KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Textbook Questions
Question 1. Answer the following questions:
1 Why are resources distributed unequally over the earth?
Answer. Resources are distributed unequally over the Earth as a number of geographical factors like altitude, terrain and climate are responsible for their distribution and these factors vary widely over the surface of the earth.
2 What is resource conservation?
Answer. Resource conservation is the practice of using the resources carefully and giving them time to get renewed. It is planned and careful use of natural resources, so that these resources can be used for a long period of time.
3 Why are human resources important?
Answer. Human resources are very important as more resources can be created when people have the knowledge, skill and technology to aid them in creating so. In order to make people a valuable resource, education and health plays a major role.
4 What is sustainable development?
Answer. Sustainable development means the careful utilisation of resources so that along with meeting the present requirements, the requirements of the future generation are also taken care of.

Kseeb Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Solutions Pdf
Question 2. Tick the Correct Answer:
1 Which one of the following does not make substance a resource?
(a) Utility
(b) Value
(c) Quantity
Answer. (c) Quantity
2 Which one of the following is a human-made resource?
(a) Medicines to treat cancer
(b) Spring water
(c) Tropical forests
Answer. (a) Medicines to treat cancer
3 Complete the Statement.
Biotic resources are:
(a) derived from living things
(b) made by human beings
(c) derived from non-living things
Answer. (a) derived from living things.
Question 3 Differentiate between the following:
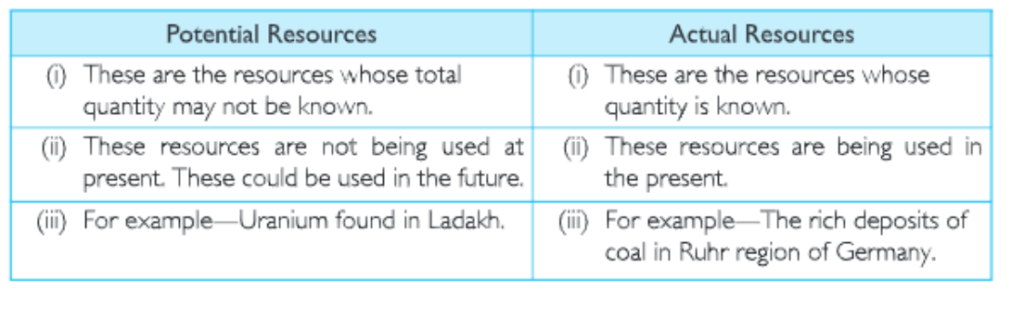
(a) Potential and actual resources
(b) Ubiquitous and localised resources
Answer.
(a) Potential and actual resources
(b) Ubiquitous and localised resources
Sslc Class 8 Geography Resources Question And Answers
Ubiquitous resources: These are those resources which are found everywhere. For example, air, water, etc.
Localised resources: Those resources which are not found everywhere. These are found only in certain places. For example, copper, coal, iron ore, etc.
Question 4 Activity
“Rahiman paani raakhiye, Bin paani sab soon. Paani gaye na ubere Mot}, manus, choon…”
[Says Rahim, keep water, as without water there is nothing. Without water pearl, swan and dough cannot exist.]
These lines were written by the poet Abdur Rahim Khankhana, one of the nine gems of Akbar’s court. What kind of resource is the poet referring to? Write in 100 words what would happen if this resource disappeared?
Answer: The poet is referring to water resources. Water is the most essential for human life. Man cannot survive without water. If this resource disappears, life will cease to exist on Earth. Earth is called a blue planet due to the presence of water on it It forms the basis of life and is of primary concern to human beings as it is directly related to domestic needs and economic activities. There will not be any plant and wildlife {flora and fauna) on Earth. Seas and oceans will dry up. The beauty of earth will vanish.
For Fun
Question 5.
(a) Pretend that you live in the pre-historic limes on a high windy plateau. What are the uses you and your friends could put the fast winds to? Can you call the wind a resource?
(b) Now imagine that you are living in the same place in the year 2138. Can you put the winds to any use? How? Can you explain why the wind is an important resource now?
Answer.
(a) In pre-historic times, technology was not as developed as today. So we couldn’t use fast winds. At this time, wind is a potential resource.
(b) In 2138, due to the advancement in technology, I can use wind for generating electricity through windmills and also for running machines.
Wind is an important resource now because at this time (2138), there will be a shortage of coal, petrol, diesel and natural gas, i.e., energy- sources. These all are non-renewable resources of energy. To fulfil energy requirements of the world, wind will play an important role.
