Karnataka Class 9 Science Model Question Papers 2023 Set 5
Choose The Correct Alternative And Write The Complete Answer Along With Its Alphabet In The Sheet Provided:
Question 1. Evaporation of liquid occurs at
- Boiling point
- A fixed temperature
- A temperature lower than the boiling point
- All temperatures
Answer: 3. A Temperature lower than the boiling point
Question 2. Chalk dissolved in water is an example of
- True solution
- Colloid
- Suspension
- Saturated solution
Answer: 3. Suspension
Karnataka 9th Standard Science Model Paper 2023 Set 5 Free PDF with Solutions
Question 3. The atomicity of K2Cr2O7 is
- 9
- 11
- 10
- 12
Answer: 2.11
Question 4. The isotope used to remove brain tumors and ____________treatment of cancer is
- U – 235
- Na – 24
- Iodine
- CO – 60
Answer: 4. CO – 60
Question 5. The animal cell which does not possess a nucleus is
- Egg of hen
- White blood cell
- Red blood cell
- Nerve cell
Answer: 3. Red blood cell

Question 6. Sieve tubes and companion cells are present in
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Cork
- Cambium
Answer: Phloem
Question 7. The plants whose leaves have parallel variation and whose roots are fibrous are called
- Dicotyledonous
- Gymnosperms
- Pteridophyta
- Monocotyledonous
Answer: 4. Monocotyledonous
Question 8. A particle travels 100 meters after starting from rest In 10 seconds. Its acceleration is
- 2m/s2
- 4m/s2
- 1m/s2
- 20m/s2
Answer: 1. 2m/s2
Class 9 Karnataka Science Model Paper 2023 Set 5 Solved Questions PDF
Question 9. When a bullet is fired from a gun, it recoils. This is due to the conservation of
- Energy
- Mass
- Momentum
- Weight
Answer: 3. Momentum
Question 10. The relation connecting acceleration due to gravity and gravitational force is
- \(\mathrm{g}=\frac{G M}{R^2}\)
- \(\mathrm{g}=\frac{G M}{R}\)
- g = GMR2
- g = GMR
Answer: 1. \(\mathrm{g}=\frac{G M}{R^2}\)
Question 11. If a body of mass 10 kg is pushed horizontally by a horizontal force of 5 newtons, then the work done by gravity is
- 50 joule
- 5 joule
- 98 joule
- 0
Answer: 4. 0
Question 12. Sound waves with frequencies below the audible range are called
- Infrasonic
- Ultrasonic
- Supersonic
- Sub supersonic
Answer: 1. Infrasonic
Question 13. AIDS is not transmitted by
- Hugs
- Breastfeeding of the child
- Infected blood transfusion
- Many sexual partners
Answer: 1. Hugs
Question 14. The organisms that damage the standing crops in a field are called
- Pathogens
- Pests
- Weeds
- Seeds
Answer: 2. Pests
Answer The Following:
Question 1. Differentiate between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures
Answer:
Homogeneous:
- It has uniform composition
- No visible boundaries of separation
- They consist of only one phase
Heterogeneous:
- It does not have a uniform composition
- Shows visible boundaries of separation
- They consist of more than one phase
Karnataka Board 9th Science Model Paper 2023 Set 5 Latest Exam Pattern
Question 2. On a hot sunny day, why do people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground?
Answer: During a hot sunny day, the surface of the roof absorbs a large amount of heat and remains hot sprinkling water on these surfaces, the water absorbs a large amount of heat from the surface due to its latent heat of vaporization thereby allowing the hot surface to cool.
Question 3. When we put raisins in water, why do they swell?
Answer: Raisins are dry with less water inside when they are kept in water, osmosis takes place, and water flows through the cell wall and cell membrane of the raisins and therefore it swells.
Question 4. What is a polyatomic ion? Give examples.
Answer: A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a polyatomic ion.
Example : \(\mathrm{Co}_3^{2-}\) , \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\)
Question What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits, and vegetables?
