KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Important Concepts
Plant and animal tissues, meristematic tissues. Permanent tissues – parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. Complex tissues – xylem and phloem, Epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue.
Tissue: A tissue may be defined as a group or collection of cells that perform a common function and have a common origin.
Meristematic tissues (meristems): A group or collection of living cells located at specific locations and dividing continuously to add new cells to the plant body.
Permanent tissues: A group or collection of living or dead cells formed by meristematic tissue that have lost their ability to divide and have been permanently placed at a fixed position in the plant body.
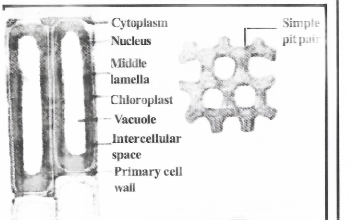
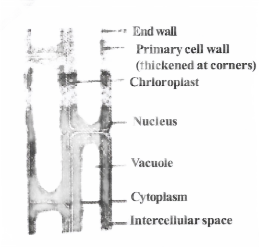
Parenchyma: Parenchyma is the most simple and unspecialized primitive tissue. It mainly consists of thin-walled cells which have intercellular spaces between them.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
Collenchyma: It is a living tissue, cells are thin-walled and provide flexibility to soft aerial parts like leaves, stems, etc.
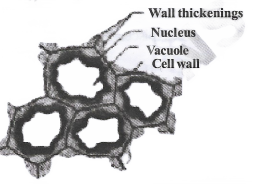
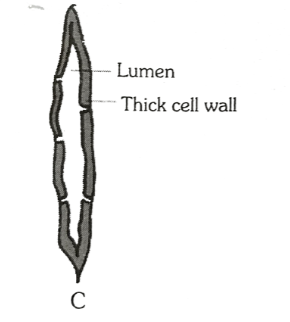
Sclerenchyma: It consists of thick-walled dead cells. These cells have hard and extremely thick secondary walls due to the uniform deposition of lignin. The cells of this tissue are dead.
Epidermis: It is the outermost layer of all soft parts of the plant like the young stem, roots, leaves, and flowers. It acts as a protective tissue, covering the plant body.
Stomata: Stomata are the minute openings of pores present in the epidermis of léaf or green parts of a plant.
Complex permanent tissue: A group of more than one type of cells having a common origin and working together as a unit to perform a common function. The xylem and phloem are complex permanent tissues.
Xylem: The xylem conducts water and mineral salts upwards from roots to leaves and to different parts of the plant. It is composed of four different types of cells:
- Tracheids,
- Vessels,
- Xylem parenchyma and
- Xylem fibers.
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |

Phloem: Phloem transports food from leaves to the storage organs and later growing regions of the plant body. It is composed of four different types of cells:
- Sieve tubes,
- Companion cells,
- Phloem parenchyma and
- Phloem fibers.
Epithelial tissue: Epithelium to the simplest kind of animal tissue that occurs as a protective covering. Epithelial tissues are classified as:
- Squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Ciliated epithelium
- Glandular epithelium
Tissues KSEEB Class 9 Question Answers
Squamous epithelium: Squamous epithelium occurs on the skin and lining of the alveoli of the lungs. It is thin and flat cells form a delicate lining. Example: Lining of the esophagus of mouth.
Cuboidal epithelium: Cuboidal epithelium consists of cube-like cells and forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands where it provides mechanical support. It also helps in absorption, excretion, and secretion.
Columnar epithelium: It is cube-like or isodiametric cells found in glands and ducts. They help in secretion and absorption.
Ciliated epithelium: It is a cuboidal, columnar cell with fine hair-like cilia, they are found in the lining of the respiratory tract and fallopian tube. It helps in the movement of mucus, eggs, and sperm.
Glandular epithelium: This epithelium consists of columnar cells modified to secrete chemicals. It lines the glands such as gastric glands, intestinal glands, etc.