Question 6. Pick up a stone, a leaf, a paper straw and a twig. Think of how you can use these as resources. See the example given below and get creative.
Resources Class 8 Geography Kseeb Important Questions
Resources Text Questions
Question 1. List out five resources you use in your home and five you use in your classroom.
Answer. Resources used in home: Ded, pillow, toothbrjsh, coffee mug, chair Resources used in classroom: black board, school bag, books, note book, lunch box,
Question 2. Think of a few renewable resources and mention how their stock may get affected by overuse.
Answer. Forests and water are a few renewable resources which get affected due to overuse. Large-scale deforestation and unjudicious use and wastage of water affects the stock of forests and water resources respectively.
Question 3. Make a list of five human-made resources that you can observe around you.
Answer. • Chair • Fan • Bed • Wall clock • Computer
Resources Activity
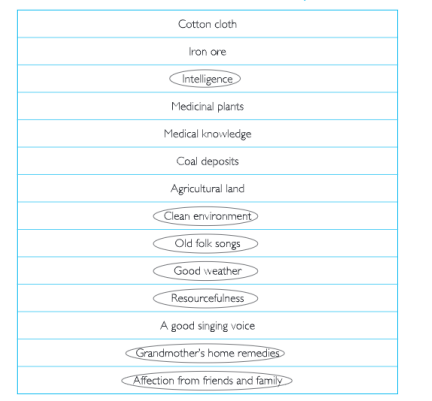
Circle those resources from Amma’s list that have no commercial value as yet.
Karnataka Sslc Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Solutions In English
Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question1 What was Amma doing?
Answer. Amma was cleaning the house.
Question 2. Who were helping Amma in cleaning the house?
Ans. Mona and Raju were helping Amma to clean the house.
Question 3. What is a resource?
Answer. Any thing that can be used is a resource.
Question 4. What is the main purpose of resources?
Answer. To satisfy the basic needs of mankind.
Question 5. Name four articles prepared from raw materials obtained from nature
Answer.
(a) Furniture,
(b) Utensils,
(c) Paper,
(id Vehides
Question 6. Name any two factors on which resource development depends.
Answer.
(a) Technology,
(b) Quality of human resources
Question 7. How does something become a resource?
Answer. Things which have a value become a resource.
Question 8. What gives a thing value?
Answer. A thing’s use or utility gives it value.
Question 9. Name two important factors that can change substances into resources.
Answer. Time and technology are two important factors that can change substance into resource.
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Resources Solved Exercises
Question 10 Name three main types of resources.
Answer. Resources are generally classified into three main types:
(a) Natural
(b) Human-made
(c) Human
Question 11. Name three natural resources essential for human life.
Answer.
(a) Air
(b) Water
(c) Plants
Question 12. Name two types of resources on the basis of stage of development and use.
Answer.
(a) Actual resources
(b) Potential resources
Question 13. Classify resources on the basis of their source of origin.
Answer. Based on their origin, resources can be abiotic or biotic. For example plants, animals, rocks, minerals, soils, etc.
Question 14. Mention two types of resources on the basis of renewability.
Answer. On the basis of renewability, resources can be categorised as renewable resources and non-renewable resources.
Question 15. Give five examples of human-made resources.
Answer. Buildings, bridges, roads, machinery and vehicles are a few examples of human-made resources.
Question 16. Name two factors which help in making people a valuable resource.
Answer. Education and health help in making people a valuable resource.
Question 17. What nightmare Mona had?
Answer. She dreamt that all the water on the earth had dried up and all the trees cut down.
Question 18. How can we conserve resources?
Answer. We can conserve resources by reducing consumption, recycling and reusing things.
Question 19 What things were made by Mona, Raju and their friends on that evening?
Answer. They made packets, shopping bags and bas<ets out of old news-papers, discarded clothes and bamboo sticks.
Question 20. What promise did Asha make with her friends?
Answer. Asha promised to make sure that water is no: wasted at home.
Question 21. Name four articles prepared from raw material obtained from nature.
Ans. Paper, vehicles, utensils and furniture.
Question 22. Name three gifts of nature.
Answer. Rocks, minerals and soil are gifts of nature.
Class 8 Geography Resources Notes Karnataka Board
Question 23. What is sedentary agriculture?
Answer. Farming of land at a fixed location is sedentary agriculture.
Question 24. What was the main sources of food for early man?
Answer. Gathering fruits, leaves and hunting were the main sources of food for early man.
