KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Questions
Question 1. Answer the following questions:
(a) Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation?
Answer. Temperature and precipitation are the main climatic factors responsible for soil formation.
(b) Write any two reasons for land degradation today.
Answer. There are many factors which lead to degradation of land. Both nature and human factors can lead to degradation of land.
(a) Growing population and their ever growing demand is the main reason of land degradation today.
(b) Deforestation is another main reason of land degradation.
(c) Why is land considered an important resource?
Answer. Land is considered an important resource because:
(a) It is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forest, mining, pastures, etc.
(b) Human beings make their houses and idea on it and it also provides most of the products they need like food, wood, etc.
(c) Human beings set up their industries, build roads and run other commercial activities.
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Solutions Pdf
(d) Name any two steps that government has taken to conserve plants and animals.
Answer. In order to conserve plants and animals, the government has taken the following steps:
(a) Many National Paries, Wildlife Sanctuaries and Biosphere Reserves have been established to protect and conserve wildlife.
(b) In India, killing of lions, tiger’s, deer, great Indian bustards and peacocks have been banned.
(e) Suggest three ways to conserve water.
Answer. Water is a vital resource for development of economic activities. Water should be conserved in the following ways:
(a) Water pollution should be prevented. Water of ocean and rivers and lakes should not be polluted. It should be saved from urban waste and chemicals of industries.
(b) Dams should be built across the rivers and lakes to store water in reservoirs.
(c) Forests and other vegetation cover slows the surface run off and replenishs underground water.
(d) Water harvesting is another method to save surface run off.

Sslc Class 8 Geography Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Question And Answers
Question 2. Tick the correct Answer
(a) Which one of the following is not a factor of soil formation?
(a) Time
(b) Soil texture
(c) Organic matter.
Answer. (b) Soil Texture.
(b) Which one of the following methods is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes?
(a) Shelter belts
(b) Mulchirg
(c) Terrace cultivation.
Answer. (c) Terrace Cultivation.
(c) Which one of the following is not in favour of the conservation of nature?
(a) Switch off the bulb when not in use.
(b) Close the tap immediately after using.
(c) Dispose pol/packs after shopping.
Answer. (c) Dispose pol/packs after shopping.
Class 8 Geography KSEEB Land, Soil, Water Notes
Question 3. Match the following:
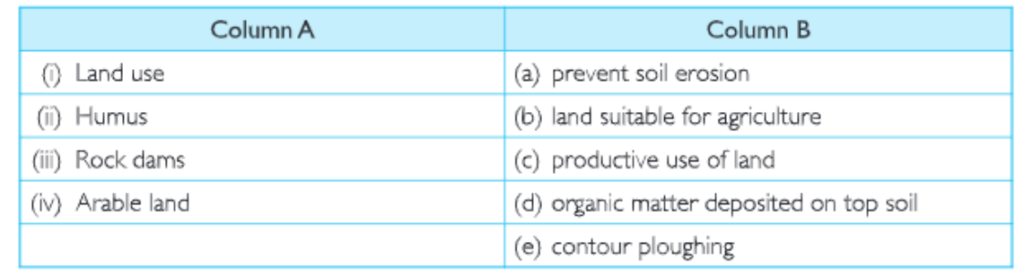
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Textbook Solutions
Answer. (i) (c); (b) (d); (c) (a); (d) (b).
Question 4. State whether the given statements are true or false. If true, write the reasons.
(a) Ganga-Brahmaputra plain of India is an ever-populated region.
Answer. It is true.
The Ganga-Brahmaputra plain of India is an over-populated region because this plain is formed by the rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra and their tributaries. This plain has fertile soil, which is good for agriculture. It is flat and level. It is very easy to construct roads, build houses and set up industries in this region. So it is thickly populated.
(b) Water availability per person in India is declining.
Answer. it is true.
India’s population is increasing rapidly, but we cannot change the amount of water available to us. It is constant. Due to increasing population, its demand is also rising.
(c) Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas, to check the wind movement, is called inter cropping.
Answer. it is false.
(d) Human interference and changes of climate can maintain the ecosystem.
Answer. it is false.
KSEEB Class 8 Geography Solutions For Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, And Wildlife
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Text Questions
Question 1. Observe the land, type of soil and water availability in the region you live. Discuss in your class, how it has influenced the lifestyle of people there.
Answer. Do it as per the instructions given.
Question 2 Talk to some elderly person in your family or neighbour hood and collect information about changes in the land use over years, where you live. Display your findings on a bulletin board in your classroom.
Answer. Do it as per the instructions given.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Activity
Question 1 . In India, soils could be alluvial, black, red, laterite, desertic and mountain soil. Collect a handful of different types of soil and observe how they are different?
Answer. Do it as per the instructions given.
