimeter = 180cm
=> a + b+c= 180
=> a+a+a = 180
=> 3a = 180
=> a = 180/3 = 60cm
∴ Area of the signal board = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2\)
KSEEB Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Solutions PDF
=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}(60)^2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 3600 & =\sqrt{3} \times 900 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \\
& =900 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Alternate method
\(s=\frac{3 a}{2}=\frac{3}{2} \times 60=90 \mathrm{~cm}\)Area of the signal board
& =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{90(90-60)(90-60)(90-60)}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
& =\sqrt{30 \times 3 \times 30 \times 30 \times 30} \\
& =900 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
2. The triangular side walls of a flyover have been used for advertisements, the sides of the walls are 122m, 22m & 120m (see fig). The adver¬tisements yield an earning of ₹5000 per m² per year. A company hired one of its walls for 3 months. How much rent did it pay?
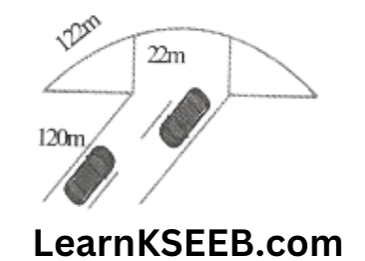
Solution:

a= 122m , b = 22m , c = 120m
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{122+22+120}{2} \\
& =\frac{264}{2}=132 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of the wall }=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& \qquad \begin{array}{l}
=\sqrt{(132)(132-122)(132-22)(132-120)} \\
=\sqrt{132 \times 10 \times 110 \times 12} \\
=\sqrt{11 \times 12 \times 10 \times 10 \times 11 \times 12} \\
=12 \times 11 \times 10 \\
=1320 \mathrm{~m}^2
\end{array}
\end{aligned}\)
1year = 12 months
Rent for 12 months per m² = ₹5000
Rent for 1 month perm² = ₹5000/12
Rent for 3 months per m² = \(=\frac{₹ 5000}{12} \times 3=₹ 1250\)
∴ Rent for 3 months of 1320m² = ₹1250 x 1320
= ₹1650000
Karnataka 9th Standard Maths Chapter 12 Notes
3. There is a slide in a park. One of its side walls has been painted in some colour with a message “KEEP THE PARK GREEN AND CLEAN”. If the sides of the wall are 15m, 11m & 6m, find the area painted in colour.
Solution: 3= 15m, 6= 11m c = 6m
\(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{15+11+6}{2}=16 \mathrm{~m}\)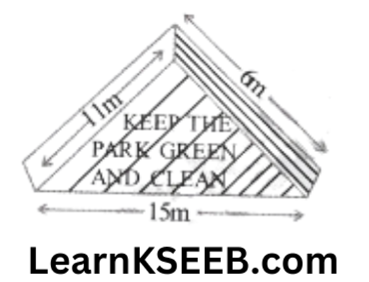
Area painted in colour
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{16(16-15)(16-11)(16-6) m^2} \\
& =\sqrt{16 \times 1 \times 5 \times 10} \\
& =\sqrt{16 \times 5 \times 5 \times 2} \\
& =20 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}^2
\end{aligned}\)
4. Find the area of a Δle two sides of which are 18cm & 10cm & the perimeter is 42cm.
Solution: 3= 18cm, b = 10cm, perimeter = 42cm
Perimeter = 42
=> a + b+c= 42
=> 18 + 10+ c = 42
=> c = 42 – 28
=> c= 14cm
\(S=\frac{42}{2}=21 \mathrm{~cm}\)Area of the Δle = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{21(21-18)(21-10)(21-14)} \\
& =\sqrt{21 \times 3 \times 11 \times 7}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
& =\sqrt{7 \times 3 \times 3 \times 11 \times 7} \\
& =7 \times 3 \sqrt{11} \\
& =21 \sqrt{11} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
5. Sides of a triangle are in the ratio of 12:17: 25 & its perimeter is 540cm. Find its area.
Solution: Let the sides of the triangle be 12k, 17k & 25k cm.
Then, perimeter = 12k + 17k + 25k = 54k
According to the question 54k = 540 =
=> k = 540/54=10
∴ a = 12k = 12×10 = 120cm
b = 17k= 17×10= 170cm
c = 25k = 25×10 = 250cm
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{120+170+250}{2} \\
& =\frac{540}{2}=270 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
\text { Area } & =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{270 \times(270-120)(270-170)(270-250)} \\
& =\sqrt{270 \times 150 \times 100 \times 20} \\
& =\sqrt{9 \times 30 \times 5 \times 30 \times 5 \times 20 \times 20} \\
& =3 \times 30 \times 5 \times 20 \\
& =9000 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
KSEEB Class 9 Maths Heron’s Formula Solutions
6. An isoscles triangle has perimeter 30cm & each of the equal sides is 12cm. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution: a= 12cm, b= 12cm, perimeter = 30cm
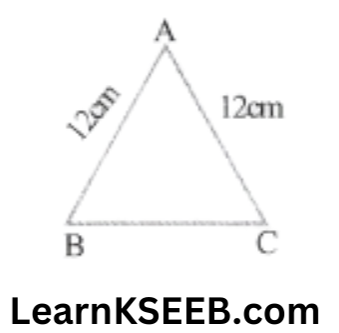
& \Rightarrow \quad a+b+c=30 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 12+12+c=30 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad c=30-24=6 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad s=\frac{30}{2}=15 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area of the Triangle = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{15(15-12)(15-12)(15-6)} \\
& =\sqrt{15 \times 3 \times 3 \times 9} \\
& =\sqrt{5 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3} \\
& =9 \sqrt{15} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
KSEEB Class 9 Maths Heron’s Formula Solutions
Heron’s Formula EXERCISES 12.2
1. A park in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has\(\lfloor C\) = 90°, AB = 9cm, BC = 12m CD = 5m & AD = 8m, How much area does it occupy.
