KSEEB Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Important Concepts
- Resources – Air, water, soil
- Pollution – Air, water, soil
- Bio-geo chemical cycles, water cycle, Nitrogen cycle
- Carbon cycle, Oxygen Cycle, Greenhouse ef-feet, and the Ozone layer.
Natural Resources: The materials present in a natural environment and useful to living organisms are called natural resources.
Examples: Air, water, soil, minerals, plants & animals.
Biosphere: It is the life-supporting zone of the earth where the atmosphere, the hydrosphere and the lithosphere interact and make life possible.
Importance of atmosphere
1)Role of atmosphere in climate control.
2)The movement of air.
3)Rain
Air pollution: It is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air.
Effects of Air pollution: Air pollution affects the respiratory system causing breathing difficulties and diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, tuberculosis and pneumonia.
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
Acid Rain: The rainwater contains a mixture of sulphuric acid and Nitric acid with a pH of less than 5.6.
Water-A wonder liquid: The oceans, rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, pools, polar ice caps, water vapour etc., collectively form the hydrosphere.
Water pollution: An undesirable change in the physical, biological or chemical qualities of water that adversely affects the aquatic life, and makes water less fit or unfit for use.
Harmful effects of water pollution: The substances like fertilizers and pesticides used in farming, and toxic metals used by industries could be poisonous. Industrial and household waste reduce the dissolved oxygen in water bodies, thereby affecting aquatic life.
Soil: It forms the upper surface of the land and supports plant growth. Soil is the layer of unconsolidated particles derived from weathered rock, organic matter, water and air.
Soil pollution: The contamination of soil (or land) with solid waste, chemicals, fertilizers and pesticides, reducing its fertility is called soil pollution.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Harmful effects of soil pollution: Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides pollute the soil, affect its fertility, the soil thus, maybe- come acidic or alkaline.
Biogeochemical cycles: The eye he flows of nutrients between non-living environments and living organisms is known as biogeochemical cycles. It is the process of transfer and circulation of essential chemical nutrients such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen in a biosphere.
Water cycle: It is the whole process in which water evaporates and falls on the land as rain and later flows back into the sea via rivers. Plants also release water to the atmosphere through transpiration. Water is also released into the atmosphere from rivers and oceans by evaporation.
Nitrogen cycle: The source of nitrogen is an atmosphere which contains 78% of the nitrogen in the form of gas. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for all life forms. The nitrogen cycle in the biosphere involves the following important steps.
1)Nitrogen fixation
2)Ammonification
3)Nitrification
4)Denitrification
Carbon cycle: Carbon is found in various forms on the earth.
1)As carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
2)As carbonates in various minerals.
3)As fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas. Plants utilise atmospheric carbon dioxide in photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates, which are taken by herbivores and then pass through carnivores.
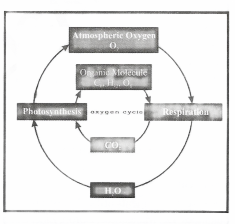
Oxygen cycle: Oxygen forms about 21 per cent of the atmospheric gases. It is also present in dissolved form in water bodies and helps in the survival of aquatic life. The oxygen cycle maintains the level of oxygen in the atmosphere. Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three processes namely combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen. Green plants are the major source of oxygen in the atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect: It is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone etc., that absorb infrared radiation, thereby increasing the global temperature.
Ozone layer: This is a layer of ozone (03) surrounding the earth. It protects the earth from harmful radiation like U. V. radiation. The (CFCs) are released into the air it accumulates in the upper atmosphere and reacts with ozone resulting in the reduction of the ozone layer by forming a hole.

Natural Resources Exercises
Question 1. Why is the atmosphere essential for life?
Answer: The atmosphere acts as a protective blanket for organisms to exist. It keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly steady during the day and even during the course of whole year. The atmosphere contains all the important gases which are required for sustaining life on earth.
Question 2. Why is water essential for life?
Answer: Organisms need water because it plays a vital role in the metabolic reactions taking place within an organism’s body. It acts as a universal solvent, providing a medium for chemical reactions to occur.