Question 2. Take two trays A and B of same size. Make six holes in the end of these trays and then fill them with the same amount of soil. Leave the soil in tray A bare while grow grass in tray B. When the grass in tray B has grown few centimetres high, place both the trays in such a way that they are on a slope. Pour one mug of water from the same height into trays. Collect the muddy water that trickles down the holes of both trays in two separate containers and compare how much soil is washed out of each tray?
Answer. Do it as per the instructions given.
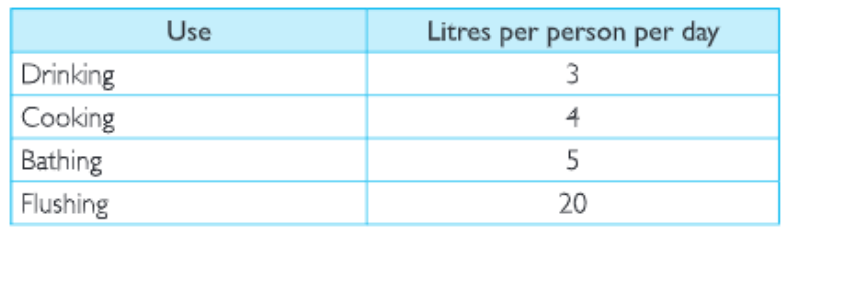
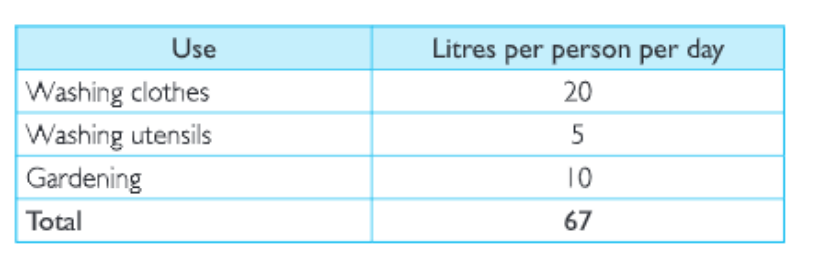
Question 3. An average urban Indian uses about 135 litres of water every day
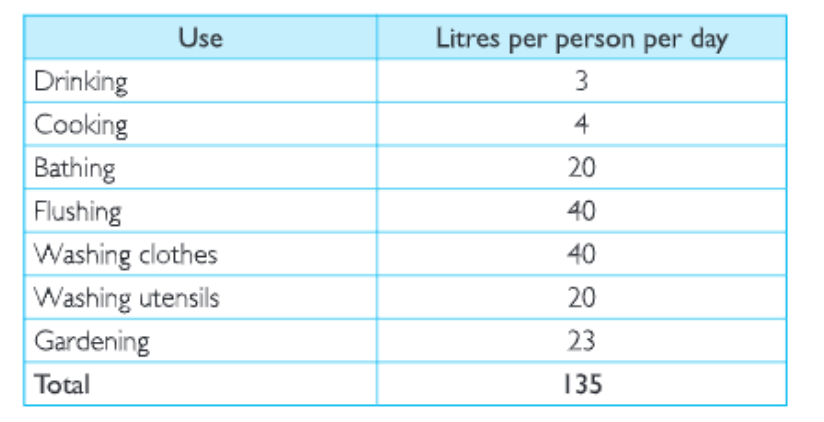
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Class 8 Geography Kseeb Important Questions
Can you suggest some ways to bring down this use?
Answer. We can save water by reducing its misuse. The following table will help in reducing water usage
Question 4. Study the given table and Answer the following questions:
Land Use in Selected Countries
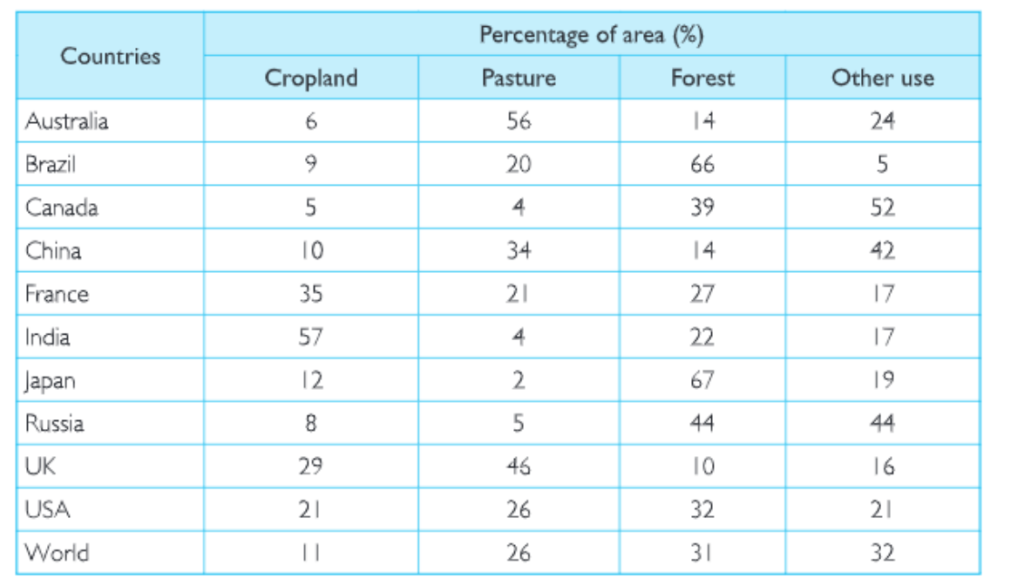
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Solved Exercises
(a) Name the countries having the highest percentage of land under cropland, forest, pasture and other uses.
