KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Important Concepts
Cell, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, unicellular and multicellular organisms, cell organelles, nucleus, and chromosomes.
Cell
Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Cells were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
Plasma membrane or cell membrane
This is the outermost covering of the cell that separates the contents of the cell from its external environment. Plasma membrane gives definite shape to the cell It is selectively permeable membrane.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5
Cell wall
Plant cells have a rigid outer protective covering called the cell wall which lies outside the plasma membrane. The cell wall is nonliving, freely per¬ meable, and mainly composed of cellulose.
Protoplasm
It is a living fluid substance of the cell. It is viscous, colorless, transparent material, and a life-giving substance of a cell.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
Nucleus
Nucleus is the largest cell structure. It is spherical or oval prominent structure, usually located in the center of the cell. The important parts of nucleus are nuclear mem¬ brane, nucleoplasm, chromatin material, and nucleolus.
Chromosomes
These are thread-like several structures which are found in the nucleus of the plant and animal cells. They contain hereditary information in the form of genes. Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein.
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Genes
It is the functional unit of a chromosome, responsible for hereditary information or specific traits of an organism
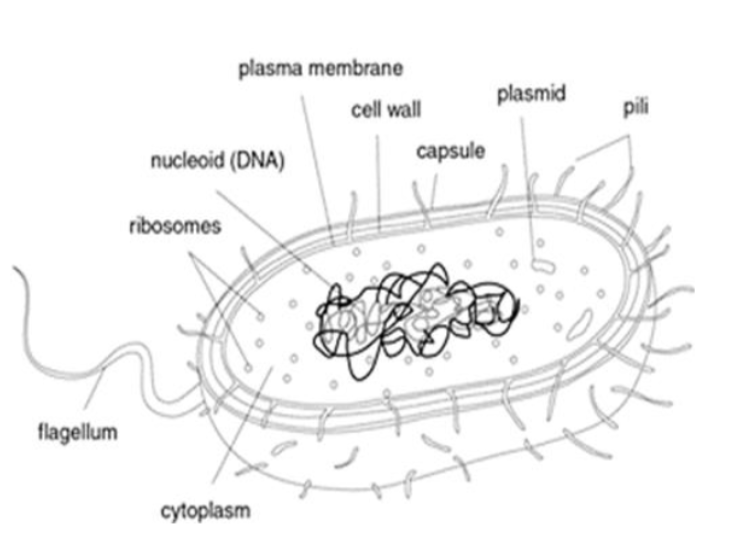
Nucleoid
The part of a cell ofa bacterium having undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid.
Cytoplasm
It is the fluid content of the cell which occurs between the plasma membrane and the nuclear en¬ envelope. It acts as a store of vital Chemicals such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, etc.
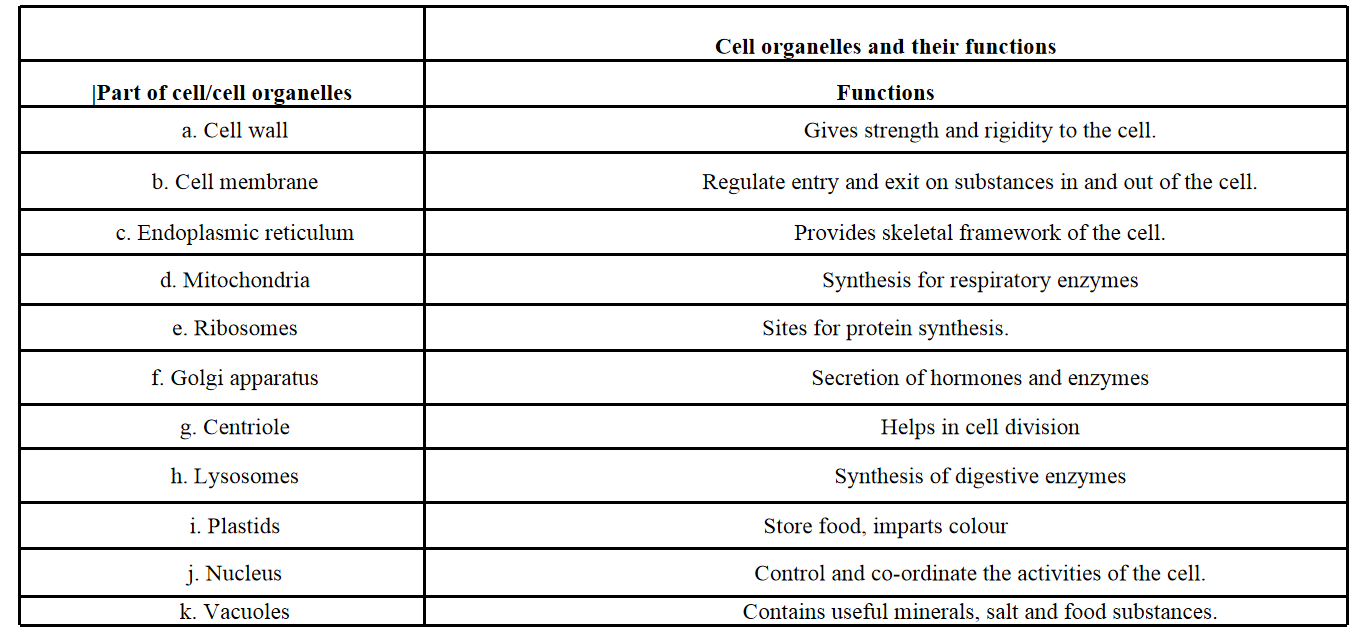
Cell organelles