Solution: Join BD
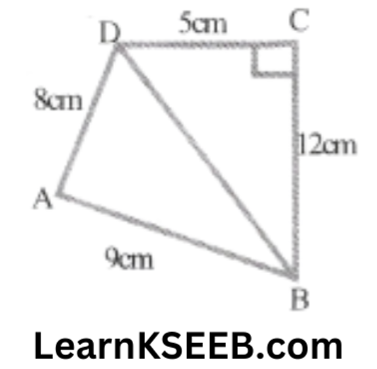
Area of right ΔBCD
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{1}{2} \times B \times H \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 12=30 \mathrm{~m}^2
\end{aligned}\)
In right ΔBCD,
BD² = BC² + CD² (by Pythagoras theorem)
= 12² + 5²= 144 + 25
=> BD= \(\sqrt{169}\) = 13m
For ΔABD
a = 13m, b = 8m, c = 9m
a + b+c 13 + 8 + 9 30
∴ \(\mathrm{s}=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{13+8+9}{2}=\frac{30}{2}=15 \mathrm{~m}\)
Area of the ΔABD = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{15(15-13)(15-8)(15-9)} \\
& =\sqrt{15 \times 2 \times 7 \times 6} \\
& =\sqrt{5 \times 3 \times 2 \times 7 \times 2 \times 3} \\
& =2 \times 3 \sqrt{7 \times 5} \\
& =6 \sqrt{35}
\end{aligned}\)
= 6 x 5.916 = 35.5m² (approx) Area of the quadrilateral
ABCD = Area of ΔBCD + Area of ΔABD = 30 + 35.5m² = 65.5m² (approx) Hence, the park occupies the area 65.5m²
2. Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 4cm DA = 5cm & AC = 5cm
Solution:
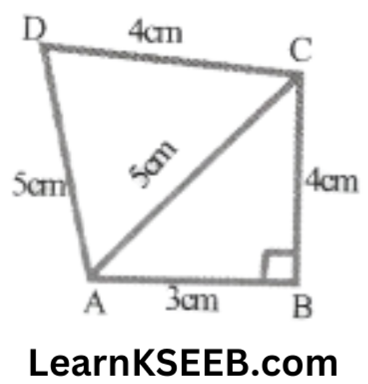
For ΔABC
a = 4cm, b = 5 cm, c = 3cm
a² + c² = b²
∴ ΔABC is right angled Angled with \(\lfloor B\) = 90°
∴ Area of right ΔABC = 1/2 xbxh
= \(=\frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4=6 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
For ΔACD
a = 4cm, b = 5cm, c = 5cm
\(\begin{aligned}s & =\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{4+5+5}{2}=\frac{14}{2}=7 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔACD = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{7(7-4)(7-5)(7-5)} \\
& =\sqrt{7 \times 3 \times 2 \times 2} \\
& =2 \sqrt{21}=2 \times 4.6=9.2 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of the quadrilateral ABCD
= Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔACD
= 6cm² + 9.2cm²
= 15.2cm² (approx.)
3. Radha made a picture of an aeroplane with coloured paper as shown in figure. Find the total area of the paper used (same fig. shown in Answer)
Solution:
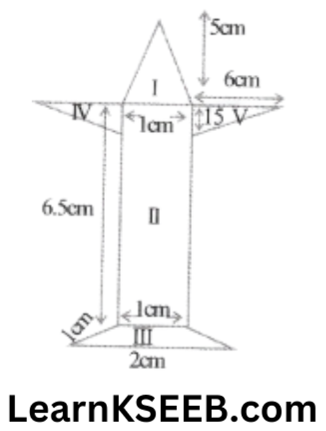
For Δle Area 1
a = 5cm , b = 5cm , c = 1cm
\(\begin{aligned}& \mathrm{s}=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{5+5+1}{2} \\
& =\frac{11}{2}=5.5 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{5.5(5.5-5)(5.5-5)(5.5-1)} \\
& =\sqrt{5.5 \times(0.5)(0.5)(4.5)} \\
& =0.5 \sqrt{(11)(0.5)(9)(0.5)} \\
& =0.5 \times 0.5 \times 3 \sqrt{11} \\
& =0.75 \sqrt{11} \\
& =0.75 \times 3.3 \text { (approx.) }
\end{aligned}\)
= 2.5cm²(approx.)
Area 2
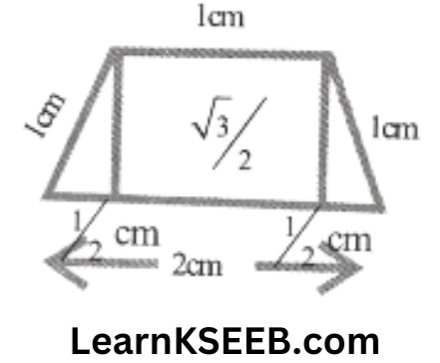
= l x b
= 6.5 x 1 = 6.5cm²
Area 3
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2} \times 2 \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\frac{1}{2} \times 1 \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \\
& =\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{4}=\frac{3 \times 1.732}{4} \text { (approx.) } \\
& =\frac{5.196}{4}=1.3 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \text { (approx.) }
\end{aligned}\)
Area 4 = \(6 \times \frac{1.5}{2}=4.5 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
Area 5 = 1/2 x 6×1.5 = 4.5 cm²
Total area of the paper used = Area 1 + Area 2 + Area 3 + Area 4+ Area 5
= 2.5 + 6.5 + 1.3 + 4.5 +4.5 = 19.3cm²
4. A Δle and a ||gm have the same base & the same area. If the side of the triangle are 26cm, 28cm & 30cm & the ||gm stands on the base 28cm, find the height of the ||gm.