Answer: Cereals give carbohydrates which provide energy. Pulses give proteins that build our bodies. Vegetables and fruits provide vitamins & minerals.
Question 6. What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer: Some gases prevent the escape of heat from the earth. An increase in the percentage of such gases in the atmosphere would cause the average temperatures to increase worldwide and this is called the greenhouse effect.
Question 7. A baby is not able to tell her/his caretakers that she/he is sick. What would help us to find out
- That the baby is sick?
- What is the sickness?
Answer:
- The symptoms like body temperature, fever, cough, cold, loose motions, nonstop crying improper or no food intake, etc., would help us to find that the baby is sick.
- The symptoms and signs of disease could help us to find out the sickness of the baby.
Question 8. Draw a sketch of Bohr’s model of an atom with three shells.
Answer:
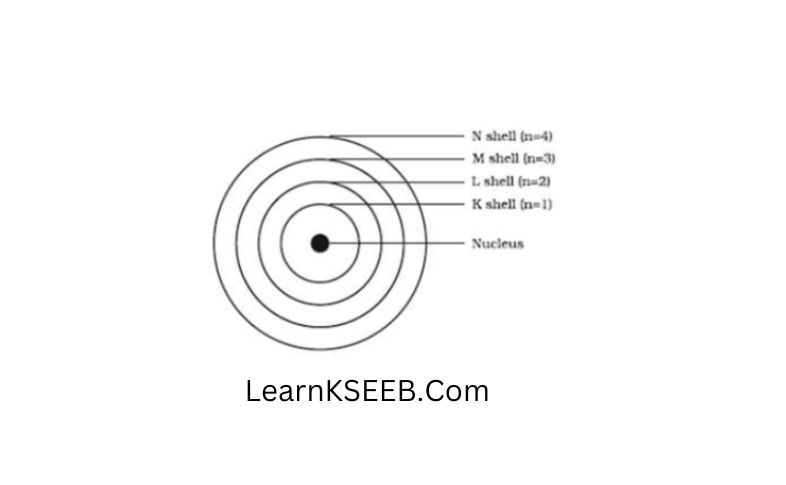 Question 9. Define
Question 9. Define
- Atomic number
- Mass number
Answer:
- Atomic number: The total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom is known as the atomic number. It is denoted by ‘Z’.
- Mass number: The sum of the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom is known as mass number. It is denoted by ‘A’.
Question 10. Name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material.
Answer: Plastids and mitochondria.
Question 11. The endoplasmic reticulum helps in membrane biogenesis. Explain how?
Answer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum manufacture proteins are then sent to various places in the cell depending on need, using the endoplasmic reticulum. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, important for cell function. Some of these proteins and lipids help in building the cell membrane.
9th Standard Karnataka Science Sample Paper 2023 Set 5 Important Questions PDF
Question 12. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer: Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
Question 13. Why are skeletal muscles called striated muscles?
Answer: Skeletal muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations when stained, appropriately, hence they are called striated muscles.
Question 14. The odometer of a car reads 200km at the start of a trip and 2400 km at the end of the trip. If the trip took 8h, calculate the average speed of the car in kmlr1 and ms1.
Answer:
Distance covered by the car
S = 2400km – 2000km = 400km
Time = 8h
The average speed of the car is
= 50kmh-1
\(=50 \frac{\mathrm{km}}{\mathrm{h}} \times \frac{1000 \mathrm{~m}}{1 \mathrm{~km}} \times \frac{\mathrm{Ih}}{3600 \mathrm{~S}}\)=13.9ms-1
The average speed of the car is 50 kmh-1 or 13.9ms-1
Question 15.Distinguish between speed and velocity
Answer:
speed:
- The distance traveled by an object in a given interval of time.
- It does not have any direction
- \(\text { speed }=\frac{\text { Distance travelled }}{\text { Time taken }}\)
- The speed of an object can never be negative.
Velocity:
- The displacement of an object in a given interval of time.
- It has a unique direction
- \(\text { velocity }=\frac{\text { Displacement }}{\text { Time interval }}\)
- The velocity of an object can be negative
Question 16. When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it, explain.