These are microscopic cytoplasmic structures which perform different functions such as synthesis of substances, secretion, digestion, and generation of energy, etc.
Endoplasmic reticulum
It is an irregular, interconnected network of flattened sacs made up of double membranes and are interconnected with each other. Depending upon the presence and absence of ribosomes on the surface of endoplasmic Reticulum these are of two types:
1. Rough endoplasmic reticulum(with ribosomes attached)
2. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum(without ribosomes attached)

Golgi apparatus
It is an organelle in animal cells consisting set of membrane-bound smooth, flattened cisternae stacked one above the other. In plant cells, they are distributed throughout the cytoplasm and are called dictyosomes.
Mitochondria
They are a double-membraned bag-like structure. The outermost membrane is very porous, while the inner membrane is produced into a finger-like projection called cristae. They are called as powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria are the largest organelles in animal cells.
KSEEB Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life Solutions
Lysosomes
They are small-sized enzymes containing vesicles which are bounded by single membrane. These are involved in autolysis or self-digestion of cells after their death, hence they are also called suicidal bags or digestive bags.
Plastids
These are found in plant cells only. On the basis of pigments present in plastids, they are divided into:
1. Leucoplasts: They are colorless and store food in the form of starch, proteins, and fats.
2. Chromoplasts: They are colored like orange, red, yellow, etc.
3. Chloroplasts: They are green-colored plastids because of the presence of chlorophyll.
Centrosome
It contains two granules like centrioles and it is found in animal cells only. It helps in cell division in animal cells.
Vacuoles
These are cytoplasmic inclusions. They are clear fluid-filled or gas-filled spaces. The vacuole is covered from the outside by a covering called tonoplast. In animal cells, vacuoles are smaller in size but in plant cells, a
the single prominent very large vacuole is present.
