KSEEB Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surrounding Important Concepts
Types of matter, states of matter, characteristics, change of state – Melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation and sublimation.
Matter
- Matter is a substance which occupies space and has mass.
- Matter exists in three different physical states – solid, liquid and gas.
- Plasma is the fourth state of matter.
- The states of matter are interconvertible.
Change of state
The state of substance depends upon temperature and pressure.
Eg: Water exists as solid at 0°C, as liquid at room temperature whereas in gaseous state at 100°C.
Read and Learn More KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science
Melting and melting p point
The process in which solid changes into liquid is called melting. The temperature at which solid changes into liquid completely is called melting point.
Boiling and boiling point
The process of converting liquid into vapour is called boiling. The temperature at which liquid changes into gas vapour is known as boiling point.
| Class 9 Social Science | Class 9 Science | Class 9 Maths |
Sublimation
The process in which a solid state directly changes into gaseous state on heating or vice versa on cooling.
Condensation
The process in which a gas changes into liquid state by giving out heat at constant temperature.
Vaporization
It is a process in which liquid changes into vapour. It is a surface phenomenon.
It takes place at all temperatures.
Evaporation
It is a surface phenomenon. Particles from the surface present in the liquid and changes into the vapour state. Evaporation causes cooling.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1
Kelvin
Kelvin is the S.I. unit of temperature.
0°C = 273.16K (273K)
To change the Kelvin into Celsius scale subtract 273.16 from the temperature given in Kelvin. For converting 0°C to Kelvin (K) add 273.16.
Pascal
It is the S.I unit of pressure. 1 atm= l.OlxKfpa

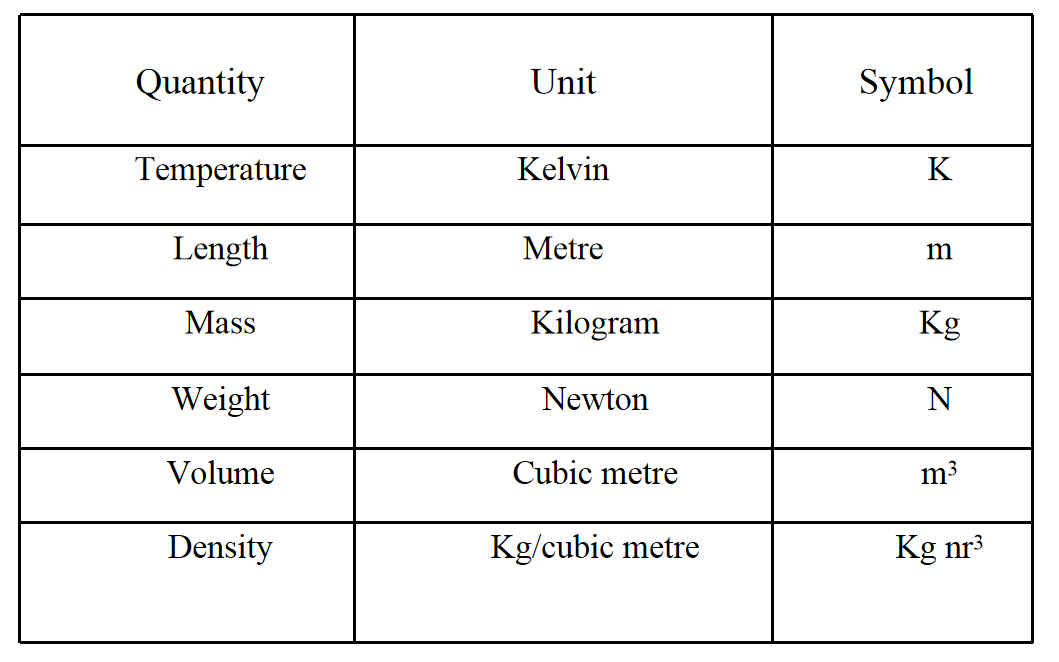
Measurable quantities and their units

Matter In Our Surrounding Exercises
Question 1. Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale,
a. 293Kb. 470K
Answer
1. Temperature in the Celsius scale
= 293 – 273 = 20°C
293K = 20°C
2. Temperature in the Celsius scale = 493 – 273 m 197°C 470K = 197°C
Question 2. Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
a. 25°C b. 373°C
Answer
1. Temperature in Kelvin = 25 + 273
— 298K = 25°C – 298K
2. Temperature in Kelvin – 373 + 273 = 646K
= 373°C = 646K
KSEEB Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings Solutions
Question 3. Give reasons for the following observations.
a. Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
b. We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer
1. By absorbing heat from the surroundings naphthalene balls slowly sublime, i.e solid naphthalene balls directly get converted into vapours and disappear with time without leaving any solid.