(b) How would you relate the land use patterns of these countries with the probable economic activities?
Answer. (a)
(a) India has the highest percentage of land under cropland.
(b) Japan has the highest percentage of land under forest.
(c) Australia has the highest percentage of land under pasture.
(d) Canada has the highest percentage of land under other uses.
Answer. (b)
(a) India is an agricultural country so it uses maximum land for the crops.
(b) Japan has mountainous land and it is covered with the forests. These forests are used as natural resources.
(c) Australia’s pasture land is very useful for cattle rearing.
(d) Canada uses its resources for Paper and Pulp industry.
Land, Soil, Water, and Natural Vegetation Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Additional Questions (Solved)
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Name the human requirements obtained from land.
Answer. Food, crops, clothing, wood for fuel, construction and housing.
Question 2. What is meant by conservation?
Answer. It means to use the natural resources carefully without wastage.
Question 3. What do you mean by land use?
Answer. The use of land for different purposes like agriculture, roads.
Question 4. Which is the most important resource for human beings?
Answer. Land is the most important resource for human beings.
Question 5. Name the physical factors which influence land use pattern.
Answer. Topography and soil.
Class 8 Geography Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Notes Karnataka Board
Question 6. Name two areas which are densely populated.
Answer. Plains and river valleys are densely populated.
Question 7. Give two reasons for dense population in plains and river valleys.
Answer.
(a) The land is flat and good for agriculture.
(b) Construction of roads is very easy.
Question 8 .What is land use pattern?
Answer. The proportion of land put to different uses is called land use pattern.
Question 9. For which purposes is land used?
Answer. Land is used for following purposes:
(a) Building houses
(b) Construction of roads
(c) Cultivation of crops
(d) Grazing
(f) Manufacturing
(g) Mining.
Question 10. Name three kinds of areas which are normally sparsely populated or uninhabitated.
Answer. The rugged topography, steep slopes of mountains and desert areas are normally sparsely populated.
Question 11. Which physical factors determine land use?
Answer. The use of land is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals and availability of water.
Question 12. Which human factors are determinant of lard use pattern?
Answer. Population and technology.
Question 13. On which basis we can divide land?
Answer. We can divide land on the basis of private land and community land.
Question 14 . Which land is also called common property resources?
Answer. Community land is also called common property resources.
Question 15. What is responsible for rapid depletion of all kinds of resources?
Answer. Increasing consumption of resources and population growth.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Class 8 Geography Summary And Explanation Kseeb
Question 16. Give one reason for variation in the level of development in world.
Answer. Highly uneven distribution of resources.
Question 17. What is fallow land?
Answer. A piece of land left uncultivated after two or three years, to restore its fertility.
Question 18. Write any two methods of land conservation.
Answer.
(a) Afforestation;
(b) Checks on over-grazing.
Question 19. What is landslide?
Answer. Landslides are the mass movement of rock, debris or earth down a slope.
Question 20. Name two factors responsible for landslides.
Answer. Earthquakes, floods and volcanoes.
Question 21. Name any two methods of soil conservation
Answer. Afforestation, building of bunds or check dams.
Question 22. Mention two types of soil erosion.
Answer. Wind erosion, gully erosion.
Question 23. Mention three physical factors causing soil erosion.
Answer.
(a) Velocity of wind;
(b) Intensity of rainfall;
(c) Slope.
Question 24. Write four human factors causing soil erosion.
Answer.
(a) Deforestation
(b) Over-grazing
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Poor agriculture practices.
Class 8 Kseeb Geography Conservation Of Natural Resources And Wildlife
Question 25. What are the elements of soil?
Answer. It consists of Doth organic and inorganic substances.
Question 26.Why the soil must be fertile?
Answer. Because the growth of plants and crops depends on the fertility of the soil.
Question 27. What is meant by land degradation?
Answer. Degradation of land means rendering the land unfrt for cultivation.
Question 28 . Name any two human activities responsible for land degradation.
Answer.
(a) Over-grazing;
(b) Deforestation.