Ribosomes
They are dense, spherical, and granular particles which occur freely in the matrix or remain attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Peroxisomes
They are small and spherical organelles found in photosynthetic cells of plants, liver and kidney cells of the vertebrates
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Exercises
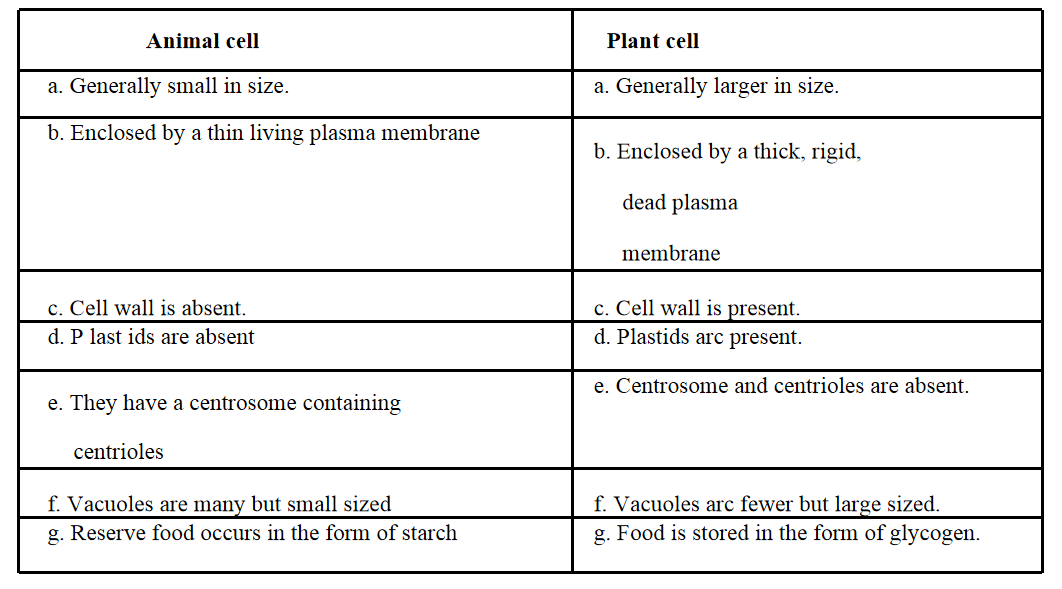
Question 1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells
Answer
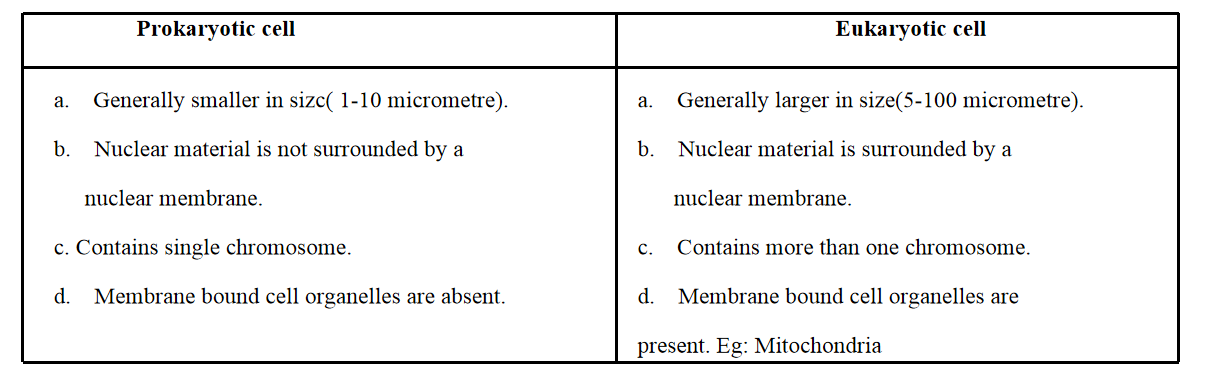
Question 2. How is prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer
Question 3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: If plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down, the constant internal chemical composition of the cell will be lost and it will not be able to perform basic functions.
Question 4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: Golgi apparatus is involved in the storage, modi¬ fiction, and packaging of materials in vesicles. The basic metabolic functions of the cells are not possible if Golgi apparatus is absent.
Karnataka Board 9th Science Chapter 5 Notes PDF
Question 5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. The mitochondria contain many oxidative enzymes which oxidize the food and convert it into energy currency of the cell in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy is used by body for making new chemical compounds and for doing mechanical work. Due to this reason mitochondria are generally called as powerhouse of the cell.
Question 6. Where do lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesized?
Answer: Lipids are synthesized in smooth endoplasmic reticulum, while proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes which are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 KSEEB Textbook Solutions
Question 7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer: Amoeba acquires its food through the process of endocytosis. This process is generally involved for the ingestion of good material.
Question 8. What is osmosis?
Answer: The diffusion of water or solvent through a semipermeable membrane from her region of higher concentration to lower concentration
Question 9. Carry out the following Osmosis experiment: Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water.
1. Keep cup A empty.
2. Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B.
3. Put one teaspoon salt in cup C.
4. Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for 2 hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following.
1. Explain why water gathers in the hollowed
portion of B and C.