Solution: For Δle
a = 26cm, b = 28cm, c = 30cm
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{26+28+30}{2}=\frac{84}{2}=42 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of the Δle = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{42(42-26)(42-28)(42-30)} \\
& =\sqrt{42 \times 16 \times 14 \times 12} \\
& =\sqrt{(6 \times 7) \times 16 \times(7 \times 2) \times(6 \times 2)} \\
& =6 \times 4 \times 7 \times 2 \\
& =336 \mathrm{~cm}^3
\end{aligned}\)
Let the height of the ||gm be ft cm
Then, area of the ||gm = Base x height
= 28 x h
According to the question
Area of Δle = Area of ||gm
=> 336 = 28h
=> h = 336/28 = 12cm
Hence, the height of the ||gm is 12cm.
5. A rhombus shaped field has green grass for 18 cows to graze. If each side of the rhombus is 30m & its longer diagonal is 48m, how much area of grass field will each cow be getting?
Solution: For ΔABC
a = 30m, b = 48m, c = 30m
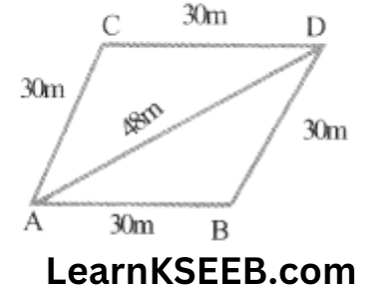
∴ \(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{30+48+30}{2} \\
& =\frac{108}{2}=54 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of ΔABC = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{54(54-30)(54-48)(54-30)} \\
& =\sqrt{54 \times 24 \times 6 \times 24} \\
& =\sqrt{9 \times 6 \times 24 \times 6 \times 24} \\
& =3 \times 6 \times 24 \\
& =432 \mathrm{~m}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Area of the rhombus = 2 Area of ΔABC
= 2 x 432 = 864m²
Area of grass for 18 cows = 864m²
Area of grass for 1cow = 864/18m² = 48m²
6. An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours (see fig) each piece measuring 20cm, 50cm & 50cm, how much cloth is required for the umbrella?

Solution: For one triangular piece
a = 20cm, b = 50cm , c = 50cm

Area of one Δle
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{60(60-20)(60-50)(60-50)} \\
& =\sqrt{60 \times 40 \times 10 \times 10} \\
& =\sqrt{20 \times 3 \times 20 \times 2 \times 10 \times 10} \\
& =200 \sqrt{6} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Area of five Δles of one colour
=\(5 \times(200 \sqrt{6}) \mathrm{cm}^2=1000 \sqrt{6} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
Hence, \(1000 \sqrt{6} \mathrm{~cm}^2\) of each colour is required for the umbrella.
7. A kite in the shape of a square with a diagonal 32cm & an isoscles Δle of base 8cm & side 6cm each is to be made of three different shades as shown in figure. How much paper of each shade has been used in it?
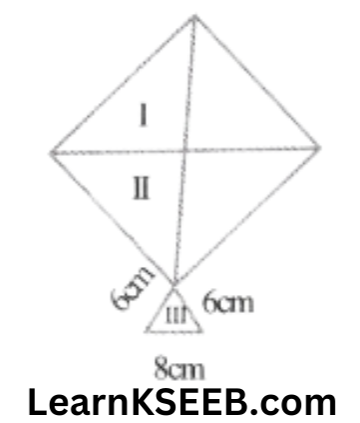
Solution: Area of paper of shade 1
\(=\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{2} \times 32 \times 32\right)=256 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)Area of paper of shade 2 = 256cm²
For paper of shade 3
a = 8cm, b = 6cm, c = 6cm
∴ \(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
\(=\frac{8+6+6}{2}\)=20/2 = 10cm
Area of paper of shade 3

& =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{10(10-8)(10-6)(10-6)} \\
& =\sqrt{10 \times 2 \times 4 \times 4} \\
& =\sqrt{5 \times 2 \times 2 \times 4 \times 4} \\
& =8 \sqrt{5}=17.92 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
8. A floral design on a floor is made up of 16 tiles which are triangular, the sides of the triangle being 9cm, 28cm & 35cm, find the cost of polishing the tiles at the rate of 50 per cm²
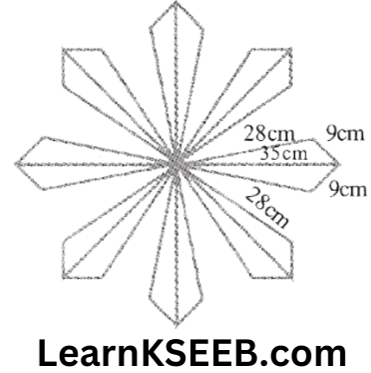
Solution: For one tile
a = 9cm , b = 28cm , c = 35cm

& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{9+8+35}{2} \\
& =\frac{72}{2}=36 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area of one tile = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{36(36-9)(36-28)(36-35)} \\
& =\sqrt{36 \times 27 \times 8 \times 1} \\
& =\sqrt{36 \times 9 \times 3 \times 4 \times 2 \times 1} \\
& =6 \times 3 \times 2 \sqrt{6} \\
& =36 \sqrt{6} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of 16 tiles = \(36 \sqrt{6} \times 16\)
= \(576 \sqrt{6} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
∴ cost of polishing the tiles at the rate of 50P per m²
\(\begin{aligned}& =576 \sqrt{6} \times 50 p=\frac{576 \sqrt{6} \times 50}{100} \\
& =₹ 288 \sqrt{6}=₹ 705.60
\end{aligned}\)
KSEEB 9th Standard Maths Chapter 12 Important Questions
9. A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25m & 10m. The non-parallel sides are 14m & 13m. Find the area of the field.
