KSEEB Solutions For 8 Class Maths Chapter 7 Practical Geometry Points To Remember
A quadrilateral has 10 parts – 4 sides, 4 angles and 2 diagonals. Five measurements can determine a quadrilateral uniquely.
Five measurements can determine a quadrilateral uniquely.
A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if the lengths of its four sides and a diagonal is given.

A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely, if its two diagonals and three sides are known.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Kseeb Solutions For 8th Class Maths Chapter 7
A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if its two adjacent sides and three angles are known.
A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if its three sides and two included angles are given.
Karnataka Board 8th Maths Chapter 7 Practical Geometry Solutions
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Solutions For Chapter 7 Practical Geometry Exercise 7.1
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals
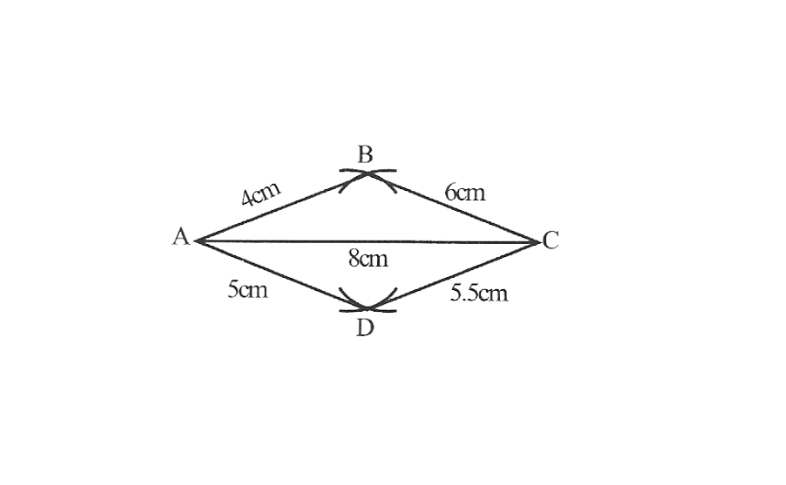
1) Quadrilateral ABCD
AB=4.5cm
BC=5.5cm
CD=4cm
AD=6cm
AC=7cm
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
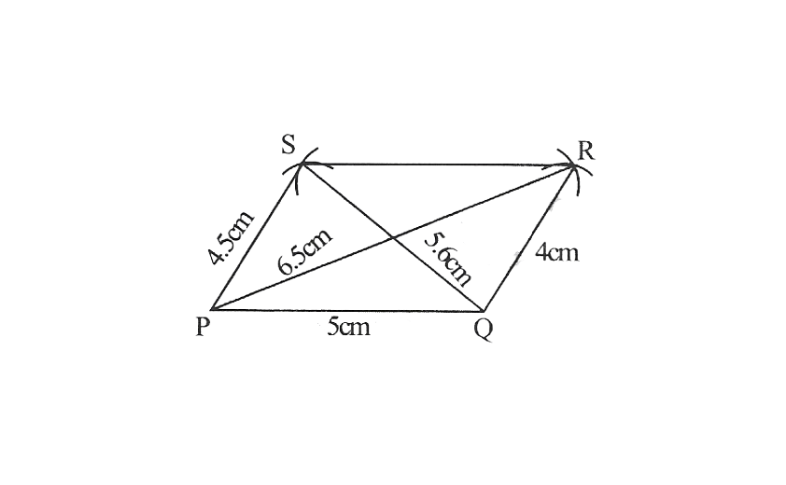
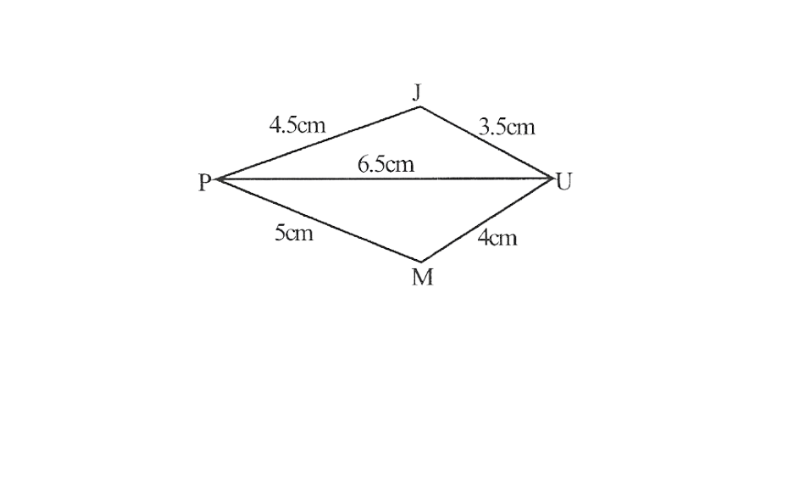
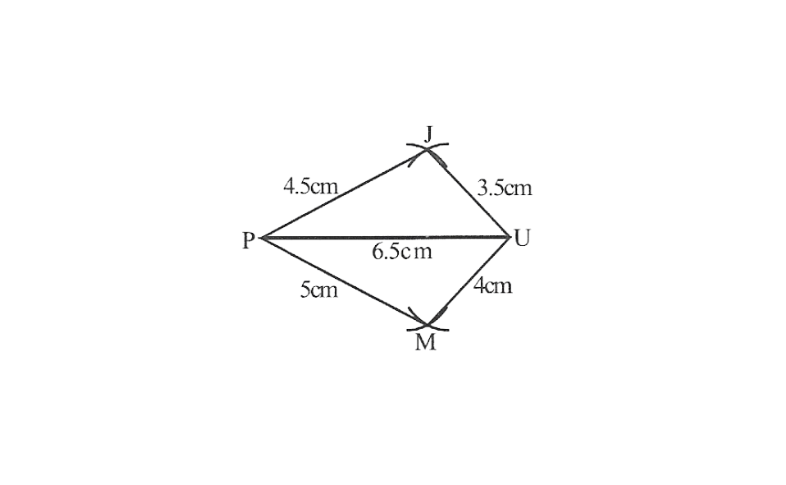
2)Quadrilateral JUMP,
JU=3.5cm
UM=4cm
MP=5cm
PJ=4.5cm
PU=6.5cm
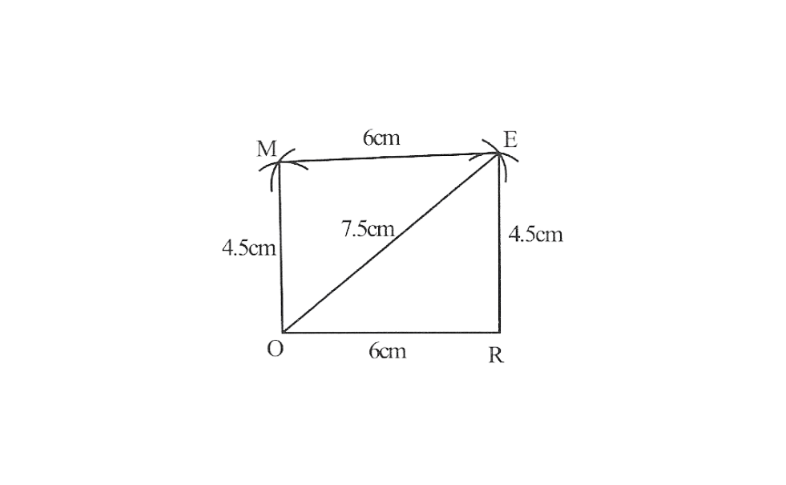
3)Parallelogram MORE
OR=6cm
RE=4.5cm
EO=7.5cm
4)Rhombus BEST
BE=4.5cm
ET=6cm
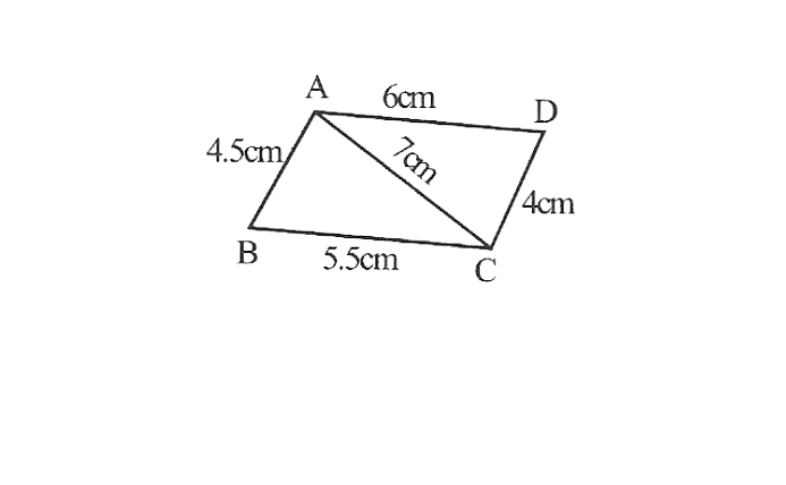
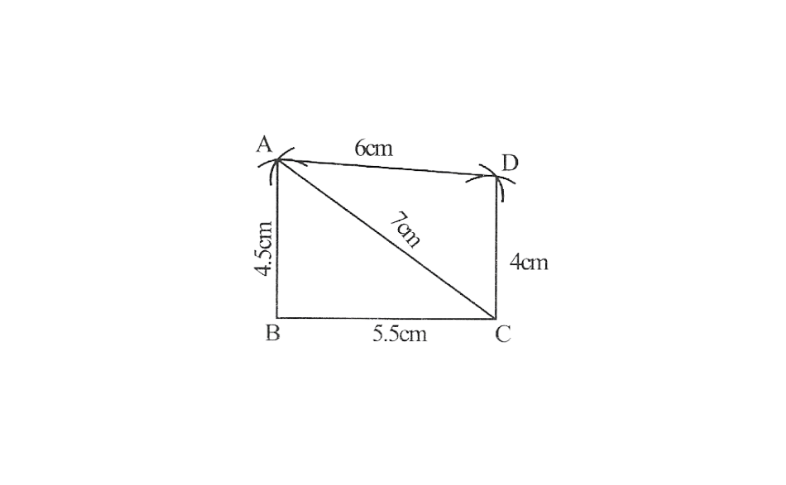
Solution:1)Quadrilateral ABCD
AB=4.5cm,BC=5.5cm, CD=4cm, AD=6cm, AC=7cm
Kseeb 8th Standard Maths Chapter 7 Textbook Solutions
1. Draw △ABC using SSS construction.
2. Vertex D is 6cm away from vertex A taking A as centre, draw an arc of radius 6cm.