Question 29. Mention two serious problems careless use of land can lead to.
Answer. Soil erosion and shortage of crop land.
Question 30. Name two ways by which soil can be conserved in hilly and mountainous areas.
Answer.
(a) Terrace farming;
(b) Contour farming.
Class 8 Geography Kseeb Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Short And Long Answer Questions
Question 31. How much part of the Earth is covered with water?
Answer. About 71 %.
Question 32. By which method can the complete disinfection of drinking water be done?
Answer. Through chlorination.
Question 33. Name a water saving technique of irrigation.
Answer. Sprinklers or drip irrigation.
Question 34. How can surface water be conserved?
Answer. Surface water can be conserved by rain water harvesting method.
Question 35. What is meant by wildlife?
Answer. It refers to a variety of life forms like birds, animals, insects, fishes which live in a natural habitat
Question 36. Name two factors that influence plant growth.
Answer.
(a) Temperature;
(b) Moisture.
Question 37. What is a biosphere?
Answer. A thin zone of contact between lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Question 38.What is an ecosystem?
Answer .In the biosphere living beings are interrelated and interdependent on each other for survival. This life supporting system is called the Ecosystem.
Question 39.What are the major vegetation types of land in the world?
Answer The major vegetation types of the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, shrubs and tundra.
KSEEB Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Important Questions
Question 40.What is afforestation?
Answer Planting of trees in new areas is known as afforestation.
Question 41.Mention the two ways by which wildlife is conserved.
Answer Wild life is conserved through National parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves.
Question 42 .Give full form of CITES.
Answer CITES means the Conservation of International Trade Endangered Species of wild fauna and flora.
Question 43 .Name two awareness programmes relating wildlife.
Answer Social forestry and Vana Mahotasava.
Question 44.Which products are obtained from forests and wildlife?
Answer. Wood, barks, leaves, rubber, medicines, dyes, food, fuel fodder, manures, etc.
Question 45. How much percentage of the total area of earth is covered by land?
Answer. 30%.
Question 46. Name two methods of saving water.
Answer.
(a) Rain water harvesting;
(b) Sprinkle irrigation.
Question 47. Why is the sea water not useful for human beings?
Answer. The sea water is saline. So it is not fit for human consumption.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Write a note on conservation of forests.
Answer. Forests are the important components of our environment. Rapid destruction of this important resource has been a cause of concern. Hence, we need to conserve this renewable resource. One of the most important measures of forest conservation is to plant trees, i.e., afforestation. Besides, preventing the reckless cutting of trees and creating an awareness about the importance of forests among all communities may help conserve the forests.
Question 2. What are the factors that control soil formation?
Answer.
Soil formation is controlled by five factors. These are:
(a) Nature of parent rock
(b) The topography
(c) The climate
(d) The organism in the soil
(e) Time.
Question 3. What shows the changes in land use pattern!
Answer.
The changing of land use pattern clearly indicates rise in yield of food-grains per hectare o’ land area. The cumulative yield has risen from 552 <g in 1951 to 1697 kg in 2000 which represents more than three times increase. It clearly shows the charge in land use pattern.
Question 4.What is the main cause of changing of land use pattern?
Answer. In some parts, forests are changed into crop lands and agricultural land is converted into buildings, factories, roads and air ports.
Question 5. Loose soil with less vegetation is more exposed to erosion. Why?
Answer. Loose soil with less vegetation is more exposed to erosion because if there is less vegetation, the running water carries the soil down the slopes and also it is carried by high velocity winds.
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation And Wildlife Mcqs With Answers
Question 6. What is the difference between private land and community land?
Answer. Land can be divided on the basis of private and community’ land. Private land is that land which is owned by individuals and it is used by them to fulfil their requirements. Whereas, the land owned by a particular community to fulfill their common needs and requirements, it is called Community land. It is used for collection of fodder, fruits, nuts or medicinal herbs etc. These community lands are also called common property resources.
Question 7. Give a brief account of Mamba’s family.
Answer. Mamba lives in a small village in Tanzania, Africa. She lives with her family. Her father is a small farmer who works hard in the fields. Her mother is a house lady. Her brothers take care of goats. She helps her family in the work.
Question 8. What do you know about Peter and his family?
Answer. Peter lives in New Zealand. His family runs a wool processing factory. Peter is a student After his school, he helps his uncle. Their sheep yard is situated on a wide grassy plain with hills in the far distance. It is equipped with the latest technology. They also grow vegetables through organic farming.
Question 9. Why does soil lose its fertility?
Answer. The soil loses its fertility when it is continuously used. When crops are grown every year it loses its nutrients, which are necessary for good soil.
Question 10. List four factors responsible for soil erosion.
Answer. The four factors responsible for soil erosion are:
(a) Deforestation or removal of forests.
(b) Over-grazing of land especially by goats and sheep.