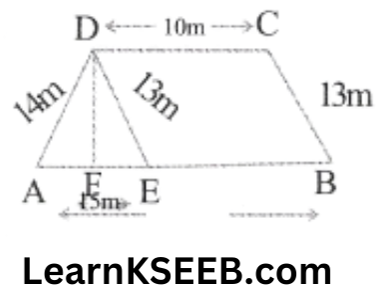
Solution: Let the given field be in the shape of a trapezium ABCD in which
AB = 25m, CD = 10m, BC = 13m & AD = 14m.
From D, draw DE || BC meeting AB at E.
Also, draw QF ⊥ AB
∴ DE = BC = 13m
AE = AB – EB = AB – DC
= 25- 10= 15m
For ΔAED,
a = 14m, b = 13m, c= 15m

\mathrm{s} & =\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{14+13+15}{2} \\
& =\frac{42}{2}=21 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of the ΔAED
\(\begin{aligned}&=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
&=\sqrt{21(21-14)(21-13)(21-1} \\
&=\sqrt{21 \times 7 \times 8 \times 6} \\
&=\sqrt{7 \times 3 \times 7 \times 4 \times 2 \times 3 \times 2} \\
&=7 \times 3 \times 2 \times 2 \\
&=84 \mathrm{~m}^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{2} \times \mathrm{AE} \times \mathrm{DF}=84 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{2} \times 15 \times \mathrm{DF}=84
\end{aligned}\) \(\Rightarrow \mathrm{DF}=\frac{84 \times 2}{15}=11.2 \mathrm{~m}\)
∴ Height of the trapezium is 11.2m
∴ Area of ||gm EBCD = b x h = EB x DF
= 10 x 11.2= 112m²
∴ Area of the field = Area of ΔAED + Area of ||gm EBCD
= 84m² + 112m²
= 196 m²
Choose The Correct Answer From The Following
1. The side of an equilateral Δle is 6cm. The area of the triangle is
- \(6 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(9 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(16 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(3 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
Solution: 2. \(9 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
2. The length of the side of an equilateral triangle whose area is \(9 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- 1cm
- 2cm
- 3cm
- 6cm
Solution: 4. 6cm
3. 1 hectare =
- 10m²
- 100m²
- 1000m²
- 10000m²
Solution: 4. 10000m²
4. The sides of a triangular park are in the ratio 25:17:12 & its perimeter is 540m. The smallest side of the park is
- 60m
- 120m
- 90m
- 45m
Solution: 2. 120m
5. A square & an equilateral Δle have equal perimeters. If the diagonal of the square is \(12 \sqrt{2}\) cm then area of the Δle is
- \(24 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(24 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(48 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(64 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
Solution: 4. \(64 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
6. Two sides of a Δle are 13 cm & 14cm & its semi perimeter is 18cm, then third side of the Δle is _
- 9cm
- 12cm
- 11cm
- 10cm
Solution: 1. 9cm
7. The perimeter of a rhombus is 20cm. If one of its diagonals is 6cm, then its area is
- 28cm²
- 36cm²
- 24cm²
- 20cm²
Solution: 3. 24cm²
8. If the length of median of an equilateral Δle be x cm, then its area is
- \(x^2\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} x^2\)
- \(\frac{x^2}{\sqrt{3}}\)
- \(\frac{x^2}{2}\)
Solution: 3. \(\frac{x^2}{\sqrt{3}}\)
9. The base of an isosceles right triangle is 30cm. Its area is
- 255cm²
- \(225 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- \(225 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
- 450cm²
Solution: 1. 255cm²
10. The sides of a Δle are 11cm, 15cm & 16cm. The altitude to the largest side is
- \(30 \sqrt{7} \mathrm{~cm}\)
- \(\frac{15 \sqrt{7}}{2} \mathrm{~cm} 6\)
- \(\frac{15 \sqrt{7}}{4} \mathrm{~cm}\)
- 30cm
Solution: 3. \(\frac{15 \sqrt{7}}{4} \mathrm{~cm}\)
One Mark Questions
1. The area of an equilateral Δle is \(16 \sqrt{3} m^2\) What is its perimeter?
Solution: Area of equilateral Δle = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2=16 \sqrt{3}\)
=> a² =16×4
=> a = 8m
Thus perimeter = 3a = 3 x 8 = 24cm
2. Calculate the side of an isosceles right Δle of hypotenuse \(5 \sqrt{2}\) cm.
Solution:
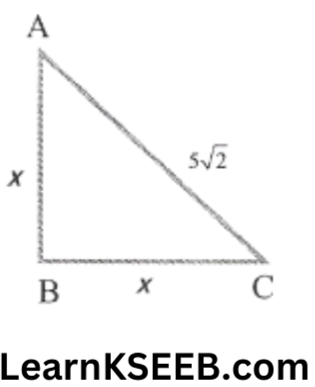
& x^2+x^2=(5 \sqrt{2})^2 \\
& 2 x^2=50 \\
& x^2=25 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad x=5 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