Answer: The water enters in the hollow portion of B and C due to the process of osmosis. Since the concentration of solute(sugar in cup B) and (salt in cup C) is higher inside the cup as compared to the water which is outside the cup. Therefore, water(solvent) from it higher concentration (outside the cup) will move towards the lower concentration(inside the cup). This process
of osmosis(moving in of solvent) is known as endosmosis.
2. Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
Answer Potato acts as a control for the experiment. This is very necessary for comparing the results of the experiment
3. Explain why water does not gather in the hol¬ lowed out portions of A and D.
Answer: Water does not get there in the hollowed portions of A and D because the hollowed portions of potato Ais empty. Thus, there is no concentration difference and therefore no osmosis takes place. The hollowed portions of potato D contain sugar inside it but this potato is boiled one. Therefore, osmosis will not take place as its semipermeable membrane is destroyed by boiling
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Textual Questions
1. Who discovered cells and how?
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered cells with the help of his self-designed microscope. Robert Hooke was examining a thin slice of cork and he saw the resemble the structure of honeycomb consisting of many compartments.
2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: All living organisms are made up of cells. Thus, cell is the structural unit of life. The cells perform basic functions suchas respiration, nutrition, reproduction, etc.
3. How do substances like water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer: CO2 moves in and out of the cell by the process of diffusion. Water moves in and out of the cell by the process of osmosis.
4. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: Plasma membrane is called selectively permeable membrane because it allows the movement of only selected molecules across it and not all of them
5. Fill in the blanks/gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
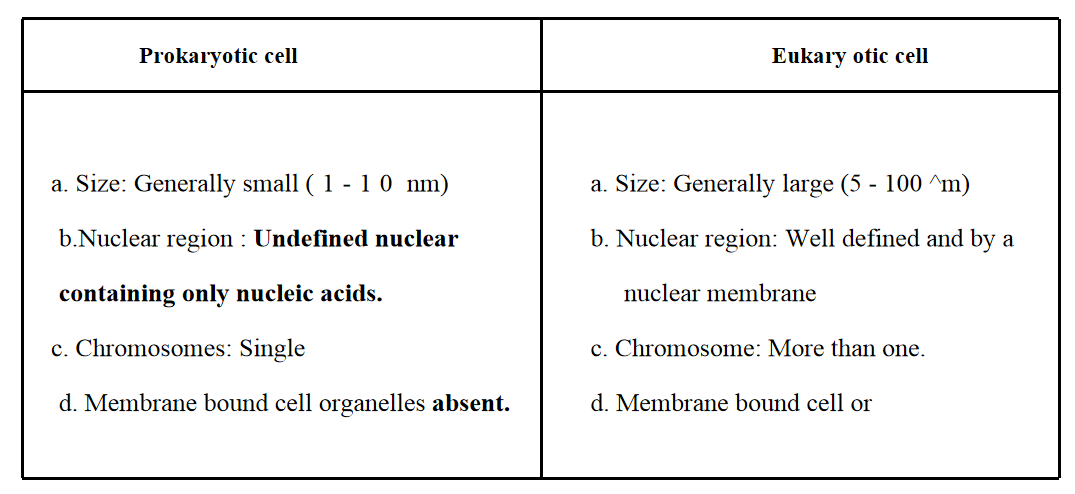
6. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:
1. Mitochondria
2. Chloroplast
7. If the organization of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: Well-organized cells maintain homeostasis, i.e, constant internal chemical composition. It I therefore able to perform basic functions like respiration, obtaining nutrition, etc. If the organization of a cell is destroyed, it will not be able to maintain homeostasis and thus will not be able to perform basic functions.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 KSEEB Solutions PDF
8. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer: Lysosomes are called the suicide bags of the cells as they contain hydrolytic enzymes which can digest incoming food materials, remove the foreign bodies, breakdown worn out cells and cell organelles to component molecules for building new organelles and cells.
9. Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer: Proteins are synthesized on ribosomes
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Additional Questions
1. Give two examples of unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Answer: Unicellular organisms are Amoeba and Paramecium. Multicellular organisms are mango and man.