Answer: The carpet with dust is in a state of rest, when it is beaten with a stick the carpet is set in motion, but the dust particles remain at rest. Due to the inertia of rest, the dust particles retain their position of rest and fall down due to gravity.
Question 17. A hammer of mass 500g, moving at 50ms1 strikes a nail. The nail stops the hammer in a very short time of 0.01s, What is the force of the nail on the hammer?
Answer:
Mass of hammer m = 500g = 0.5kg
The initial velocity of hammer u = 50ms-1
Final velocity of hammer v = 0 and time = 0.01s
∴ Acceleration of the hammer
∴ Force applied by the nail on hammer F = ma = 0.5 x (- 5000)
= – 2500 N
– ve sign of force suggests that the force is opposing the motion of the hammer.
Question 18. A ship made of Iron does not sink but the Iron rod sinks in water, why?
Answer: The Iron rod sinks due to high density and less buoyant force exerted by the water on it, but in the case of the ship the surface area is increased, and the upthrust experienced by the body is more, so it floats on water.
Karnataka Class 9 Science Previous Year Model Paper 2023 Set 5 Download PDF
Question 19. State the universal law of gravitation.
Answer: Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Question 20.
- What is the kinetic energy of an object?
- Write an expression for the kinetic energy of an object.
Answer:
- The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion is called kinetic energy.
- \(\mathrm{KE}=1 / 2 \mathrm{MV}^2\)
where m = mass, v = velocity.
Karnataka Board 9th Class Science Model Question Paper 2023 Set 5 with Answer Key
Question 21. An object of mass 15kg is moving with a uniform velocity of 4ms1. What is the kinetic energy possessed by the object?
Answer:
mass of the object m = 15kg
The velocity of the object V = 4ms-1
= 15 x 4 x 2
KE = 120J
Question 22. Why are sound waves called Mechanical waves?
Answer: Some mechanical energy is required to make an object vibrate. Sound energy cannot be produced on its own. The mechanical energy of a vibrating object travels through a medium and finally reaches the ear. Therefore, sound waves are called mechanical waves.
Question 23. Distinguish between loudness and intensity sound.
Answer: The loudness depends on the energy per unit area of the wave and on the response of the ear but intensity depends only on the energy per unit area of the wave and is independent of the response of the ear.
Karnataka State Board Class 9 Science Model Paper 2023 Set 5 with Step-by-Step Solutions
Question 24. State any two conditions for good health
Answer:
- State of physical, mental, and social well-being.
- Better surroundings or environment.
Answer The Following:
Question 1. State the principle of the process of centrifugation and write its two applications.
Answer: The principle is that the denser particles are forced to the bottom and the lighter particles stay at the top when spun rapidly.
Applications:
- Used in diagnostic laboratories for blood and urine tests.
- Used in washing machines to squeeze out water from wet clothes.
Question 2.Which elements of the xylem help in
- Transport of water
- Storage of water
- Mechanical support
Answer:
- Transport of water = xylem vessel & tracheids
- Storage of water = parenchyma
- Mechanical support = fibers
Question 3.
- Why are road accidents at high speed very much worse than accidents at low speed?
- State the law of motion involved in the removal of dust from a carpet is beaten with a stick
- Name the physical quantity where a unit is kg m/s2
Answer:
- Because the momentum of a high-speed vehicle is more than that of a low-speed vehicle.