(c) Velocity of winds-when winds ta<e the shape of dust storms they lead to soil erosion.
(d) Intensity of rainfall-Torrential rains cause greater erosion.
Question 11. In what way can we check soil erosion from wind action in a dry region?
Answer. We can check soil erosion from wind action in a dry’ region by growing trees in rows. It will check the movement of the w ind and protect the soil cover.
Question 12. What is meant by conservation?
Answer. Conservation means to conserve. It means to use the natural resources carefully without wastage. They are important to us, so they should be used wisely so that they are not exhausted and we may have to face their scarcity. Conservation allows generations to enjoy the things which the people are enjoying today.
Question 13. What factors control the utilisation of land?
Answer. The physical and human factors control the utilisation of land. These include:
(a) Relief of features;
(b) Climatic conditions;
(c) Soils;
(d) Density of population;
(e) Technical level j of the people;
(f) Land tenure;
(g) Duration of the occupation of the area, etc. The interplay of j physical and human factors has developed many types of land uses.
Question 14. What is soil?
Answer. The upper most layer of the earth’s crust is called soil. It is loose, fragmented and useful for plants.
Question 15. What are alluvial soils?
Answer. These soils are formed by the deposits brought down by the rivers year after year. These are very-fertile soils.
Question 16. What factors control the cultivation of land in India?
Answer. India is the only country in the world having the highest percentage of land (57%) under cropland. Land is needed to produce food camps for human beings and raw materials for industries. All types of land cannot be cultivated. The cultivation of land depends upon:
(a)The fertility of soil;
(b) The relief of the land;
(c) The availability of water,
(d) The need of the people.
Question 17. What is landslide? What are its factors?
Answer. The mass movement of rock, debris or earth down a slope is defined as landslide. It is often caused by earthquakes, floods and volcanoes. A heavy– or long spell of rain can cause heavy landslide. Sometimes, it can block the river flow for quite sometime.
Simplified Notes for KSEEB Class 8 Land, Soil, Water, And Wildlife
Question 18. What are the reasons of forest fire?
Answer. Forest fire is a major threat to entire region of flora and fauna. There are three main reasons of it are:
(a) Natural fire due to lightning.
(b) Fire due to heat generated in the litter due to carelessness of people.
(c) Purposely caused fire by local inhabitants.
Question 19. List three basic ways through which energy s obtained.
Answer. Energy is the capacity to do work. It car be obtained by:
(a) Direct heating like: fire, sun, etc.
(b) Electricity
(c) Stored energy in the form of a battery-.
Question 20. Discuss the factors influencing the plant and wild life resources.
Answer. There are many factors which influence the pant and wild life resources.
(a) The environment has a great influence or the type of organism living in an area.
(b) The climatic conditions also bring variations in the types of plants and animals which are found in a particular region.
(c) Moisture and temperature affect the plants. The areas with heavy rainfall, have thick forests and as rainfall decreases, the forests also become scarce.
Question 21. What are the different techniques of rain water harvesting?
Answer. The different techniques for rain water harvesting are:
(a)Construction of percolation pits, trenches and fields.
(b) Refilling of dug wells.
(c) Roof rain water harvesting,
(d) Bunds and small dams on small rivulets.
(e) Recharging of hand pumps.
Question 22. What is sheet erosion?
Answer. When heavy rains and storm take away the soil cover with its water, it is called sheet erosion. It turns the land into a waste rendering it useless.
Question 23. What is wind erosion?
Answer. In dry areas, particularly in deserts, winds carry away the top layer of the soil and deposit them in other areas. This is called wind erosion and the fertile land is turned into a waste land.
Question 24. What are the features of black soils?
Answer.
(a) These are very good for cotton.
(b) These are generally shallow in depth.
(c) These are derived from metamorphic rocks.
Question 25. What is terrace farming?
Answer. Terrace farming is the growing of crops on level steps or terraces that have been constructed on hillsides.
Question 26. What is a wildlife sanctuary?
Answer. A wildlife sanctuary is dedicated to protect wild life and conserve forests.
Question 27. What are the effects of deforestation?
Answer. The effects of deforestation are as under:
(a) It affects the ecosystem.
(b) It increases soil erosion.
(c) It affects underground flow of water.
(d) Disappearance of wildlife as well as variety of plants.
(e) Leads to serious deterioration of genetic reserves.
Question 28. What are protected forests?
Answer. These are also forests reserved for timber but grazing is allowed subject to minor restrictions. These are 29.2% of the total forests.
Question 29. What is contour ploughing?
Answer. The technique of ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope rather than up and down the slope, so as to reduce soil erosion.
Question 30. What is strip cropping?
Answer. Strip Cropping is the growing of different crops on parallel narrow strips of ground, usually following the contour patterns.
KSEEB Solutions For Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
Question 31. What is a shelter belt?