Question 25. Why is Nagercoil famous? Or What do you find in Nagercoil?
Answer. Nagercoil (Tamil Nadu) is famous for windmills.
Question 26. Name two renewable resources which are continuously available.
Answer. Solar energy and wind energy.
Question 27. Name two non-renewable resources.
Answer. Coal and oil.
Question 28. What are flow resources?
Answer. When the rate of consumption of resources does not exceed the rate of renewal, it is called flow resources.
Question 29. What are recyclable resources?
Ans. Resources like metallic ores can be used again and again after processing. They are called recyclable resources.
Question 30. What is technology?
Answer. Technology is human-made resource. It is the application of latest knowledge and skill in doing or \ making things.
Resources Class 8 Geography Summary And Explanation Kseeb
Question 31. What are human-made resources?
Answer. The techniques used for utilising the physical materials are called human-made resources such as machines, tools, roads, etc.
Question 32. What is economic development?
Answer. Productivity of a nation is known as economic development.
Question 33. What hinders economic development?
Answer. Rapid population growth hinders economic development.
Question 34. What is the harmful effect of rising demand of resources?
Answer. It causes degradation of resources.
KSEEB Notes For Class 8 Geography Resources
Question 35. What has been the effect of over-use of soil?
Answer. Infertility of soil.
Question 36. On what factor, the future of planet Earth depends?
Answer. To presen/e the life support system.
Question 37. What harmful effect has occurred due to misuse or over-use of resources?
Ans. The quality of air, water and land has degraded.
Question 38. ‘Processed goods become more useful’. Give one example.
Answer. Raw materials are processed to make useful and valuable items. One kg of sugar is more useful than one kg of sugarcane.
Question 39. Name three non-recyclable resources.
Answer. Coal, mineral oil and natural gas.
Question 40. What are abiotic resources?
Answer. The non-living resources are abiotic resources.
Resources Class 8 KSEEB Questions And Answers
Question 41. Give two examples of abiotic resources.
Answer. Soil and rocks.
Question 42. What do you mean by patent?
Answer. It means the exclusive right over any idea or invention.
Question 43. Define stock of resource.
Answer. It is the amount of resources available for use
Question 44. What do you mean by economic development?
Answer. It refers to changes in the amount, growth, distribution and consumption of resources.
Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is a resource?
Answer. All the useful elements of environment which satisfy human needs are called resources. Resources are called ‘Gifts of nature’ such as soil, rivers, plants, animals, rocks and minerals. These are valuable for mankind.
Question 2. Why are humans also called a resource?
Answer. They are called a resource because only by developing human skills, the resources can be developed. Resources can only be develoDed by man.
Question 3. What do you mean by a reserve?
Answer. It refers to that portion of resources which can be developed profitably, w ith the ava lable technology. For example: High quality iron is used for steel making but sometimes a low grade iron ore or coal (lignite) is also used for steel making. Lignite coal in Salem (Tamil Nadu) is a reserve resource.
Question 4. What is the use of inexhaustible resources?
Answer. Inexhaustible resources include those resources which are used again and again. All non-conventionaJ resources of energy, water resources and wind energy etc., are used for power as resources.
Question 5. What do you mean by appropriate technology?
Answer. The technology suitable for a particular type of resource or on a particular occasion is called appropriate technology.
Question 6. What is recycling?
Answer. Recycling is a process by which wastes of natural and manufactured substances or goods are broken down and then reconstituted into useful material.
Sslc Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Workbook Answers
Question 7. Give two examples of aesthetic values.
Answer.
(a) Lakes and rivers
(b) Mountains These resources have natural scenic beauty.
Question 8. Mention three ways in which natural resources are classified.
Answer.
(a) On the basis of origin
(b) On the basis of renewability
(c) On the basis of utility.
Question 9. On what factors does the utility of resources depend?
Answer.
(a) Human skill
(b) Technology
(c) Stage of human development
Question 10. Which countries use the resources more?
Answer. Developed countries use the resources mo’e than developing countries.
Question 11. Give three examples of human-made resources.
Answer.
(a) Machines
(b) Buildings
(c) Roads
(d) Bridges
Question 12. Distinguish between actual resources and reserve resources.
Answer. Actual resources depend upon physical condrtons of environment. These are surveyed. Their quantity is determined and are actually used. Reserve resources are a part of actual resources. These can be made useful with technology. A grade coal-lignite is a reserved resource in some areas.
Question 13. How can a gift of nature become a resource?