3. taking C as centre, drawn arc of radius 4cm, cutting the previous arc at point D
4. ABCD is the required quadrilateral
2) Rough sketch of the quadrilateral JUMP
Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Kseeb Important Questions And Answers
1. Draw △JUP using SSS construction
2. Vertex M is 5cm away from vertex P and 4cm away from Vertex U. Taking P and U as centres, draw arcs of radii 5cm and 4cm respectively. Let the point of intersection be M
3. Join M to P and U
4. JUMP is the required quadrilateral.
3) Parallelogram MORE
OR=6cm, RE=4.5cm, EO=7.5cm
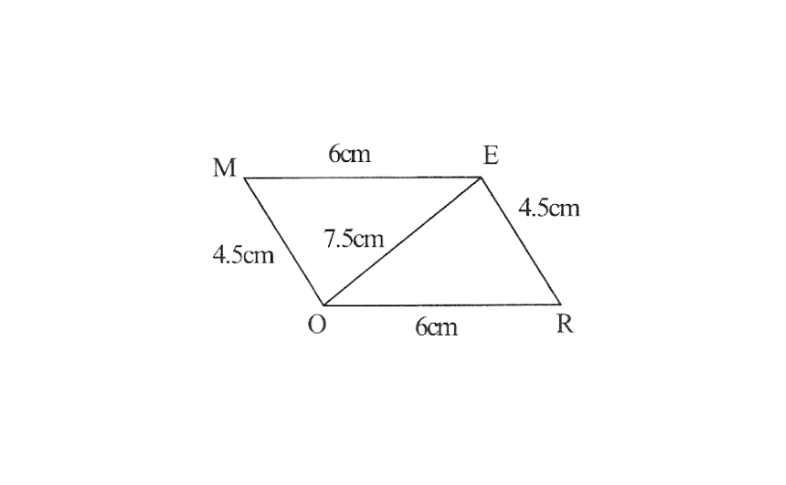
1. △EOR can be constructed by using SSS.
2. Vertex M is 4.5cm away from Vertex O and 6cm away from vertex E.
∴ While taking O and E as centres draw arcs of 4.5cm radius and 6cm radius respectively these will interest each other at point M.
3. Join M to O and E
MORE is the required parallelogram.
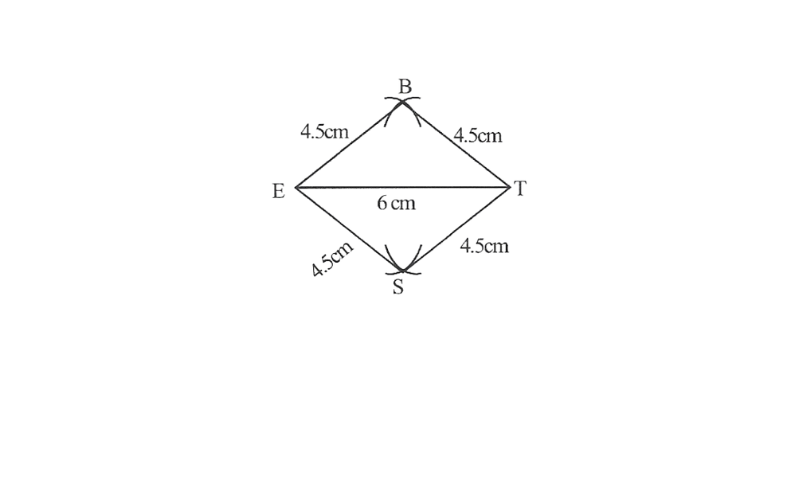
4) All sides of a rhombus are of the same measure. Hence, BE=ES=ST=TB
A rough sketch of this rhombus can be drawn as follows
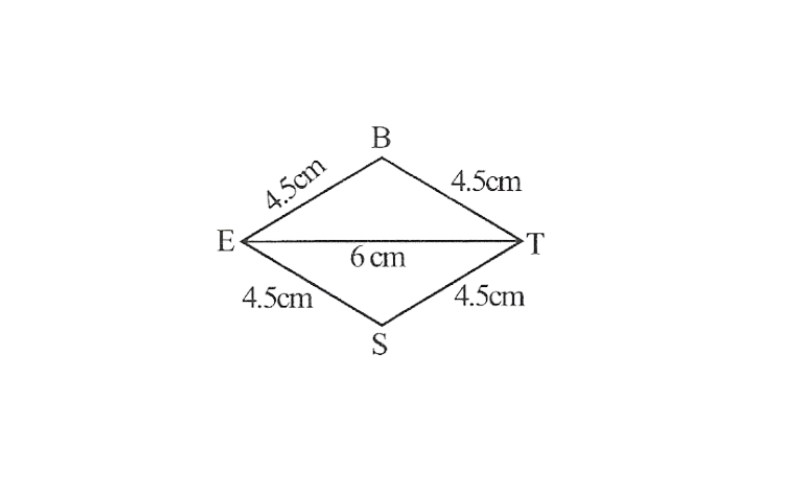
Step 1. △BET can be drawn using SSS.
2. Vertex S is 4.5cm away from vertex E and also from vertex
∴ While taking E and T as centres, draw arcs of 4.5cm radius, which will be intersecting each other at point S.
3. Join S to E and T.
BEST is the required Rhombus.
Practical Geometry Solutions KSEEB Class 8 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 7.2
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
1) Quadrilateral LIFT,
LI=4cm
IF=3cm
TL=2.5cm
LF=4.5cm
IT=4cm
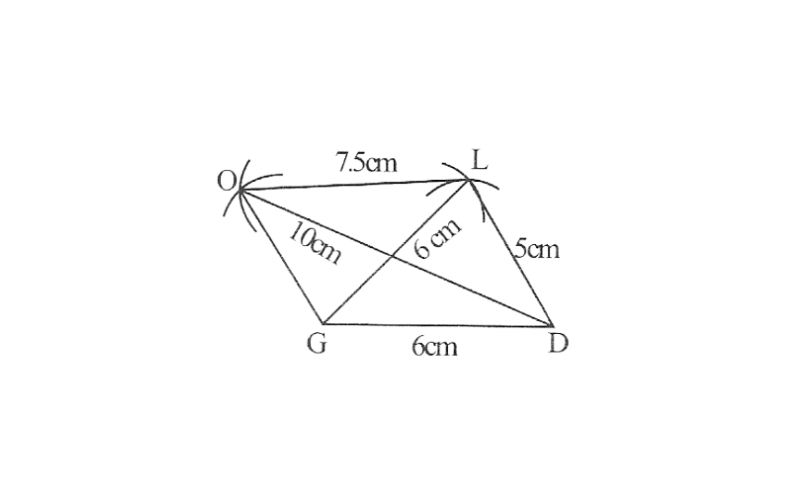
2) Quadrilateral GOLD,
OL=7.5cm
GL=6cm
GD=6cm
LD=5cm
OD=10cm
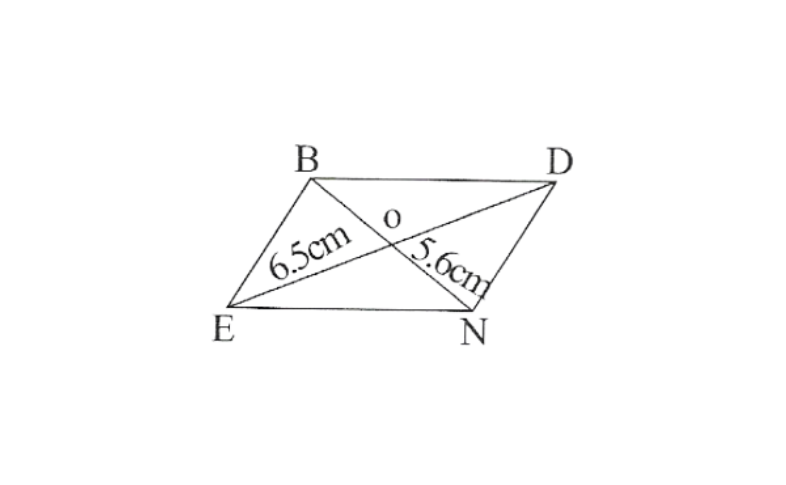
3) Rhombus BEND,
BN=5.6cm
DE=6.5cm
Solution:
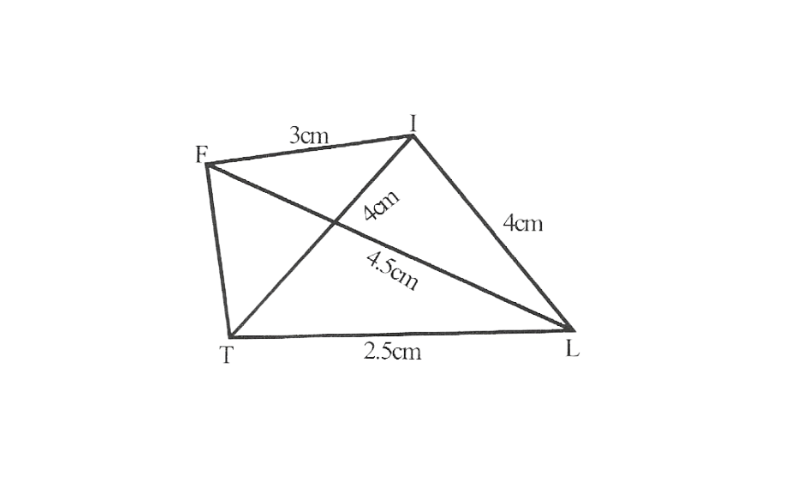
Step 1. △ITL can be constructed by using SSS construction.