3. The perimeter of an equilateral Δle is 60m. What will be its area?
Solution: Perimeter = 3a = 60
a = 20m
Area \(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 20^2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 400 \\
& =100 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Karnataka Board Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 MCQs
4. What is the area of ΔABC in which AB = BC = 4cm & \(\lfloor B\) = 90°
Solution:
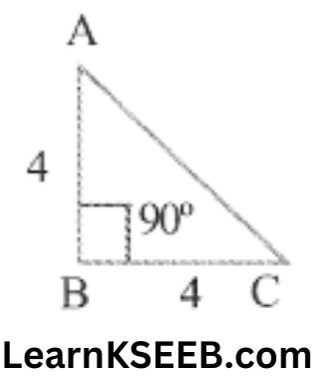
Area of ΔABC
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2} \times \mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{BC} \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 4 \\
& =8 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
5. Area of an isosceles right Δle is 8cm² What is its hypotenuse?
Solution:
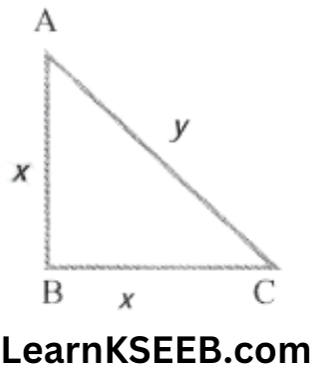
Area of an isosceles right
\(\begin{aligned}& \Delta^{l e}=\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \\
& 8=\frac{1}{2} \times x \times x \\
& 16=x^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad x=4 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
hypotenuse (y) = \(\sqrt{x^2+x^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{4^2+4^2}=\sqrt{32} \mathrm{~cm}\)
6. The perimeter of a Δle is 36cm & its side are in the ratio a : b : c = 3 : 4 : 5 then, find the value of a, b, c respectively.
Solution: Sides are 3x, 4x, 5x
Then 3x + 4x + 5x = 36
12x= 36
=> x = 3
∴ Sides are 9cm, 12cm, 15cm
7. The sides of ΔABC are 8cm, 7cm & 5cm, respectively, find out its semi-perimeter.
Solution: \(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{8+7+5}{2}=\frac{20}{2}=10 \mathrm{~cm}\)
8. If a, b & c are the sides of the Δle & S is semi perimeter, then calculate the area of a triangle.
Solution: A= \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
9. Two sides of a Δle are I2cm & 13cm & its semi-perimeter is 20cm, then what will be the third side of the Δle?
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& 20=\frac{12+13+c}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 40=25+c \\
& \Rightarrow \quad c=40-25=15 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
10. Side of an equilateral Δle is 4cm, calculate its area.
Solution: Area of an equilateral Δle
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2 \\
& =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 4^2 \\
& =4 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Two Mark Questions
1. A square & an equilateral Δle have equal perimeters. If the diagonal of the square is
\(12 \sqrt{2}\) cm, then find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
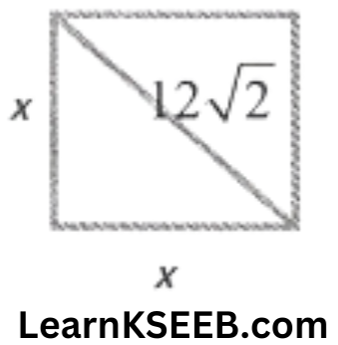
x^2+x^2=(12 \sqrt{2})^2 \\
2 x^2=144 \times 2 \\
x=12 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}\)
Given 3a = 4x (a, b, c aside of Δle)
3a = 4 x 12
a= 16cm
Area of Δle \(=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 16^2\)
\(=64 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)2. The area of a rhombus is 96cm². If one of its diagonals is 16cm, then find out the length of its sides.
Solution:
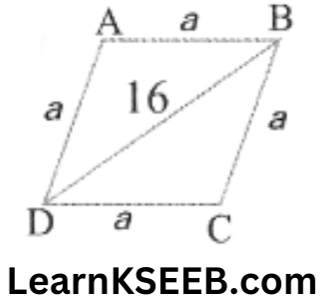
For ΔBCD
\(\begin{aligned}s & =\frac{16+a+a}{2} \\
& =\frac{16+2 a}{2}=8+a
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔBCD
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{(a+8)(a+8-16)(a+8-a)(a+8-a)} \\
& =\sqrt{(a+8)(a-8) \times 8 \times 8} \\
& =8 \sqrt{a^2-64}
\end{aligned}\)
Area of rhombus = 2 x Area of ΔBCD
\(\begin{aligned}& 96=2 \times 8 \sqrt{a^2-64} \\
& \frac{96}{16}=\sqrt{a^2-64} \\
& 6=\sqrt{a^2-64}
\end{aligned}\)
square both side
\(\begin{aligned}& \Rightarrow \quad 36=a^2-64 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 36+64=a^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a^2=100 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a=10 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ The side of a rhombus is 10cm
3. The base of a right Δle is 6cm & hypotenuse is 10cm, what will be its area?
Solution: AB² = AC² – BC² (bypythagora’s theorem)
\(\begin{aligned}\mathrm{AB} & =\sqrt{10^2-6^2} \\
& =\sqrt{100-36}=\sqrt{64}=8 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ AB = 8cm
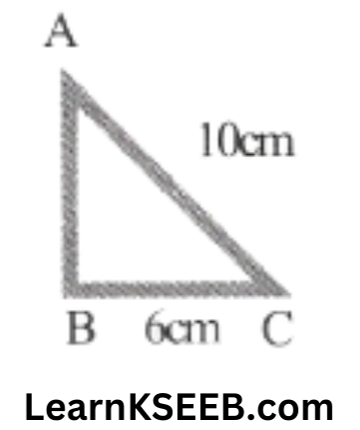
Area of right Δle = \(\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\)
\(=\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 8=24 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)4. Find the area of an equilateral Δle whose, perimeter is 120cm.