2. The molecules of perfume when entering in the air, diffuse in all directions as they are volatile and, therefore we can smell the perfume sitting several metres away.
Question 4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer Oxygen, water and sugar.
Question 5. What is the physical state of water at___
a) 25°C b)0°C c) 100°C
Answer
1. In liquid state at 25°C.
2. In solid state at 0°C, when the heat is removed from it.
3. In gaseous state at 100°C when the heat is
supplied to it.
6. Give two reasons to justify____
a) water at room temperature is a liquid.
b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer
a. 1. Intermolecular spaces are large.
2. Intermolecular forces are less and kinetic energy is more.
b. 1. Intermolecular forces are very large.
2. Intermolecular spaces and kinetic energy are very small.
Question 7. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer When the ice at 0°C (273K), there will be a change in phase, whereas in case of water at 0°C (273K) there will be no change in phase. Hence, lesser energy will be taken from the medium.
Question 8. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer Steam produces more severe bums. Steam has the highest specific latent heat of vapourisation.
Question 9. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
Answer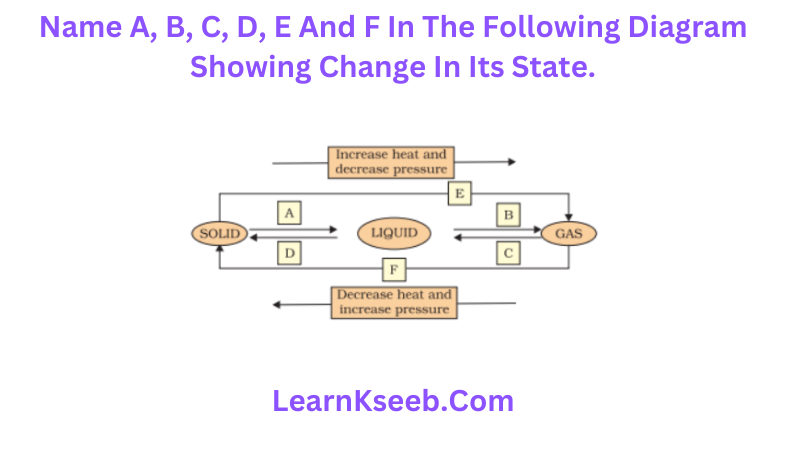
- Solid changes into liquid state by process of melting.
- Liquid state changes to gaseous state by the process o (Vaporization or boiling.
- Gaseous state changes to liquid state by the process of condensation.
- Liquid state changes into gaseous state by the process of freezing.
- Solid changes into gaseous state by the process of sublimation.
- Gas changes into solid by the process of sublimation.
Matter In Our Surrounding Textual Questions
Question 1. Which of the following are matter? (Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cool drink and smell of perfume).
Answer Matter – chair, air, smell, almonds, cool drink
Question 2. Give reasons for the following observation,
a. The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer The smell of hot sizzling food particles possesses large kinetic energy and diffuses in air rapidly and reaches several metres away, whereas the particles of cold food process less kinetic energy and are not able to reach several metres away.
Question 3. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer The force of attraction between the particles is not strong. This is a property of liquid. These are spaces in between the particles of water.
Question 4. What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Answer
1. All matter (elements or compounds) consists of very small particles which can exist independently and are called molecules.
2. There are intermolecular spaces in between the particles of matter.
3. Particles move continuously and possess kinetic energy
Karnataka Board Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Notes
Question 5. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density – mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density – air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk cotton and iron.
Answer The order of increasing density is exhaust from air, chimneys, cotton, water honey, chalk and iron.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 KSEEB Textbook Solutions
Question 6. a. Tabulate the difference in characteristics of states of matter.
b. Comment upon the following. Rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Question 7. Give reasons.
a. A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Answer The particles of a gas are constantly moving in all directions and hence they completely fill the vessel in which they are kept.
b. A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Answer The particles of gas move in all directions with different speeds and the particles of the gas collide with one another and also against the walls of the container.
c. A wooden table should be called a solid.
Answer A wooden table has definite shape, fixed volume and is rigid.
d. We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a Karate expert.
Answer We can move our hand easily in air because the force of attraction between the particles of a gas is very weak. The particles of solid are very closely packed the force of attraction is very strong. Hence we need Karate expert to break a wood.
Question 8. Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice Boats on water. Find out why?