2. Vertex F is 4.5cm away from vertex L and 3cm away from Vertex I.
∴ while taking L and I as centres draw arcs of 4.5cm radius and 3cm radius respectively, which will be intersecting each other at point F.
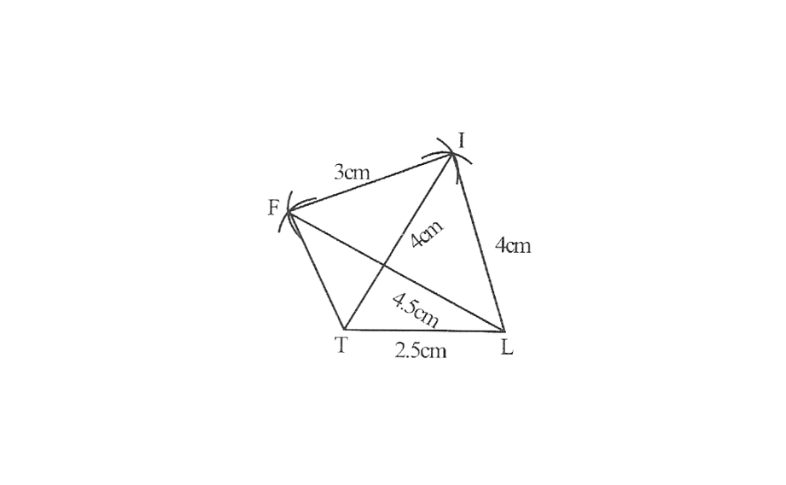
2) A rough sketch of this quadrilateral can be drawn as follows.
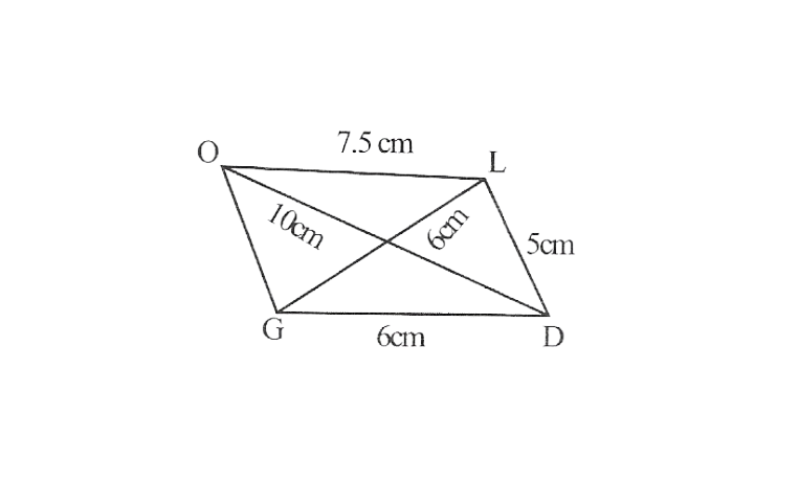
Step 1. △GDL can be constructed by using SSS construction.
2. Vertex O is 10cm away from vertex D and 7.5cm away from vertex L.
∴ while taking D and L as centres, draw arcs of 10cm radius and 7.5 cm radius respectively. These will intersect each other at point O.
3. Join O to G and L
GOLD is the required quadrilateral.
3) wkt The diagonals of a rhombus always bisect each other at 90°. Let us assume that these are intersecting each other at point O in this rhombus.
Hence, EO=OD=3.25cm
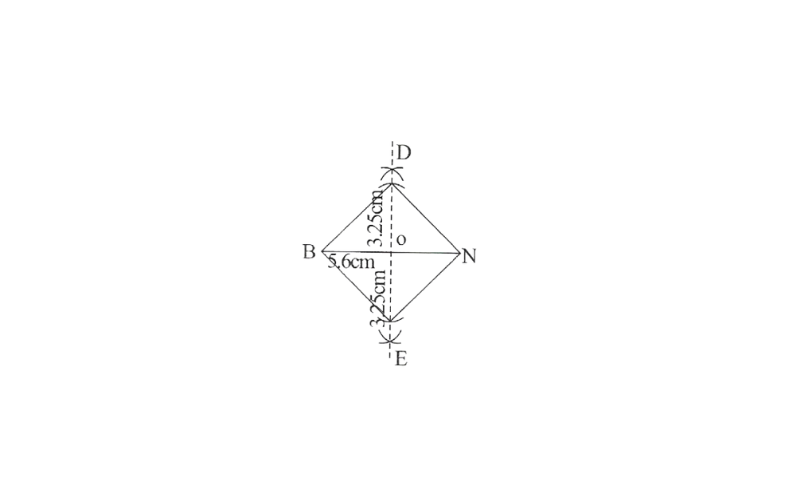
Step 1. Draw a line segment BN of 5.6cm and also draw its perpendicular bisector. Let it intersect the line segment BN at O.
2. Taking O as centre, draw arcs of 3.25cm radius to intersect the perpendicular bisector at point D and E.
3. Join points D and E to points B and N.
BEND is the required quadrilateral.
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Solved Problems Practical Geometry Exercise 7.3
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
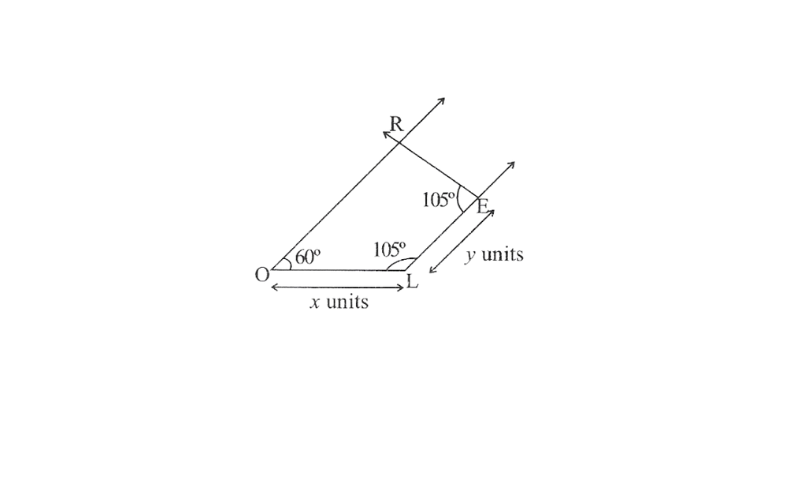
1) Quadrilateral MORE,
MO=6cm
OR=4.5cm
∠M=60°
∠O=105°
∠R=105°
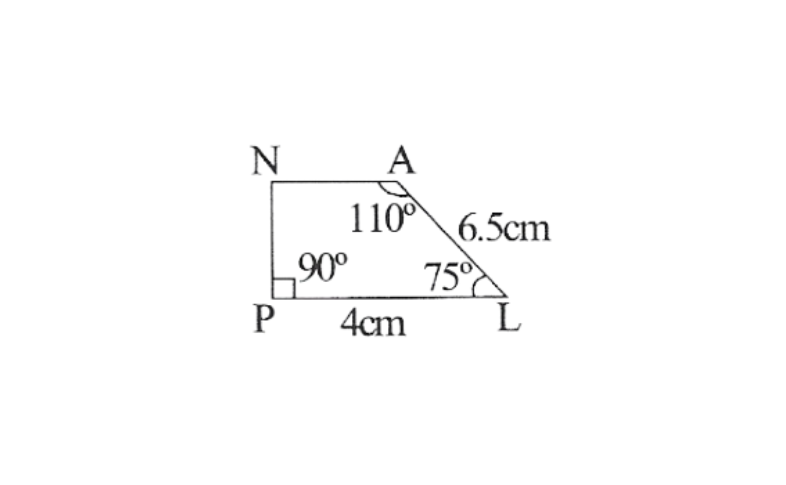
2) Quadrilateral PLAN,
PL=4cm
LA=6.5cm
∠P=90°
∠A=110°
∠N=85°
3) Parallelogram HEAR,
HE=5cm
EA=6cm
∠R=85°
4) Rectangle OKAY,
OK=7cm
KA=5cm
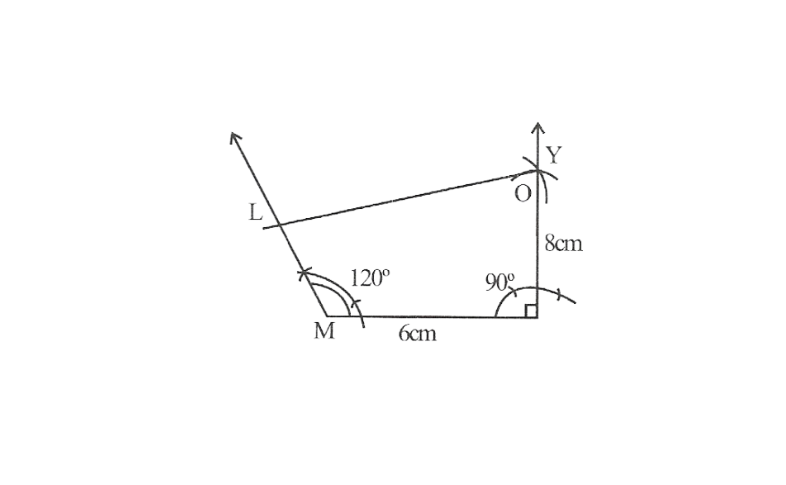
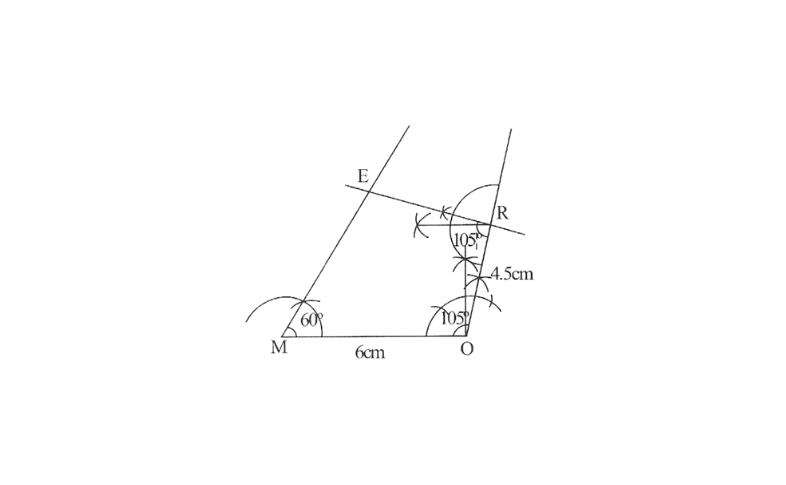
Solution: 1) Rough sketch of this quadrilateral can be drawn as follows.