Connective tissue: The connective tissue is specialized to connect the various body organs. Cells of connective tissue are living, loosely spaced, and embedded in an intercellular matrix. Connective tissues are of 5 types:
- Areolar tissue
- Dense regular tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Skeletal tissue
- Fluid tissue
Areolar loose connective tissue: These are loose and cellular connective tissue and consist of two kinds of fibers- white collagen fibers and yellow elastic fibers. They are found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves.
Dense regular tissue: It is a fibrous connective tissue having a densely packed collection of fibers and cells. It is the principal component of tendons and ligaments.
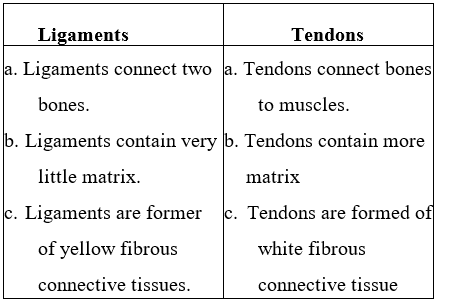
Tendons: It is not an elastic fiber that joins skeletal muscles to bones and is composed of white fibrous tissue.
Ligaments: It is elastic fiber that connects bones to bones and is composed of yellow elastic tissues.
Adipose tissue: This tissue is made up of fat cells. Fat-storing adipose tissue is found below the skin and between internal organs.
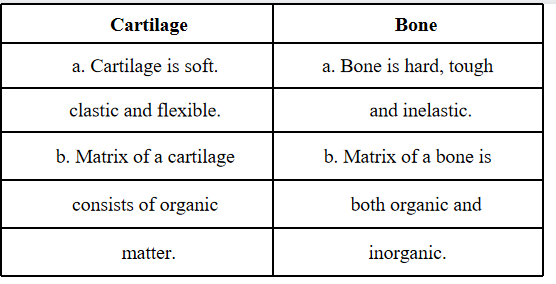
Skeletal tissue: This tissue includes cartilage and bones which forms the endoskeleton of the vertebrate body and protects the vital organs of the body. Cartilage is a specialized ‘connective tissue made up of an extensive matrix of collagen fibers. Cartilage is present in the nose, ear, trachea, and larynx. Bone is a very strong and non-flexible tissue embedded in a hard matrix made up of protein, calcium, and phosphorus compounds. It provides shape and also skeletal support to the body.
Fluid or vascular tissue: It consists of a fluid matrix in which are suspended free-floating cells. Fluid tissue includes blood and lymph.
Blood: It is a fluid(liquid) connective tissue. The blood contains cells called RBC, WBC, Platelets, and Plasma. The RBC or Erythrocytes are circular disc-shaped cells having no nucleus and contain a pigment called hemoglobin. The WBC or leukocytes are colorless, they have a nucleus. WBCs are of two types:
- Granulocytes include basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils.
- Agranuclocytes including lymphocytes and monocytes. The plasma contains proteins, salts, and hormones and its main function is the transportation of materials. The platelets are irregularly shaped non-nucleated fragments. They play a role in blood clotting.