Solution: Perimeter of an equilateral Δle = 3a
\(\begin{aligned}& \Rightarrow \quad 3 a=120 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a=120 / 3=40 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 40 \times 40\)
= \(400 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
5. If the area of an equilateral Δle is\(81 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2\) find its perimeter
Solution: Area of an equilateral Δle = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2\)
\(\begin{aligned}& \Rightarrow 81 \sqrt{3}=\frac{\sqrt{3} a^2}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow a^2=81 \times 4 \\
& \Rightarrow a=9 \times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow a=18 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Perimeter = 3a
= 3×18 = 54cm
6. The sides of a Δle are 7cm, 24cm & 25cm. What will be its area?
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{7+24+25}{2}=\frac{56}{2}=28 \mathrm{~cm} \\
& \text { Area }=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{28(28-7)(28-24)(28-25)} \\
& =\sqrt{28 \times 21 \times 4 \times 3} \\
& =\sqrt{(7 \times 4) \times(7 \times 3) \times 4 \times 3} \\
& =7 \times 4 \times 3 \\
& =84 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
7. The edges of a triangular board are 6cm, 8cm & 10cm, calculate the cost of painting it at the rate of 9 paise per cm².
Solution:
\(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{6+8+10}{2}=12 \mathrm{~cm}\) \(\begin{aligned}\text { Area } & =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{12(12-6)(12-8)(12-10)} \\
& =\sqrt{12 \times 6 \times 4 \times 2}
\end{aligned}\)
=12cm²
\(\text { Cost of painting }=\frac{24 \times 9}{100}=₹ 2.16\)8. Using Heron’s formula, find the area of an equilateral Δle with side 16cm.
Solution: \(s=\frac{16+16+16}{2}=\frac{48}{2}=24 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(\begin{aligned}\text { Area } & =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{24(24-16)(24-16)(24-16)} \\
& =\sqrt{24 \times 8 \times 8 \times 8} \\
& =\sqrt{8 \times 3 \times 8 \times 8 \times 8} \\
& =64 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
9. Find the area of an isosceles Δle whose equal sides are of length 12cm each & third side is 12cm.
Solution: a = 15cm, b=15cm c=12cm
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& \frac{15+15+12}{2}=\frac{42}{2}=21 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area \(=\sqrt{21(21-15)(21-15)(21-12)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\sqrt{21 \times 6 \times 6 \times 9} \\
& =18 \sqrt{21} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
10.The cross-section of a canal is in the shape of a trapezium. If the canal is 12m wide at the top & 8m wide at the bottom & the area of its cross-section is 84m² determine its depth
Solution: Let the depth be ‘h’m
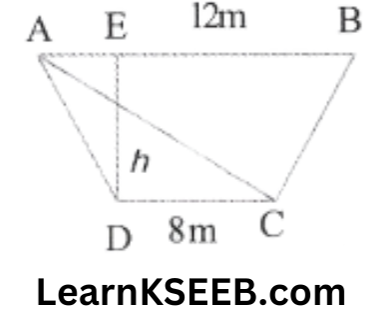
Area of trapezium = 84m²
=> Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔADC = 84m²
\(\begin{aligned}\Rightarrow & \frac{1}{2}(\mathrm{AB})(\mathrm{DE}) \\
& +\frac{1}{2}(\mathrm{DC})(\mathrm{DE})=84 \\
\Rightarrow & \frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times h+\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times h=84 \\
\Rightarrow & 6 h+4 h=84 \\
\Rightarrow & 10 h=84 \\
\Rightarrow & h=\frac{84}{10}=8.4 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}\)
Hence, the depth of the canal is 8.4m
Three Mark Questions
1. An umbrella is made by stitching ten triangular pieces of cloth, each measuring 60cm, 60cm & 20cm. Find the area of the cloth required for the umbrella.
Solution: Area of cloth required = 10 x Area of cloth for one piece Area of one piece of cloth is made by side 60cm, 60cm & 20cm is
\(s=\frac{60+60+20}{2}=\frac{140}{2}=70 \mathrm{~cm}\)Area = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{70(70-60)(70-60)(70-20)} \\
& =\sqrt{70 \times 10 \times 10 \times 50} \\
& =\sqrt{7 \times 10 \times 10 \times 10 \times 10 \times 5} \\
& =100 \sqrt{35} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
\text { Area of cloth required } & =10 \times 100 \sqrt{35} \\
& =1000 \sqrt{35} \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
2. The sides of a triangular field are 51m, 37m & 20m, Find the number of rose beds that can be prepared in the field if each rose bed occupies a space of 6 sq. m.
Solution:
\(\begin{gathered}s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{51+37+20}{2} \\
=\frac{108}{2}=54 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}\)
Area = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{54(54-51)(54-37)(54-20)} \\
& =\sqrt{54 \times 3 \times 17 \times 34} \\
& =306 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
No. of rose beds = \(=\frac{\text { Total area of triangular field }}{\text { Area occupied by each rose bed }}\)
\(=\frac{306}{6}=51\)3. Find the percentage increase in the area of a triangle, if its each side is doubled.