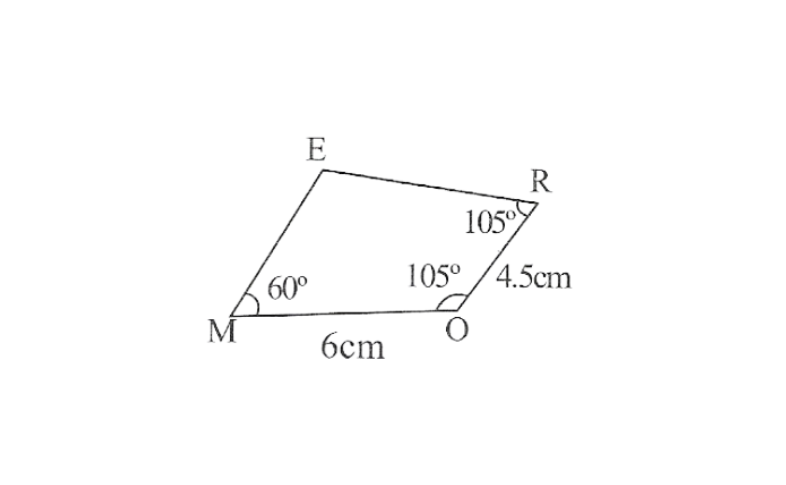
Practical Geometry Class 8 Kseeb Notes Pdf
Step 1. Draw a line segment MO of 6cm and an angle of 105° at point O. As vertex R is 4.5cm away from the vertex O. Cut a line segment OR of 4.5cm from this ray.
2. Again draw an angle of 105° at point R.
3. Draw an angle of 60° at point M. Let this ray meet the previously drawn ray from R at point E.
MORE is the required quadrilateral.
2) The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
1) In quadrilateral PLAN,
∠P+ ∠L+ ∠A+ ∠N=360°
90°+ ∠L+110°+85°=360°
∠L=360°-285°=75°
2)A rough sketch of this quadrilateral is as follows.
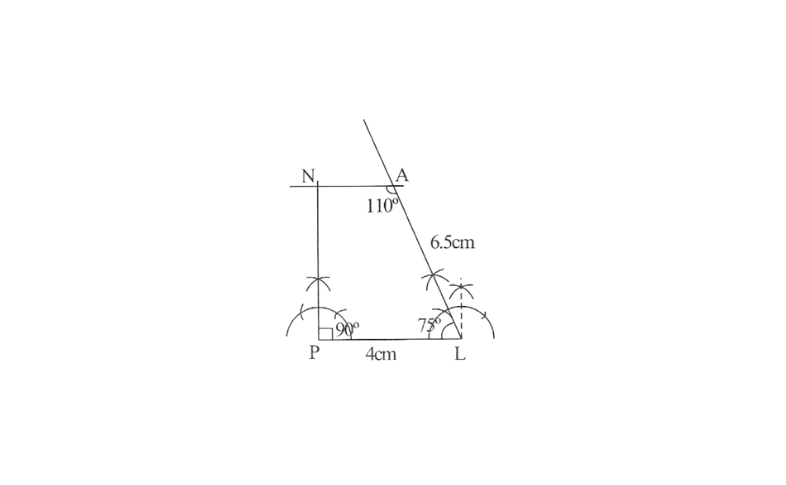
3) Draw a line segment PL of 4cm and draw an angle of 75° at point L. As vertex A is 6.5 away from vertex L, cut a line segment LA of 6.5cm from this ray.
4) Again draw an angle of 110° at point A.
5) Draw an angle of 90° at point P. This ray will meet the previously drawn ray from A at point N. PLAN is the required quadrilateral.
Kseeb 8th Maths Chapter 7 Exercise Solutions Step By Step
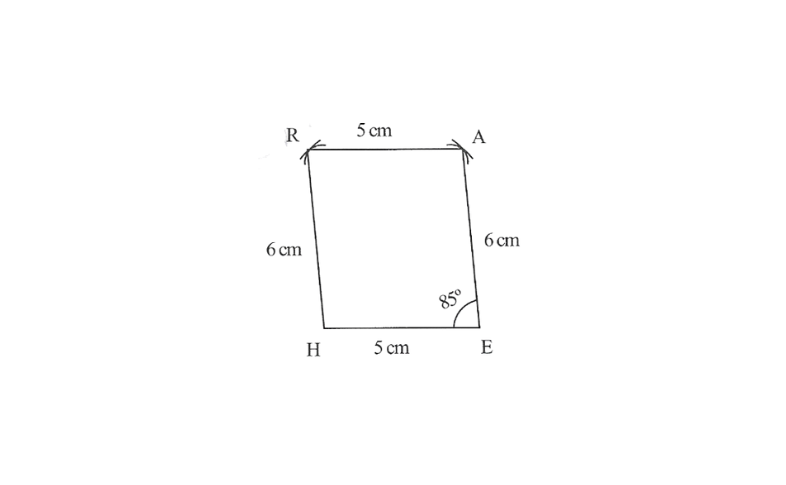
3. 1) A rough sketch of this quadrilateral
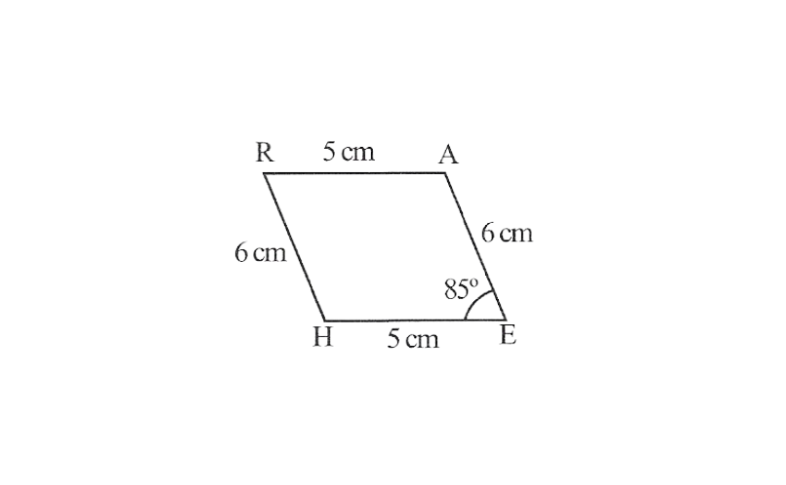
2) Draw a line segment HE of 5cm and an angle of 85° at point E. As vertex A is 6cm away from vertex E, cut a line segment EA of 6cm from this ray.
3) Vertex R is 6cm and 5cm away from vertex H and A respectively, these will be intersecting each other at point R.
4) Join R to H and A.
HEAR is the required quadrilateral.
4. 1) A rough sketch of this Rectangle as follows.