Lymph: The Lymph is a colorless fluid tissue having plasma and WBCs. Lymph escapes out from capillaries blood into body tissues. The lymph protects the body against protection. The muscular tissues are made up of muscle cells that are elongated and large-sized and are so-called muscle fibers. These tissues help in various types of movements of body parts and locomotion. They are three types:
- Striated
- Unstriated
- Cardiac muscles
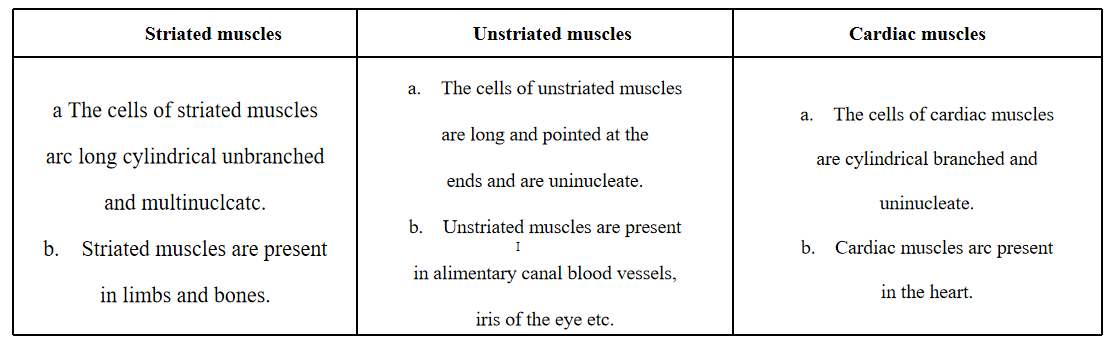
Striated or skeletal muscles: They are attached to the bones and help in movement and so-called skeletal muscles. The striated muscle cells are long or elongated, cylindrical unbranched, and multinucleated. These muscles are voluntary muscles occurring in muscles of limbs, body wall, face, neck, etc
Unstriated are smooth muscles: They occur as bundles or elongated spindle-shaped cells or fibers with nuclei. The fibrous do not bear bands or striations, they are called smooth muscles. These muscles are involuntary muscles found in the iris of the eye, bronchi of the lungs, etc
Cardiac muscles: These muscles are branched, cylindrical and uninucleated cells. This type of muscle tissue is present in the muscles of the heart. Cardiac muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Nervous tissue: The tissue consists of neurons containing granular cytoplasm and distinct nuclei with dendrons, and dendrites axon. They are found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The tissue controls all the body activities, and conduction of impulses and simulates other tissues for activity.
Tissues Exercises
Question 1. Define the term tissue.
Answer: A group of cells that are similar in structure and Muscular tissues work together to achieve a particular function.
Question 2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
The four types of elements together make up the xylem tissue. The xylem elements are:
- Xylem tracheids: They are tubular structures, transport water, and minerals vertically.
- Xylem vessels: They are long tube-like structures. The walls are lignified to transport water and minerals.
- Xylem parenchyma: It consists of living cells, stores food, and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
- Xylem fibers: They have elongated dead cells with tapering ends and thick cell walls. They are supportive in function. The elements together make up the xylem tissue.
The xylem elements are:
Xylem tracheids: They are tubular structures, transport water, and minerals vertically.
Xylem vessels: They are long tube-like structures. The walls are lignified to transport water and minerals. ;
Xylem parenchyma: It consists of living cells, stores food, and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
Xylem fibers: They have elongated dead cells with tapering ends and thick cell walls. They are supportive in function.
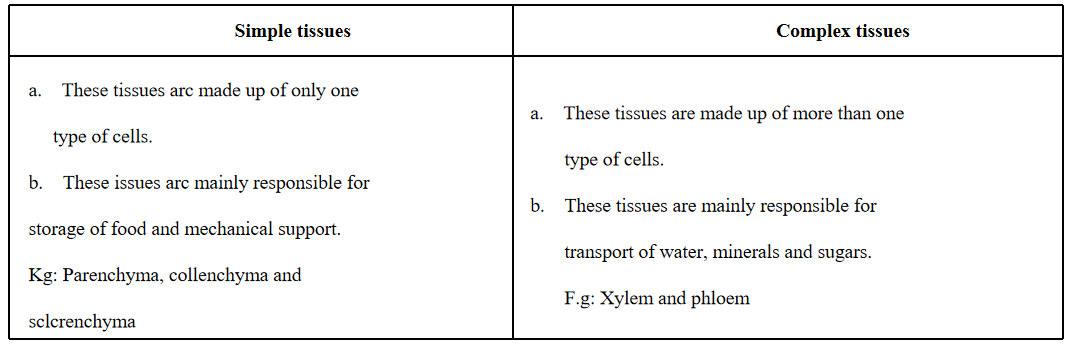
Question 3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
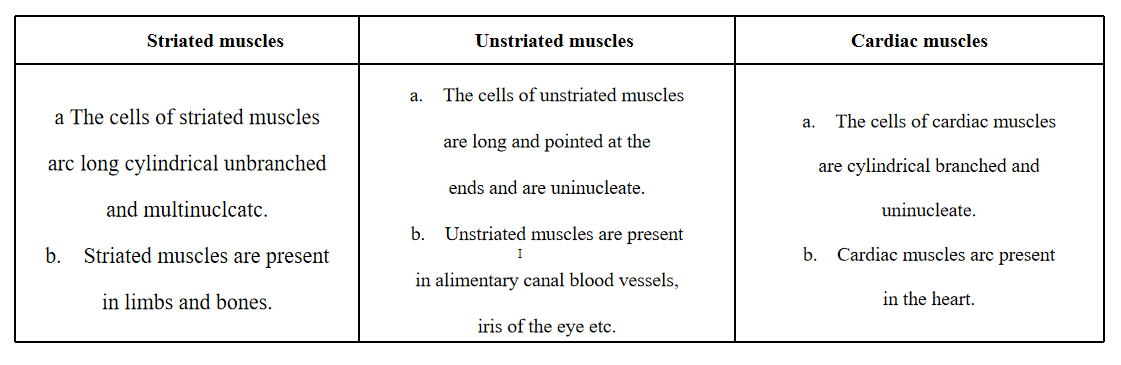
Question 4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Answer:
Question 5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
The important functions of stomata are:
- Exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
- Loss of water in the form of water vapors,
i.e, transpiration.