Answer. A gift of nature can become a resource if the people have sufficient knowledge and skill to use it for satisfying their needs.
Question 14. On which factors do human needs depend?
Answer. Human needs are not the same everywhere. They vary not only from region to region, but also from time to time. Human needs actually depend on their natural environment and also on the level of social, cultural and technological development.
Question 15. Discuss the role of technology in the utilisation of resources.
Answer. Technology helps in the development of the means of production. It increases the value of natural resources. Technology depends upon the human skill and technical knowledge. The mechanism helps in the better utilisation of natural resources. A resource is no resource until it is used.
Question 16. ‘India is poor in technology but rich in natural resources.’ Comment.
Answer. It is true that India is poor in technology but has large amounts of natural resources. These are the basis of the Indian economy. Large arable land, long growing season, perennial rivers, huge mineral resources are sufficient resources but these have not been utilised fully. This is due to the fact that India is poor in technology.
Question 17. What is economic development? What factors encourage or hinder it?
Answer. It refers to change in the amount, growth, distribution and consumption of growth. High productivity of a nation produces more services and goods However, human resources are most crucial because the health and education of the population contribute to the growth in productivity. Rapid population growth may prohibit it
Kseeb Class 8 Geography Resources Mcqs With Answers
Question 18. What are four types of values associated with resources?
Answer. There are four types of values associated with resou’xes. These are:
(a) Economic value
(b) Legal value
(c) Ethical value
(d) Aesthetical value
Question 19. What is meant by conservation?
Answer. It means to use the natural resources carefully w ithout wastage. They are mportant to us, so they should be used wisely so that they are not exhausted and we may have to face their scarcity.
Question 20. What are the characteristics of resources?
Answer. The characteristics ox resources are:
(a) Limited quantity’
(b) Utility
(c) Help to create goods
(d) Provide services.
Question 21 How do inventions create resources? Give three examples.
Answer Inventions create resources in the following ways:
(a) The discover)’ of fire led to the practice cf cooking.
(b) Invention of wheel resulted in means of transport.
(c) Technology has created hydro-electricity.
Question 22 What are actual resources? Give three examples.
Answer The resources being used in the present are called actual resources. Such as:
(a) Coal in Ruhr (Germany)
(b) Petroleum in West-Asia
(c) Black soils of Deccan Plateau.
Question 23 What is resource conservation?
Answer Resource conservation is:
(a) To use resources carefully.
(b) Giving resources time to renew.
Question 24 What is sustainable development?
Answer Balancing the need to use resources and conserve these for the future.
Question 25 What are the aims of conservation of resources?
(a) To meet the needs and aspirations of future generations.
(b) Sustainable benefits to the present generation.
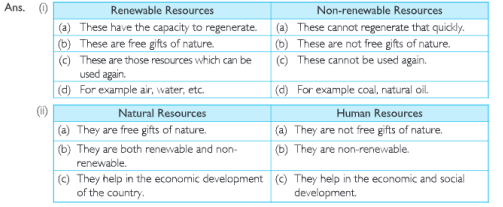
Question 26 Distinguish between
(a) Renewable and Non-renewable Resources.
(b) Natural Resources and Human Resources.
Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the four types of values associated with resources? Explain.
(a) Black soils of Deccan Plateau.
(b) Legal value: Clean Air Act has legal value. This act is an example of legal value attached to the quality of air as a resource.
(c) Aesthetic value: Natural scenic beauty of forests, mountains, lakes and rivers have aesthetic value.
(d) Ethical value: National Parks to preserve wildlife have ethical value. The responsibility to preserve our national parks for future generation reflects the ethical value attached to such resources.
Question 2. Why consumption of resources is higher in developed nations than developing nations?
Answer. The demand for resources varies from region to region and country to country. The demand is
more in developed countries as compared to developing countries.
Following reasons are responsible for the higher consumption of resources in developed countries:
(a) Developed countries are economically developed. So their demand increases fester.
(b) Developed countries use more resources
(c) The per capita income is high in these countries. As a result, with more wealth, the consumption of the resource is more.
Class 8 Kseeb Geography Types And Classification Of Resources
Question 3. What are the ill effects of overuse of resources? What are the measures to make the earth habitate?
Answer. Ill effects of overuse of resources:
Degradation of resources: The rising demand for various resources has caused degradation or deDletion of many valuable resources.
Example:
(a) Overuse of soil has caused infertility in many areas.
(b) Similarly, widespread deforestation and killing of birds arid animals have endangered many plant and animal species.