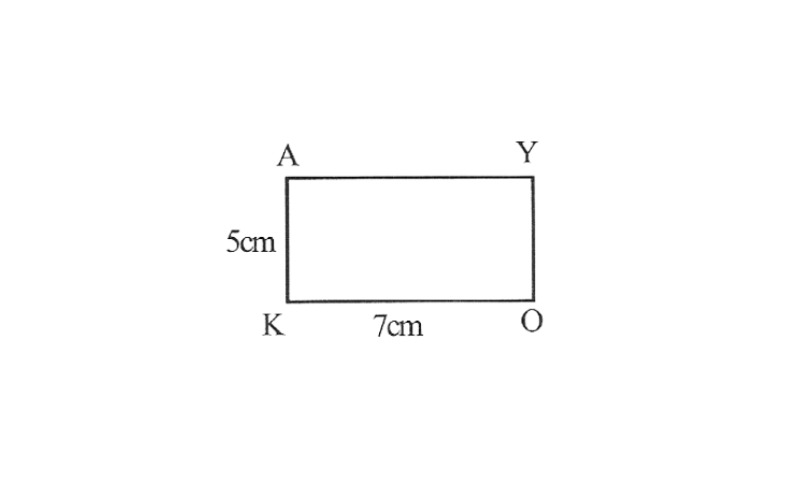
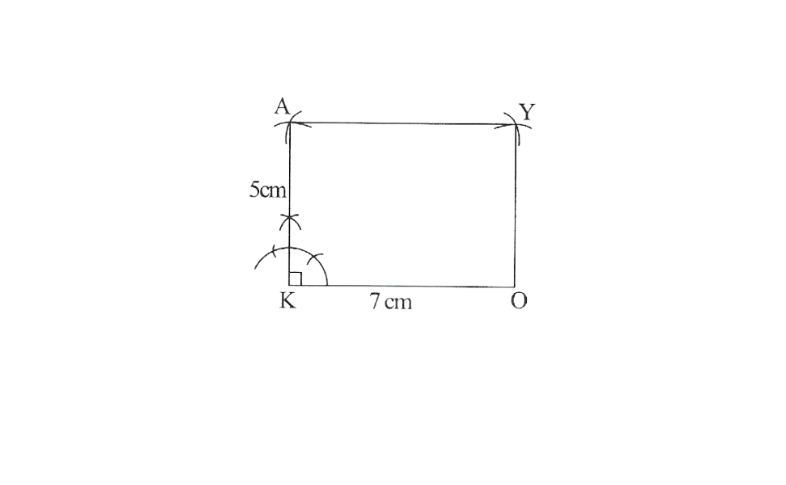
2) Draw a line segment OK of 7cm and an angle of 90° at point K. As vertex A is 5cm away from vertex K. Cut a line segment KA of 5cm from this ray.
3) Vertex Y is 5cm and 7cm away from vertex O and A respectively. By taking radius as 5cm and 7cm draw arcs from point O and A respectively, these will be intersecting each other at point Y.
4) Join Y to A and O
OKAY is the required Rectangle.
KSEEB Maths Class 8 Practical Chapter 7 Geometry Practical Geometry Exercise 7.4
1. Construct the following Quadrilaterals.
1) Quadrilateral DEAR
DE=4cm
EA=5cm
AR=4.5cm
∠E=60°
∠A=90°
2) Quadrilateral TRUE
TR=3.5cm
RU=3cm
UE=4cm
∠R=75°
∠U=120°
Solution: Steps
1. A rough sketch of this quadrilateral can be drawn as follows
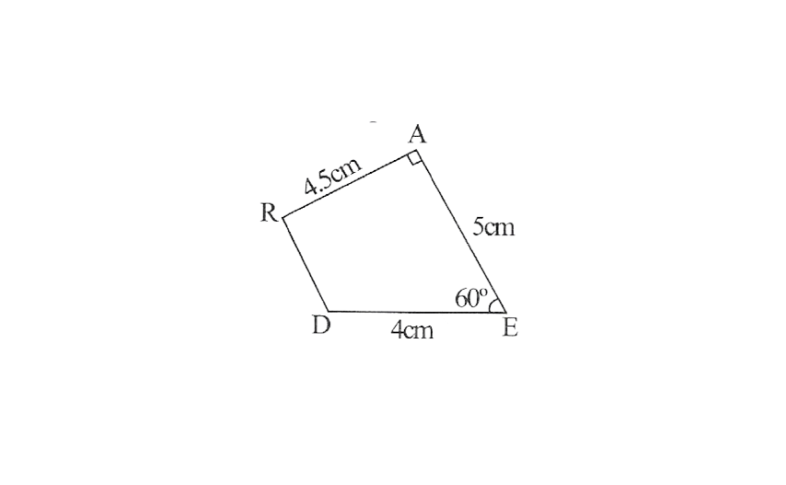
2. Draw a line segment DE of 4cm and an angle of 60° at point E. As vertex A is 5cm away from vertex E, cut a line segment EA of 5cm from this ray.
3. Again draw an angle of 90° at point A. As vertex R is 4.5cm away from vertex A, cut a line segment RA of 4.5cm from this ray.
4. Join D to R
DEAR is the required quadrilateral.
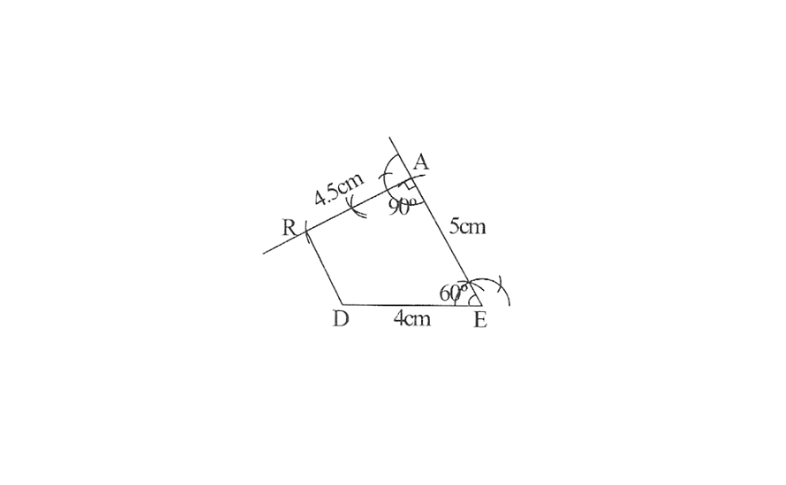
2) Steps
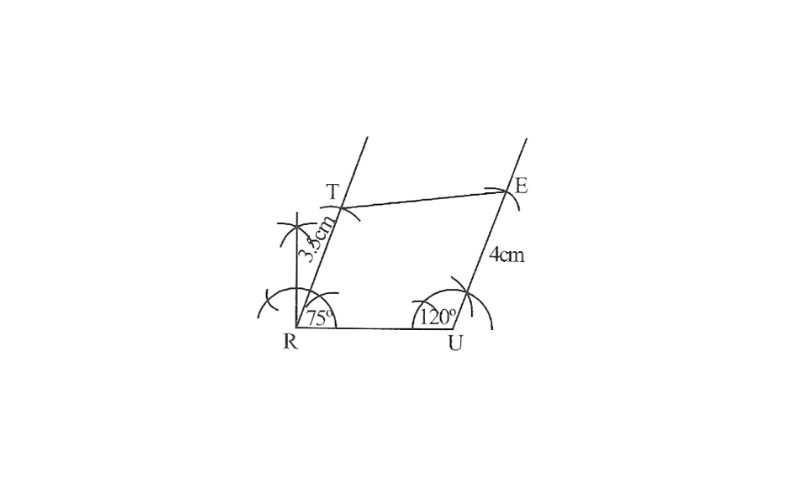
1. A rough sketch of this quadrilateral can be drawn as follows
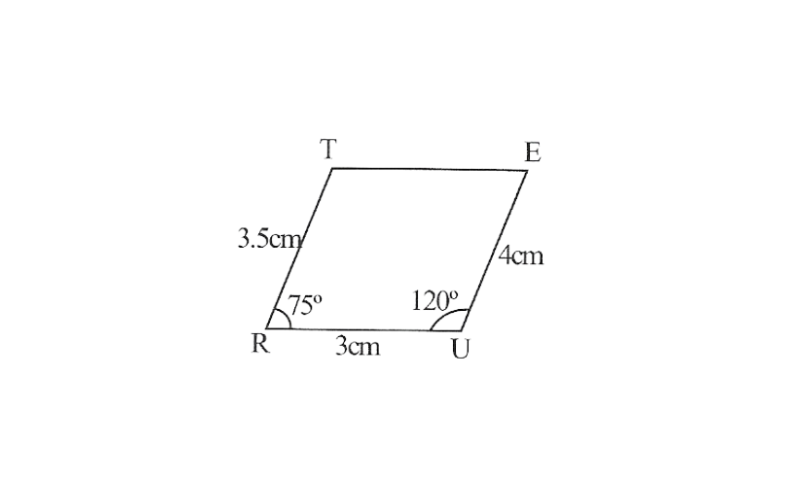
2. Draw a line segment RU of 3cm and an angle of 120° at point U. As vertex E is 4cm away from vertex U, cut a line segment UE of 4cm from this ray.
3. Draw an angle of 75° at point R as vertex T is 3.5cm away from vertex R, cut a line segment RT of 3.5cm from this ray.