Karnataka Board Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Solutions PDF
Question 3. How are living organisms dependent on the soil? Are organisms that live in water totally independent of soil as a resource?
Answer: Soil is a complex mixture comprising of minerals, organic matter, water, air and living organisms. Soil provides a natural habitat for different organisms and also provides nutrients to the plants for their growth and development. Aquatic organisms dependent on the soil as a resource because decomposers present in the bottom sediments of water bodies decompose dead, decaying organic matter into simple, in organic substances.
Question 4. You have seen weather reports on television and in newspapers. How do you think we are able to predict the weather?
Answer: Weather report can be recorded by information such as direction and speed of wind, temperature, humidity and patterns of cloud formation.
Question 5. We know that many human activities lead to increasing levels of pollution of the air, water-bodies and soil -• Do you think that isolating these activities to specific and limited areas would help in reducing pollution?
Answer: Human activities lead to increasing the levels of pollution of the air, water bodies and soil. Isolating such activities to specific and limited areas may help in reducing pollution of the air, water bodies and soil. Isolating sub-activities to specific and limited areas may help in reducing pollution.If we follow the safety measures we can check or stop the pollution.
Question 6. Write a note on how forests influence the quality of air, soil and water resources.
Answer: Forests influence the quality of air, soil and water resources in the following ways.
Air:
Forests help in minimising the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Plants maintain the oxygen balance in the atmosphere.
Soil:
The roots of trees prevent erosion of topsoil by holding the soil particles tightly.
Water:
Forests help in maintaining the water cycle as well as the water resources of the earth.
Natural Resources Textual Questions
Question 1. How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on venus and mars?
Answer: On planets Venus and mars, carbon dioxide is the major constitute but nitrogen, oxygen and water vapour are absent, so life does not exist. On our planet earth, the atmosphere contains a mixture of many gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapour hence life exist.
Question 2. How does the atmosphere act as a blanket?
Answer: The atmosphere keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly steady during the day and even during the course of the whole year.
Question 3.What cause winds?
Answer: The movement of air from one region to another creates winds when the solar radiations fall on the earth, some are absorbed and a majority of these are reflected back or re-radiated by the land and water bodies. These reflected or re-radiated solar radiations heat up the atmosphere from below. As a result convection currents are set up in the air. But since land gets heated faster than the water, the air above the land gets heated faster then the air over water bodies. During the day, the air over land gets heated faster and starts rising, creating a low pressure below. As a result the air over the sea moves into this region of low pressure.
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Notes
Question 4. How are clouds formed?
Answer: The water evaporates due to the Heating up of water bodies and other biological activities. The air also heats and rises, on rising, it expands and cools to form tiny droplets. These droplets grow bigger, expand and form clouds, and they fall down in the form of rain.
Question 5. List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Answer:
The human activities that leads to air pollution are,
1)Burning of fossil fuels.
2)Smoke from automobiles.
3)Forest fires, excessive use of chloroform carbons and industrialisation.
Question 6. Why do organisms need water?
Answer:
Organisms need water for the following reasons.
1)It plays a vital role in the metabolic reactions taking place in the organisms.
2)It transports the substances from one part of the body to the other in the dissolved form.
3)It helps in the digestion of food and absorption of nutrients in the blood.
Question 7. What is the major source of fresh water in the city/town/village where you live?
Answer: The major source of fresh water in the city/village/town were we live is underground water.
Question 8. Do you know of any activity which may be polluting this water source?
Answer: Sewage and industrial wastes are the major sources of water pollution.
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Important Questions Karnataka Board
Question 9. How is soil formed?
Answer: The rocks are broken down by various physical, chemical and biological processes. The breakdown of bigger rocks into small, file soil particles is called weathering. Even the sun, wind, water also helps in soil formation.
Question 10. What is soil erosion?
Answer: The removal of topsoil which is rich in humus and nutrients by flowing water or wind is called soil erosion.