Solution: Let a, b, c be the given sides semi-perimeter of Origin, \(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}\)
Area of Original triangle = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
Again 2a, 2b, 2c be the new sides, then
semi perimeter of new triangle = \(\frac{2 a+2 b+2 c}{2}\)
\(=\frac{2(a+b+c)}{2}=2 s\)New area = \(\sqrt{2 s(2 s-2 a)(2 s-2 b)(2 s-2 c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{2 s \times 2(s-a) \times 2(s-b) \times 2(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{4 s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c) \times 4} \\
& =4 \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}=4 \times \text { original area }
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Increase in area = 4 x original area 1 x original area = 3 x original area
\(\begin{aligned}& \% \text { Increase in area }=\frac{3 \times \text { original area } \times 100}{\text { original area }} \\
& =300 \%
\end{aligned}\)
4. Compute the area of the trapezium shown in the figure
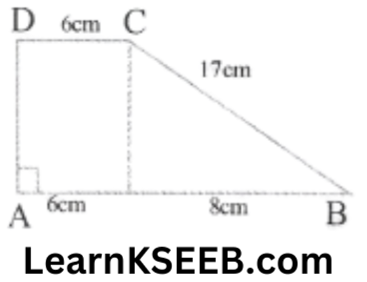
Solution: Area of trapezium ABCD = Area of rectangle AOCD + Area of ΔOBC

In ΔOBC, by pythagora’s theorem
BC² = OC² + OB²
17² = OC² + 8²
OC² = 289-64 = 225
OC = 15cm
Area of rectangle AOCD = 6 x 15 = 90cm²
Area of ΔOBC = \(\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 15=60 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
∴ Area of trapezium ABCD = 90+ 60 = 150cm²
5. Find the area of a right angled Δle if the radius of its circumcircle is 3cm & the altitude drawn to the hypotenuse is 2cm
Solution: Let ABC be the right-angled Δle, right angled at B.
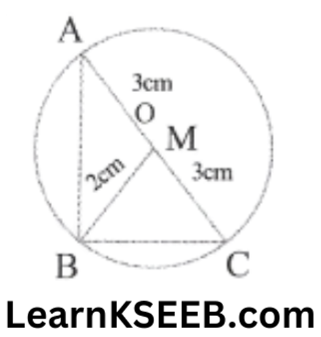
Let O be the centre of the circumcircle, then O is the midpoint of the hypotenuse AC.
∴ Hypotenuse AC = diameter of the circle.
= 2 x radius of the circumcircle
= 2×3 = 6cm
Let BM be the perpendicular from B on AC.
∴ BM = 2cm
∴ Area of the right angled Δle ABC = \(\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2} \times \mathrm{AC} \times \mathrm{BM} \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 2=6 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
6. The sides of a triangular park are 8m, 10m & 6m respectively. A small circular area of diameter 2m is to be left out & the remaining area is to be used for growing roses. How much area is used for growing roses? (use π =3.14)
Solution: For triangular park
6² + 8² = 10²
∴ Angular between sides of length 6m & 8m = 90°
∴ Area of the triangular park = \(\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 8\) = 24m²
Radius of circular area (r) = \(\frac{2}{2} m=1 m\)
∴ Circular area = πr² =π(1)² =π = 3.14m²
∴ Area used for growing roses =Area of the triangular part – circular area
= 24-3.14
= 20.86m²
7. Find the area of a rhombus whose perimeter is 200m & one of the diagonals is 80m.
Solution: Let each of the equal sides of the rhombus be a cm, then
Perimeter = a+a+a + a = 4am
According to the question, 4a = 200
\(a=\frac{200}{4}=50 m\)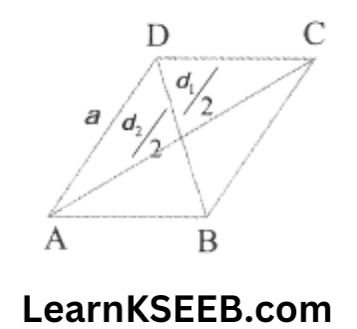
d1 = 80m
\(\begin{aligned}& a^2=\left(\frac{d_1}{2}\right)^2+\left(\frac{d_2}{2}\right)^2 \\
& \Rightarrow 50^2=40^2+\left(\frac{d_2}{2}\right)^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad\left(\frac{d_2}{2}\right)^2=50^2-40^2=30^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \frac{d_2}{2}=30 \\
& \Rightarrow d_2=60 \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area = \(\frac{1}{2} d_1 d_2\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2} \times 80 \times 60 \\
& =2400 m^2
\end{aligned}\)
8. The lengths of the sides of a Δle are 5cm, 12cm & 13cm, Find the length of the perpendicular from the opposite vertex to the side whose length is 13cm.
Solution:
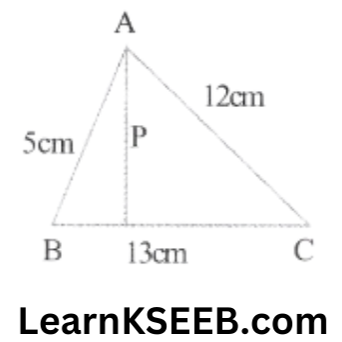
Here a = 5, b= 12 &c = 13
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{5+12+13}{2} \\
& =\frac{30}{2}=15 \mathrm{~cm} \\
& s=\frac{5+12+13}{2}=\frac{30}{2}=15 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area }=\sqrt{15(15-5)(15-12)(15-13)} \\
& \quad=\sqrt{15 \times 10 \times 3 \times 2}=\sqrt{5 \times 3 \times 5 \times 2 \times 3 \times 2}=30 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
Let l be the length of the perpendicular from vertex A on the side BC, then
\(\begin{aligned}A & =\frac{1}{2} \times 13 \times \ell \\
30 & =\frac{1}{2} \times 13 \times \ell \\
& \Rightarrow \ell=\frac{30 \times 2}{13}=\frac{60}{13} \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Class 9 Maths Heron’s Formula KSEEB Guide
9. The sides of a triangular ground are 5m, 7m & 8m respectively. Find the cost of levelling the ground at the rate of ₹10 perm² (use \(\sqrt{3}\) =1.73)
Solution: For triangular ground
a=5m, b = 7m, c = 8m
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{5+7+8}{2}=\frac{20}{2}=10 \mathrm{~m} \\
& \text { Area }=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{10(10-5)(10-7)(10-8)} \\
& =\sqrt{10 \times 5 \times 3 \times 2}=\sqrt{5 \times 2 \times 5 \times 3 \times 2} \\
& =5 \times 2 \sqrt{3}=10 \sqrt{3}=10 \times 1.73=17.3 \mathrm{~m}^2 \\
&
\end{aligned}\)
∴ cost of levelling = 17.3 x 10
= ₹173
Four Mark Questions
1. Black & white coloured triangular sheets are used to make a toy as shown in figure, find the total area of black & white colour sheets used for making the toy.