- Law of inertia
- It is the momentum of the body
Question 4. Draw the structure of
- Unstriped muscles
- Cardiac muscle
Answer:
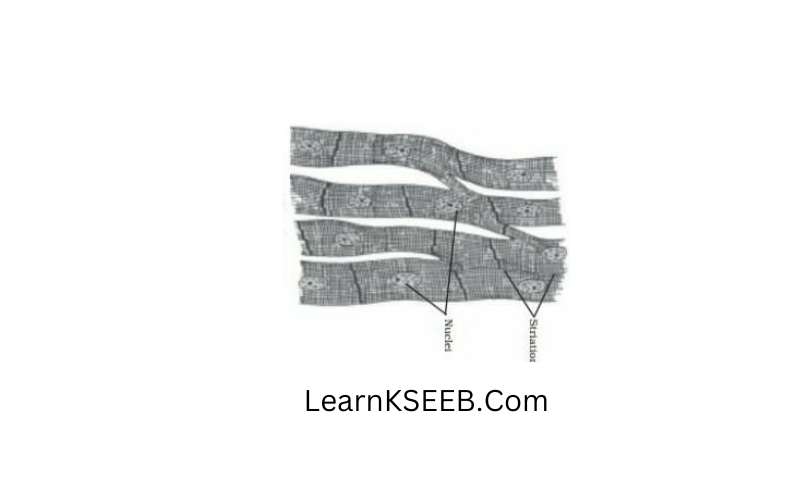
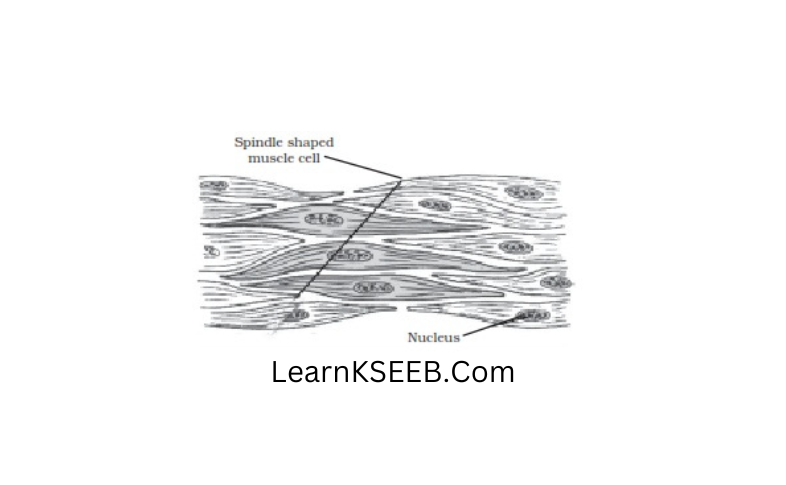

Answer The Following:
Question 1.
- Define Retardation
- Define SI unit of force
- What is the effect of balanced forces on a body?
- When do we say that work is done?
Answer:
- Negative acceleration is called retardation.
- kg ms-2
- The object does not change its position
- Work is done when a force applied to a body moves it through a distance in the direction of the force.
Karnataka 9th Science Sample Paper 2023 Set 5 for Board Exam Preparation
Question 2. Mention the four differences between physical and chemical changes.
Answer:
Physical:
- It is temporary and easily reversible
- No new substance is formed during the change.
- No alteration in mass takes place
- No change in energy during a physical change
Chemical:
- It is permanent times reversible.
- New substances are formed
- The mass of the substance is altered.
- Energy is involved in a chemical change
Question 3.
- write the significance of the universal law of gravitation.
- Define acceleration due to gravity
- What happens to the gravitational force between two objects if
(1)The mass of an object is doubled.
(2)The distance between the objects is halved.
Answer:
- The force that binds us to the earth. The motion of the moon around the earth.
- Whenever an object falls toward the earth, acceleration is involved which is due to the earth’s gravitational force hence it is known as acceleration due to gravity.
- Let two masses are M1 and M2 distance be d and force F
\(\text { Then } \mathrm{F}=\frac{\mathrm{GM}_1 \mathrm{M}_2}{\mathrm{~d}^2}\)
(1) If is M1 doubled new force
\(\mathrm{F}_1=\frac{\mathrm{G}\left(2 \mathrm{M}_1\right) \mathrm{M}_2}{\mathrm{~d}^2}=2 \mathrm{~F}\)Force will become twice the original force.
(2) will become four times larger
\(\mathrm{F} \alpha \frac{4}{d^2}\) force will become four times larger.