Answer. In dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement for protecting soil cover.
These are called Shelter Belts.
Question 32. State the importance of forests.
Answer. Forests play an important role in human life They provide food, wood and timber to us. Many medicinal plants are found in the forests. They also help in maintaining ecological balance and checking soil erosion. They play an important role in the economy of our country-.
Question 33. Discuss the ways to preserve wildlife.
Answer. Ways to preserve wildlife are:
(a) We should not cut trees thought lessely for our needs so that wildlife may survive and multiply there.
(b) We should not hunt them during the mating season.
(c) There should be a total ban on hunting.
(d) We should grow more trees.
(e) We should co-operate with the government in their efforts to preserve wildlife.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is the most important feature of land use pattern in India?
Answer.
(a) India has total geographical area of 828 million sq. km. (3280 lakh hectares). The land use data is available for about 93% of the total area, h shows that in 2007-08, 140 million hectares (46%) is net sown area. Thus, India has a very high percentage (47%) of total area under cultivation. No other big country has such a large area under cultivation.
(b) Another satisfying feature is that 8.2% land is fallow’ land which is not cultivated so as to restore the fertility of the land. It is notable that fallow land has risen to 8.2% in 2007-08 from earlier figure of 6.4% in 1970-71. It reflects that care for land resources has become essential.
(c) The area under pastures is also small (3.4% in 2007-08).
(d) The a^ea under cultivable waste is 4.3%. This waste land can be brought under cultivation to increase productivity.
(e) The forest cove-* is low, only 23%. It is desirable to have about one third of the total land area under forests to maintain a healthy environment
Question 2. Explain the factors controlling soil formation.
Answer. Soil formation is controlled by five factors;
(a) Parent Rock: The original rock called parent rock, from which the soil is formed, determines its basic characteristics. For example, shales contribute clays, while sand stones contribute sand grains.
(b) Climate: Temperature and precipitation are the main climatic factors affecting soil formation. Frequent temperature changes and presence of water quicken soil formation through increased weathering.
(c) Topography: Topography affects the drainage of an area. On a steep slope, there is hardly any chance of accumulation of weathered rocks. They are moved down the slope by water and under force of gravity. In plains and areas with gentle slope, soils are accumulated without any hind-ance.
(d) Organisms: Dead plants and animals provide humus to the soil. Organisms like earthworms and ants through their movements create space for air and water in the soil.
(e) Time: Time factor is also important because longer the time for soil formation, more deeper is the soil layer. Besides weathering of rocks, soil is also formed by deposition of materials by moving waters (rivers) and winds in low-lying areas. Alluvial soils of river valleys are very fertile and deep.
Question 3. What are water resources? What are their uses?
Answer. Water is a unique liquid because there is no alternative for it. It is essential for all forms of life. Compared to most other liquids, water has a high capacity to absorb or store heat Water is a major body constituent of several plant and animal species. Seventy per cent of the human body consists of water. Humans use water for various purposes-domestic (drinking, cooking, washing, etc.), agricultural (irrigation), industrial and generation of electricity.
Class 8 Geography KSEEB Land, Soil, Water Notes
Question 4. Explain the factors influencing land use pattern.
Answer. Factors affecting land use pattern. Land is used for different purposes such as cultivation of crops, grazing of animals, building houses and roads, mining and manufacturing. It is called land use pattern. Several factors influence lard use pattern of a country or a region at a given time.
Physical factors: Topography, soil, climate, availability of water and mineral resources determine the probable use of land.
Example:
(a) Fertile plains—They are used as croplands.
(b) Mining—Occurrence of mineral deposits favour mining.
(c) Economic factors Area having low-grade ores may not develop mining owing to its high cost.
(d) Human factors—In densely populated areas, encroachment on forest and croplands may be more for meeting other human requirements like buildings, houses, roads and rails etc.
Question 5. Suggest measures for land conservation.
Answer. Land resources must be conserved to provide food for huge population. The following methods are used:
(a) Terrace Farming: Crops are grown on terraces or level steps on hill sides. It controls shifting cultivation.
(b) Contour Ploughing: Land is ploughed parallel to the contours of hill-slopes, ft avoids soil erosion.
(c) Strip Cropping: It me Answer growing of different crops on parallel narrow’ strips. It reduces gully erosion.
(d) Shelter Belts: In dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check wind action and soil erosion.
Question 6. Describe the characteristics of different types of forests.
Answer. The types of forests are:
A. Evergreen Forests: Trees in these forests do not shed their leaves simultaneously during any season of the year. These forests may also be grouped into
(a) tropical,
(b) mid-latitude evergreen forests,
(c) mediterranean,
(d) coniferous forests.