Question 11. What are the methods of preventing or reducing soil erosion?
Answer:
Soil erosion can be prevented by.
1)Afforestation
2)Sowing grasses
3)Terrace forming
4)Preventing overgrazing.
Question 12. What are the different states in which water is found during the water cycle?
Answer:
Water exists in all three states of matter during the water cycle.
1)Gaseous state “Evaporation of water from the water bodies in the form of water vapour.
2)liquid state – Water vapour condenses and forms rain.
3)Solid state – Sometimes the freezing of liquid droplets in the snow.
Question 13. Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and Nitrogen.
Answer:
1)Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
2)Proteins
Question 14. List any three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of air.
Answer:
1)Burning of fossil fuels.
2)Industries and automobiles
3)Deforestation.
Question 15. What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer: Some greenhouse gases like co2 prevent the escape of heat from the earth. An increase in the atmosphere would cause the average temperatures to increase worldwide and this is called the greenhouse effect.
Question 16. What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Answer:
1) oxygen (o2)
2) Ozone (o3)
The other sources are oxides and biological molecules.
Natural Resources Additional Questions
Question 1. What are biodegradable pollutants?
Answer: Pollutants which can be decomposed by microbial activity.
Example: Organic wastes like traits of vegetables.
Question 2. Write any two uses of carbon dioxide gas
Answer:
1)Carbon dioxide is fixed by plants to prepare food by photosynthesis.
2)Carbon dioxide can trap heat and prevent its escape from the atmosphere of the earth, maintaining temperature.
Question 3. Name two types of biogeochemical cycles.
Answer:
1)Gaseous cycle.
Example: Oxygen
2)Sedimentary cycle.
Example: Phosphorous
Question 4. What is biomagnification?
Answer: The phenomenon of an increase in the concentration of harmful non-biodegradable substances in the body of living organisms at each tropic level of the food chain is called biomagnification.
Question 5. What is eutrophication?
Answer: It is the process in which excessive growth of algal (algal bloom) occurs as a result of a high content of nutrients (nitrates and phosphates) in the water body. Eutrophication leads to the depletion of dissolved oxygen in water resulting in the killing of aquatic organisms.
Question 6. Name two acids that are usually present in acid rain.
Answer: Sulphuric acid and Nitric acid
Question 7. How are CFCS harmful for the environment and living beings?
Answer: The CFCs are not degraded by any biological process. It reacts with the ozone layer and causes hole in the ozone layer.
Karnataka State Board 9th Science Natural Resources Exercise Solutions
Question 8. What causes the movement of air?
Answer: The movement of air is caused by the uneven heating of the atmosphere in different regions of the earth.
Question 9. Write the biotic and abiotic components of our environment.
Answer: Biotic components are plants, Animals and microorganisms Abiotic components are land, air, water etc.
Question 10. What is the atmosphere? List its four concentric layers.
Answer: The envelope of air that surrounds our planet earth is called the atmosphere. The four main concentric layers of the atmosphere are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere.
Question 11. What is smog? Mention its harmful effect.
Answer: Smoke containing fog particles result in smog. It causes breathing problems.
Natural Resources High-Order Thinking Questions
Question 1. Why do not lichens occur in Bengaluru whereas they commonly grow in Darjeeling?
Answer: Lichens act as bioindicators o fair pollution and are sensitive to sulphur dioxide. Bengaluru has the maximum number of vehicles vehicular exhaust has increased concentrations of sulphur dioxide and it kills lichens.
Question 2. State reasons for the following:
1)Excess burning of coal causes the greenhouse effect.
2)Temperature ranges from – 190°C to 110°C on the surface of the moon.
Answer:
1) Excess burning of coal produces greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide methane etc. These gases have a tendency to trap the beat of the sun thereby causing the greenhouse effect,
2)The moon has no atmosphere. The atmosphere helps to regulate the temperature. In absence of an atmosphere, the temperature on the surface of the moon ranges from 190°C – 110°C
Question 3. What is nitrogen fixation? Why do plants need to fix nitrogen?