(c) The quality of air, water arid land resources has also been affected badly due to misuse or overuse of resources.
Measures to make the Earth habitate: Future of our planet and its people, therefore, is linked with our ability’ to maintain and preserve the life support system that nature provides. This makes it our duty to ensure that:
(a) All uses of renewable resources are suitable.
(b) The diversity of life on the earth is conserved and
(c) The damage to natural environmental syr.em is minimised.
Question 4. Explain the functional theory of resources.
Answer. Natural resources help human beings in the following ways:
(a) These provide material, energy for development.
(b) They constitute natural environment.
(c) Air, water and forests are essential for human survival.
Resources become resources only when they are utilised. Coal became a resource only when man used it as a source of energy .
Class 8 Geography Kseeb Resources Short And Long Answer Questions
Question 5. In how many ways man uses his environment?
Answer. Environment means a set of surroundings. It provides many resources to get food, shelter and clothing. Man uses land for crops, houses, factories and the construction oi transport network. Man uses minerals for industries and forests for timber, herbs and shrubs. Man gets fish and other benefits from seas and oceans.
Detailed Notes On Resources KSEEB Geography
Question 6. Classify resources. Describe the main characteristic and example of each.
Answer. Resources are generally classified into three types:
1 Natural
2 Human
3 Human made.
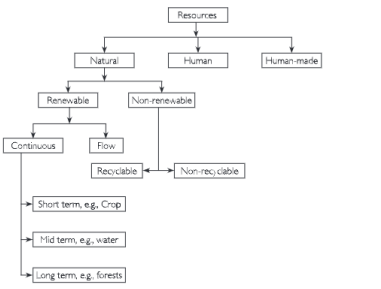
1 Natural Resources: Any matter or energy derived from the envronment that is used by living things and humans is called natural resource. Example: air, water, soil, minerals, fossil fuels, plants and wildlife are called natural resources.
Classification of Natural Resources:
(a) Natural resources are classified in many ways. They may be categorised on the basis of the source of their origin. Accordingly, there are land, soil, water, plant, animal, mineral and energy resources.
Types of Resource
(b) Another method of classification is according to the stage of development of resource.
- Potential Resource: Those resources which are found in the region but have not been put to a proper use are called potential resources.
- Actual Resources: The resources, which have been surveyed and quantified (quantities determined properly) for actual use are called actual resources.
- Reserve Resources: That portico of the actual resource, which can be developed profitably with available technology is termed as a reserve.
(c) Natural resources are also classified on the basis of renewability. The natural resources are categorised into renewable and non-renewable resources.
- Renewable Resources: Resources which get renewed or replenished fast, are called renewable resources. Some of these resources are always available (continuous) like solar and wind energy. Some resources like crop take a short time for renewal.
- Non-renewable Resources: Non-renewable Resources have been built-up over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are the examples of such resources since their rate of formation is extremely slow. Some of these resources such as metallic ores (rocks containing minerals like gold, silver and iron) are recyclable in nature. It means that the metal content drawn from the ore may be used again and again after necessary¬processing. Fossil fuels such as coal, mineral oil and natural gas get exhausted for ever, once consumed. Hence, they are non-recyclable.
2 Human Resources: Human resources mean the number (quantity) and abilities (mental and physical) of the people. Education anc health help people to acquire competencies required for developing resources.
The utility of a resource depends upon:
(a) Human Skill
(b) Stage of Human Development
(a) Technology.
3 Human-Made Resources: These are the techniques of production which have been created by people to utilise the physical materials of the environment. Thus, machines, tool, houses, and buildings are the examples of such resources.
Question 7 What is sustainable development? What are its basic principles?
By sustainable development, we refer to the careful utilisation of resources so that along with meeting the present requirements, the requirements of the future generation is also taken care of. Some methods of conservation are as follows:
(a) Respect and care for all forms of life (ii) Improving the quality of human life
(b) Conserving the Earth’s vitality and diversity (iv) Minimising the depletion of natural resources
(c) Changing personal attitude and practices towards the environment
(d) Enabling communities to care for their own environment
Question 8. What is our duty to ensure regarding resources?
Answer. It is our duty to ensure that:
(a) The diversity of life on the earth is conserved.
(b) All uses of renewable resources are sustanable.
(c) The damage to natural environmental system is minimised.
Resources Hots Corner
Question 1. All natural resources run in cycles.’ Give examples.