(a) Tropical Evergreen Forests: Rainfall is very heavy in the equatorial as well as tropical coastal regions. Hot and humid conditions favour luxuriant growth of a variety of vegetation. Trees have broad leaves. There is a very dense growth of vegetation. Canopy of the forest always looks green. These forests have hard wood trees such as mahogany, ebony and rosewood. Their trunks and branches are of dark colour. Cutting of trees for commercial purposes is, therefore, not very easy.
(b) Mid-Latitude Evergreen Forests: These are found on the eastern margins of continents. These forests contain hardw’ood trees with broad leaves. South China, south eastern USA, South Brazil, east coast of South Africa and south eastern Australia have such forests. Oak, eucalyptus, and wattle are some economically important trees of these forests.
(c) Mediterranean Forests: On the western margins of continents in middle latitudes, winter has moderate rainfall and summer is dry. Plants, therefore, have spiny, waxy or small leaves to reduce transpiration. They have deep roots. Barks are also thick so as to prevent loss of moisture. Cork, olde and chestnut are the common trees of these forests.
(d) Coniferous Forests (Taiga Forests): These forests extend as a continuous belt around the North Polar- region and high mountains in Europe, Asia and North America. Trees don’t shed their leaves and hence look evergreen. They are tall and conical in shape. Leaves protect themselves from cold winter. Softwood trees like pine, cedar and fir are found in these forests. They have been in great demand for commercial use.
b. Deciduous Forests: Deciduous forests are those in which trees shed their leaves in a particular season in order to conserve loss of moisture through Aspiration.
(a) Tropical deciduous forests are found in sub-tropical regions with a distinct dry season. Monsoon Asia, parts of Central America, Brazil and Northern Australia have such forests. Trees shed their leaves during summer. Teak, sal and shisham and valuable hardwood trees are of these forests.
(b) Mid-latitude deciduous forests occur in the coastal temperate regions. Western Europe, north¬eastern China, Japan, north-eastern USA, New Zealand and southern Chile have such forests. During winter, temperature in these areas fall below 6°C. Therefore, trees shed their leaves in winter to protect themselves from such cold. Forests cover about 30 per cent of the land area of the world
Question 7. What is soil erosion? What are the causes of soil erosion? Describe the different types of soil erosion.
Answer. The destruction and removal of top soils by running water, wind etc. is known as soil erosion. It has become a major problem in many areas. Soil formation is a very slow process and it takes thousands of years to develop soil but it may be removed in a matter of few years. Soil erosion results from the many causes.
Causes of soil erosion:
(a) Steep Slopes: Steep slopes affect the rapidity of running water. On the steep slopes, intensity of soil erosion increases.
(b) Torrential Rainfall: Heavy rainfall loosens the soil particles and scoops out the soil forming gullies and ravines. This gives rise to a dissected surface called badland as in Chambal Valley of India.
(c) Strong Winds: Winds and dust storm bow away soil in dry areas. This process is known as deflation.
(d) Over-grazing: Due to over-grazing, the vegetation becomes too thin to protect the soil. Rain and wind can easily erode the loose soil.
(e) Over-cropping: Crop rotation maintains soil fertility. But over-cropping and shifting cultivation render soils infertile.
(f) Deforestation: Deforestation means the removal of forest cover and it exposes the area of soil erosion. Reckless cutting of trees has resulted in soil erosion by chos along the Shiwalik hills.
Human misuse of the land through wrong farming practices, deforestation, etc. leads to the removal uf soil cover.
Types of Soil Erosion:
(a) Sheet Erosion: When the soil is washed away in thin layers by water or wind, it is called Sheet Erosion. Fine silt and clay is removed from the top soil.
(b) Gully Erosion. It is done by running water by cutting channels. Gullies and ravines are formed by rapid run off. Bad land is formed over clay soils in the Chambal Valley.
Question 8. Write a short note on conservation of soils.
Answer. Soil is a fundamental natural resource. Soil formation is a slow process, but it is easily lost by soil erosion. In fact, more soil is being lost each year than nature makes. Soil erosion must be checked. Sound farming practices and measures be acopted to conserve, protect, renew and maintain soil fertility. These methods constitute soil conservation.
(a) Afforestation: In some areas, the original vegetation cover has been removed such as :n Shiwalik hills. In such areas; afforestation and reforestation is needed to hold the soil. Advance of deserts can be checked by planting trees along the margins of deserts.
(b) Controlled Grazing: The number of catte to be grazed on slopes should be according to the carrying capacity of the pastures.
(c) Terraced agriculture: Slopes must be cut into a series of terraces (fields) for cultivation so as to slow down tone flow of rain water.
(d) Contour Ploughing: It is done to check soil wash on slopes. Ploughing is done at right angles to the hill slopes.
(e) Crop Rotation: Crop rotation system be applied and the land should be allowed fallow for some time. Soil fertility can be maintained in this way.