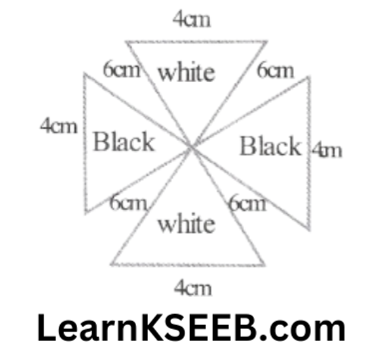
Solution: a = 6cm, b = 6cm, c = 4cm
\(\begin{aligned}& s=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{6+6+4}{2}
\end{aligned}\)
=16/2 = 8cm
Area of one triangular sheet
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{8(8-6)(8-6)(8-4)} \\
& =\sqrt{8 \times 2 \times 2 \times 4} \\
& =\sqrt{4 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 4} \\
& =4 \times 2 \sqrt{2}=8 \sqrt{2} cm^2
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of two black Δles required = \(8 \sqrt{2} \times 2=16 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
Area of two white triangles required= \(8 \sqrt{2} \times 2=16 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~cm}^2\)
2. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 7cm, BC = 6cm, CD = 12cm DA = 15cm & AC = 9cm
Solution: The diagonal AC divides the quadrilateral ABCD into two Δles ABC & ACD
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔACD
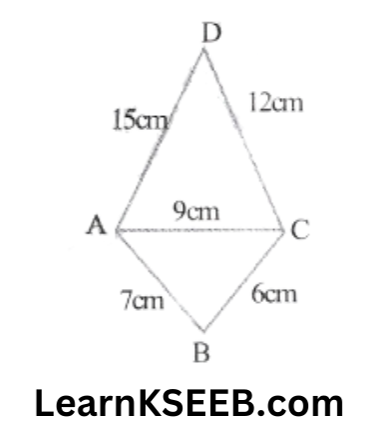
For ΔABC
\(\begin{aligned}s & =\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{7+6+9}{2}=\frac{22}{2}=11 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned}
& A=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{11(11-7)(11-6)(11-9)} \\
& =\sqrt{11 \times 4 \times 5 \times 2} \\
& =\sqrt{440} \mathrm{~cm}^2 \Rightarrow 20.98 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
For ΔACD, we have
\(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{15+12+9}{2}=\frac{36}{2}=18 \mathrm{~cm}\) \(\begin{aligned}& A=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} \\
& =\sqrt{18(18-15)(18-12)(18-9)} \\
& =\sqrt{18 \times 3 \times 6 \times 9} \\
& =\sqrt{9 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 2 \times 9} \\
& =9 \times 3 \times 2=54 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of Quadrilateral ABCD = 20.98 + 54 = 74.98cm²
KSEEB Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise Solutions
3. In the following figure, calculate the area of the shaded portion
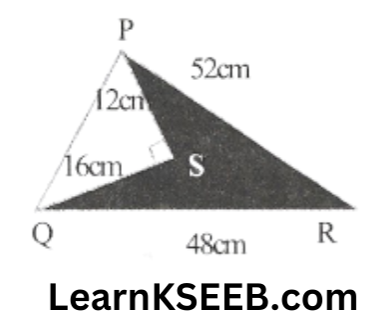
Solution:
In right Δle PSQ
PQ² = PS² + QS²
= 12²+ 16²
= 144 + 256
= 400
=> PQ = \(\sqrt{400}\) = 20cm
Now for ΔPQR

a = 20cm, b = 48cm, c= 52cm
\(s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}=\frac{20+48+52}{2}=\frac{120}{2}=60 \mathrm{~cm}\)Area of ΔPQR = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{60(60-20)(60-48)(60-52)} \\
& =\sqrt{60 \times 40 \times 12 \times 8} \\
& =\sqrt{6 \times 10 \times 4 \times 10 \times 6 \times 2 \times 4 \times 2} \\
& =6 \times 10 \times 4 \times 2
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔPSQ = \(\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\)
\(=\frac{1}{2} \times 16 \times 12=96 \mathrm{~cm}^2\)Area of the shaded portion = Area of ΔPQR – Area of ΔPSQ
= 480 – 96
= 384cm²
4. The adjacent sides of a ||gm ABCD measure 34cm & 20cm & the diagonal AC measures 42cm. Find the area of the ||gm.
Solution:
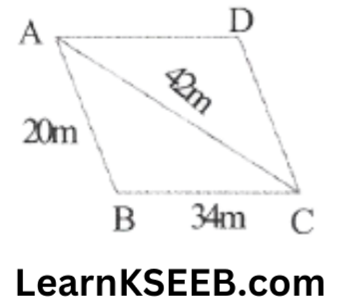
For ΔABC
a = 34cm, b= 42 cm, c = 20cm
\(\begin{aligned}s & =\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
& =\frac{34+42+20}{2}=\frac{96}{2}=48 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔABC = \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{48(48-34)(48-42)(48-20)} \\
& =\sqrt{48 \times 14 \times 6 \times 28} \\
& =336 \mathrm{~cm}^2
\end{aligned}\)
∴ Area of ||gm ABCD = 2 x Area of ΔABC
= 2×336
= 672cm²