Answer. Cycle is a period of time for the formation of a resource. All natural resources are part of natural cycles, such as hydrological cycle, rock cycle and carbon cycle. But the time taken in completing these cycles varies. While some cycles, like the hydrological cycle may be completed soon, others such as rock cycle may take millions of years. Thus, one of the common ways of classifying natural resources is on the basis of renewability. This refers to the ability of a natural resource to renew or replenish itself within a few generations of human lives. Minerals and fossil fuels are built over a long geological time. Their rate of formation is very slow.
Question 2. ‘Resources are not, they become so.’ Explain.
Answer. Resources are elements of the bio-physical environment. But these become resources only when humans preserve them. Coal was always there, but it became a resource only when man used it as a source of energy. Hence, it has been rightly said that resources are not, they become so.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources
Question 3. How are development and resources inter-dependent?
Answer. Development is possible through resources. Resources are the foundation of development. These have economic significance for human beings. Land, water and air are the basic requirements for agriculture. We can’t do agriculture without these resources. MineraJs are basic requirement for industries. Industries cannot run without minerals. Thus, development and resources are inter¬dependent.
Question 4. Future of our planet is linked with life support system. Discuss.
Answer. Our Earth is the only planet where life exists. Future of our planet and its people, is linked w ith our ability to maintain and preserve the life support system that nature provides. This makes it our duty to ensure that the natural environment is preserved and properly managed.
Question 5. How does man use his environment?
Answer. Environment means set of surroundings. It provides many resources to get food, shelter and clothing. Man uses land for crops, minerals for industries and forests for timber. Man gets fish from seas and oceans.
Simplified Notes For KSEEB Class 8 Geography Resources
Resources Miscellaneous Questions A. Multiple Choice Questions
Tick the correct option from the choices provided:
Question 1. Metals have a value:
(a) Economic
(b) Legal
(c) Aesthetic
Answer. (a) Economic
Question 2. Invention of wheel has resulted in the development of:
(a) Transport
(b) Industries
(c) Agriculture
Answer. (a) Transport
Question 3. Which of the following is not a natural resource?
(a) Soil
(b) Air
(c) Water
Answer. (d) Manufactured goods
Question 4. What type of resource is uranium in Ladakh?
(a) Actual
(b) Potential
(c) Biotic
Answer. (b) Potential
Question 5. Which of the following is an abiotic resource?
(a) Forests
(b) Water
(c) Rocks
Answer. (c) Rocks
KSEEB Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources
Question 6. Which of the following is a non-renewable resource?
(a) Coal
(b) Solar energy
(c) Water power
Answer. (a) Coal
Question 7. Which of the following is a renewable resource?
(a) Forests
(b) Rock
(c) Minerals
Answer. (a) Forests
Question 8. Which of the following is a man-made resource?
(a) Roads
(b) Forests
(c) Rocks
Answer. (a) Roads
Question 9. Which of the following is not a man-made resource?
(a) Roads
(b) Bridges
(c) Buildings
Answer. (d) Rocks.
B. One Word/Sentence Answers
Resources Answer the following questions in one word Sentence
(a) What is the prime quality of a substance to become a resource?
Answer. Utility
(b) Name of the resources whose quantity is known are called?
Answer. Actual resources
(c) What is also known as manpower resources?
Answer. Human resources
KSEEB Class 8 Geography solutions for Resources
(d) What do we call those resources which get replenished after use?
Answer. Renewable resources
(e) ‘Respect and care for all forms of life.’ What does the sentence refer to?
Answer. Sustainable development
Resources Passage Interpretation
Read the below passage and answer the questions tiat follow:
Time and technology are two important factors required for chang ng substances into resources. For example, soil is necessary for plant growth. It takes hundreds to thousand years to form just one layer of soil. Similarly, fire became an important resource, when man discovered its uses and learnt to make fire. The technology helped him to create more resources.
(a) What is required for a substance to be a resource?
Answer. Time and technology.
(b) Give two examples of substances which become a resource with the realisation of its utility. Ans. Use of soil for agriculture and use of fire are two examples of resources.
Resources Picture Interpretation
Look at the following picture and answer the questions that follow:
(a) What does the picture depict?

Answer. The picture is related to the conservation of resources. The basic principle of conservation is ‘Reduce- Recycle-Reuse’ (3Rs). Conservat or thus, does not prohibit the use of resources but emphasises their efficient use. We need to reduce the consumption of resources and their wastes. The wastes such as those of paper, aluminium, water, etc., can be recycled and then re-used in many forms. Some examples are home-made paper by Khadi Gram Udyog.