4. Join T to E
TRUE is required quadrilateral
Karnataka Board Class 8 Maths Practical Geometry Problems And Answers
Practical Geometry KSEEB Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 7.5
1. Draw the following.
1. The square READ with RE=5.1cm
2. A rhombus whose diagonals are 5.2cm and 6.4cm long
3. A rectangle with adjacent sides of lengths 5cm and 4cm.
4. A parallelogram OKAY where OK=5.5cm and KA=4.5cm Is it unique?
Solution: Steps
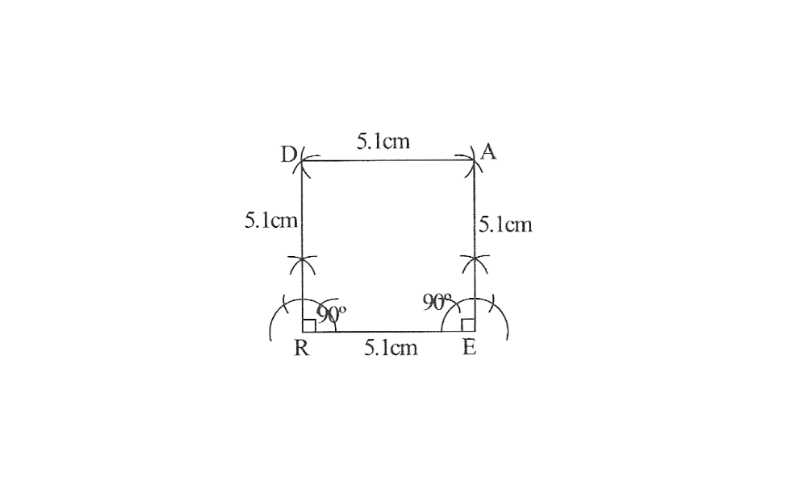
1) 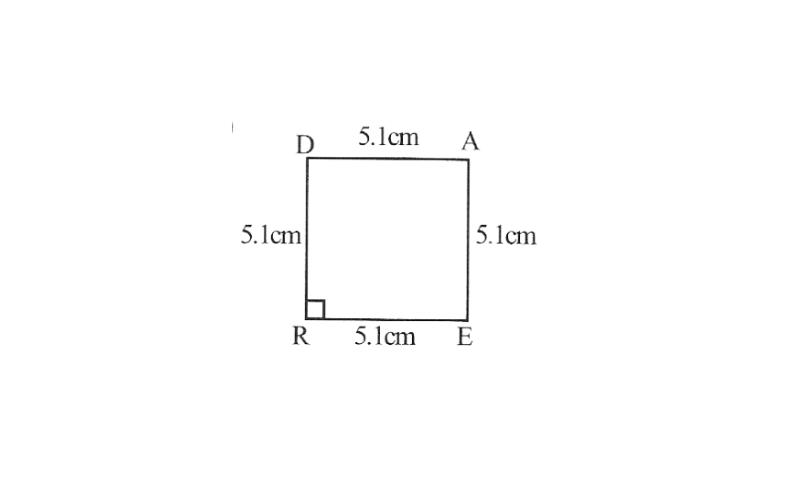
2) Draw a line segment RE of 5.1cm and an angle of 90° at point R and E.
3) As vertex A and D are 5.1cm away from vertex E and R respectively, cut line segment EA and RD, each of 5.1cm from these rays.
4. Join D to A
READ is the required square.
2. Steps
1. A rough sketch of Rhombus ABCD is as follows.
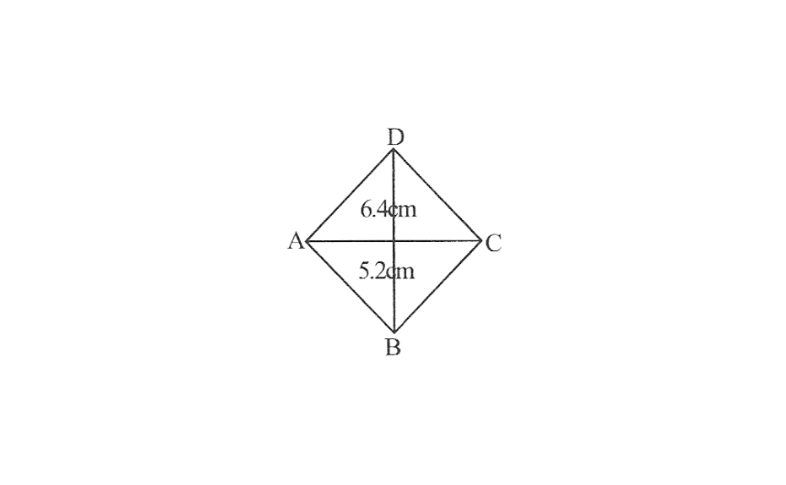
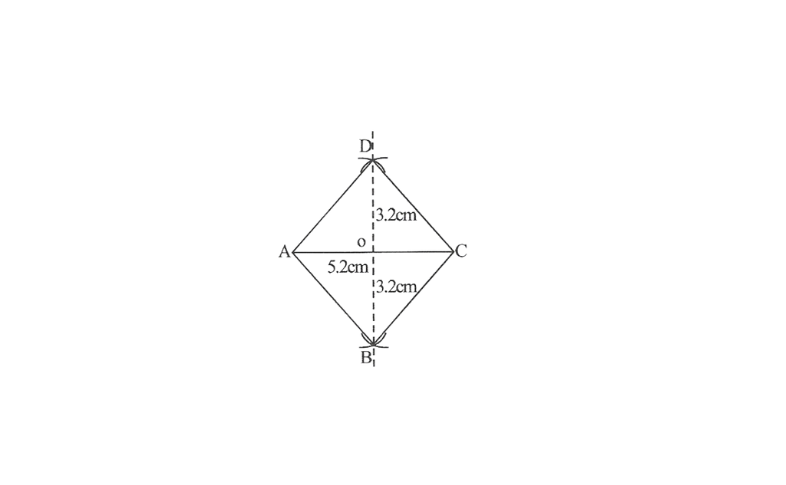
2. Draw a line segment AC of 5.2cm and draw its perpendicular bisector. Let it intersect the line segment AC at point O.
3. Draw arcs of 3.2cm \(\left(\frac{6.4}{2} \mathrm{~cm}\right)\) on both sides of this perpendicular bisector. Let the arcs intersect the perpendicular bisector at point B and D with points A and C.
4. Join points B and D with points A and C.
ABCD is the required rhombus.
How To Solve Practical Geometry Problems In Class 8 Kseeb Maths
3. Steps
1. A rough sketch of Rhombus ABCD can be drawn as follows.
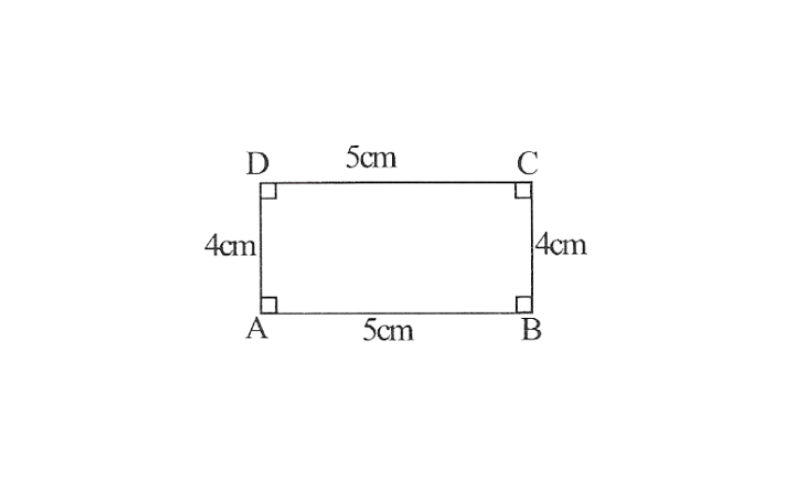
2. Draw a line segment AB of 5cm and an angle of 90° at point A and BC
3. As vertex C and D are 4cm away from vertex B and A respectively, cut line segments AD and BC each of 4cm from these rays.
4. Join D to C
ABCD is the required rectangle.
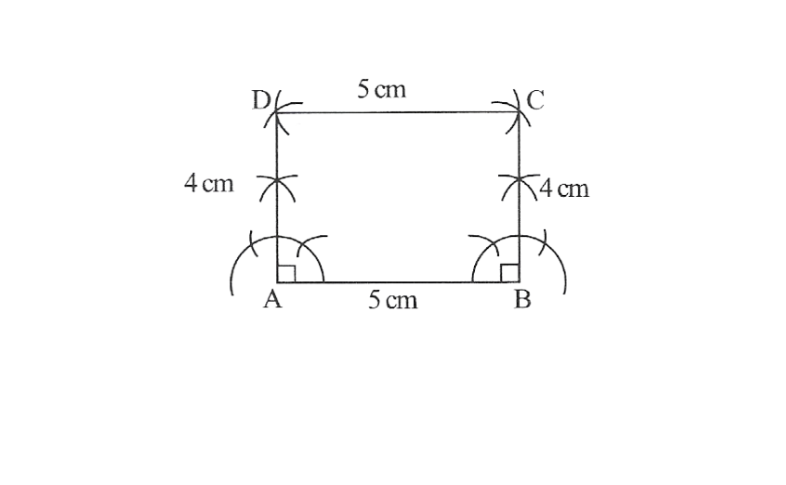
4. Steps
1. A rough sketch of parellelogram OKAY is as follows.
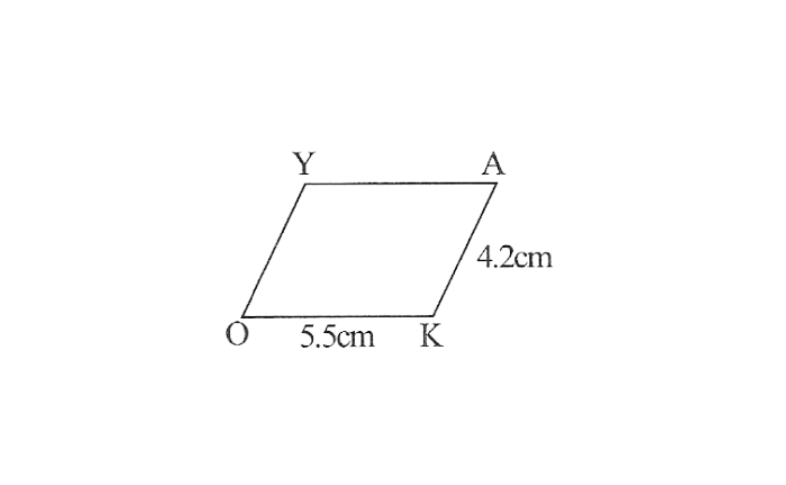
2. Draw a line segment OK of 5.5cm and a ray at point K at a convenient angle.
3. Draw a ray at point O parallel to the ray at K. As the vertices, A and Y are 4.2cm away from the vertex K and O respectively, cut line segments KA and OY, each of 4.2cm from these rays.