KSEEB Class 8 Geography solutions for Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife
Question 9. Describe the problems of water quality.
Answer. The main problem of water quality is pollution. Water is being polluted by many means, like untreated or partially treated sewage, agricultural chemicals and industrial effluents are the major contaminants, with nitrates, metals and pesticides as the main problems. As a result, many water supplies are being damaged by pollution, with declining water quality. Human and animal wastes introduce pathogens that cause serious diseases, i.e., cholera, infections, dysentery, etc. This accounts for over three- quarters of all diseases in developing countries. Improvements in water supplies and sanitation could reduce child mortality by more than a half
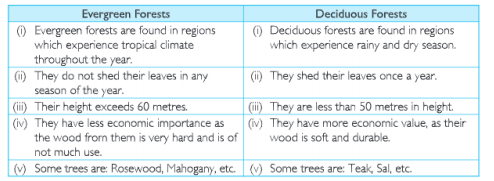
Question 10 .Distinguish between Evergreen Forests and Deciduous Forests.
Answer.
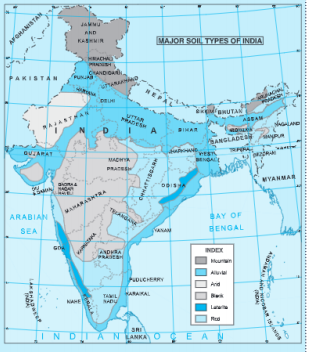
Question 11 .Collect a handful of different types of Indian soils and find out how they are different.
In the following ways, the Indian soils are different:
(a) Alluvial soil: It is laid by rivers. It is fine in nature. It is grey in colour. It is very fertile. The Great no’them plains are formed by this soil.
(b) Black soil: It is formed from volcanic activity. It is made up of lava. It is black in colour. It is fertile and best for cotton cultivation. It is mostly found in the Deccan Plateau.
(c) Red soil: It is red in colour due to high iron content It is developed from old crystalline rock in ‘situ’. These soils are pomus. It is found in Tamil Nadu, Andhara Pradesh,
Oaisha, etc.
(d) Laterice soil: The latehte soil is the result of intense leaching. It is less fertile. The organic matter like nitrogen, phosphate and calcium are low in this soil. It is found in Karnataka, Kerala, Assam, etc.
(e) Desert soils: These are also called arid soils. These are red to brown in colour. These are sandy and alkaline. These are lacking in moisture and humus content is normal. It is found n Rajasthan, Gujarat, etc.
(f) Mountain soils: These soils are mostly thin and infertile. These include peat, meadow and forest hill soils. This soil is mostly found in the mountain areas.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Hots Corner
Question 1. How do landslide prove dangerous?
Answer. Landslides occur due to earthquakes, floods and volcanoes. A long heavy rainfall can cause heavy landslide that can block the flow of river for quite sometime. It can cause havoc to the settlements downstream on its bursting. In the hilly areas, landslides have been a major and widely spread natural disaster that often strike life and property and occupy a position of major concern.
Question 2. What are the role of insects in soil formation?
Answer. Insects play a very important role in soil formation. Without worms and insects, the work of soil formation will Die incomplete. They do it both through physical or mechanical means by speeding up the chemical reactions.
Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Miscellaneous Question
Question 1. Land covers about percent of total surface area of the Earth.
(a) 26
(b) 27
(c) 28
(d) 29
Answer. (d) 29
Question 2. Water occupies percent of surface area of the earth.
(a) 65
(b) 70
(c) 71
(d) 74
Answer. (c) 71
Question 3. Net sown area in India is about:
(a) 44%
(b) 46%
(c) 48%
(d) 50%
Answer. (b) 46%
Question 4. An average urban Indian uses about litres of water daily.
(a) 130
(b) 132
(c) 134
(d) 135
Answer. (d) 135
Detailed Notes On Natural Vegetation And Wildlife KSEEB Geography
Question 5. How much percentage of population occupies 30% land?
(a) 70
(b) 80
(0 90
(d) 95
Answer. (c) 90
Question 6. Which is not a sparsely populated area?
(a) Mountain
(b) Desert
(c) Steep slopes
(d) Plains
Answer. (d) Plains
Question 7. Which is not a major threat to environment?
(a) Land degradation
(b) Landslide
(c) Agriculture
(d) Soil erosion
Answer. (c) Agriculture
Question 8. Which is a common method of conservation of land?
(a) Afforestation
(b) Agriculture
(c) Industry
(d) Dry farming
Answer. (a) Afforestation
Question 9. Mass movement of rock down a slope is called
(a) Reclamation
(b) Afforestation
(c) Terraced farming
(d) Landslide
Answer. (d) Landslide
Question 10. Pangi village where landslide occurred is in state of:
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Jammu and Kashmir
(d) Himachal Pradesh
Answer. (d) Himachal Pradesh