Answer The density of ice is lower than that of water and hence ice floats over water.
Question 9. Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale.
a. 300K b. 573K
Answer a. 300K = 300-273 = 27°C
b. 573K= 573-273 = 300°C
Question 10. What is the physical state of water at
a. 250°C b. 100°C
Answer a. The physical state of water at 250°C is gaseous state i.e steam.
b. The physical state of water at 100°C is liquid as well as gas.
Question 11. For any substance why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer During the change of state, heat is absorbed but this heat gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the force of attraction between the particles, thus there is no change in temperature although heat is being absorbed constantly.
Question 12. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer By cooling the gases under high pressure and lower temperature, the atmospheric gases can be liquefied.
Question 13. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer In a hot dry day temperature of the atmosphere is high and the humidity of air is low. Both these factors increase the rate of evaporation and thus enormous cooling is produced.
Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings KSEEB PDF
Question 14. How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Answer An earthen pot has small pores in the walls. The water oozes out slowly as it comes out of the surface of earthen pot, it evaporates. Hence evaporation makes earthen pot become
cool during summer.
Question 15. Why does our palm feel cold can we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer Acetone or petrol or perfume has low boiling points. When these are put on the palm, they quickly evaporate.
Question 16. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer The rate of evaporation is faster in saucer because of the surface area.
Question 17. What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Answer In summer we sweat more, therefore to keep our body cool we must wear cotton clothes, since cotton clothes are good absorber of water.
Matter In Our Surrounding Additional questions
Question 1. Give examples in which matter is present in the plasma state.
Answer Fluorescent tube and neon sign bulbs.
Question 2. Which gas is called dry ice? Why?
Answer Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice because solid carbon dioxide gets converted directly into gaseous state without coming into liquid state when is kept pressure is kept constant at 1 atmosphere.
Question 3. Convert -10°C Into Kelvin scale.
Answer -10°C = -10 + 273 = 263K.
Question 4. What is the difference between a gas and a vapour?
Answer Gas will be in the stable state. Eg: Oxygen, nitrogen. Vapour will be in the unstable state.
Eg: Water vapour.
Question 5. Which phenomenon occurs during the following changes?
1. Formation of clouds.
Answer a. Condensation
2. Drying of wet clothes.
Answer b. Evaporation
3. Size of naphthalene balls decreases.
Answer c. Sublimation
Question 6. Can solid diffuse into solid? Give example.
Answer Yes solid diffuses into solid.
Eg: Chalk gets diluted into board.
KSEEB 9th Science Chapter 1 Exercise Solutions
Question 7. What is the fifth state of matter?
Answer Bose-Einstein condensate.
8. How interconversion of matter can be achieved?
Answer
1. By changing the temperature,
2. By changing the pressure.
Question 9. Why alcohol is more volatile than water?
Answer The boiling point of alcohol is 7 8°C which is lower than that of water 100°C, therefore alcohol is more volatile than water.
Question 10. What happens when a solid is heated?
Answer First solid changes into liquid and then to gaseous state.
Matter In Our Surrounding High-order thinking questions
Question 1. Out of dry and wet air which is heavier?
Answer Wet air is heavier than dry air because water vapours are heavier than air.
Question 2. Give reasons
1. A gas fills the vessel in which it is kept.
Answer a. The force of attraction between the particles of gas is very less and particles move freely in all directions.
2. A wet handkerchief is placed on forehead of a person suffering from fever.
Answer Evaporation cause cooling.
3. When sugar crystals dissolve in water, the level of water does not rise appreciably.
Answer c. Particles of sugar crystals occupy the space between the particles of water,
4. A wooden table should be called a solid.
Answer Wooden table has a fixed shape as well as fixed volume.
Question 3. Conversion of solid-state to liquid state is called fusion. What is meant by latent heat of fusion?
Answer The amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid at one atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as latent heat of fusion.
Matter In Our Surrounding Unit Test Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Evaporation is called as _____
- Surface phenomenon
- Bulk phenomenon
- pressure phenomenon
- Unique phenomenon
Answer (1)
Question 2. When water gets solidified into ice, then heat is_____
- Evolved
- Absorbed
- First absorbed then evolved
- Initially evolved and then absorbed
Answer (1)
Question 3. Seetha visited an LPG unit and found that the gas can be liquefied at specified conditions of temperature and pressure. Help her to identify the correct set of conditions.____
- High temperature and high pressure
- Low temperature and low pressure
- Low temperature and high pressure
- High temperature and low pressure
Answer (3)
Matter In Our Surrounding Fill in the blank
1. The temperature at which solid changes into liquid is
called melting point
2. The physical state of Iodine is solid
3. ST unit of temperature is Kelvin
Matter In Our Surrounding Answer the following
1. Why oxygen is called gas?
Answer Oxygen has neither fixed shape nor fixed volume. Oxygen diffuses in air easily.