4. Join Y to A
OKAY is the required parallelogram.
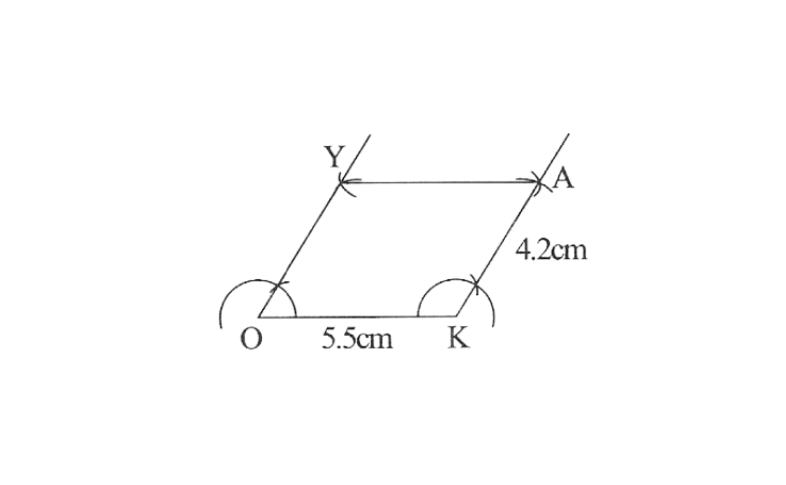
It is a unique parallelogram.
KSEEB Class 8 Maths Of Practical Geometry Additional Problems
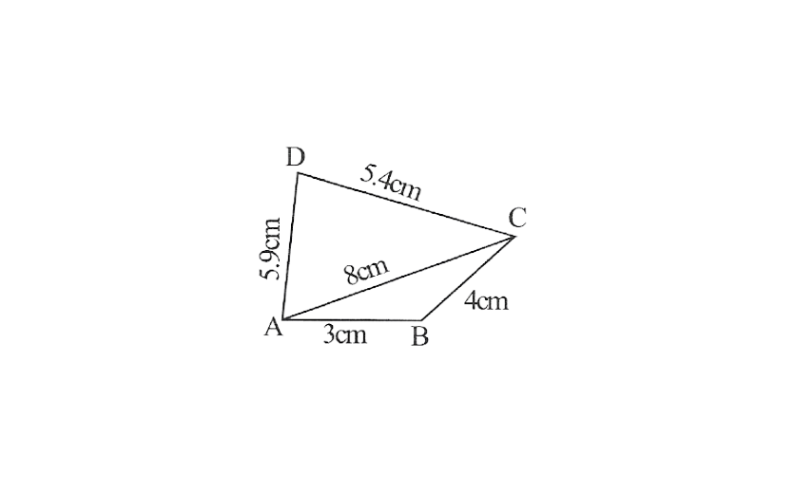
1. Is it possible to construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 5.4cm, DA = 5.9cm and diagonal AC = 8cm? If not, why?
Solution: No.
In a △le, sum of two sides is always greater than the third side but here
AB+BC<AC.
2.Is it possible to construct a quadrilateral ROAM in which RO = 4cm, OA = 5cm,
∠0 = 120°, ∠R = 105° and ∠A = 135° ? If not, why?
Solution: No, We know that the sum of four angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
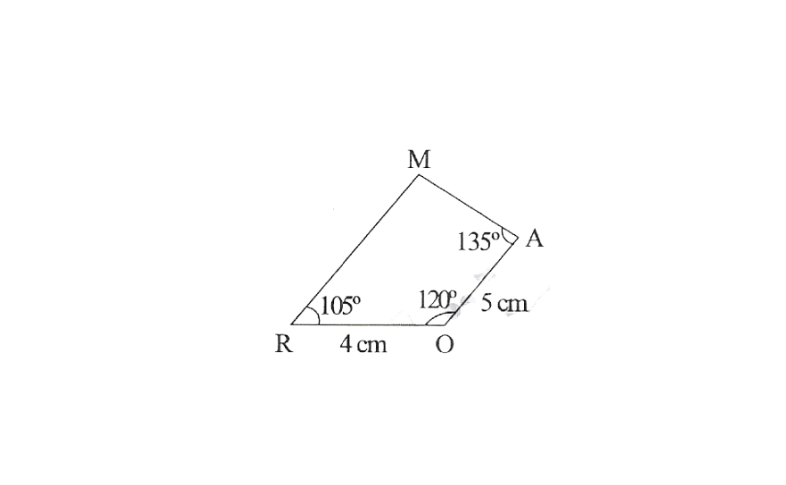
But, here, ∠O+ ∠R+ ∠A
= 120°+105°+135°
= 360°
∴ Construct of quadrilateral ROAM is not possible.
3.Draw a circle of radius 3cm and draw its diameter and label it as AC. Construct its perpendicular bisector and let it intersect the circle at B and D. What type of quadrilateral is ABCD? Justify your answer.
Solution: Cyclic quadrilateral Justification,
∠B = ∠D = 90°
(Angle in a semicircle)
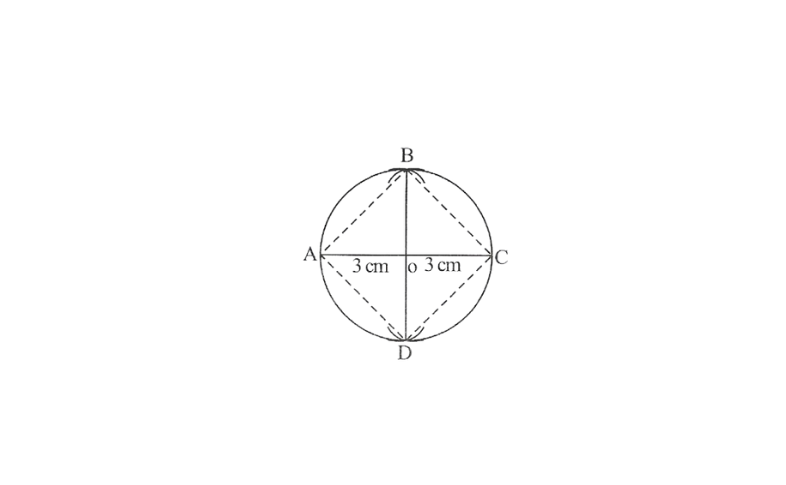
∠A = ∠C = 90°
(Angle in a semicircle)
∠B + ∠D = 180°
∠A + ∠C = 180°
(opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
4.Construct a trapezium ABCD where AB || CD, AD = BC = 3.2cm AB = 6.4cm and CD =9.6cm. Measure ∠B and ∠A.
(Hint: Difference of two parallel sides gives an equilateral △le ).