2. Name the scientist who proposed ‘Cell theory’.
Ans: Cell theorywas given bySchleidenand Schwann
3. Name three basic components of a typical Eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
1. Plasma membrane
2. Nucleus
3. Cytoplasm
4. Name the nucleic acids that are present in
an animal cell.
Answer: Deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA) , Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
5. Give two examples of osmosis in plants.
Answer:
1. Absorption of water by roots of plants from the soil.
2. Stomata open and closed due to osmotic movements of water.
6. Classify the following as osmosis or diffusion.
Answer:
1. Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration Diffusion
2. Swelling up of raisins on keeping and water Osmosis
3. Spreading of virus on sneezing – Diffusion
7. List various components of the nucleus.
Answer: Nuclear envelope, nuclear sap, chromatin material, nucleolus, and nuclear matrix.
8. What are chromosomes? List their function.
Answer: Chromosomes are thread-like structures usually present in the nucleus. They are composed of DNA and protein.
Functions
1. Chromosomes contain hereditary information of the cell.
2. DNA of chromosomes also controls all the activities of the cell.
9. State two types of plastids. Write one function of each.
Answer: Two types of plastids in plant cells are leucoplast and chromoplast.
1. Leucoplast are colorless plastid store carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the cell.
2. Chromoplasts are colored plastids.
Example: Chloroplast synthesize food in the presence of sunlight by the process called photosynthesis.
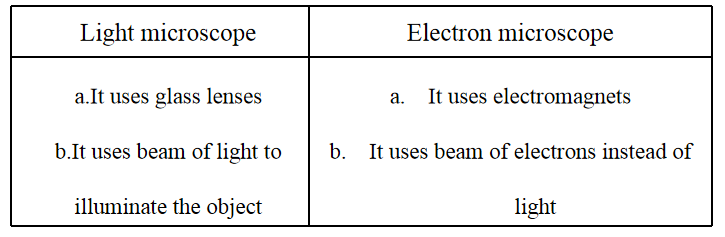
10. Write the differences between light microscope and electron microscope.
Answer:
1. Why plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: Plasma membrane regulate the flow ofselected materials in andout ofthe cell.
2. Define the following terms
1. Endocytosis
2. Phagocytosis
3. Exocytosis
Answer:
1. Endocytosis: It is the process of ingestion of materials by the cells through the plasma membrane.
2. Phagocytosis: Method of feeding in some organisms such as Amoeba and sponges. The WBCs engulfcells debris and microbes with the help of this process.
3. Exocytosis: It is the process by which the plasma membrane remove its contents to the surrounding medium
3. Every multicellular organism has come from a single cell. Justify the statement.
Answer: Single cellis zygote. It is the first cell formed after fertilization.
4. What is the role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum in liver cells?
Answer: It helps in detoxifying many poisons and drugs.
5. What will happen when human red blood cells are placed in hypotonic sugar solution?
Answer: They will swell up or burst
6. A student soaked 5 g of raisins in a beaker A containing 25 ml of ice-chilled water and another 5 g of raisins in beaker B containing 25 ml of tap water at room temperature. What is the observation after1 hour?
Answer: Water absorbed by raisins in beaker B was more than that absorbed by raisins of beakers A.
7. Why does the skin ofyourfinger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Answer: The soap solution is hypertonic compared to concentration of our skin cells. Continuous washing of clothes with hands causes exosmosis in the skin cells resulting in flow of water from skin cells to outside. This results in shrinkage of skin over the fingers.
8. How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell?
Answer: Bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell and an onion peel cell is a plant cell(eukaryotic cell)
9. Name the smallest known cell.
Answer: PPLO- Pleuro-Pneumonia-like organism. It is about 0.1 p in diameter.
10. How do lysosomes helps in cleansing the cell?
Answer: Lysosomes help in removing dead, wornout cell organelles and eat up the damaged cell.