Question 2. Arrange honey, water and hydrogen in descending order on the basis of following properties exhibited by them.
a. Kinetic energy b. Density
Answer:
kinetic energy – Hydrogen > water > honey Density – Honey > water > hydrogen
Question 3. At what temperature vaporization takes place?
Answer At all temperatures.
Question 4. Why do we feel cool after applying shave lotion or perfume?
Answer Because shave lotion or perfume gets evaporated and causes cooling.
Question 5. The following triangle exhibits inter-conversion of three states of matter. Complete the triangle by labelling the arrows marked A, B, C and D. Liquid
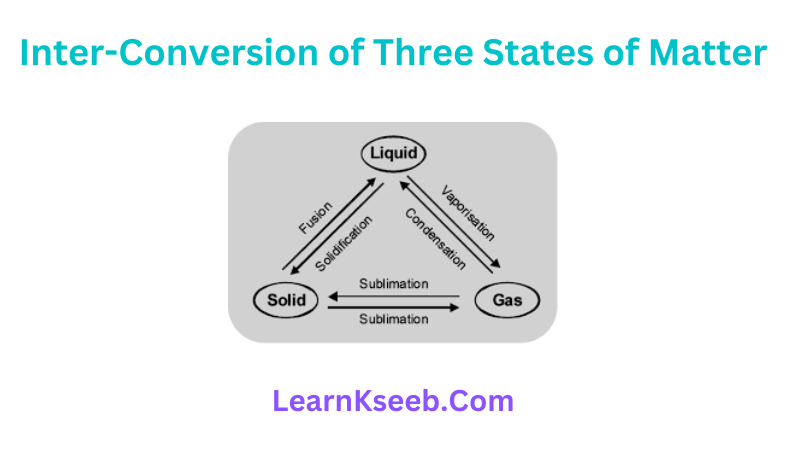
Answer
- Fusion
- Vaporization
- Condensation
- Sublimation
Activity
Question 1. To demonstrate that particles of matter have space between them.

Answer Take a 100 ml beaker. Fill half the beaker with water and mark the level of water. Dissolve some salt with the help of a glass rod.
1`. Where does salt disappear?
Answer 1 . When we dissolve salt in water, the particles of salt get into the spaces between particles of water.
Question 2. To show that rate of intermixing increases the temperature.
Answer Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water and another containing cold water. Do not stir the solution. Allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
KSEEB Class 9 Science Textbook Solutions Chapter 1
1. Does the rate of intermixing increase the temperature?
Answer Yes, with increase in temperature the kinetic energy of the particles increases. As a result, the rate of intermixing increases and hence the solid dissolves more quickly in hot water than in cold water.
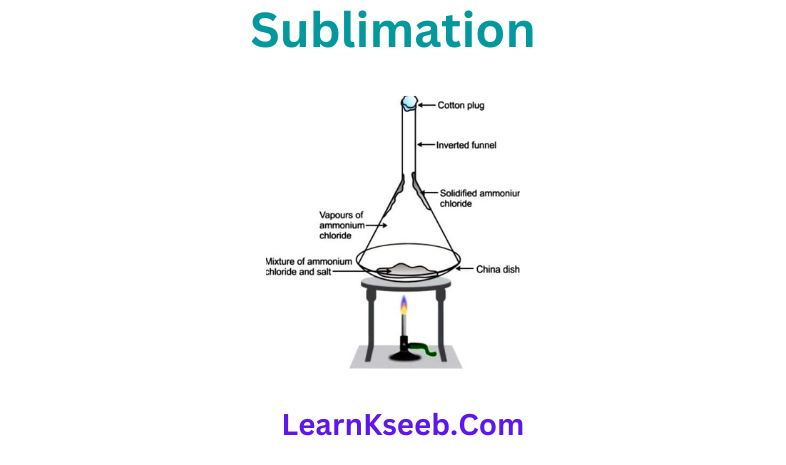
Question 3. To demonstrate the process of sublimation.
AnswerTake some camphor or ammonium chloride, crush it and put it in a China dish. Put on inverted funnel over the China dish. Put a cotton plug on the stem of the funnel and heat slowly and observe.
1. What do you infer from the above activity?
Answer A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state or vice versa is called sublimation.