Solution:
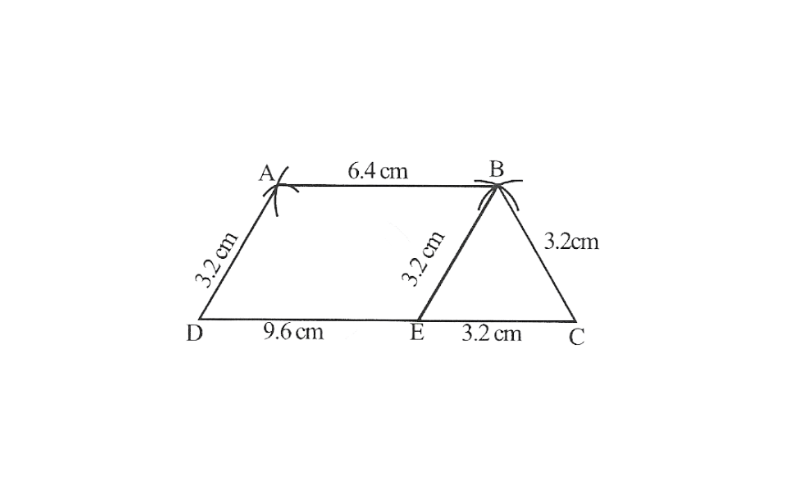
△BEC is an equilateral △le
∴ ∠BEC = 60°
⇒ ∠BED = 120°
Now, ∠A = ∠BED = 120°
(Opposite angles of a parallelogram)
∠A + ∠D = 180° (Adjacent angle of parallelogram)
∠D = 180° – ∠A = 180° —120°= 60°= ∠ABE Finally, ∠B = ∠ABE + ∠CBE
⇒ ∠B = 60° +60° = 120°
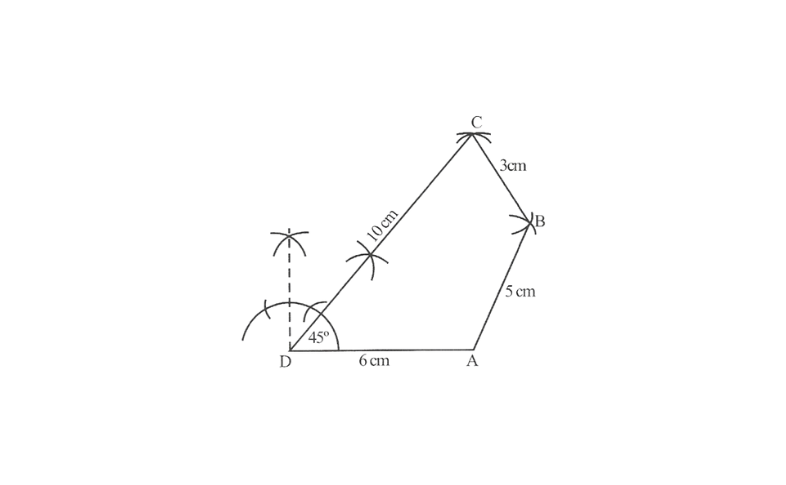
5.Construct a quadrilateral ABCD such that AB = 5cm, BC = 3cm, CD = 10cm, DA = 6cm,∠D = 45°
Solution: Rough sketch of a quadrilateral can be drawn as follows:
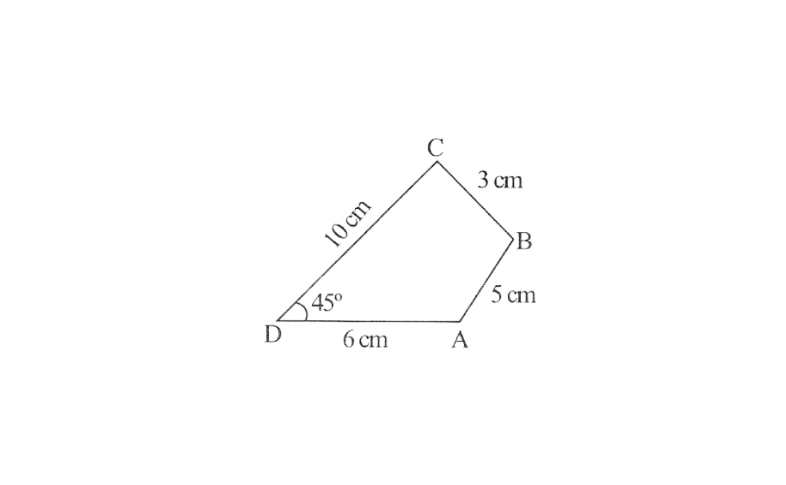
Steps 1. Draw a line segment DA of 6cm and angle of 45° at point D.
2. With D as centre and 1 Ocm as radius, mark an arc intersecting DX at the point C.
3. With C as the centre and 3 cm as radius draw an arc intersecting DX at the point C.
4. With C as the centre and 3cm as radius draw an arc
5. With A as centre and 5cm as radius, draw another arc intersecting the previous one at the point B.
6. Join BC and AB.
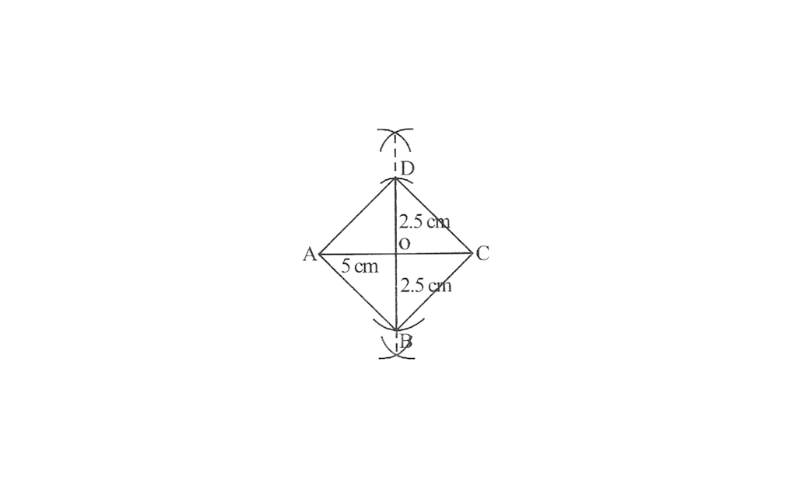
6. Construct a square in which each diagonal is 5cm long
Solution: Steps of construction
1.Draw AC = 5cm
2.Draw a perpendicular bisector of AC.
3.with O as centre cut off OB = OD = 2.5cm along the bisector line.
4.Join AD, CD, AB and CB
This is the required square ABCD
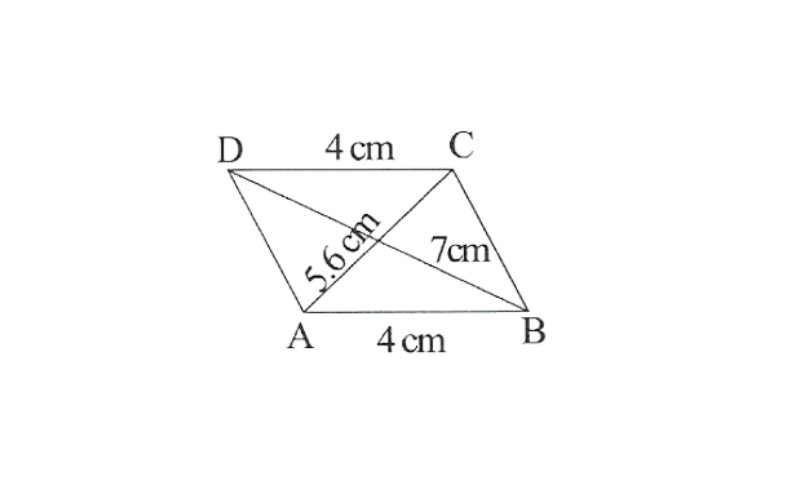
7. Construct a parallelogram when one of its side is 4cm and its two diagonals are 5.6cm and 7cm. Measure the otherside.
Solution: Rough sketch of a given parallelogram can be drawn as follows.
Steps of construction.
1. Draw AB = 4cm
2.with A as centre and radius 2.8cm, draw an arc.
3.with B as centre and radius 3.5cm, draw another arc cutting the previous arc at O.
4.Join OA and OB
5.produce AO to C such that OC = AO and produce BO to D such that OD = BO
6.Join AD, BC and CD
Thus ABCD is the required parallelogram and other side measures 5 cm.
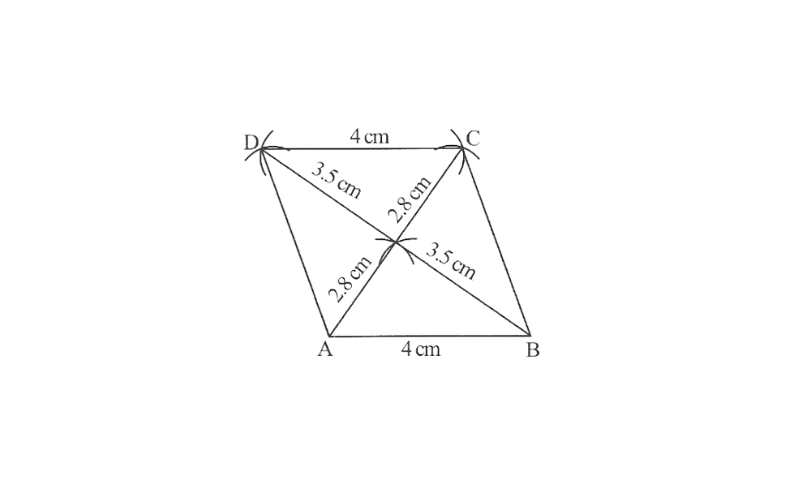
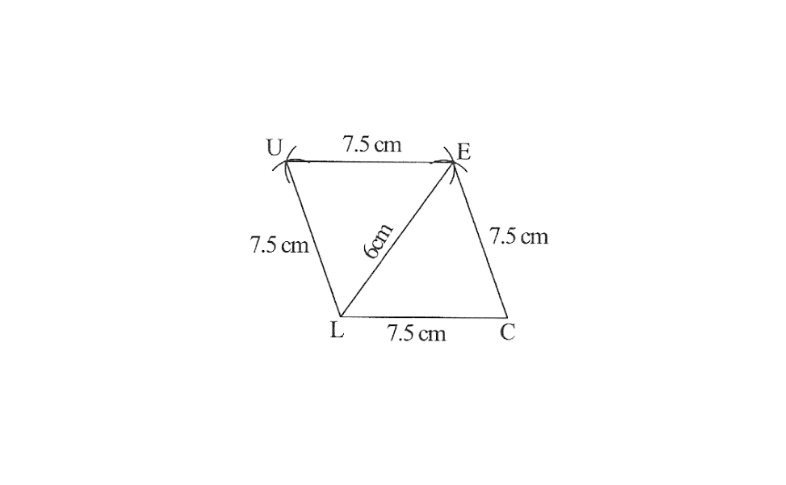
8.Construct a Rhombus CLUE in which CL = 7.5cm and LE = 6cm.
Solution: Rough sketch of a given
Rhombus can be drawn as follows.
Steps of construction
1. Draw a line segment LC = 7.5cm.
2. with C as centre draw an arc CE = 7.5cm
3. with L as centre draw another arc LE = 6cm which cut off previous arc CE.
4. with L as centre draw an arc LU = 7.5cm and E as centre draw an arc UE = 7.5cm which cut off previous arc LU.
5. Now Join UL, CE and EU
Thus CLUE is the required rhombus.