Answer: The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation, plants cannot absorb atmospheric nitrogen directly so they need to fix nitrogen. Rhizobium and blue-green algae fix nitrogen.
Question 4. There is mass mortality of fish in a pond. What may be the reasons?
Answer:
1)Thermal pollution
2)Addition of toxic compound in water.
3)Addition of pollution.
Question 5. Justify “Dust is a pollutant”?
Answer: Dust particles remain suspended in the air and can cause allergies and other respiratory diseases.
Question 6. Why do people love to fly kites near the seashore?
Answer: Due to the differential heating of land and water during the day there is a movement of air from sea to land. It helps in flying the kite high and the air provides relief near the seashore.
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Summary KSEEB
Question 7. Why are root nodules useful for plants?
Answer: Root nodules of leguminous plants have nitrogen-fixing bacteria Rhizobium.
Natural Resources Unit Test
Question 1. When we breathe in air, nitrogen also goes inside along with oxygen. What is the fate of this nitrogen______
1)It moves along with oxygen into the cells.
2)It comes out with the carbon dioxide during exhalation
3)It is absorbed only by the nasal cells.
4)Nitrogen concentration is already more in the cells so it is not at all absorbed.
Answer: (2) It comes out with the carbon dioxide during exhalation
Question 2. Air is a mixture of gases with the following gas in maximum percentage_______
1)Nitrogen
2)Oxygen
3)Hydrogen
4)Carbon dioxide
Answer: (1) Nitrogen
Question 3. When water mixes with carbon dioxide in the air it forms______
1)sulphuric acid
2)carbonic acid
3)Hydrochloric acid
4)Ozone
Answer: (2) carbonic acid
Question 4. In which layer of atmospheric ozone is maximumly concentrated________
1)Troposphere
2)Stratosphere
3)Ionosphere
4)Mesosphere
Answer: (2) Stratosphere
Natural Resources Answer the following Questions
One Mark
Question 1. What keeps the temperature on earth steady?
Answer: Air prevents sudden increases in temperature during day and slows down the loss of heat at night.
Question 2. What is global warming?
Answer: Increase in atmospheric temperature due to increase in carbon dioxide.
Question 3. What is rainwater harvesting?
Answer: The method used to store rainwater by making special water harvesting structures.
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Important Questions
Question 4. List the name of chemicals whose biomagnification result in the following diseases in human.
1)Minamata disease
2)Itai Itai disease
Answer:
1)Mercury
2)Cadmium
Question 5. Name any two climatic events that take place in the atmosphere
Answer:
1)Cloud formation
2)Convection currents – Winds
Question 6. Name the winds which bring rain in India.
Answer:
1)South-west monsoon
2) North-east monsoon.
Two Marks
Question 1. State any two harmful effects each of
1)Air pollution
2)Water pollution
Answer:
1)Harmful effects of air pollution are respiratory problems, Global warming and acid rain.
2)Harmful effects of water pollution are waterborne diseases such as typhoid cholera, and Eutrophication.
Question 2. State the harmful effects of ozone depletion.
Answer: Ozone prevents the harmful radiation of sun from reaching the surface of the earth. Depletion of this layer may harm many life forms by causing skin cancer, cataract in the eyes and cause global warming.
Question 3. What are the various forms in which oxygen is available?
Answer:
1) In the atmosphere, oxygen is found in its elemental form.
2) In combined form, it occurs as carbon dioxide.
3) It is also found in carbohydrates, proteins of Organic Molecule fats.
Natural Resources Chapter 14 Class 9 KSEEB Textbook Solutions Free PDF
Question 4. Define humus and state its function.
Answer: The dark-coloured, partially decayed organic matter found in the top layer of soil is called humus. Humus makes the soil porous which helps the soil to increase its water-holding capacity and the content of the air.
Natural Resources Schematic Representation
1. Nitrogen cycle in nature.
2. Carbon cycle in nature
KSEEB Class 9 Science Natural Resources Extra Questions with Answers
3. Oxygen cycle in nature