Question 6. Diagrammatically show the difference in three types of muscle fibers.
Answer:
Types of muscle fibers
- Striated muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
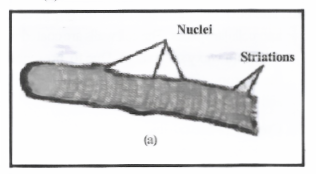
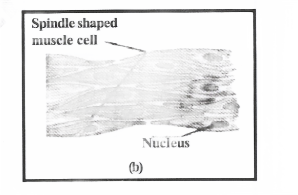
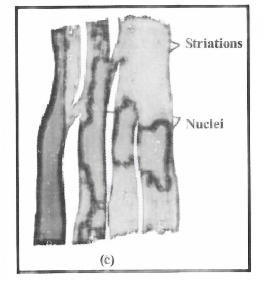
Question 7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer: The specific function of the cardiac muscle is rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life without fatigue.
Question 8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
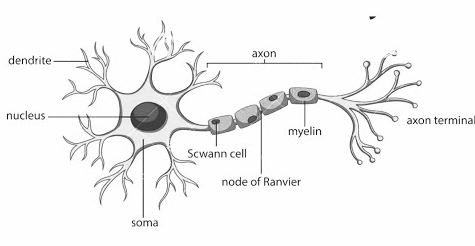
Question 9. Draw a labeled diagram of a neuron.
Answer: Neuron – Unit of nervous tissue.
Question 10. Name the following
Answer:
- Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth: Squamous epithelium
- Tissue that connects muscle to bones in humans were: Tendons
- Tissue that transports food in plants: Phloem
- Tissue that stores fat in our body: Adipose tissue
- Connective tissue with a fluid matrix: Blood
- Tissue present in the brain: Nervous tissue
Question 11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, the bark of the tree, the lining of the kidney tubule, vascular bundle, bone
Answer:
- Squamous epithelium
- Epidermal tissue
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Conductive tissue
- Connective tissue
Question 12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer: Parenchyma is present in the cortex and pith of the stem and roots. It is present in the mesophyll of leaves.
Question 13. What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Answer: The epidermis acts as protective tissue in plants and provides protection to underlying tissues. This layer forms the outer covering of various plant organs and remains in direct contact with the environment.
Question 14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer: The cork cells are dead and do not have any intercellular spaces. The cell walls are coated with suberin(a waxy substance). Due to the presence of these properties cork acts as a protective tissue and protects the underlying tissues.
Question 15. Complete the table.
Answer:
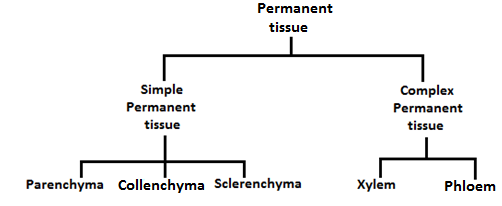
Tissues Textual Questions
Question 1. What is a tissue?