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Unit Test Multiple choice questions
1. In the cell, complex sugars are made from single sugar by_
1. Nucleolus
2. Mitochondria
3. Golgi apparatus
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: (3)
2. The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell is________
1. Mitochondria
2. Ribosomes
3. Plastids
4. Lysosomes
Answer:(2)
3. Animal cells do not show plasmolysis because_____
1. They do not exhibit osmosis
2. They do not possess cell wall
3. They are living cells
4. Theyhave intercellular spaces
Answer: (2)
KSEEB 9th Science Chapter 5 Important Questions
4. The term Protoplasm was coined by _______
1. Robert Hooke
2. Robert Brown
3. Purkinje
4. Schwann
Answer: (3)
KSEEB Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Important Questions
5. Animal cell lacking nuclei would also lack in_______
1. Ribosome
2. Chromosome
3. Lysosome
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: (2)
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Fill In The Blanks
1 . Cytoplasm is the fluid content inside the plasma membrane.
2. The primary function of leucoplast is storage
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Answer the following
1. Does plant cell have lysosomes?
Answer: No, plant cells do not have lysosomes.
2. Which is the longest human body cell?
Answer: Nerve cell
3. Name the process by which carbon dioxide and oxygen transported across the plasma membrane.
Answer: Diffusion
4. Where are genes located?
Answer: Genes are located on chromosome.
KSEEB Class 9 Science Textbook Solutions Chapter 5
5. Organelles which show the anology written as under
1. Transporting channels of the cell
Answer: Endoplasmic reticulum
2. Powerhouse of the cell
Answer: Mitochondria
3. Packing and dispatching unit of the cell
Answer: Golgi apparatus
4. Digestive bag of the cell
Answer: Lvsosome
5. Storage sacs of the cell
Answer: Vacuole
6. Kitchen ofthe cell
Answer: Chloroplast
7. Control room of the cell
Answer: Nucleus
6. Name cell organelles having double membrane envelope.
Answer: Nucleus, mitochondria andplastids.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 KSEEB Question Answer
7. Oxysomes are the part of which organelle?
Answer: Mitochondria
8. What is the role of cellulose in cell wall?
Answer: It provides structural strength to plants.
9. Why do plant cells possess large-sized vacuole?
Answer: Vacuoles not only store many important substances, they also contain cell sap that gives turgidity to cell.
10. Name the energy currency of the cell. Which cell organelle releases this energy?
Answer: The energy currency of cell is ATP. The mitochondria is a cell organelle which releases energy
1. State cell theory. Name the scientist who proposed it.
Answer cell theory is
1. All the plants and animals are composed of cells.
2. Cell is the basic unit of life.
3. All cell arises from pre-existing cells.
The cell theory was proposed by Schleiden and Schwann.
2. What are the consequences ofthe following conditions?
1. A cell having higher water concentration than the surrounding medium.
2. A cell having lower water concentration than the surrounding medium.
3. Acell having equal water concentration to it’s sounding medium.
Answer:
1. The cell will lose water by osmosis, therefore the cell will shrink (hypertonic solution).
2. The cell will gain water by osmosis, therefore cell will swell up(hypotonic solution).
3. In case of equal concentration there will be net moment of water, therefore the cell will stay at same size(isotonic solution)
Cell Structure And Functions Explained Class 9 KSEEB Solutions
3. Give few examples where Osmosis is helpful.
Answer:
1. The movement of water in plant cells take place due to osmosis.
2. Absorption of water by the root hairs take place due to osmosis.
3. Osmosis plays a major role in the opening and closing of stomata.
4. Osmosis process help cells, tissues, and soft organs of the plant to maintain turgidity
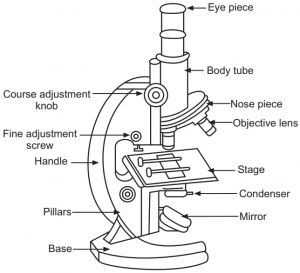
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Diagrams
1. Compound microscope
2. Prokaryotic cell
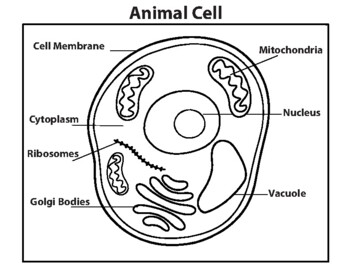
3. Animal cell
4. Plant cell
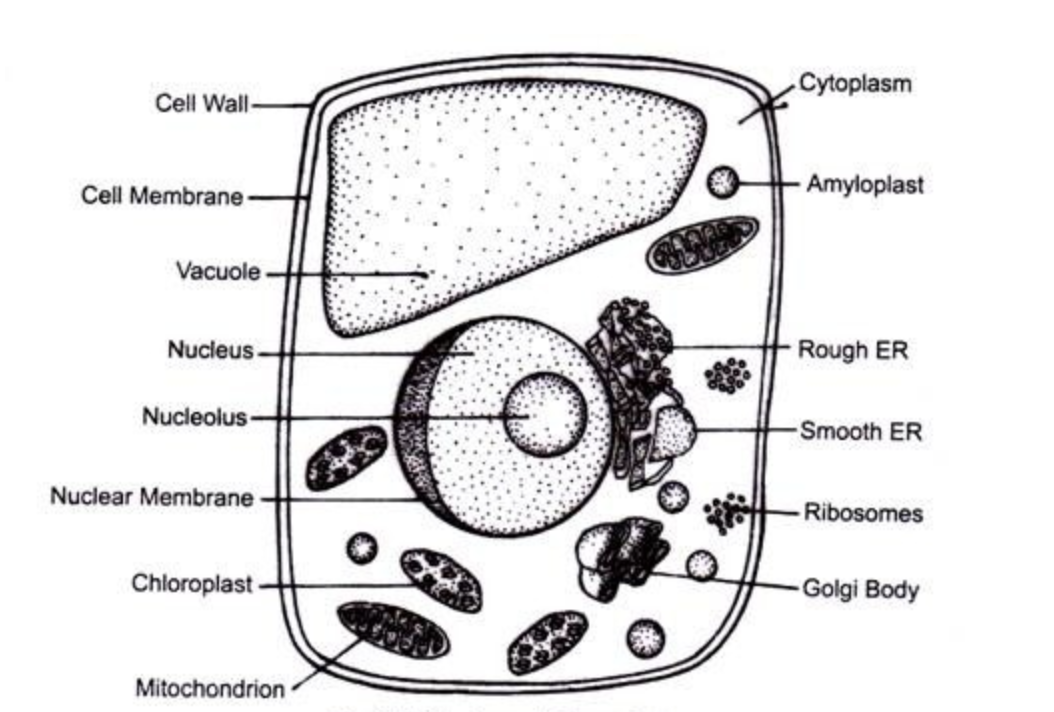
Karnataka Board 9th Science Chapter 5 MCQs
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Activity
1. Experiment: Demonstration of osmosis with hen’s egg.
Answer: Procedure
Take two hen’s eggs and remove their egg shells by putting them in dilute hydrochloric acid(HCl). These two processed eggs are now enclosed by thick outer skincalled shell membrane.
1. Put one processed egg in pure water in a beaker and observe for 3-5 minutes.
2. Put other processed egg in concentrated salt solution another beaker and observe for 5 minutes.
Observation
1. First egg, placed in pure water swells up.
2. Second egg, placed in concentrated salt solution shrinks.
Conclusion
1. The first egg is kept in hypotonic solution has lesser concentration of solute and greater concentration of water than inside the egg contents. Due to osmosis, more water molecules move into the egg through semipermeable shell membrane. Consequently, the processed egg swells up.
2. The second egg is kept in hypertonic solution which has greater concentration of solute and lesser concentration of water than the inside of the egg contents. Due to osmosis, the egg contents lose water to the surrounding hypertonic solution through semipermeable shell membrane. Consequently, the processed eggs shrink
2. To demonstrate plasmolysis in Rheo leaf cells.
Answer: Procedure:
Take a clean glass slide and put few drops of water on it. Now place a complete Rheo leaf in water and examine the cells of leaf under the high power of compound microscope. Put a few drops of concentrated salt or sugar solution on the mounted Rheo leaf on the glass slide. Wait for a minute and again observe the leaves under the high power of compound microscope.
Observation
1. In the first instance, you will locate cells having small green granules i.e, chloroplast containing chlorophyll pigments. These are turgid cells(plasma membrane)
2. In the second instance when we put a few drops of salt solution on the mounted leaf, you will observe that the cell contents are separated from the cell wall.
Conclusion
Plasmolysis has occurred due to exosmosis, i.e, loss ofwater from the vacuole of leaves cells to the surrounding hypertonic medium.