Answer: Tissue is a group of cells that work together to achieve a particular function and have a common origin.
Question 2. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer: In multicellular organisms, the different types of tissues perform different functions. Since a particular group of cells carry out only a particular function, they do it very efficiently. So, multicellular organisms possess a definite division of labor.
Question 3. Name the types of simple tissues.
Answer:
There are three types of simple tissues:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Question 4. Where is apical meristem found?
Answer: Apical meristem is found in the shoot apex and root apex.
Question 5. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer: Sclerenchymatous fibers.
Question 6. What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
- Sieve tube
- Companion cell
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibers
Question 7. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer: Muscular tissue.
Question 8. What does a neuron look like?
Answer: A neuron consists of a flat and broad cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm from which long thin hair-like parts called dendrites to arise. Each neuron has a single long part called the axon and many short, branched parts called dendrites.
Question 9. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
- Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
- The cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleated.
- Cardiac muscles show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
Question 10. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer: Aerolar tissue fills the space inside the organs and thus forms a packing tissue between organs lying in the body. It also supports many delicate organs in the body.
Tissues Additional Questions
Question 1. What are vascular bundles?
Answer: Xylem and phloem together form vascular bundles.
Question 2. Name the meristem which is responsible for the increase of girth of the root.
Answer: Lateral meristem
Question 3. State the following activities on the basis of voluntary or involuntary muscles.
Answer:
- Jumping of frog: Voluntary
- Pumping of heart: Involuntary
- Movement of chocolate in our intestine: Involuntary
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Textbook Solutions
Question 4. Water hyacinth floats on the water’s surface. Explain.
Answer: The water hyacinth plant has tissue that encloses plenty of air in its spongy petioles. Air makes the plant lighter than water enabling it to float on the surface of the water.
Question 5. Name the tissue which
- Allows aquatic plants to float c. Ligaments are formed c. Tendons are formed
- Provides flexibility to plants of yellow fibrous. white fibrous
Answer:
- Allows aquatic plants to float: Aerenchyma connective tissues. connective tissue
- Provides flexibility to plants: Collenchyma
Question 6. Differentiate between chlorenchyma and aerenchyma.
Answer:
- Parenchyma which contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis is known as chlorenchyma.
- Parenchyma which has air cavities in aquatic plants and helps in buoyancy is called aerenchyma.
Question 7. What are stomata? Write two functions of stomata.
Answer: Stomata are small pores found in the epidermis of the leaves of plants. The functions of stomata are gaseous exchange and transpiration.
Question 8. Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
- Meristematic tissue: Cells of the meristematic tissue divide throughout their life.
- Permanent tissue: Permanent tissue loses the ability to divide to take up a specific function.
Question 9. Write the functions of the epithelial tissue. walls of cork cells. It makes cell wall impervious
Answer: The functions of epithelial tissue are protection, prevent wear and tear, absorption, and secretion.
Question 10. List the differences between ligaments and tendons.
Answer:
Tissues High Order Thinking Questions
Question 1. Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but lack a vacuole. Give reason.
Answer: The vacuoles only provide turgidity and rigidity to the plant cells. Since the role of cells of meristematic tissue is to divide continuously, therefore there is no need for vacuoles for the cells of meristematic tissue.
Question 2. Why do sclerenchyma cells have a narrow lumen?
Answer: Due to the deposition of lignin there is no internal space inside the cell. This makes the wall of the sclerenchymatous tissue thickened.
Question 3. Give the characteristics and roles of the following:
- Cutin
- Suberin
Answer:
- Cutin: It is a waterproof layer of waxy substance. The epidermis is one cell thick and is covered with cuticles.
- Suberin: It is a complex polymer present in the walls of cork cells. It makes the cell wall impervious to gases and water.
Question 4. What will happen if:
- Apical meristem is cut or damaged?
- Striated muscles contract rapidly for a long time.
- Ligaments are overstretched?
- Bone is dipped in HCI?
- Heparin is absent in the blood?
Answer:
- The growth of plants in length will stop.
- Fatigue will occur due to the accumulation of lactic acid.
- A sprain will occur.
- The mineral matter will dissolve.
- Blood clotting will occur inside the blood vessels.
Question 5. Why do muscles contain contractile proteins?
Answer: Contractile proteins help in the contraction and relaxation of muscles to cause movement.
Question 6. What is meant by division of labor?
Answer: The distribution of different functions among different parts of the organism’s body which get specialized for the particular function.
Question 7. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Answer:
- Voluntary muscles can be moved by conscious will when we want to move them.
Example: Muscles of limbs - Involuntary muscles function on their own.
Example: Cardiac muscles
Question 8. What is the function of tissue present in the lining of the kidney tubule?
Answer: The lining of the kidney tubule is made up of cuboidal epithelium which provides mechanical support.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues MCQs With Answers KSEEB
Tissues Unit Test
Multiple choice questions
Question 1. Fats are stored in the human body as
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Adipose tissue
- Bones
- Cartilage
Answer: 2. Adipose tissue
Question 2. The girth of the stem of the root increases due to
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- All of these
Answer: 2. Lateral meristem
Question 3. A person met with an accident in which two long bones of the hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be the possible reason?
- Tendon break
- Skeletal muscle break
- Ligament break
- Areolar tissue break
Answer: 3. Ligament break
Question 4. A student was asked to select a simple permanent tissue that makes the plant hard and stiff and consists of dead cells. He selected_____________
- Xylem
- Cork
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
Answer: 3. Sclerenchyma
Question 5. If the tip of the sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. It is due to the presence of________
- Cambium
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Answer: 4. Intercalary meristem
Tissues Answer the following
Question 1. What is the chief function of RBCs?
Answer: Transport of oxygen
Question 2. Where is the intercalary meristem located?
Answer: Intercalary meristem is located in between the regions of permanent tissue, usually at the base of the node, the base of the internode, or at the base of the leaf.
Question 3. What is the function of tissues present in the bark of a tree?
Answer: The bark of a tree contains cells that are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They provide mechanical support.
Question 4. Why there are numerous layers of the epidermis in cacti?
Answer: To prevent water loss.
Question 5. Define the process of differentiation.
Answer: The loss of ability to divide by taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation.
Tissues Answer the following
Question 1. Note the relationship between the first pair of words and accordingly fill in the blanks.
- Heart: Cardiac muscles: :______________:Smooth muscles
- Plasma: Blood :: Axon:___________
Answer:
- Ureters
- Neuron
Question 2. Write the differences between plant and animal tissue.
Answer:

Question 3. Differentiate between cartilage and bone.
Answer:
Question 4. Name two complex permanent tissues in vascular plants. What are these commonly called?
Answer: The xylem and phloem are complex permanent tissues. Xylem is called wood and phloem is called bast.
Tissues Activity
Question 1. Demonstration of growth of roots in onion bub.
Answer:

Procedure: Take two glass jars and fill them with water. Now, take two onion bulbs and place one in each jar. Observe the growth of roots in both bulbs for a few days. Measure the length of roots on days 1,2 and 3. On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion bulb in jar two by about 1 cm. After this, observe the growth of the roots in both jars and measure their lengths each day for 5 more days and record the observations.
Observation:
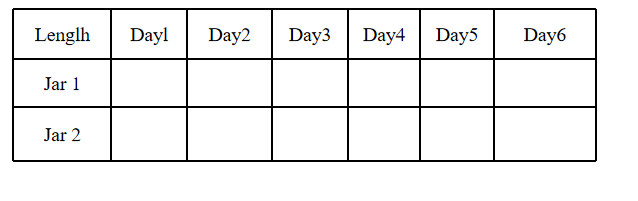
Conclusion:
- The roots of onion bulbs in jar A kept on growing.
- The roots of jar B stopped growing when the tips of the growing roots were cut on day 4. The growth of roots occurs due to the activity of dividing cells present at the apical meristem.
Tissues Diagrams
Question 1. Location of meristematic tissue in the plant body.
Answer:

Question 2. Various types of simple tissues.
Answer: